【Cartopy】1.库的安装和使用
安装cartopy库
首先上官方文档地址:cartopy
-
在线conda 安装:
conda install cartopy(安装成功就不需要再看离线安装方法) -
离线安装: http://www.lfd.uci.edu/~gohlke/pythonlibs/#cartopy
注意:需要一些必须的软件包Shapely、pyshp,Cartopy所依赖的这两个库也都从上面的网址下载。
测试
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
import cartopy.crs as ccrs
plt.figure(figsize=(6, 3))
ax = plt.axes(projection=ccrs.PlateCarree(central_longitude=180))
ax.coastlines(resolution='110m')
ax.gridlines()
plt.show()
测试失败 error/ warning: 没有地图文件。这里是因为cartopy运行程序默认从Natural Earth下载地图文件。可以优先下载地图文件放在本地文件夹下。
下载Natural Earth地图数据
- 下载10m、50m和110m分辨率的cultural 和 physical类型数据。
- 解压到本地路径:C:\Users\Administrator.local\share\cartopy\shapefiles\natural_earth\physical or C:\Users\Administrator.local\share\cartopy\shapefiles\natural_earth\cultural 中。
注:如果找不到,搜索 C:\Users\xxx.local\share\cartopy\shapefiles\natural_earth\physical
解压完成后,不能重新运行测试代码,要对代码进行修改
绘制地图测试代码
demo: 其中scale参数用于调整使用哪种分辨率的地图,全球地图建议用1:110的,小尺度地图可以用1:50的或1:10的。
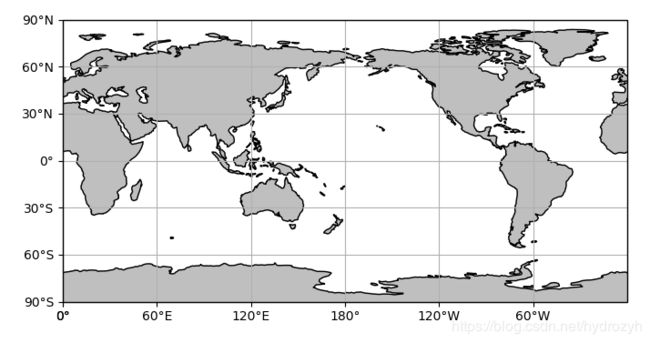
1 Global map
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
import cartopy.crs as ccrs
import cartopy.feature as cfeature
from cartopy.mpl.ticker import LongitudeFormatter, LatitudeFormatter
scale = '110m' # 补充1
fig = plt.figure(figsize=(8, 10))
ax = plt.axes(projection=ccrs.PlateCarree(central_longitude=180))
ax.set_global()
# 补充部分
###### start #####
land = cfeature.NaturalEarthFeature('physical', 'land', scale, edgecolor='face',
facecolor=cfeature.COLORS['land'])
ax.add_feature(land, facecolor='0.75')
ax.coastlines(scale)
###### end ######
# 标注坐标轴
ax.set_xticks([0, 60, 120, 180, 240, 300, 360], crs=ccrs.PlateCarree())
ax.set_yticks([-90, -60, -30, 0, 30, 60, 90], crs=ccrs.PlateCarree())
# zero_direction_label用来设置经度的0度加不加E和W
lon_formatter = LongitudeFormatter(zero_direction_label=False)
lat_formatter = LatitudeFormatter()
ax.xaxis.set_major_formatter(lon_formatter)
ax.yaxis.set_major_formatter(lat_formatter)
# 添加网格线
# gl = ax.gridlines()
ax.grid()
plt.show()
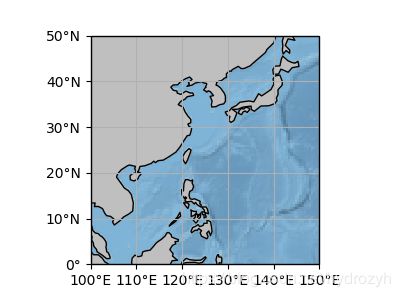
2. reginal map
import numpy as np
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
import cartopy.crs as ccrs
import cartopy.feature as cfeature
from cartopy.mpl.ticker import LongitudeFormatter, LatitudeFormatter
box = [100, 150, 0, 50]
scale = '50m' # 补充1 此处50m不知道为什么还是不能加载
xstep, ystep = 10, 10
fig = plt.figure(figsize=(8, 10))
ax = plt.axes(projection=ccrs.PlateCarree())
# set_extent需要配置相应的crs,否则出来的地图范围不准确
ax.set_extent(box, crs=ccrs.PlateCarree())
# 补充部分
###### start #####
land = cfeature.NaturalEarthFeature('physical', 'land', scale, edgecolor='face',
facecolor=cfeature.COLORS['land'])
ax.add_feature(land, facecolor='0.75')
ax.coastlines(scale)
###### end ######
# ===================================================
# 图像地址D:\Program\Anaconda\pkgs\cartopy-0.17.0-py37h5ae9855_1\Lib\site-packages\cartopy\data\raster\50-natural-earth-1-downsampled.png
# 如果有其它高精度图像文件,改名替换即可
ax.stock_img()
# ===================================================
#标注坐标轴
ax.set_xticks(np.arange(box[0], box[1]+xstep,xstep), crs=ccrs.PlateCarree())
ax.set_yticks(np.arange(box[2], box[3]+ystep,ystep), crs=ccrs.PlateCarree())
# zero_direction_label 用来设置经度的0度加不加E和W
lon_formatter = LongitudeFormatter(zero_direction_label=False)
lat_formatter = LatitudeFormatter()
ax.xaxis.set_major_formatter(lon_formatter)
ax.yaxis.set_major_formatter(lat_formatter)
# 添加网格线
ax.grid()
plt.show()
注:仔细观察可以发现上图scale依然是110m的分辨率,因为50m不能运行,经过测试需要把Natural Earth下载的地图文件修改名称,ne_50m_land.shp修改为50m_land.shp(去掉ne_)
因为懒,所以选择用程序修改文件名,在本文末,附上批量化修改文件名的代码
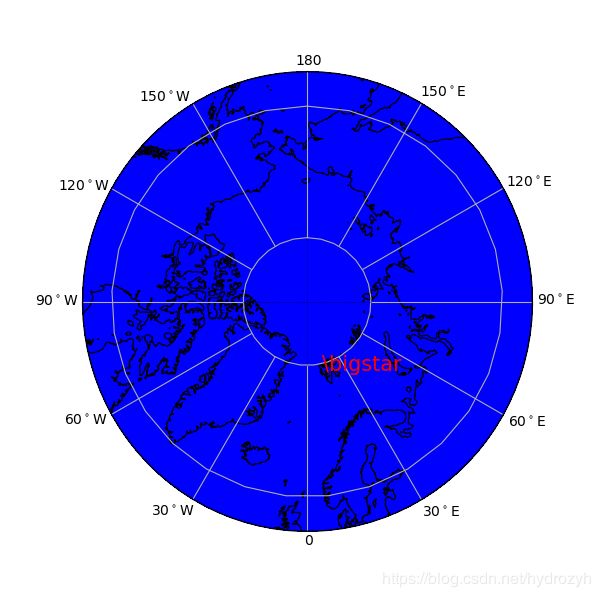
3. Polar projection map
import matplotlib.path as mpath
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
import numpy as np
import matplotlib.ticker as mticker
import cartopy.crs as ccrs
import cartopy.feature as cfeature
fig = plt.figure(figsize=(6, 6))
ax = plt.axes(projection=ccrs.NorthPolarStereo())
box = [-180, 180, 55, 90]
xstep, ystep = 30, 15
# Limit the map to -60 degrees latitude and below.
ax.set_extent(box, crs=ccrs.PlateCarree())
# ===================================================
scale = '50m' # 补充1
land = cfeature.NaturalEarthFeature('physical', 'land', scale, edgecolor='face',
facecolor=cfeature.COLORS['land'])
ocean = cfeature.NaturalEarthFeature('physical', 'ocean', scale, edgecolor='face',
facecolor=cfeature.COLORS['water'])
ax.add_feature(land, facecolor='0.75')
ax.add_feature(ocean, facecolor='blue')
ax.coastlines(scale, linewidth=0.9)
# ===================================================
# 标注坐标轴
line = ax.gridlines(draw_labels=False)
line.ylocator = mticker.FixedLocator(np.arange(40, 90, 20)) # 手动设置x轴刻度
line.xlocator = mticker.FixedLocator(np.arange(-180, 210, 30)) # 手动设置x轴刻度
# Compute a circle in axes coordinates, which we can use as a boundary
# for the map. We can pan/zoom as much as we like - the boundary will be
# permanently circular.
theta = np.linspace(0, 2 * np.pi, 100)
center, radius = [0.5, 0.5], 0.5
verts = np.vstack([np.sin(theta), np.cos(theta)]).T
circle = mpath.Path(verts * radius + center)
ax.set_boundary(circle, transform=ax.transAxes)
# 创建要标注的labels字符串
ticks = np.arange(0, 210, 30)
etick = ['0'] + ['%d$^\circ$E' % tick for tick in ticks if (tick != 0) & (tick != 180)] + ['180']
wtick = ['%d$^\circ$W' % tick for tick in ticks if (tick != 0) & (tick != 180)]
labels = etick + wtick
# 创建与labels对应的经纬度标注位置
# xticks=[i for i in np.arange(0,210,30)]+[i for i in np.arange(-32,-180,-30)]
xticks = [-0.8, 28, 58, 89.1, 120, 151, 182.9, -36, -63, -89, -114, -140]
yticks = [53] + [53] + [54] + [55] * 2 + [54.5] + [54] + [50] + [49] * 3 + [50.6]
# 标注经纬度
# ax.text(0.01,0.23,'60$^\circ$W',transform=ax.transAxes,rotation=25)
# ax.text(-63,50,'60$^\circ$W',transform=ccrs.Geodetic(),rotation=25)
for xtick, ytick, label in zip(xticks, yticks, labels):
ax.text(xtick, ytick, label, transform=ccrs.Geodetic())
x = [180, 180, 0, 0]
y = [50, 90, 90, 50]
ax.plot([-180, 0], [80, 80], ':', transform=ccrs.Geodetic(), color='k', linewidth=0.4)
ax.plot([-90, 90], [80, 80], ':', transform=ccrs.Geodetic(), color='k', linewidth=0.5)
# ax.plot([90,0],[50,50],'-.',transform=ccrs.Geodetic(),color='r', linewidth=6)
ax.text(11.9333, 78.9166, r'\bigstar', transform=ccrs.Geodetic(), size=15, color='r')
plt.show()
批量修改文件名
import os
path = r'E:\temp'
fileLists = os.listdir(path)
for f in fileLists:
if f[:3] == 'ne_'
oldname = path + os.sep + f
newname = path + os.sep + f[3:]
os.rename(oldname, newname)