机器学习案例:验证码识别(Captcha)
验证码(CAPTCHA,全自动区分计算机和人类的图灵测试)的缩写,是一种区分用户是计算机还是人工智能的全自动程序。
实验步骤:
- 1、创建验证码
- 2、对验证码进行01值化
- 3、降噪
- 4、对验证码进行切分
- 5、对切分后的验证码进行图片转数字化
- 6、使用逻辑回归建模
- 7、对新输入的图片进行预测
验证码的创建
1、随机生成验证码的颜色
2、随机生成验证码数字
3、使用PIL进行画图
import os
from PIL import Image
from PIL import ImageDraw
from PIL import ImageFont
import random
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
def getRandomColor():
"""
获取一个随机颜色(r,g,b)格式的
:return:
"""
c1 = random.randint(0, 255)
c2 = random.randint(0, 255)
c3 = random.randint(0, 255)
if c1 == 255:
c1 = 0
if c2 == 255:
c2 = 0
if c3 == 255:
c3 = 0
return (c1, c2, c3)
def getRandomStr():
"""
获取一个随机数字,每个数字的颜色也是随机的
:return:
"""
random_num = str(random.randint(0, 9))
return random_num
def generate_captcha():
"""
使用PIL画图步骤
:return:
"""
# 获取一个Image对象,参数分别是RGB模式。宽150,高30, 随机颜色
image = Image.new('RGB', (150, 50), (255, 255, 255))
# 获取一个画笔对象,将图片对象传过去
draw = ImageDraw.Draw(image)
# 获取一个font字体对象参数是ttf的字体文件的目录,以及字体的大小
font = ImageFont.truetype("arlrdbd.ttf", size=32) # 如果找不到字体,需要从网上下载到本地
label = ""
# 随机生成有5个数字的字符串
for i in range(5):
random_char = getRandomStr()
label += random_char
# 在图片上写东西,参数是:定位,字符串,颜色,字体
draw.text((10+i*30, 0), random_char, getRandomColor(), font=font)
# 画出随机噪点噪线
width = 150
height = 30
# 画线
for i in range(3):
x1 = random.randint(0, width)
x2 = random.randint(0, width)
y1 = random.randint(0, height)
y2 = random.randint(0, height)
draw.line((x1, y1, x2, y2), fill=(0, 0, 0))
# 画点
for i in range(5):
draw.point([random.randint(0, width), random.randint(0, height)], fill=getRandomColor())
x = random.randint(0, width)
y = random.randint(0, height)
draw.arc((x, y, x + 4, y + 4), 0, 90, fill=(0, 0, 0))
# 保存到硬盘,名为test.png格式为png的图片
image.save(open(''.join(['captcha_images/', label, '.png']), 'wb'), 'png')
# image.save(open(''.join(['captcha_predict/', label, '.png']), 'wb'), 'png')
执行代码之后,会在‘captcha_images’下生成实验所需的图片,如图:
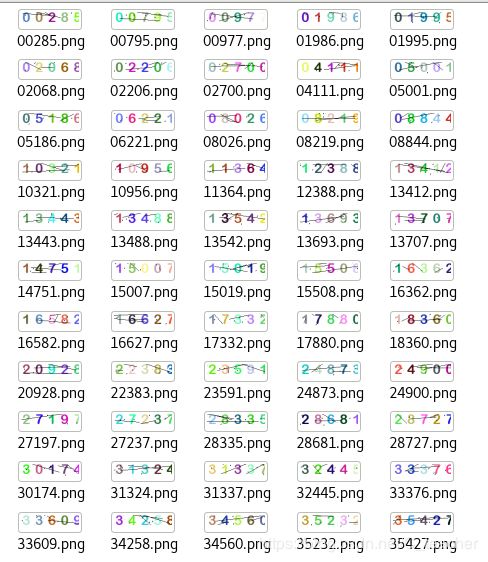
图像处理:对生成的图片进行处理
(1)对验证码图片二值化,首先把图像从RGB 三通道转化成Gray单通道,然后把灰度图(0~255)转化成二值图(0,1)。
(2)将处理好的二值图进行降噪,去除图片中的噪点和噪线
from PIL import Image
import numpy as np
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
import os
def binarization(path):
"""
把一个rgb的图转换成一个二值图
:param path:
:return:
"""
# 通过path把图像laod进来
img = Image.open(path)
# 把图像转化成一个灰度图
img_gray = img.convert("L")
# 把灰度图组装成数组形式
img_gray = np.array(img_gray)
# print(img_gray)
# 得到灰度图的宽和高
w, h = img_gray.shape
for x in range(w):
for y in range(h):
# 得到每一个像素块里的灰度值
gray = img_gray[x, y]
# 如果灰度值小于等于220, 就把它变成黑色
if gray <= 220:
img_gray[x, y] = 0
# 如果灰度值大于220,就把它变成白色
else:
img_gray[x, y] = 1
plt.figure("")
plt.imshow(img_gray, cmap="gray")
plt.axis("off")
plt.show()
return img_gray
def noiseReduction(img_gray, label):
"""
降噪,也就是处理离群点
如果一个像素点周围只有小于4个黑点的时候,那么这个点就是离群点
:param img_gray:
:param label:
:return:
"""
height, width = img_gray.shape
for x in range(height):
for y in range(width):
cnt = 0
# 白色的点不用管
if img_gray[x, y] == 1:
continue
else:
try:
if img_gray[x-1, y-1] == 0:
cnt += 1
except:
pass
try:
if img_gray[x-1, y] == 0:
cnt += 1
except:
pass
try:
if img_gray[x-1, y+1] == 0:
cnt += 1
except:
pass
try:
if img_gray[x, y-1] == 0:
cnt += 1
except:
pass
try:
if img_gray[x, y+1] == 0:
cnt += 1
except:
pass
try:
if img_gray[x+1, y-1] == 0:
cnt += 1
except:
pass
try:
if img_gray[x+1, y] == 0:
cnt += 1
except:
pass
try:
if img_gray[x+1, y+1] == 0:
cnt += 1
except:
pass
if cnt < 4: # 周围少于4个点就算是噪点
img_gray[x, y] = 1
plt.figure(" ")
plt.imshow(img_gray, cmap="gray")
plt.axis("off")
plt.savefig("".join(["clean_captcha_img/", label, ".png"]))
def image_2_clean():
"""
把所有的图像都转化成二值图
:return:
"""
captchas = os.listdir("".join(["captcha_images/"]))
for captcha in captchas:
label = captcha.split(".")[0]
image_path = "".join(["captcha_images/", captcha])
# 二值化
im = binarization(image_path)
# 降噪
noiseReduction(im, label)
if __name__ == '__main__':
image_2_clean()
# path = "captcha_images/00006.png"
# img_gray = binarization(path)
# noiseReduction(img_gray, label='00006')
import os
from PIL import Image
from PIL import ImageDraw
from PIL import ImageFont
import random
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
def cutImg(label):
"""
把图像的每一个数字都切分出来,并且存到新的文件夹下
:param label:
:return:
"""
labels = list(label)
img = Image.open("".join(['clean_captcha_img/', label, '.png']))
for i in range(5):
pic = img.crop((100*(1+i), 170, 100*(1+i)+100, 280))
plt.imshow(pic)
# seq就是我们需要存到文件的文件名
seq = get_save_seq(label[i])
pic.save("".join(["cut_number/", str(label[i]), "/", str(seq), '.png']))
def get_save_seq(num):
"""
得到需要保存的数据的文件名
每一个数文件下的文件名,都是从0开始保存 0.png, 1.png....
:param num:
:return:
"""
nmlist = os.listdir("".join(["cut_number/", num, "/"]))
if len(nmlist) == 0 or nmlist is None:
return 0
else:
max_file = 0
for file in nmlist:
if int(file.split(".")[0]) > max_file:
max_file = int(file.split(".")[0])
return int(max_file) + 1
def clean_to_cut():
"""
对每一个文件都进行切分
:return:
"""
captchas = os.listdir("".join(["clean_captcha_img"]))
for captcha in captchas:
label = captcha.split(".")[0]
cutImg(label)
def create_dir():
for i in range(10):
os.mkdir("".join(["cut_number/", str(i)]))
if __name__ == '__main__':
# create_dir()
clean_to_cut()
图片转数字化:对切分后的图片灰度化、二值化,使用Image.open()打开图片文件,得到plt图片对象,将plt图片对象转换为ndarray对象,将二值化后的图像转化为1行n列,存入X列表中,并将其对应的数字存入Y列表中。
模型的生成:将X,Y传入逻辑回归模型中,使用交叉验证和网格搜索寻找最优的参数。
import os
from PIL import Image
import numpy as np
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
from sklearn.linear_model import LogisticRegression
from sklearn.model_selection import train_test_split
from sklearn.model_selection import GridSearchCV
from sklearn.externals import joblib
from sklearn.metrics import confusion_matrix
from sklearn.metrics import precision_score
from sklearn.metrics import recall_score
def load_data():
"""
把数据从cut_number里面导出来
其中X指的是每一个数字的01值的排列, Y指的是这个数字是什么
:return:
"""
X, Y = [], []
cut_list = os.listdir("cut_number")
# 循环cut_number文件夹下的每一个自文件夹(1,2,3,4,5...)
for numC in cut_list:
num_list_dir = "".join(["cut_number/", str(numC), "/"])
nums_dir = os.listdir(num_list_dir)
# 循环子文件夹中的每一个图片
# print(np.array(Image.open(''.join(['cut_number/', str(numC), '/', '0.png']))))
for num_file in nums_dir:
# 导入数字图片
img = Image.open("".join(["cut_number/", str(numC), "/", num_file]))
# print(np.array(img))
# 对数字图片做灰度化
img_gray = img.convert("L")
# plt.imshow(img_gray)
# 把灰度化图片保存到数组里
img_array = np.array(img_gray)
w, h = img_array.shape
# 把灰度化的图片做二值化
for x in range(w):
for y in range(h):
gray = img_array[x, y]
if gray <= 220:
img_array[x, y] = 0
else:
img_array[x, y] = 1
# 把二值化的图片reshape成1行,n列
img_re = img_array.reshape(1, -1)
# print(img_re[0])
X.append(img_re[0])
Y.append(int(numC))
return np.array(X), np.array(Y)
def generate_model(X, Y):
"""
生成模型
:param X:
:param Y:
:return:
"""
# 区分测试集和训练集,37开
X_train, X_test, Y_train, Y_test = train_test_split(X, Y, test_size=0.3)
log_clf = LogisticRegression(multi_class="ovr", solver="sag", max_iter=10000)
# log_clf.fit(X_train, Y_train)
# 利用交叉验证选择参数
param_grid = {"tol": [1e-4, 1e-5, 1e-2], "C": [0.4, 0.6, 0.8]}
grid_search = GridSearchCV(log_clf, param_grid=param_grid, cv=3)
grid_search.fit(X, Y)
print(grid_search.best_params_)
print("模型生成成功")
# 将模型持久化
joblib.dump(log_clf, "captcha_model/captcha_model.model")
print("模型保存成功")
if __name__ == '__main__':
X, Y = load_data()
generate_model(X, Y)
图片的预测:
输入要预测的图片,对其进行灰度化,二值化,并进行分割,将分割出来的五个图片输入进模型中。
import os
from PIL import Image
import numpy as np
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
from sklearn.linear_model import LogisticRegression
from sklearn.model_selection import train_test_split
from sklearn.model_selection import GridSearchCV
from sklearn.externals import joblib
from sklearn.metrics import confusion_matrix
from sklearn.metrics import precision_score
from sklearn.metrics import recall_score
from .captcha_logistic import *
def get_model():
model = joblib.load('captcha_model/captcha_model.model')
return model
def model_predict():
path = 'captcha_predict/unknown.png'
pre_img_gray = binarization(path)
noiseReduction(pre_img_gray, 'unknown')
# cut image
labels = ['0', '1', '2', '3', '4']
img = Image.open(''.join(['clean_captcha_img/unknown.png']))
for i in range(5):
pic = img.crop((100 * (1 + i), 170, 100 * (1 + i) + 100, 280))
plt.imshow(pic)
pic.save(''.join(['captcha_predict/', labels[i], '.png']))
result = ''
model = get_model()
for i in range(5):
path = ''.join(['captcha_predict/', labels[i], '.png'])
img = Image.open(path)
img_gray = img.convert('L')
img_array = np.array(img_gray)
w, h = img_array.shape
for x in range(w):
for y in range(h):
gray = img_array[x, y]
if gray <= 220:
img_array[x, y] = 0
else:
img_array[x, y] = 1
img_re = img_array.reshape(1, -1)
X = img_re[0]
y_pre = model.predict([X])
result = ''.join([result, str(y_pre[0])])
return result
if __name__ == '__main__':
result = model_predict()
print(result)

