webpack4+react配置多页面移动端应用程序
webpack4+react配置多页面移动端应用程序
- 前言
- 技术栈
- 项目目录结构
- 移动端适配方案
- webpack配置
- 基础配置
- 开发环境配置
- react+redux热重载
- 生产环境配置
- .babelrc配置
- 总结
前言
最近在搞一个基于react的多页面移动端应用程序。构建工具使用的是webpack,脚手架并不是使用create-react-app这个官方推荐的脚手架,而是利用webpack从0到1搭建起来的脚手架。在搭建项目环境的过程中遇见了不少难点,所以就想着把它记录下来,分享出来,希望可以帮助到有需要的同学。项目github地址https://github.com/c10342/webpack4-react-multipage
技术栈
首先说一下这个项目所使用的的技术栈。主要是webpack,react,node-sass。这里需要注意的是node-sass的安装,国内用户可能会因为需要的原因会安装失败,所以需要设置一下node-sass的安装源,设置如下:npm config set sass-binary-site http://npm.taobao.org/mirrors/node-sass,这种方式是设置全局的安装源,以后再次node-sass安装就会直接从这个镜像源下载;或者npm install --save node-sass --registry=https://registry.npm.taobao.org --disturl=https://npm.taobao.org/dist --sass-binary-site=http://npm.taobao.org/mirrors/node-sass,这种方式就是局部有效,只在本次安装有效。但是我建议是在项目根目录下新建一个名为.npmrc的文件,然后写上sass_binary_site=https://npm.taobao.org/mirrors/node-sass/,这样即使别人拿到你的项目也可以直接安装了,不用设置这么多。下面先贴一下依赖包的版本号吧。
"devDependencies": {
"@babel/core": "^7.8.7",
"@babel/plugin-transform-runtime": "^7.8.3",
"@babel/preset-env": "^7.8.7",
"@babel/preset-react": "^7.8.3",
"autoprefixer": "^9.7.4",
"babel-loader": "^8.0.6",
"clean-webpack-plugin": "^3.0.0",
"copy-webpack-plugin": "^5.1.1",
"css-loader": "^3.4.2",
"file-loader": "^5.1.0",
"html-webpack-plugin": "^3.2.0",
"mini-css-extract-plugin": "^0.9.0",
"node-sass": "^4.13.1",
"postcss-loader": "^3.0.0",
"react-hot-loader": "^4.12.19",
"sass-loader": "^8.0.2",
"sass-resources-loader": "^2.0.1",
"style-loader": "^1.1.3",
"url-loader": "^3.0.0",
"webpack": "^4.42.0",
"webpack-cli": "^3.3.11",
"webpack-dev-server": "^3.10.3",
"webpack-merge": "^4.2.2"
},
"dependencies": {
"@babel/runtime-corejs3": "^7.8.7",
"axios": "^0.19.2",
"core-js": "^3.6.4",
"react": "^16.13.0",
"react-dom": "^16.13.0",
"react-loadable": "^5.5.0",
"react-redux": "^7.2.0",
"react-router-dom": "^5.1.2",
"redux": "^4.0.5",
"redux-thunk": "^2.3.0",
"regenerator-runtime": "^0.13.3"
}
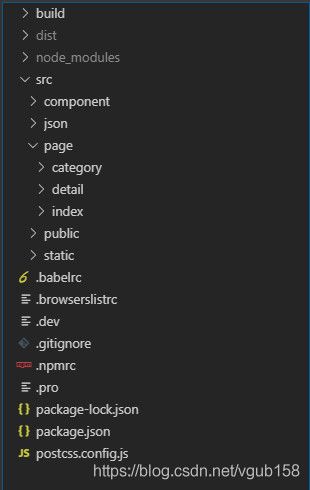
项目目录结构
- build:放置webpack的配置文件的
- node_modules:这个就不用说了,安装依赖包的
- dist:打包后的静态资源文件
- src:写代码的地方
- page:用来存放多页面的,page目录下每一个文件夹都代表着一个页面,每个文件夹下必须有一个 index.js和index.html,它们分别是入口文件和html模板文件。
- component:存放每个页面可能会使用到的通用组件。
- json:mock数据。
- public:每个页面可能会使用到css或者js。
- static:静态资源目录,这个目录下的文件会原封不动的复制到打包出来的dist目录下的static文件夹。
- .babelrc:babel-loader的配置文件。
- .browserslistrc:需要兼容的浏览器版本。
- .npmrc:npm的配置文件,上面所说的安装node-sass就是在这个文件设置下载镜像源的。
- .dev:开发环境的变量
- .pro:生产环境的变量
- postcss.config.js:postcss-loader的配置文件
移动端适配方案
移动端适配方案有很多种,比如媒体查询,flex+rem,百分比布局等等。我一开纠结的是使用flex+rem还是那种可以自动将px转换为rem的第三方插件,比如postcss-pxtorem。使用第三方插件的好处就是只需要简单的配置就可以在开发的时候可以直接使用px作为单位,打包过后就会自动转换为rem。最后我还是选择使用flex+rem,主要是因为我对这些第三方插件的配置文件也不熟悉,不清楚内部的转换原理,然后有些功能的实现上需要获取具体rem对应的px值或者具体px对应的rem值这些。然后flex+rem使用上相对比较灵活,你可以自己去定义换算规则。代码如下:
- px转化为rem
function px2rem(px) {
const ratio = 375 / 10
return px / ratio
}
- rem转化为px
function realPx(px) {
const maxWidth = window.innerWidth > 500 ? 500 : window.innerWidth
return px * (maxWidth / 375)
}
- 根据屏幕尺寸动态设置html的font-size的值
function initRem(){
function initHtmlFontSize(){
let fontSize = window.innerWidth / 10
fontSize = fontSize > 50 ? 50 : fontSize
const html = document.querySelector('html')
html.style.fontSize = fontSize + 'px'
}
document.addEventListener('DOMContentLoaded', initHtmlFontSize)
window.addEventListener('resize',initHtmlFontSize())
}
webpack配置
基础配置
基础配置我就直接上代码了,因为还是比较简单,基本上代码的每一行我都有做解释的。这里我要说明一下要注意哪些loader的顺序,它们的执行顺序是从下往上,从右往左执行的,代码如下:
const path = require('path')
const fs = require('fs')
const CopyPlugin = require('copy-webpack-plugin')
// src目录路径
const srcRoot = path.resolve(__dirname, '../src')
// 多页面存放路径
const pageDir = path.resolve(srcRoot, 'page')
// 打包输出路径
const outputPath = path.resolve(__dirname, '../dist')
//.pro文件路径
const proVariablePath = path.resolve(__dirname,'../.pro')
//.dev文件路径
const devVariablePath = path.resolve(__dirname,'../.dev')
// 每个页面的入口文件名
const mainFile = 'index.js'
// 每个页面的html模板文件名
const mainHtml = 'index.html'
// 获取page下的所有入口文件
function getEntry() {
let entryMap = {}
fs.readdirSync(pageDir).forEach(function (pathName) {
const fullPathName = path.resolve(pageDir, pathName)
let stat = fs.statSync(fullPathName)
let fileName = path.resolve(fullPathName, mainFile)
if (stat.isDirectory() && fs.existsSync(fileName)) {
entryMap[pathName] = fileName
}
})
return entryMap
}
//读取文件,主要是用来读取.dev和.pro文件的内容,将a=123这种形式转化为对象
//这里参考了vue-cli的做法
function readFileContentToEnvObj(pathStr) {
let obj = {}
if (fs.existsSync(pathStr) && fs.statSync(pathStr).isFile()) {
const result = fs.readFileSync(pathStr).toString()
if (result) {
const envArr = result.split('\r\n')
if (envArr.length > 0) {
for (let i = 0; i < envArr.length; i++) {
try {
const envItem = envArr[i].split('=')
if (envItem.length > 0) {
const a = envItem[0].trim()
const b = envItem[1].trim()
if (a && b) {
obj[a] = JSON.stringify(b)
}
}
} catch (error) { }
}
}
}
}
return obj
}
// 入口
const entry = getEntry()
const baseConfig = {
entry,
// 输出
output: {
path: outputPath,
filename: 'js/[name].[hash].js'
},
resolve: {
// 可以忽略的扩展名
extensions: ['.js', '.jsx'],
// 有些目录层级比较深,所以要是用别名
alias: {
'@': path.resolve(__dirname, '../src')
}
},
module: {
rules: [
{
test: /\.(js|jsx)$/,
use: ['babel-loader'],
include: srcRoot
},
{
test: /\.(png|jpg|jpeg|gif|eot|ttf|svg)$/,
use: {
loader: 'url-loader',
options: {
name: '[name].[hash].[ext]',
outputPath: 'images/',
limit: 10240 //小于10240的转化为base64
}
}
}
]
},
plugins:[
// 将src目录下的static文件夹原封不动拷贝一份到输出目录下的static文件夹,并替换原有的文件
new CopyPlugin([
{
from: path.resolve(srcRoot,'./static'),
to: path.resolve(outputPath,'./static'),
force:true
},
])
]
}
//将.dev文件内容读取成对象
const devObj = readFileContentToEnvObj(devVariablePath)
//将.pro文件内容读取成对象
const proObj = readFileContentToEnvObj(proVariablePath)
module.exports = {
baseConfig,
pageDir,
mainHtml,
entry,
srcRoot,
outputPath,
devObj,
proObj
}
开发环境配置
我就直接上代码,在代码里面做解释,这样至更加直观,代码如下:
const path = require('path')
const fs = require('fs')
const HtmlWebpackPlugin = require('html-webpack-plugin')
const webpack = require('webpack');
const webpackMerge = require('webpack-merge')
const {
baseConfig,
pageDir,
mainHtml,
entry,
outputPath,
srcRoot,
devObj
} = require('./webpack.config.base')
//获取每个页面指定的html模板文件,生成并返回HtmlWebpackPlugin数组
function getHtmlArray(entryMap) {
let htmls = []
Object.keys(entryMap).forEach(function (key) {
const fullPathName = path.resolve(pageDir, key)
const fileName = path.resolve(fullPathName, mainHtml)
if (fs.existsSync(fileName)) {
htmls.push(new HtmlWebpackPlugin({
filename: key + '.html',
template: fileName,
chunks: [key] //需要注入的js,开发环境下不抽取分离js代码,
//所以这里的chunk只有一个,就是对应的入口文件的chunk
}))
}
})
return htmls
}
const htmlArray = getHtmlArray(entry)
const devConfig = {
//模式,必须设置
mode: 'development',
//webpack-dev-server的配置
devServer: {
//自动打开浏览器
open: true,
//服务器根路径,这里需要注意的是开发环境下打包的东西都是直接进内存的,不会出现在磁盘的
contentBase: outputPath,
//热加载
hot: true
},
module: {
rules: [
{
test: /\.css$/,
use: [
'style-loader',
{
loader: 'css-loader',
options: {
//有些css是通过@import 引进来的,有可能会不走下面的loader,
//所以这里要指定下面还有几个loader,
//@import引进来的css才会继续走下面的loader
importLoaders: 1
}
},
'postcss-loader'
],
include: srcRoot
},
{
test: /\.scss$/,
use: [
'style-loader',
{
loader: 'css-loader',
options: {
importLoaders: 2
}
},
'postcss-loader',
'sass-loader',
{
//这个loader是用来将指定的scss文件注入到每个scss文件中的
loader: 'sass-resources-loader',
options: {
//需要注入到每一个scss文件的scss文件,
//多个文件使用数组的方式,
//这里需要注意的是不要将一些通用的css样式写在style.scss中,
//不然打包出来的css文件会重复出现这些通用的样式,
//style.scss只适合写一些变量或者方法
resources: srcRoot + '/public/css/style.scss'
}
}
],
include: srcRoot
}
]
},
plugins: [
//html-wenpack-plugin插件
...htmlArray,
new webpack.DefinePlugin({
'process.env':{
mode:JSON.stringify('development'),
...devObj
}
}),
//webpack.NamedModulesPlugin和webpack.HotModuleReplacementPlugin是用来做热重载的
//配合上面的devServer.hot一期使用的
new webpack.NamedModulesPlugin(),
new webpack.HotModuleReplacementPlugin()
]
}
//将开发配置和基础配置合并
module.exports = webpackMerge(baseConfig,devConfig)
react+redux热重载
要实现react和redux的热重载,必须要在开发配置中开启热重载这个功能,我上面的配置已经开启了
react实现热重载需要借助react-hot-loader这个插件,大家可以参考react-hot-loader官方文档的写法,我这里提供另外一种写法,代码如下
//react-hot-loader的引入要在最顶层,否则可能会不生效
import {hot} from 'react-hot-loader'
import {HashRouter} from 'react-router-dom'
import { Provider } from 'react-redux'
import store from './redux/store'
import Main from './container/Main/Main.jsx'
const App = () => {
return (
<Provider store={store}>
<HashRouter>
<Main></Main>
</HashRouter>
</Provider>
)
}
//module是自带的,不需要引入
const HotApp = hot(module)(App)
ReactDOM.render(
<HotApp/>,
document.getElementById('root')
)
redux热重载的代码如下:
import { createStore,applyMiddleware,compose } from 'redux'
import thunk from 'redux-thunk'
import reducers from './reducers'
const store = createStore(reducers,compose(
applyMiddleware(thunk),
window.__REDUX_DEVTOOLS_EXTENSION__ && window.__REDUX_DEVTOOLS_EXTENSION__()
))
if (module.hot) {
module.hot.accept('./reducers/index.js', () => {
const nextRootReducer = require('./reducers/index.js').default;
store.replaceReducer(nextRootReducer)
});
}
export default store
生产环境配置
我就直接上代码,在代码里面做解释,这样至更加直观,代码如下:
const path = require('path')
const fs = require('fs')
const HtmlWebpackPlugin = require('html-webpack-plugin')
const MiniCssExtractPlugin = require('mini-css-extract-plugin');
const webpackMerge = require('webpack-merge');
const webpack = require('webpack');
const {CleanWebpackPlugin} = require('clean-webpack-plugin')
const { baseConfig, pageDir, mainHtml, entry,srcRoot,proObj } = require('./webpack.config.base')
//获取每个页面指定的html模板文件,生成并返回HtmlWebpackPlugin数组
function getHtmlArray(entryMap) {
let htmls = []
Object.keys(entryMap).forEach(function (key) {
const fullPathName = path.resolve(pageDir, key)
const fileName = path.resolve(fullPathName, mainHtml)
if (fs.existsSync(fileName)) {
htmls.push(new HtmlWebpackPlugin({
filename: key + '.html',
template: fileName,
//这里因为对js进行抽取分离,所以这里比开发环境的配置多了2个chunk
//为什么是`vendors.${key}`?因为chunk名就是分组名+连接符+入口名
chunks: [`vendors.${key}`, `default.${key}`, key]
}))
}
})
return htmls
}
const htmlArray = getHtmlArray(entry)
const proConfig = {
mode: 'production',
module: {
rules: [
{
test: /\.css$/,
use: [
//这里使用了MiniCssExtractPlugin.loader提取css就不能使用style-loader
//因为style-loader是直接用style标签挂载上去的,
//MiniCssExtractPlugin.loader是提取出来之后使用link标签引进去的
//两者同时使用时出现报错,所以这里要注意一下和开发环境的配置的区别
MiniCssExtractPlugin.loader,
{
loader: 'css-loader',
options: {
importLoaders: 1
}
},
'postcss-loader'
],
include: srcRoot
},
{
test: /\.scss$/,
use: [
MiniCssExtractPlugin.loader,
{
loader: 'css-loader',
options: {
importLoaders: 2
}
},
'postcss-loader',
'sass-loader',
{
loader: 'sass-resources-loader',
options: {
resources: srcRoot + '/public/css/style.scss'
}
}
],
include: srcRoot
},
]
},
plugins: [
...htmlArray,
//这个插件会在每次打包前清空上一次的打包文件
new CleanWebpackPlugin(),
//提取css
new MiniCssExtractPlugin({
filename: 'css/[name].[contenthash].css',
chunkFilename: 'css/[name].[contenthash].chunk.css',
}),
new webpack.DefinePlugin({
'process.env':{
mode:JSON.stringify('production'),
...proObj
}
})
],
optimization: {
// 使package.json中sideEffects的文件不会被Tree Shaking掉
//Tree Shaking是指会把一些没有使用到的js代码清除掉
//特别是类似 import '../xx/xx.js'; 这种很可能会被清除掉,所以要特别注意
usedExports: true,
// 抽离代码
splitChunks: {
// all:同步引入的代码和异步引入的代码都进行代码分割
chunks: 'all',
// 第三方库大于30kb才会被抽离出来
minSize: 30000,
// 组和文件名连接符
automaticNameDelimiter: '.',
// 分组内有filename就使用filename
name: true,
// 分组,符合上面的代码分割要求的都会跑到这里来进行分组
cacheGroups: {
vendors: {
// 在node_modules中的第三方库都会被抽离到这个分组中
test: /[\\/]node_modules[\\/]/,
// 当被抽离的代码符合多个分组时,会优先打包到priority值比较大的分组中
priority: -10,
// 打包后的文件名,使用懒加载(异步加载)的时候不能写文件名,否则会有冲突报错
// filename: 'js/venders.js'
},
default: {
// 默认分组,所有没有匹配到分组的都会被放到这里来
priority: -20,
// 已经被打包过的文件不会被再次打包,会复用前面已经打包过的文件
reuseExistingChunk: true,
}
}
}
}
}
module.exports = webpackMerge(baseConfig, proConfig)
.babelrc配置
老规矩,先上代码,在逐一讲解:
{
"presets": [
[
"@babel/preset-env",
{
"useBuiltIns": "usage",
"corejs": 3,
"targets": {
"chrome": "58",
"ie": "9"
}
}
],
"@babel/preset-react",
],
"plugins": [
[
"@babel/plugin-transform-runtime",
{
"absoluteRuntime": false,
"corejs": 3,
"helpers": true,
"regenerator": true,
"useESModules": false
}
]
]
}
- “useBuiltIns”: “usage” usage 会根据配置中需要兼容的浏览器,以及代码中用到的 API 来进行 polyfill,实现了按需添加。
- “corejs”: 3 babel最新文档上写着babel-loader从7.4.0开始就不能在使用 @babel/polyfill,需要使用以下代码替代
import "core-js/stable";
import "regenerator-runtime/runtime";
而要使用上面这段代码,runtime-corejs的版本必须是3,项目babel-loader的版本是8.0.6,所以corejs这里必须填写3
总结
项目环境的搭建难点主要是在于对webpack配置的理解。遇见不懂的地方多查阅文档以及参考别人的一些技术博客。最后我已经将这个项目的代码上传到了我的github上,有需要得可以下载下来观摩参考