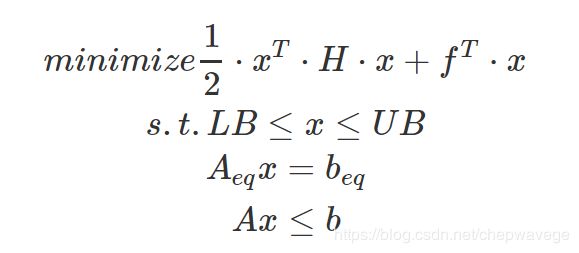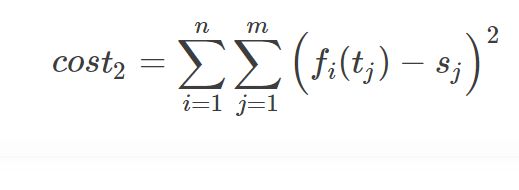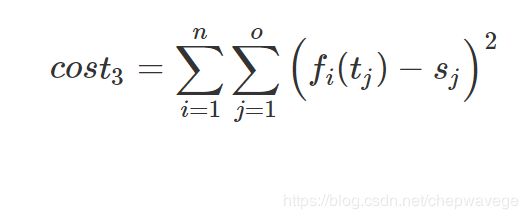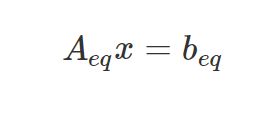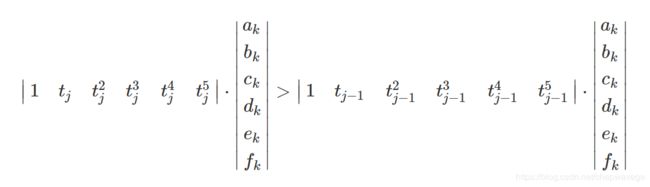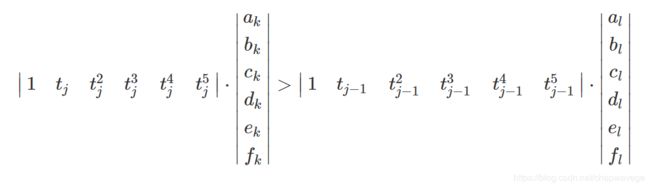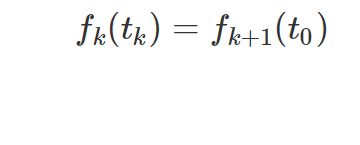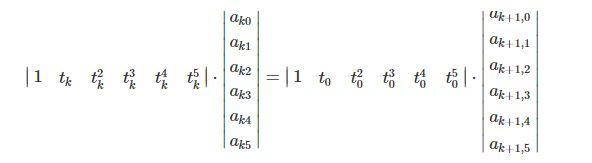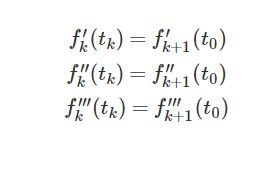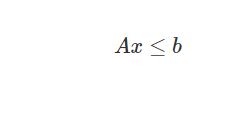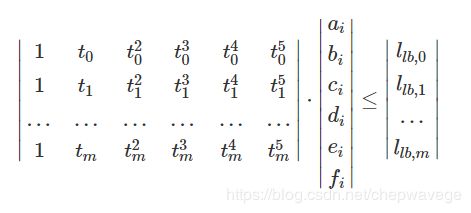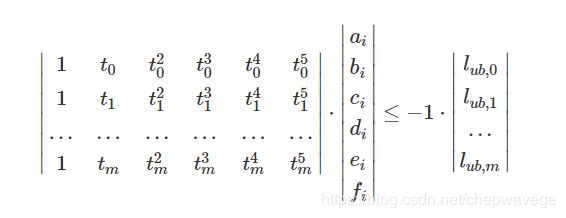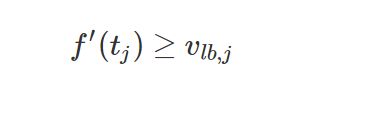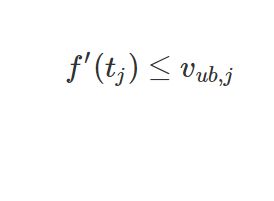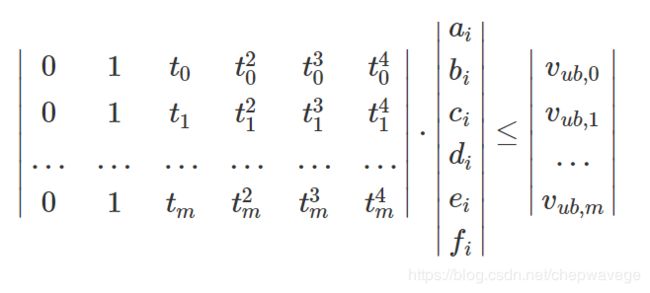Apollo_ADS_路径规划3- 速度曲线 优化_QP-Spline-ST-Speed Optimizer
QP-Spline-ST-Speed Optimizer
ST纵向距离 VS 时间,station-time (S-T)
S 纵向arc length VS Lateral 横向距离 station-lateral
https://github.com/ApolloAuto/apollo/blob/master/docs/specs/qp_spline_st_speed_optimizer.md
1 Definition
After finding a path in QP-Spline-Path, Apollo converts all obstacles on the path and the ADV (autonomous driving vehicle) into an path-time (S-T) graph, which represents that the station changes over time along the path. The speed optimization task is to find a path on the S-T graph that is collision-free and comfortable.
Apollo uses splines to represent speed profiles, which are lists of S-T points in S-T graph. Apollo leverages Quadratic programming to find the best profile. The standard form of QP problem is defined as:
在QP样条路径中找到路径后,Apollo将路径上的所有障碍物和ADV(自动驾驶车辆)转换为路径-时间(S-T)图,表示站点(ego 行驶的位置纵坐标)在路径上随时间的变化。速度优化任务是在S-T图上找到一条无碰撞且舒适的路径。
Apollo使用样条来表示速度profile,这是S-T图中S-T点的列表。阿波罗利用二次规划来寻找最佳profile。QP问题的标准形式定义为: s.t.=constrains
2 Objective function 目标函数
2.1 Get spline segments 获取样条曲线段
Split the S-T profile into n segments. Each segment trajectory is defined by a polynomial.多项式
2.2 Define function for each spline segment 定义样条曲线 (泰勒级数)
Each segment i has an accumulated (积分) distance d_i along a reference line. And the trajectory for the segment is defined as a polynomial of degree five by default. The degree of the polynomials are adjustable by configuration parameters. 这里用了5阶,阶数软件可以配置。
距离关于时间的函数,如果求导,一阶导数得到v,二阶加速度,三阶 jerk. ... notes: 这里,只有纵向的一个坐标(所以一个方程)
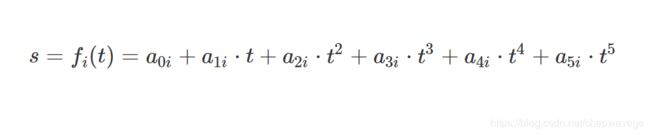 2.3 Define objective function of optimization for each segment 定义样条平顺 优化函数
2.3 Define objective function of optimization for each segment 定义样条平顺 优化函数
Apollo first defines cost_1 to make the trajectory smooth: (注意这里把 t 换成了s=v*t,v 认为恒定)ds的意义?)意义就是获得从A到B获得的速度,加速度,jerk 平方的加权
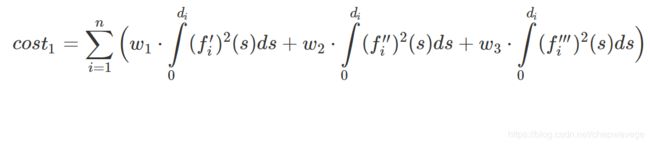 Then Apollo defines cost_2 as the difference between the final S-T trajectory (目标路径) and the cruise S-T (ego行驶实际路径)trajectory (with given speed limits — m points): Sj的定义, ???--- Sj 为第j 个点的纵向坐标--目标值??, 下面计算了所有规划点和目标点的方差
Then Apollo defines cost_2 as the difference between the final S-T trajectory (目标路径) and the cruise S-T (ego行驶实际路径)trajectory (with given speed limits — m points): Sj的定义, ???--- Sj 为第j 个点的纵向坐标--目标值??, 下面计算了所有规划点和目标点的方差
理解:固定一段曲线-方程为f1,其中采样j个点 sj。
Similarly, Apollo defines cost_3 that is the difference between the first S-T path and the follow(紧接着的) S-T path (o points):
Finally, the objective function is defined as:
cost = cost_1 + cost_2 + cost_3
3 Constraints
3.1 The init point constraints 初始点约束
Given已知 the assumption that the first point is (t0, s0), and s0 is on the planned path f_i(t) , f'i(t), and f_i(t)'' (position, velocity, acceleration). Apollo converts those constraint into QP equality constraints:
如何实现? 应该就是把初始条件带入即可
3.2 Monotone 单调性 constraint
The path must be monotone, e.g., the vehicle can only drive forward.--汽车向前开,s一直变大
Sample m points on the path, for each j and j-1 point pairs 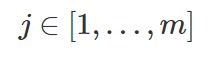 :
:
If the two points on the same spline k:
If the two points on the different spline k and l:
3.3 Joint smoothness constraints
节点连续性(位置、速度,加速度都是联系变化的)约束
This constraint is designed to smooth the spline joint. Given the assumption that two segments, seg_k and seg_k+1, are connected, and the accumulated s of segment seg_k is s_k, Apollo calculates the constraint equation as:
Namely:
Then
The result is t_0 = 0 in the equation.
Similarly calculate the equality constraints for
3.4 Sampled points for boundary constraint 纵向位置边界约束
在路径上均匀采集n个点,Evenly sample m points along the path, and check the obstacle boundary at those points. Convert the constraint into QP inequality constraints, using:
Apollo first finds the lower boundary at those points
at those points ![]() ,
, based on the road width and surrounding obstacles. Then it calculates the inequality 不等式 constraints as:
based on the road width and surrounding obstacles. Then it calculates the inequality 不等式 constraints as:
下边界
Similarly, for upper boundary 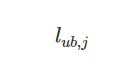 , Apollo calculates the inequality constraints as: 上边界
, Apollo calculates the inequality constraints as: 上边界
notes: 注意上下边界的这个不等式,| | 不是绝对值,是矩阵, 上边界这个等式,如何理解呢, 障碍物的坐标都是相对ego的,在ego 后面的目标(被超过了),纵向的位置为负数, 好像还是有问题。。。。 ,对照路径的SL, 感觉等式左边 。里面漏了负号。
3.5 Speed Boundary constraint 速度边界约束
Apollo establishes a speed limit boundary as well.
Sample m points on the st curve, and get speed limits defined as an upper boundary and a lower boundary for each point $j$, e.g., ![]() and
and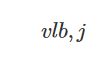 . The constraints are defined as:
. The constraints are defined as:
Namely
And
Namely
还可以加上其他的约束,比如车辆动力学,加速度,jerk 法规的约束。
总结:
速度profile的优化:
1.定义ST坐标系下的,纵向位置曲线多项式方程(5阶) S--t
2.定义目标函数,考虑 位置,速度,jerk 。 跟随的偏差(位置)
3.加上约束与边界
- 初始条件
- 单调性(位置)
- 连续性(s,v,jerk)
- 障碍物的边界(位置)
- 限速信息的边界(速度)
- 加速度边界
- jerk 边界
- 车辆动力学 etc.