Android 自定义View系列之必备api
目录表
- android自定义view必备api
- android可拖动圆环刻度条
- android仿滴滴大头针跳动波纹效果
- android仿网易云鲸云音效
写本篇博客的意图是想总结一下在实际的自定义view开发中,常被我们所用到的api方法,之所以有了这个想法,是因为自定义view写的多了,总感觉掌握的知识点越来越杂,毫无章法。所以也就有了这么一个想串串知识点的念头。本文不从概念起笔,也不教你如何实现一个view,把它简单看作一个私人的api文档就好。
线段
这里贴下画线的api代码:
drawLine(float startX, float startY, float stopX, float stopY, Paint paint)
这里贴下简单的代码片段:
/**
* @params startX 线段起点的x坐标
* @params startY 线段起点的Y坐标
* @params stopX 线段终点的x坐标
* @params stopY 线段终点y的坐标
*/
canvas.drawLine(0,0
, CommentUtils.dip2px(mContext, 150)// px
, CommentUtils.dip2px(mContext, 150)// px
, linePaint);
这是xml中的布局片段:
<com.mjzuo.views.view.GeometricFigureView
android:layout_width="150dp"
android:layout_height="150dp"
android:background="#787878"
android:layout_marginLeft="50dp"
android:layout_marginTop="50dp"
/>
矩形
这里贴下矩形的api方法:
public RectF (float left,
float top,
float right,
float bottom)
public void drawRect (RectF rect, Paint paint)
这里贴下使用的代码片段:
/**
* RectF:
* left 矩形左侧的x坐标
* top 矩形顶部的y坐标
* right 矩形右侧的x坐标
* bottom 矩形底部的y坐标
*/
if(rectF == null)
rectF = new RectF(0, 0
, CommentUtils.dip2px(mContext, 150)// 单位都是px
, CommentUtils.dip2px(mContext, 75));
canvas.drawRect(rectF, rectPaint);
这是xml中的布局片段:
<com.mjzuo.views.view.GeometricFigureView
android:layout_width="150dp"
android:layout_height="150dp"
android:background="#f0f0f0"
android:layout_marginLeft="50dp"
android:layout_marginTop="50dp"
/>
圆形
这里贴下圆形的api方法:
public void drawCircle (float cx, float cy, float radius, Paint paint)
这里贴下使用的代码片段:
/**
* float cx 中心点的x坐标
* float cy 中心点的y坐标
* float radius 半径
*/
canvas.drawCircle(CommentUtils.dip2px(mContext, 75)
, CommentUtils.dip2px(mContext, 75)
, CommentUtils.dip2px(mContext, 75)
, circlePaint);
这是xml中的布局片段:
<com.mjzuo.views.view.GeometricFigureView
android:id="@+id/view_circle"
android:layout_width="150dp"
android:layout_height="150dp"
android:background="#787878"
android:layout_marginLeft="50dp"
android:layout_marginTop="50dp"
/>
默认画出的圆是实心圆,可以通过设置画笔属性来画空心圆,代码如下:
circlePaint = new Paint();
circlePaint.setColor(0xFFCCFFFF);
// 充满
// circlePaint.setStyle(Paint.Style.FILL);
// 镶边
circlePaint.setStyle(Paint.Style.STROKE);
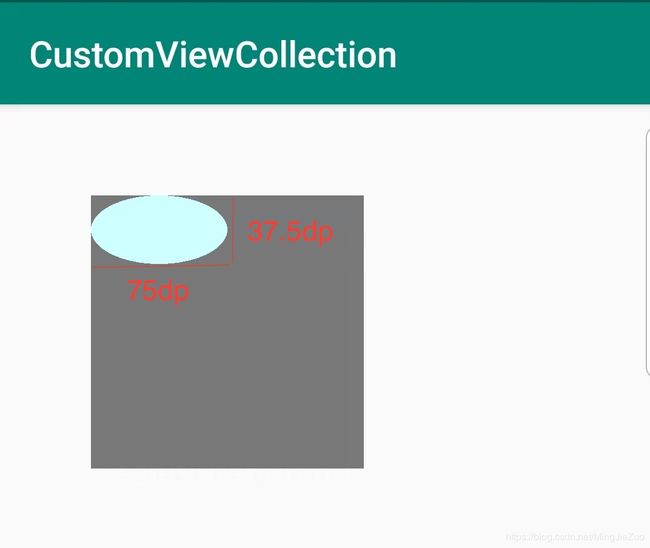
椭圆
这是画椭圆的api:
// added in api level 21
// public void drawOval (float left, float top, float right, float bottom, Paint paint)
public void drawOval (RectF oval, Paint paint)
方法中RectF即是椭圆的外切矩形。这里贴下椭圆的api方法:
if(mOvalRectF == null)
mOvalRectF = new RectF(0, 0
, CommentUtils.dip2px(mContext, 75)// 单位都是px
, CommentUtils.dip2px(mContext, 37.5f));
canvas.drawOval(mOvalRectF, mOvalPaint);
这是xml中的布局片段:
<com.mjzuo.views.view.GeometricFigureView
android:layout_width="150dp"
android:layout_height="150dp"
android:background="#787878"
android:layout_marginLeft="50dp"
android:layout_marginTop="50dp"
custom:draw_type="3"
/>
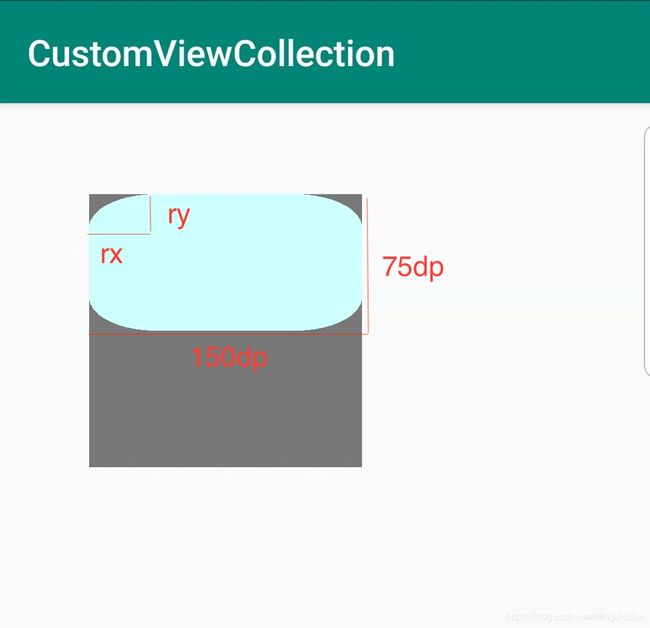
圆角矩形
这里贴下圆角矩形的api方法:
// added in api level 21
//public void drawRoundRect (float left, float top, float right, float bottom, float rx, float ry, Paint paint)
public void drawRoundRect (RectF rect, float rx, float ry, Paint paint)
这里贴下圆角矩形的方法:
/**
* RectF:矩形区域
* rx:在x轴的半径,焦点在x轴的椭圆长半轴
* ry:在y轴的半径,焦点在x轴的椭圆短半轴
* 可以理解成,在rectF矩形左上角的一个长轴短轴分别为2rx、2ry的标准内切椭圆
*/
if(mRoundRectF == null)
mRoundRectF = new RectF(0, 0
, CommentUtils.dip2px(mContext, 150)// 单位都是px
, CommentUtils.dip2px(mContext, 75));
canvas.drawRoundRect(mRoundRectF
, CommentUtils.dip2px(mContext, 36.5f)
, CommentUtils.dip2px(mContext, 18.25f)
, mRoundRectFPaint);
这是xml中的布局片段:
<com.mjzuo.views.view.GeometricFigureView
android:layout_width="150dp"
android:layout_height="150dp"
android:background="#787878"
android:layout_marginLeft="50dp"
android:layout_marginTop="50dp"
custom:draw_type="4"
/>
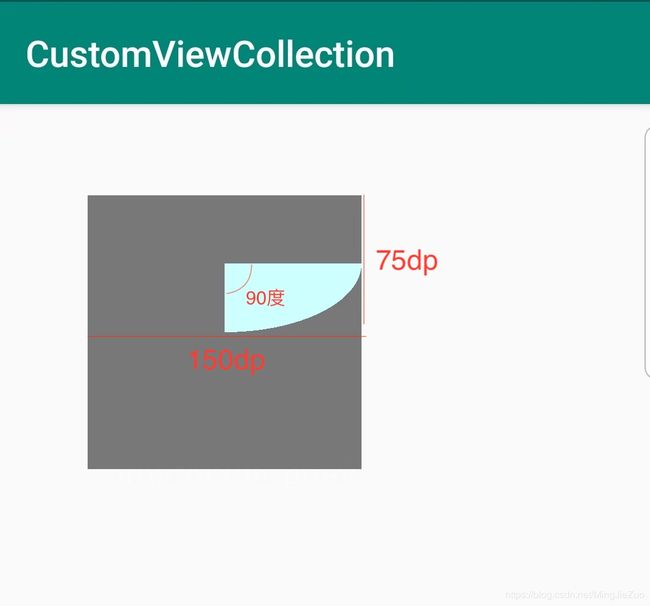
弧
这里贴下弧的api方法:
public void drawArc (RectF oval, float startAngle, float sweepAngle, boolean useCenter, Paint paint)
这里贴下使用弧的方法:
/**
* RectF:矩形边界
* startAngle:开始弧的角度,手表3点钟的方向为0
* sweepAngle:顺时针的扫过的总角度
* useCenter:椭圆的中心是否包含在弧里
*/
if(mArcRectF == null)
mArcRectF = new RectF(0, 0
, CommentUtils.dip2px(mContext, 150)// 单位都是px
, CommentUtils.dip2px(mContext, 75));
canvas.drawArc(mArcRectF
, 0
, 90
, true
, mArcPaint);
这是xml中的布局片段:
<com.mjzuo.views.view.GeometricFigureView
android:layout_width="150dp"
android:layout_height="150dp"
android:background="#787878"
android:layout_marginLeft="50dp"
android:layout_marginTop="50dp"
custom:draw_type="5"
/>
多边形
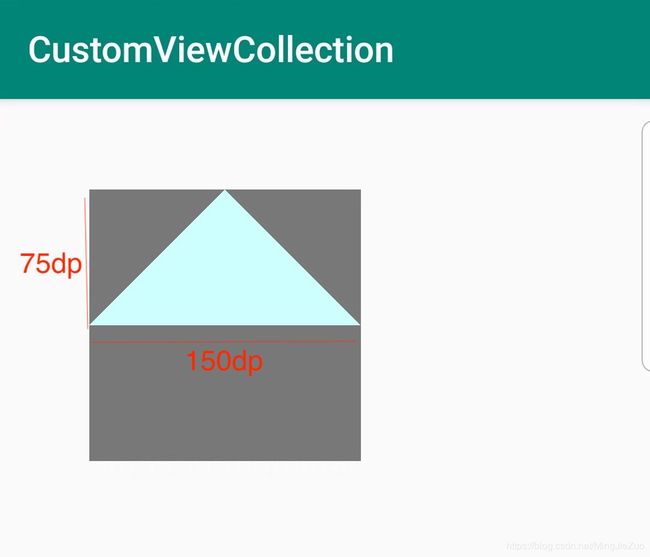
我们主要通过path方法来绘制多边形,当然如果配合画布的旋转、平移等会更加方便,在本demo中是以三角形为例,来演示path的用法,代码片段如下:
/**
* 绘制多边形,这里以三角形为例
*/
private void drawMoreFigure(Canvas canvas) {
// 三角形的起点
if(mMoreFIgurePath == null)
mMoreFIgurePath = new Path();
// 三角形的起点
mMoreFIgurePath.moveTo(CommentUtils.dip2px(mContext, 75), 0);
// (75,0)->(0,75)画线
mMoreFIgurePath.lineTo(0, CommentUtils.dip2px(mContext, 75));
// (0,75)->(150,75)画线
mMoreFIgurePath.lineTo(CommentUtils.dip2px(mContext, 150)
, CommentUtils.dip2px(mContext, 75));
// (150,75)->(75,0)画线,常用close替代
// mMoreFIgurePath.lineTo(CommentUtils.dip2px(mContext, 75), 0);
// 闭合路径
mMoreFIgurePath.close();
canvas.drawPath(mMoreFIgurePath, mMoreFigurePaint);
}
在xml中的代码片段如下:
<com.mjzuo.views.view.GeometricFigureView
android:layout_width="150dp"
android:layout_height="150dp"
android:background="#787878"
android:layout_marginLeft="50dp"
android:layout_marginTop="50dp"
custom:draw_type="6"
/>
效果图如下:
mMoreFigurePaint = new Paint();
mMoreFigurePaint.setColor(0xFFCCFFFF);
mMoreFigurePaint.setStyle(Paint.Style.STROKE);// 镶边
填充颜色
这里填下填充颜色的api:
// int:16进制。29以下默认模式:PorterDuff.Mode.SRC_OVER,即源像素直接绘制在目标像素上
public void drawColor (int color)
// long:将RGB转换成10进制的值
public void drawColor (long color)
// 两个参数的重载方法,具体model请查看源码或官网文档
public void drawColor (int color, PorterDuff.Mode mode)
// api 29新增方法,相较PorterDuff.Mode新增了一些方法,相当于一个包装类
public void drawColor (int color, BlendMode mode)
填充颜色的方法代码:
canvas.drawColor(0xFFCCFFFF, PorterDuff.Mode.SRC_OVER);
这是xml中的布局片段:
<com.mjzuo.views.view.GeometricFigureView
android:layout_width="150dp"
android:layout_height="150dp"
android:layout_marginLeft="50dp"
android:layout_marginTop="50dp"
custom:draw_type="7"
/>
文本
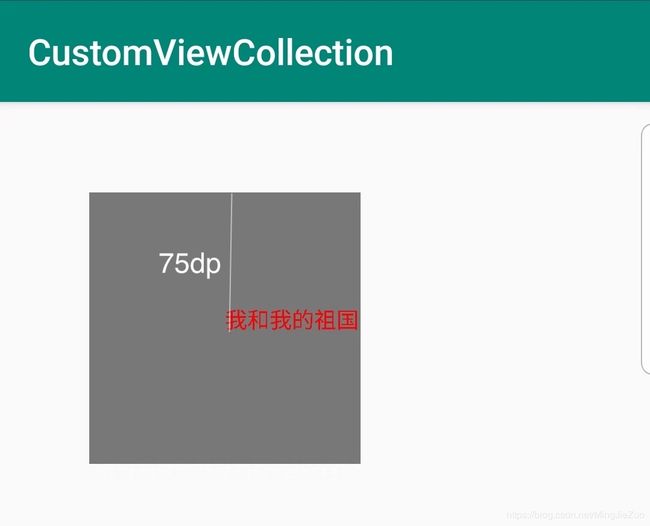
这里是绘制文本的api:
public void drawText (String text,
float x,
float y,
Paint paint)
这是绘制文字的代码:
/**
* text:绘制文本
* textX:绘制文本的原点x坐标
* textY:绘制文本基线的y坐标
*/
canvas.drawText("我和我的祖国"
, CommentUtils.dip2px(mContext, 75)
, CommentUtils.dip2px(mContext, 75)
, textPaint);
这是xml中的布局片段:
<com.mjzuo.views.view.GeometricFigureView
android:layout_width="150dp"
android:layout_height="150dp"
android:layout_marginLeft="50dp"
android:layout_marginTop="50dp"
custom:draw_type="8"
/>
bitmap
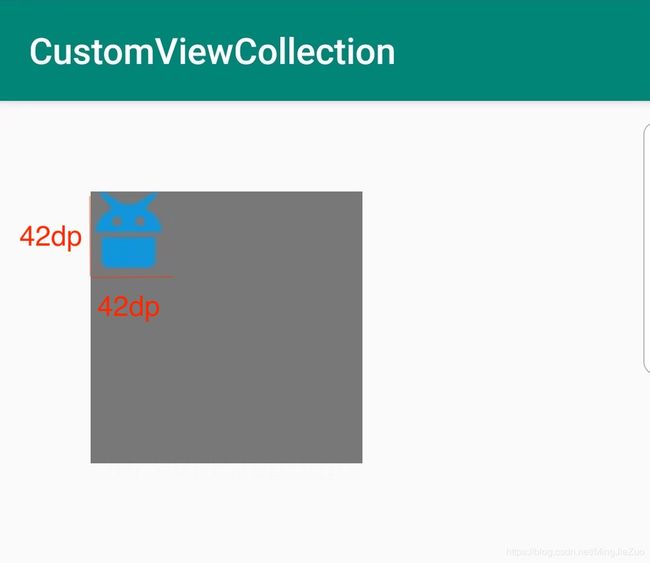
绘制图片位图的api:
public void drawBitmap (Bitmap bitmap,
float left,
float top,
Paint paint)
绘制位图的代码片段:
/**
* bitmap
* left:绘制的位图的左侧位置
* top:绘制位图的上方位置
*/
if(mBitmap == null){
// 将资源图片转换成bitmap,R.mipmap.android:资源图片
mBitmap = BitmapFactory.decodeResource(mContext.getResources(), R.mipmap.icon_android);
// 将mBitmap缩放成固定大小
mBitmap = BitmapUtils.conversionBitmap(mBitmap
, CommentUtils.dip2px(mContext, 42)
, CommentUtils.dip2px(mContext, 42));
}
canvas.drawBitmap(mBitmap
, 0
, 0
, mBitmapPaint);
这是xml中的布局片段:
<com.mjzuo.views.view.GeometricFigureView
android:layout_width="150dp"
android:layout_height="150dp"
android:background="#787878"
android:layout_marginLeft="50dp"
android:layout_marginTop="50dp"
custom:draw_type="9"
/>
画布裁剪
这是根据path裁剪canvas的代码片段:
private void drawClipPathOnCanval(Canvas canvas) {
if(mClipPath == null){
mClipPath = new Path();
// path为圆形矩形。裁剪圆形,弧等都同理
if(mClipRectF == null)
mClipRectF = new RectF(0, 0
, CommentUtils.dip2px(mContext, 150)// 单位都是px
, CommentUtils.dip2px(mContext, 150));
/**
* RectF:矩形轮廓
* rx:圆角矩形的圆角的x半径
* ry:圆角矩形的圆角的y半径
* direction:cw:顺时针、CCW:逆时针
*/
mClipPath.addRoundRect(mClipRectF
, CommentUtils.dip2px(mContext, 15)
, CommentUtils.dip2px(mContext, 15)
, Path.Direction.CW);
}
canvas.clipPath(mClipPath);
}
在onDraw方法中进行绘制,本例中是在裁剪后的canvas上绘制了3个矩形,代码片段如下:
// 锁定当前画布
canvas.save();
// 裁剪画布
drawClipPathOnCanval(canvas);
// 画红色矩形,矩形方法见上
drawRedRect(canvas);
// 画黄色矩形
drawYeRect(canvas);
// 画绿色矩形
drawGrRect(canvas);
// 恢复画布
canvas.restore();
在xml中的布局片段:
<com.mjzuo.views.view.GeometricFigureView
android:layout_width="150dp"
android:layout_height="150dp"
android:background="#787878"
android:layout_marginLeft="50dp"
android:layout_marginTop="50dp"
custom:draw_type="10"
/>
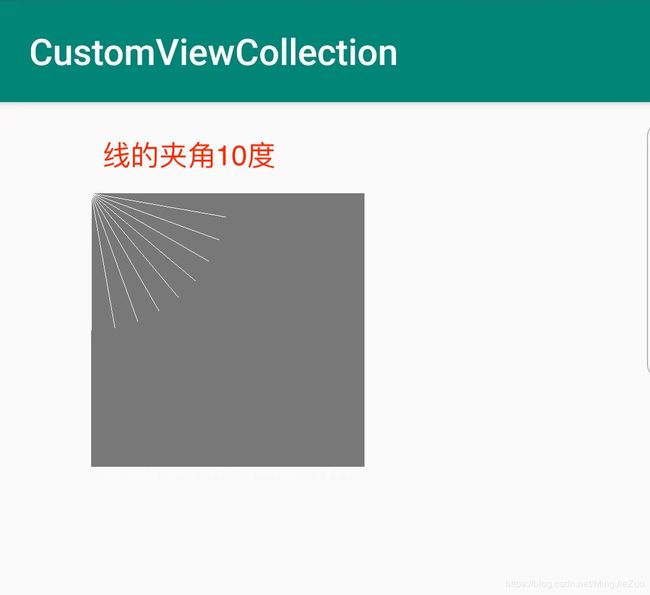
画布旋转
这是旋转画布的代码片段:
private void drawRotate(Canvas canvas) {
// 画10条线,画线的方法同上
for(int index = 0; index < 9; index ++){
// 画布旋转的角度,每次+10
canvas.rotate(10f);
// 因为画布旋转了,所以绘制出来的线段也就跟着旋转了
drawLine(canvas);
}
}
这是onDraw中的方法,需要在每次旋转前保存下当前的canvas:
// 锁定当前画布
canvas.save();
// 画线
drawRotate(canvas);
// 恢复画布
canvas.restore();
这是画线的方法,同上:
private void drawLine(Canvas canvas) {
/**
* @params startX 线段起点的x坐标
* @params startY 线段起点的Y坐标
* @params stopX 线段终点的x坐标
* @params stopY 线段终点y的坐标
*/
canvas.drawLine(0,0
, CommentUtils.dip2px(mContext, 75)
, 0
, linePaint);
}
这是xml中的布局的代码片段:
<com.mjzuo.views.view.GeometricFigureView
android:layout_width="150dp"
android:layout_height="150dp"
android:background="#787878"
android:layout_marginLeft="50dp"
android:layout_marginTop="50dp"
custom:draw_type="11"
/>
画布平移
在上面画布旋转代码的基础上,我们将画布中的线段起点挪动到view的中心点位置,代码片段如下:
private void drawTranslate(Canvas canvas){
/**
* dx: 要在x中转换的距离
* dy: 要在y中转换的距离
*/
canvas.translate(CommentUtils.dip2px(mContext, 75)
, CommentUtils.dip2px(mContext, 75));
}
在onDraw中绘制线段,并平移旋转画布:
// 锁定当前画布
canvas.save();
// 挪动画布
drawTranslate(canvas);
// 画线
drawRotate(canvas);
// 恢复画布
canvas.restore();
在xml中的代码片段:
<com.mjzuo.views.view.GeometricFigureView
android:layout_width="150dp"
android:layout_height="150dp"
android:background="#787878"
android:layout_marginLeft="50dp"
android:layout_marginTop="50dp"
custom:draw_type="12"
/>