Android设计模式之状态模式
状态模式定义
当一个对象的内在状态改变时允许改变其行为,这个对象看起来像是改变了其类。
状态模式的使用场景
1.一个对象的行为取决于它的状态,并且它必须在运行时根据状态改变它的行为。
2.代码中包含大量与对象状态有关的条件语句,例如,一个操作中包含于庞大的多分支语句(if-else或switch-case),且这些分支依赖于该对象的状态。
状态模式将每一个条件分支放入一个独立的类中,这使得你可以根据对象自身的状况将对象的状态作为一个对象,这一对象可以不依赖于其他对象而独立变化,这样通过多态来去除过多的、重复的if-else等分支语句。
Android源码中的状态模式
Wi-Fi 设置界面
public class WifiSettings extends RestrictedSettingsFragment
implements Indexable, WifiTracker.WifiListener, AccessPointListener,
WifiDialog.WifiDialogListener, FloatActionMenuView.OnFloatActionMenuSelectedListener {
//Wi-Fi管理器
protected WifiManager mWifiManager;
//Wi-Fi 开关控制器
private WifiEnabler mWifiEnabler;
//构造方法
public WifiSettings() {
super(DISALLOW_CONFIG_WIFI);
}
//监听Wi-Fi状态相关的广播
/// M: add no WAPI certification action @{
private BroadcastReceiver mReceiver = new BroadcastReceiver() {
@Override
public void onReceive(Context context, Intent intent) {
handleEvent(intent);
}
};
}#WifiSettings
@Override
public void onResume() {
final Activity activity = getActivity();
super.onResume();
// Because RestrictedSettingsFragment's onResume potentially requests authorization,
// which changes the restriction state, recalculate it.
final boolean alreadyImmutablyRestricted = mIsRestricted;
mIsRestricted = isUiRestricted();
if (!alreadyImmutablyRestricted && mIsRestricted) {
restrictUi();
}
if (mWifiEnabler != null) {
mWifiEnabler.resume(activity);
}
}#WifiSettings
@Override
public void onActivityCreated(Bundle savedInstanceState) {
super.onActivityCreated(savedInstanceState);
//1.获取WifiManager
mWifiManager = mWifiTracker.getManager();
... ...
}
#WifiSettings
@Override
public void onStart() {
super.onStart();
// On/off switch is hidden for Setup Wizard (returns null)
//将actionbarSwitch与WifiEnable关联起来
mWifiEnabler = createWifiEnabler();
mWifiTracker.startTracking();
if (mIsRestricted) {
restrictUi();
return;
}
onWifiStateChanged(mWifiManager.getWifiState());
}
#WifiSettings
/** Called when the state of Wifi has changed. */
@Override
public void onWifiStateChanged(int state) {
if (mIsRestricted) {
return;
}
final int wifiState = mWifiManager.getWifiState();
switch (wifiState) {
case WifiManager.WIFI_STATE_ENABLED:
conditionallyForceUpdateAPs();
break;
case WifiManager.WIFI_STATE_ENABLING:
removeConnectedAccessPointPreference();
mAccessPointsPreferenceCategory.removeAll();
addMessagePreference(R.string.wifi_starting);
setProgressBarVisible(true);
break;
case WifiManager.WIFI_STATE_DISABLING:
removeConnectedAccessPointPreference();
mAccessPointsPreferenceCategory.removeAll();
addMessagePreference(R.string.wifi_stopping);
break;
case WifiManager.WIFI_STATE_DISABLED:
setOffMessage();
setAdditionalSettingsSummaries();
setProgressBarVisible(false);
break;
}
}
#WifiSettings
/**
* @return new WifiEnabler or null (as overridden by WifiSettingsForSetupWizard)
*/
private WifiEnabler createWifiEnabler() {
final SettingsActivity activity = (SettingsActivity) getActivity();
return new WifiEnabler(activity, new SwitchBarController(activity.getSwitchBar()),
mMetricsFeatureProvider);
}
WifiSettings中的这个Fragment作用主要是构建一个设置界面、Wi-Fi开关切换按钮、一个Wi-Fi热点显示列表,当Wi-Fi启动后,开始扫描周边Wi-Fi,并且将扫描到的Wi-FI显示到ListView中。在这里有一个重要的类WifiEnabler ,就是一个Wi-Fi开关的控制类,在onStart()函数中创建,它的创建函数如下:
new WifiEnabler(activity, new SwitchBarController(activity.getSwitchBar()),
mMetricsFeatureProvider);
这个SwitchBar就是Wi-Fi开关的控制按钮,与按钮建立关联到底是怎么回事呢?我们直接看看WiFiEnable程序。
public class WifiEnabler implements SwitchWidgetController.OnSwitchChangeListener {
}
#WifiEnabler
private final BroadcastReceiver mReceiver = new BroadcastReceiver() {
@Override
public void onReceive(Context context, Intent intent) {
String action = intent.getAction();
if (WifiManager.WIFI_STATE_CHANGED_ACTION.equals(action)) {
handleWifiStateChanged(mWifiManager.getWifiState());
} else if (WifiManager.SUPPLICANT_STATE_CHANGED_ACTION.equals(action)) {
if (!mConnected.get()) {
handleStateChanged(WifiInfo.getDetailedStateOf((SupplicantState)
intent.getParcelableExtra(WifiManager.EXTRA_NEW_STATE)));
}
} else if (WifiManager.NETWORK_STATE_CHANGED_ACTION.equals(action)) {
NetworkInfo info = (NetworkInfo) intent.getParcelableExtra(
WifiManager.EXTRA_NETWORK_INFO);
mConnected.set(info.isConnected());
handleStateChanged(info.getDetailedState());
}
}
};
#WifiEnabler
public WifiEnabler(Context context, SwitchWidgetController switchWidget,
MetricsFeatureProvider metricsFeatureProvider) {
this(context, switchWidget, metricsFeatureProvider, new ConnectivityManagerWrapper(
(ConnectivityManager) context.getSystemService(Context.CONNECTIVITY_SERVICE)));
}
#WifiEnabler
@VisibleForTesting
WifiEnabler(Context context, SwitchWidgetController switchWidget,
MetricsFeatureProvider metricsFeatureProvider,
ConnectivityManagerWrapper connectivityManagerWrapper) {
mContext = context;
mSwitchWidget = switchWidget;
mSwitchWidget.setListener(this);
mMetricsFeatureProvider = metricsFeatureProvider;
mWifiManager = (WifiManager) context.getSystemService(Context.WIFI_SERVICE);
mConnectivityManager = connectivityManagerWrapper;
mIntentFilter = new IntentFilter(WifiManager.WIFI_STATE_CHANGED_ACTION);
// The order matters! We really should not depend on this. :(
mIntentFilter.addAction(WifiManager.SUPPLICANT_STATE_CHANGED_ACTION);
mIntentFilter.addAction(WifiManager.NETWORK_STATE_CHANGED_ACTION);
setupSwitchController();
}
#WifiEnabler
public void setupSwitchController() {
final int state = mWifiManager.getWifiState();
handleWifiStateChanged(state);
if (!mListeningToOnSwitchChange) {
mSwitchWidget.startListening();
mListeningToOnSwitchChange = true;
}
mSwitchWidget.setupView();
}
#WifiEnabler
public void resume(Context context) {
mContext = context;
// Wi-Fi state is sticky, so just let the receiver update UI
//注册广播接收器
mContext.registerReceiver(mReceiver, mIntentFilter);
if (!mListeningToOnSwitchChange) {
mSwitchWidget.startListening();
mListeningToOnSwitchChange = true;
}
}
WifiEnable类创建了一个广播来监听Wi-Fi状态的改变,并且自身实现了SwitchWidgetController.OnSwitchChangeListener 接口,这个接口会监听Wi-Fi开关按钮的状态修改。当Wi-Fi状态需要改变时首先会被广播接收器mReceiver接收到,此时会通过 handleWifiStateChanged(state) 函数修改Wi-Fi开关按钮状态。代码如下:
private void handleWifiStateChanged(int state) {
// Clear any previous state
mSwitchWidget.setDisabledByAdmin(null);
switch (state) {
case WifiManager.WIFI_STATE_ENABLING: //Wi-Fi开启中
break;
case WifiManager.WIFI_STATE_ENABLED: //Wi-Fi已开启
setSwitchBarChecked(true);
mSwitchWidget.setEnabled(true);
break;
case WifiManager.WIFI_STATE_DISABLING: //Wi-Fi关闭中
break;
case WifiManager.WIFI_STATE_DISABLED: //Wi-Fi已关闭
setSwitchBarChecked(false);
mSwitchWidget.setEnabled(true);
break;
default:
setSwitchBarChecked(false);
mSwitchWidget.setEnabled(true);
}
if (mayDisableTethering(!mSwitchWidget.isChecked())) {
if (RestrictedLockUtils.hasBaseUserRestriction(mContext,
UserManager.DISALLOW_CONFIG_TETHERING, UserHandle.myUserId())) {
mSwitchWidget.setEnabled(false);
} else {
final EnforcedAdmin admin = RestrictedLockUtils.checkIfRestrictionEnforced(mContext,
UserManager.DISALLOW_CONFIG_TETHERING, UserHandle.myUserId());
mSwitchWidget.setDisabledByAdmin(admin);
}
}
}Wi-Fi状态修改之后会导致mSwitchWidget开关按钮的状态的修改,而mSwitchWidget的状态修改又会触发
#SwitchBarController
SwitchBarController这个类封装了SwitchBar的操作,SwitchBarController所有操作实际调用的都是 SwitchBar的操作。
public class SwitchBarController extends SwitchWidgetController implements
SwitchBar.OnSwitchChangeListener {
private final SwitchBar mSwitchBar;
public SwitchBarController(SwitchBar switchBar) {
mSwitchBar = switchBar;
}
@Override
public void updateTitle(boolean isChecked) {
mSwitchBar.setTextViewLabel(isChecked);
}
@Override
public void startListening() {
mSwitchBar.addOnSwitchChangeListener(this);
}
@Override
public void stopListening() {
mSwitchBar.removeOnSwitchChangeListener(this);
}
@Override
public void setChecked(boolean checked) {
mSwitchBar.setChecked(checked);
}
@Override
public boolean isChecked() {
return mSwitchBar.isChecked();
}
@Override
public void setEnabled(boolean enabled) {
mSwitchBar.setEnabled(enabled);
}
@Override
public void onSwitchChanged(Switch switchView, boolean isChecked) {
if (mListener != null) {
mListener.onSwitchToggled(isChecked);
}
}
}
#SwitchBar
public class SwitchBar extends LinearLayout implements CompoundButton.OnCheckedChangeListener,
View.OnClickListener {
public interface OnSwitchChangeListener {
/**
* Called when the checked state of the Switch has changed.
*
* @param switchView The Switch view whose state has changed.
* @param isChecked The new checked state of switchView.
*/
void onSwitchChanged(Switch switchView, boolean isChecked);
}
... ...
}
#WifiEnabler WifiEnabler实现了SwitchWidgetController.OnSwitchChangeListener接口
@Override
public boolean onSwitchToggled(boolean isChecked) {
//Do nothing if called as a result of a state machine event
if (mStateMachineEvent) {
return true;
}
// Show toast message if Wi-Fi is not allowed in airplane mode
if (isChecked && !WirelessUtils.isRadioAllowed(mContext, Settings.Global.RADIO_WIFI)) {
Toast.makeText(mContext, R.string.wifi_in_airplane_mode, Toast.LENGTH_SHORT).show();
// Reset switch to off. No infinite check/listenenr loop.
mSwitchWidget.setChecked(false);
return false;
}
// Disable tethering if enabling Wifi
if (mayDisableTethering(isChecked)) {
mConnectivityManager.stopTethering(ConnectivityManager.TETHERING_WIFI);
}
if (isChecked) {
mMetricsFeatureProvider.action(mContext, MetricsEvent.ACTION_WIFI_ON);
} else {
// Log if user was connected at the time of switching off.
mMetricsFeatureProvider.action(mContext, MetricsEvent.ACTION_WIFI_OFF,
mConnected.get());
}
if (!mWifiManager.setWifiEnabled(isChecked)) {
// Error
mSwitchWidget.setEnabled(true);
Toast.makeText(mContext, R.string.wifi_error, Toast.LENGTH_SHORT).show();
}
return true;
}
mWifiManager = (WifiManager) context.getSystemService(Context.WIFI_SERVICE);
WifiManager的setWifiEnabled函数也是一个空壳,它实际上转发给了WifiService类的setWifiEnable方法,这个WifiService和ActivityManagerService、WindowManagerService一起在系统启动时被注入到ServiceManager中。在如下代码中:
#SystemServiceRegistry.java
这里注册了WifiService
registerService(Context.WIFI_SERVICE, WifiManager.class,
new CachedServiceFetcher() {
@Override
public WifiManager createService(ContextImpl ctx) throws ServiceNotFoundException {
IBinder b = ServiceManager.getServiceOrThrow(Context.WIFI_SERVICE);
IWifiManager service = IWifiManager.Stub.asInterface(b);
return new WifiManager(ctx.getOuterContext(), service,
ConnectivityThread.getInstanceLooper());
}});
#WifiManager
@SystemService(Context.WIFI_SERVICE)
public class WifiManager
#WifiManager 构造方法
/**
* Create a new WifiManager instance.
* Applications will almost always want to use
* {@link android.content.Context#getSystemService Context.getSystemService()} to retrieve
* the standard {@link android.content.Context#WIFI_SERVICE Context.WIFI_SERVICE}.
* @param context the application context
* @param service the Binder interface
* @hide - hide this because it takes in a parameter of type IWifiManager, which
* is a system private class.
*/
public WifiManager(Context context, IWifiManager service, Looper looper) {
mContext = context;
mService = service;
mLooper = looper;
mTargetSdkVersion = context.getApplicationInfo().targetSdkVersion;
/// M: Hotspot manager implementation
mWifiHotspotManager = new WifiHotspotManager(service);
}
/**
* Enable or disable Wi-Fi.
*
* Note: This method will return false if wifi cannot be enabled (e.g., an incompatible mode
* where the user has enabled tethering or Airplane Mode).
*
* Applications need to have the {@link android.Manifest.permission#CHANGE_WIFI_STATE}
* permission to toggle wifi. Callers without the permissions will trigger a
* {@link java.lang.SecurityException}.
*
* @param enabled {@code true} to enable, {@code false} to disable.
* @return {@code true} if the operation succeeds (or if the existing state
* is the same as the requested state). False if wifi cannot be toggled on/off when the
* request is made.
*/
public boolean setWifiEnabled(boolean enabled) {
Log.d(TAG, "setWifiEnabled " + enabled + ", uid:" + Process.myUid());
try {
//实际上调用的是WifiService的setWifiEnabled
return mService.setWifiEnabled(mContext.getOpPackageName(), enabled);
} catch (RemoteException e) {
throw e.rethrowFromSystemServer();
}
}
MtkWifiServiceImpl 继承了 IWifiManager.Stub
#MtkWifiServiceImpl
public abstract class MtkWifiServiceImpl extends IWifiManager.Stub {
}
#WifiServiceImpl
public class WifiServiceImpl extends MtkWifiServiceImpl {
/**
* see {@link android.net.wifi.WifiManager#setWifiEnabled(boolean)}
* @param enable {@code true} to enable, {@code false} to disable.
* @return {@code true} if the enable/disable operation was
* started or is already in the queue.
*/
@Override
public synchronized boolean setWifiEnabled(String packageName, boolean enable)
throws RemoteException {
... ...
//代码省略
mWifiController.sendMessage(CMD_WIFI_TOGGLED);
return true;
}
}
这不是真正实现功能的地方,实际工作是通过mWifiController 发送一个 CMD_WIFI_TOGGLED , 看起来和Handler很像,private WifiController mWifiController;mWifiController 的类型是 WifiController ,sendMessage这个方法在 WifiController 的父类
StateMachine中,如下:
**
* WifiController is the class used to manage on/off state of WifiStateMachine for various operating
* modes (normal, airplane, wifi hotspot, etc.).
*/
public class WifiController extends StateMachine {
}
#StateMachine
WiFo controller的父类, StateMachine类
public class StateMachine {
/**
* Enqueue a message to this state machine.
*
* Message is ignored if state machine has quit.
*/
//发送消息
public void sendMessage(int what) {
// mSmHandler can be null if the state machine has quit.
SmHandler smh = mSmHandler;
if (smh == null) return;
//通过SmHandler对象发送消息
smh.sendMessage(obtainMessage(what));
}
/**
* Enqueue a message to this state machine.
*
* Message is ignored if state machine has quit.
*/
public void sendMessage(int what, Object obj) {
// mSmHandler can be null if the state machine has quit.
SmHandler smh = mSmHandler;
if (smh == null) return;
smh.sendMessage(obtainMessage(what, obj));
}
... ...
其实这个StateMachine 类重载了多个 sendMessage 方法
}
#StateMachine 类的内部类SmHandler
StateMachine中的sendMessage方法实际上是通过StateMachine的内部类SmHandler对象发送的消息,如下是SmHandler相关代码:
private static class SmHandler extends Handler {
/** Reference to the StateMachine */
private StateMachine mSm;
/**
* Information about a state.
* Used to maintain the hierarchy.
*/
//状态信息类,用于管理状态层级
private class StateInfo {
/** The state */
//当前状态
State state;
/** The parent of this state, null if there is no parent */
//当前状态的上一个状态
StateInfo parentStateInfo;
/** True when the state has been entered and on the stack */
//当前状态是否被激活,如果已被激活则为true。
boolean active;
}
/**
* Handle messages sent to the state machine by calling
* the current state's processMessage. It also handles
* the enter/exit calls and placing any deferred messages
* back onto the queue when transitioning to a new state.
*/
//处理发送到StateMachine 的消息
@Override
public final void handleMessage(Message msg) {
if (!mHasQuit) {
if (mSm != null && msg.what != SM_INIT_CMD && msg.what != SM_QUIT_CMD) {
mSm.onPreHandleMessage(msg);
}
if (mDbg) mSm.log("handleMessage: E msg.what=" + msg.what);
/** Save the current message */
mMsg = msg;
/** State that processed the message */
State msgProcessedState = null;
if (mIsConstructionCompleted) {
/** Normal path */
//1.处理消息,并且返回处理了该消息的状态
msgProcessedState = processMsg(msg);
} else if (!mIsConstructionCompleted && (mMsg.what == SM_INIT_CMD)
&& (mMsg.obj == mSmHandlerObj)) {
/** Initial one time path. */
mIsConstructionCompleted = true;
invokeEnterMethods(0);
} else {
throw new RuntimeException("StateMachine.handleMessage: "
+ "The start method not called, received msg: " + msg);
}
//2.执行状态转换
performTransitions(msgProcessedState, msg);
// We need to check if mSm == null here as we could be quitting.
if (mDbg && mSm != null) mSm.log("handleMessage: X");
if (mSm != null && msg.what != SM_INIT_CMD && msg.what != SM_QUIT_CMD) {
mSm.onPostHandleMessage(msg);
}
}
}
}
SmHandler通过消息的消息的机制类控制wifi的状态,当Wifi状态发生改变时,外部通过sendMessage发送一个对应的消息,在SmHandler中的handleMessage方法中首先调用processMsg将这个消息交给当前状态进行处理,如果当前状态不能处理,那么就会交给它的上一个状态处理,最后返回处理了这个消息的状态,具体代码如下:
#StateMachine
/**
* Process the message. If the current state doesn't handle
* it, call the states parent and so on. If it is never handled then
* call the state machines unhandledMessage method.
* @return the state that processed the message
*/
private final State processMsg(Message msg) {
StateInfo curStateInfo = mStateStack[mStateStackTopIndex];
if (mDbg) {
mSm.log("processMsg: " + curStateInfo.state.getName());
}
//是否退出消息
if (isQuit(msg)) {
transitionTo(mQuittingState);
} else {
//调用了状态对象的processMessage 函数来处理消息
while (!curStateInfo.state.processMessage(msg)) {
/**
* Not processed
*消息没有被处理,那么交给parent state处理
*这里类似于触摸事件的消息机制
*/
curStateInfo = curStateInfo.parentStateInfo;
if (curStateInfo == null) {
/**
* No parents left so it's not handled
*/
//到最后都没有被处理,则调用 mSm.unhandledMessage
mSm.unhandledMessage(msg);
break;
}
if (mDbg) {
mSm.log("processMsg: " + curStateInfo.state.getName());
}
}
}
return (curStateInfo != null) ? curStateInfo.state : null;
}
处理完该状态之后,会调用performTransitions函数退出 旧的状态,并且进入新的状态,具体代码如下:
/**
* Do any transitions
* @param msgProcessedState is the state that processed the message
*/
//进行状态转换
private void performTransitions(State msgProcessedState, Message msg) {
/**
* If transitionTo has been called, exit and then enter
* the appropriate states. We loop on this to allow
* enter and exit methods to use transitionTo.
*/
//原始状态
State orgState = mStateStack[mStateStackTopIndex].state;
/**
* Record whether message needs to be logged before we transition and
* and we won't log special messages SM_INIT_CMD or SM_QUIT_CMD which
* always set msg.obj to the handler.
*/
boolean recordLogMsg = mSm.recordLogRec(mMsg) && (msg.obj != mSmHandlerObj);
if (mLogRecords.logOnlyTransitions()) {
/** Record only if there is a transition */
if (mDestState != null) {
mLogRecords.add(mSm, mMsg, mSm.getLogRecString(mMsg), msgProcessedState,
orgState, mDestState);
}
} else if (recordLogMsg) {
/** Record message */
mLogRecords.add(mSm, mMsg, mSm.getLogRecString(mMsg), msgProcessedState, orgState,
mDestState);
}
//目标状态
State destState = mDestState;
if (destState != null) {
/**
* Process the transitions including transitions in the enter/exit methods
*/
while (true) {
if (mDbg) mSm.log("handleMessage: new destination call exit/enter");
/**
* Determine the states to exit and enter and return the
* common ancestor state of the enter/exit states. Then
* invoke the exit methods then the enter methods.
*/
//退出某些状态,并且进入新的状态
StateInfo commonStateInfo = setupTempStateStackWithStatesToEnter(destState);
// flag is cleared in invokeEnterMethods before entering the target state
mTransitionInProgress = true;
invokeExitMethods(commonStateInfo);
int stateStackEnteringIndex = moveTempStateStackToStateStack();
//进入某个wi-fi状态
invokeEnterMethods(stateStackEnteringIndex);
// 后续处理以及判断跳出循环,代码省略
/**
* Since we have transitioned to a new state we need to have
* any deferred messages moved to the front of the message queue
* so they will be processed before any other messages in the
* message queue.
*/
moveDeferredMessageAtFrontOfQueue();
if (destState != mDestState) {
// A new mDestState so continue looping
destState = mDestState;
} else {
// No change in mDestState so we're done
break;
}
}
mDestState = null;
}
/**
* After processing all transitions check and
* see if the last transition was to quit or halt.
*/
if (destState != null) {
if (destState == mQuittingState) {
/**
* Call onQuitting to let subclasses cleanup.
*/
mSm.onQuitting();
cleanupAfterQuitting();
} else if (destState == mHaltingState) {
/**
* Call onHalting() if we've transitioned to the halting
* state. All subsequent messages will be processed in
* in the halting state which invokes haltedProcessMessage(msg);
*/
mSm.onHalting();
}
}
}
/**
* Invoke the enter method starting at the entering index to top of state stack
*/
//调用状态的enter函数
private final void invokeEnterMethods(int stateStackEnteringIndex) {
for (int i = stateStackEnteringIndex; i <= mStateStackTopIndex; i++) {
if (stateStackEnteringIndex == mStateStackTopIndex) {
// Last enter state for transition
mTransitionInProgress = false;
}
if (mDbg) mSm.log("invokeEnterMethods: " + mStateStack[i].state.getName());
//执行状态的enter()函数
mStateStack[i].state.enter();
mStateStack[i].active = true;
}
mTransitionInProgress = false; // ensure flag set to false if no methods called
}
下面是需要关注的状态类State,它代表了Wi-Fi的某一个状态,这个状态如下:
/**
* {@hide}
*
* The class for implementing states in a StateMachine
*/
public class State implements IState {
/**
* Constructor
*/
protected State() {
}
/* (non-Javadoc)
* @see com.android.internal.util.IState#enter()
*/进入当前状态之后调用该函数
@Override
public void enter() {
}
/* (non-Javadoc)
* @see com.android.internal.util.IState#exit()
*/退出该状态之后调用该函数
@Override
public void exit() {
}
/* (non-Javadoc)
* @see com.android.internal.util.IState#processMessage(android.os.Message)
*/处理消息
@Override
public boolean processMessage(Message msg) {
return false;
}
/**
* Name of State for debugging purposes.
*
* This default implementation returns the class name, returning
* the instance name would better in cases where a State class
* is used for multiple states. But normally there is one class per
* state and the class name is sufficient and easy to get. You may
* want to provide a setName or some other mechanism for setting
* another name if the class name is not appropriate.
*
* @see com.android.internal.util.IState#processMessage(android.os.Message)
*/
@Override
public String getName() {
String name = getClass().getName();
int lastDollar = name.lastIndexOf('$');
return name.substring(lastDollar + 1);
}状态之间并不是可以随意切换的,它们有一种层级关系,这些层级关系在StateMachine 的构造函数中被定义
public class WifiStateMachine extends StateMachine implements WifiNative.WifiRssiEventHandler,
WifiMulticastLockManager.FilterController {
... ...
}
#WifiStateMachine
public WifiStateMachine(Context context, FrameworkFacade facade, Looper looper,
UserManager userManager, WifiInjector wifiInjector,
BackupManagerProxy backupManagerProxy, WifiCountryCode countryCode,
WifiNative wifiNative,
WrongPasswordNotifier wrongPasswordNotifier) {
... ...
// CHECKSTYLE:OFF IndentationCheck
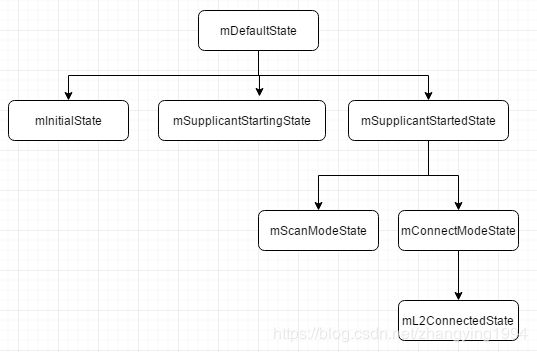
addState(mDefaultState);
addState(mInitialState, mDefaultState);
addState(mSupplicantStartingState, mDefaultState);
addState(mSupplicantStartedState, mDefaultState);
addState(mScanModeState, mSupplicantStartedState);
addState(mConnectModeState, mSupplicantStartedState);
addState(mL2ConnectedState, mConnectModeState);
addState(mObtainingIpState, mL2ConnectedState);
addState(mConnectedState, mL2ConnectedState);
addState(mRoamingState, mL2ConnectedState);
addState(mDisconnectingState, mConnectModeState);
addState(mDisconnectedState, mConnectModeState);
addState(mWpsRunningState, mConnectModeState);
addState(mWaitForP2pDisableState, mSupplicantStartedState);
addState(mSupplicantStoppingState, mDefaultState);
addState(mSoftApState, mDefaultState);
// CHECKSTYLE:ON IndentationCheck
//初始化模式为mInitialState
setInitialState(mInitialState);
... ...
}
在上述构造函数中调用addState函数,这些函数最终都会调用SmHandler中addState函数。
#StateMachine
* Add a new state to the state machine
* @param state the state to add
* @param parent the parent of state
*/
public final void addState(State state, State parent) {
mSmHandler.addState(state, parent);
}
#StateMachine
/**
* Add a new state to the state machine, parent will be null
* @param state to add
*/
public final void addState(State state) {
mSmHandler.addState(state, null);
}
#StateMachine
/**
* Removes a state from the state machine, unless it is currently active or if it has children.
* @param state state to remove
*/
public final void removeState(State state) {
mSmHandler.removeState(state);
} private static class SmHandler extends Handler {
#SmHandler
/**
* Add a new state to the state machine. Bottom up addition
* of states is allowed but the same state may only exist
* in one hierarchy.
*
* @param state the state to add
* @param parent the parent of state
* @return stateInfo for this state
*/
//在构造函数中调用了addState函数,这些函数最终会调用SmHandler中的addState函数
//添加状态,state为当前状态,parent为上一个状态,也就是parent状态。
private final StateInfo addState(State state, State parent) {
if (mDbg) {
mSm.log("addStateInternal: E state=" + state.getName() + ",parent="
+ ((parent == null) ? "" : parent.getName()));
}
StateInfo parentStateInfo = null;
//获取parent对应的StateInfo
if (parent != null) {
parentStateInfo = mStateInfo.get(parent);
if (parentStateInfo == null) {
// Recursively add our parent as it's not been added yet.
parentStateInfo = addState(parent, null);
}
}
//获取当前状态的StateInfo
StateInfo stateInfo = mStateInfo.get(state);
if (stateInfo == null) {
stateInfo = new StateInfo();
mStateInfo.put(state, stateInfo);
}
// Validate that we aren't adding the same state in two different hierarchies.
if ((stateInfo.parentStateInfo != null)
&& (stateInfo.parentStateInfo != parentStateInfo)) {
throw new RuntimeException("state already added");
}
//建立层级关系
stateInfo.state = state;
//上一个StateInfo
stateInfo.parentStateInfo = parentStateInfo;
stateInfo.active = false;
if (mDbg) mSm.log("addStateInternal: X stateInfo: " + stateInfo);
return stateInfo;
}
}
该函数就是在状态之间建立一个层级关系,这是一个树形的层级关系。例如:
从StateMachine 的构造函数中可以得到状态之间的部分层级图。
状态之间不是跨越式转换的,当前状态只能转换到上一状态或者下一状态,例如:Wi-Fi的状态为mDefault时,它不能直接跳到mConnectModeState 状态,需要先转换到 mSupplicantStartedState状态,然后才能转换到 mConnectModeState状态。StateMachine 内部就是维护了一个状态切换序列,并且对于不同的状态下对于相同的事件有不同的处理。
状态之间也需要一个转换规则来控制的,这个转换规则就是我们这里的层级关系。不完整(不包含所有的状态)
不同状态对于不同的指令的反应也是完全不一样的。
Wi-Fi工作状态机制也是同理,除了对状态之间的转换进行控制之外,还通过状态模式来对不同的命令进行不同的处理。上文说过,State类是状态类的基类,它与Wi-Fi相关的子类都定义在WifiStateMachine中。
public class WifiStateMachine extends StateMachine implements WifiNative.WifiRssiEventHandler,
WifiMulticastLockManager.FilterController { }
State类有enter、exit、processMessage三个函数,进入状态之后会调用enter函数,退出时会调用exit函数,处理具体的消息时则会调用processMessage。上文中讲到的状态模式的核心是“当一个对象的内部状态改变时允许改变其行为”,processMessage就是关注点,不同的状态下就是依赖这个函数实现不同的行为。这里我们以WiFi扫描功能来说明状态模式。
在请求扫描Wi-Fi 时,会发送一个CMD_START_SCAN消息,请求Wi-Fi驱动进行WI-Fi扫描,但是,在初始(InitialState)状态下,WiFi驱动还没有进行加载与启动,因此,在初始状态下该命令不会被处理。具体代码如下:
/* Temporary initial state */ 临时初始状态
private State mInitialState = new InitialState();
#WifiStateMachine
InitialState 是 WifiStateMachine 的内部类
class InitialState extends State {
private void cleanup() {
// Tearing down the client interfaces below is going to stop our supplicant.
mWifiMonitor.stopAllMonitoring();
mDeathRecipient.unlinkToDeath();
//Wi-Fi驱动被卸载
mWifiNative.tearDown();
}
@Override
public void enter() {
mWifiStateTracker.updateState(WifiStateTracker.INVALID);
cleanup();
}
@Override
public boolean processMessage(Message message) {
logStateAndMessage(message, this);
switch (message.what) {
case CMD_START_SUPPLICANT:
Pair statusAndInterface =
mWifiNative.setupForClientMode();
if (statusAndInterface.first == WifiNative.SETUP_SUCCESS) {
mClientInterface = statusAndInterface.second;
} else {
incrementMetricsForSetupFailure(statusAndInterface.first);
}
if (mClientInterface == null
|| !mDeathRecipient.linkToDeath(mClientInterface.asBinder())) {
setWifiState(WifiManager.WIFI_STATE_UNKNOWN);
cleanup();
break;
}
try {
// A runtime crash or shutting down AP mode can leave
// IP addresses configured, and this affects
// connectivity when supplicant starts up.
// Ensure we have no IP addresses before a supplicant start.
mNwService.clearInterfaceAddresses(mInterfaceName);
// Set privacy extensions
mNwService.setInterfaceIpv6PrivacyExtensions(mInterfaceName, true);
// IPv6 is enabled only as long as access point is connected since:
// - IPv6 addresses and routes stick around after disconnection
// - kernel is unaware when connected and fails to start IPv6 negotiation
// - kernel can start autoconfiguration when 802.1x is not complete
mNwService.disableIpv6(mInterfaceName);
} catch (RemoteException re) {
loge("Unable to change interface settings: " + re);
} catch (IllegalStateException ie) {
loge("Unable to change interface settings: " + ie);
}
if (!mWifiNative.enableSupplicant()) {
loge("Failed to start supplicant!");
setWifiState(WifiManager.WIFI_STATE_UNKNOWN);
cleanup();
break;
}
if (mVerboseLoggingEnabled) log("Supplicant start successful");
mWifiMonitor.startMonitoring(mInterfaceName, true);
mWifiInjector.getWifiLastResortWatchdog().clearAllFailureCounts();
setSupplicantLogLevel();
transitionTo(mSupplicantStartingState);
break;
case CMD_START_AP:
transitionTo(mSoftApState);
break;
case CMD_SET_OPERATIONAL_MODE:
mOperationalMode = message.arg1;
if (mOperationalMode != DISABLED_MODE) {
sendMessage(CMD_START_SUPPLICANT);
}
break;
//以上是其他命令处理。
//扫描Wi-Fi的命令直接返回 NOT_HANDLED ,也就是未处理
default:
return NOT_HANDLED;
}
return HANDLED;
}
}
当处在Wi-Fi驱动加载中状态(DriverStartingState)时,扫描Wi-Fi的请求会被延后处理,Wi-Fi驱动加载完之后该请求重新提交,DriverStartingState类如下:
/* Driver loaded, waiting for supplicant to start */
驱动程序已加载,等待请求者启动
private State mSupplicantStartingState = new SupplicantStartingState();
class SupplicantStartingState extends State {
private void initializeWpsDetails() {
String detail;
detail = mPropertyService.get("ro.product.name", "");
if (!mWifiNative.setDeviceName(detail)) {
loge("Failed to set device name " + detail);
}
detail = mPropertyService.get("ro.product.manufacturer", "");
if (!mWifiNative.setManufacturer(detail)) {
loge("Failed to set manufacturer " + detail);
}
detail = mPropertyService.get("ro.product.model", "");
if (!mWifiNative.setModelName(detail)) {
loge("Failed to set model name " + detail);
}
detail = mPropertyService.get("ro.product.model", "");
if (!mWifiNative.setModelNumber(detail)) {
loge("Failed to set model number " + detail);
}
detail = mPropertyService.get("ro.serialno", "");
if (!mWifiNative.setSerialNumber(detail)) {
loge("Failed to set serial number " + detail);
}
if (!mWifiNative.setConfigMethods("physical_display virtual_push_button")) {
loge("Failed to set WPS config methods");
}
if (!mWifiNative.setDeviceType(mPrimaryDeviceType)) {
loge("Failed to set primary device type " + mPrimaryDeviceType);
}
}
@Override
public boolean processMessage(Message message) {
logStateAndMessage(message, this);
switch(message.what) {
case WifiMonitor.SUP_CONNECTION_EVENT:
if (mVerboseLoggingEnabled) log("Supplicant connection established");
mSupplicantRestartCount = 0;
/* Reset the supplicant state to indicate the supplicant
* state is not known at this time */
mSupplicantStateTracker.sendMessage(CMD_RESET_SUPPLICANT_STATE);
/* Initialize data structures */
mLastBssid = null;
mLastNetworkId = WifiConfiguration.INVALID_NETWORK_ID;
mLastSignalLevel = -1;
mWifiInfo.setMacAddress(mWifiNative.getMacAddress());
initializeWpsDetails();
sendSupplicantConnectionChangedBroadcast(true);
///M: ALPS03503585 Disable EAP-SIM AP if modem is not ready
MtkEapSimUtility.disableSimConfigWhenSimNotLoaded();
transitionTo(mSupplicantStartedState);
break;
case WifiMonitor.SUP_DISCONNECTION_EVENT:
if (++mSupplicantRestartCount <= SUPPLICANT_RESTART_TRIES) {
loge("Failed to setup control channel, restart supplicant");
mWifiMonitor.stopAllMonitoring();
mWifiNative.disableSupplicant();
transitionTo(mInitialState);
sendMessageDelayed(CMD_START_SUPPLICANT, SUPPLICANT_RESTART_INTERVAL_MSECS);
} else {
loge("Failed " + mSupplicantRestartCount +
" times to start supplicant, unload driver");
mSupplicantRestartCount = 0;
setWifiState(WIFI_STATE_UNKNOWN);
transitionTo(mInitialState);
}
break;
case CMD_START_SUPPLICANT:
case CMD_STOP_SUPPLICANT:
case CMD_START_AP:
case CMD_STOP_AP:
case CMD_SET_OPERATIONAL_MODE:
messageHandlingStatus = MESSAGE_HANDLING_STATUS_DEFERRED;
deferMessage(message);
break;
default:
return NOT_HANDLED;
}
return HANDLED;
}
}
在Wi-Fi驱动加载完之后进入DriverStartedState状态,扫描Wi-Fi的命令会被处理,此时会请求Wi-Fi驱动进行扫描工作。代码如下:
/* Driver loaded and supplicant ready */ 驱动程序加载和请求者准备好了
private State mSupplicantStartedState = new SupplicantStartedState();
class SupplicantStartedState extends State {
@Override
public void enter() {
.... //其他工作
}
@Override
public boolean processMessage(Message message) {
logStateAndMessage(message, this);
switch(message.what) {
case CMD_START_SCAN:
// TODO: remove scan request path (b/31445200)
handleScanRequest(message);
break;
default:
return NOT_HANDLED;
}
return HANDLED;
}
@Override
public void exit() {
mWifiDiagnostics.stopLogging();
mIsRunning = false;
updateBatteryWorkSource(null);
mScanResults = new ArrayList<>();
final Intent intent = new Intent(WifiManager.WIFI_SCAN_AVAILABLE);
intent.addFlags(Intent.FLAG_RECEIVER_REGISTERED_ONLY_BEFORE_BOOT);
intent.putExtra(WifiManager.EXTRA_SCAN_AVAILABLE, WIFI_STATE_DISABLED);
mContext.sendStickyBroadcastAsUser(intent, UserHandle.ALL);
mBufferedScanMsg.clear();
mNetworkInfo.setIsAvailable(false);
if (mNetworkAgent != null) mNetworkAgent.sendNetworkInfo(mNetworkInfo);
mCountryCode.setReadyForChange(false);
}
}
在不同状态下对于扫描WiFi这个请求的处理是完全不一样的。在初始化状态下扫描请求被直接忽略,在驱动加载中状态下Wi-Fi请求被添加到延迟处理的消息列表,在驱动加载完成状态下扫描WiFi的请求被直接处理。
不同的状态下改变了扫描Wi-Fi请求的行为,这就是状态模式的精髓,它的实现原理就是将请求的处理封装到状态类中,在不同的状态类中对同一个请求进行不同的处理。
参考《Android源码设计模式》