Integrated Web Design: Strategies for Long-Term CSS Hack Management
Integrated Web Design: Strategies for Long-Term CSS Hack Management
- By Molly Holzschlag.
- Article is provided courtesy of Sams.
- Date: Jun 25, 2004.
SaveDiggDel.icio.us
DiscussPrintE-mail
Article Information
Contents
- Hacking Strategies
- Hacks and Workarounds
- Filtration Systems
- Hack it Up, Take It Home
Article Description
Using CSS in a contemporary browser? You'll probably need to use a variety of CSS hacks to accomplish the best possible cross-browser compatibility. Molly Holzschlag helps you determine if you need hacks, how to manage them effectively if so, and which hacks you can employ to solve a range of common compatibility problems.Hack management? What the heck is that? Well, if you're working with CSS and you're trying to address the oddities of multiple browsers, you simply cannot achieve consistency between those browsers without employing hacks.
So, how is a hack defined? That's another issue up for debate, but for the purposes of this article, a hack occurs any time we use an element, property, or other syntax within a language for a purpose other than its intended application.
Depending upon your site needs, you might be one of the lucky few who never has to employ a CSS hack, but I doubt it (at least for now and at least if you're working with CSS and addressing numerous browser concerns). So, this article will provide you with a variety of hacks as well as offer some incredibly intelligent strategies for managing your hacks and ensuring that they quickly disappear when you don't need a given hack anymore.
After all, we really don't want to use hacks. The biggest hack of all in web design has been the use of tables for layout, and we all know what a mess that's gotten us into.
Hacking Strategies
Before you get hacking, you'll want to know a bit about how to effectively use hacks—or not use them. This section will help you set up your strategy before using a hack.
General Tips
Here are some tips to ensure that you'll manage your hacks with expertise:
-
Don't need them? Don't use them. If you know your target audience and browsers well enough that you don't have to support especially problematic browsers, don't use hacks. A good example is if you're in an intranet situation and have total control over the browsers in use.
-
Know CSS and know your hacks. Although this article will go a long way toward helping you understand the how and why of hacking CSS, knowing CSS itself and how it works in various browsers will be one of your first-line defense systems in ensuring that you use only what you have to use for as long as you have to use it. So many problems arise out of copying and pasting markup and CSS it's not funny! Sure, we all do it, but for professional applications, we have to know what it is we're working with to optimize it and use it as properly as possible.
-
Comment, comment, comment. Although it's always a great idea to adequately comment your markup and CSS, if you're working with hacks, be sure to comment the hack. This helps co-workers as well as those surfing around swiping your CSS to understand what you're doing and why. If the hack has a specific name, make sure to name the hack in your comment, such as
/* Box Model Hack to correct Box Model implementations */
After you determine that you will require hacks and are committed to managing them effectively, you're ready for the surgical correction strategy.
Surgical Correction Strategy
This is a strategy I heard Tantek Çelik (perhaps the creator of more CSS hacks known to humankind than anyone) discuss at a recent SXSW panel on CSS. As a developer of browsers as well as a CSS expert, Çelik has had to manage browser inconsistencies with CSS for a long time. Although not a proponent of hacking by choice, Çelik realized that we need to provide options to use CSS as effectively as possible, but removing those hacks as soon as they are no longer needed will enable us to move forward without being encumbered by them.
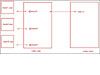
This strategy makes your hacks easy to manage by placing the CSS syntax in unique files. Then, you can import them into your main style sheet using the @import property. By doing this, you import your hacks into the main CSS rather than actually coding them in the main CSS itself. Let's say you've got a document, hi-pass.css, in which you have the syntax for the hi-pass filter (discussed later in this article). The hack is resident in a file all its own and then imported into the main sheet:
/* importing hi-pass filter */
@import "hi-pass.css";
After you determine that the hack is no longer necessary, you simply delete this syntax from the main sheet, delete the hi-pass.css file, and you are then that much closer to a hack-free environment with very little muss and fuss.
Figure 1 illustrates the surgical connection strategy.