2019独角兽企业重金招聘Python工程师标准>>> ![]()
需要实现一个文件目录树,用于文件的快速查询,因此打算实现一个快速的树形结构。
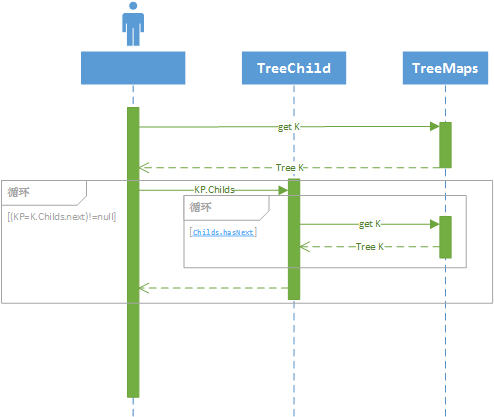
设计思路是所有树节点均存储在map中,根中保留有子节点的key的Set字段child。因此树也可以根据需要改造成为有序树,可以修改childInit或使用构造器Forest(Supplier> childInit)即可将默认的HashSet修改为TreeSet。完成有序树。 获得以某节点作为根的树形结构
效率:
因为节点均存储在hashmap中,在1.8的haspMap实现中,主要是依据hash+红黑树,因此构建节点数m,时间复杂度为mlog(m) 构建|移动|删除 时间复杂度为2NO(log(n)),n=节点数,appendChain(ks.length=2); 获取某节点O(log(n)) n=总节点个数.
先根遍历在不考虑栈的情况下,某树下的所有节点 nO(nlog(n)) n=子树节点数
注:
key 的判断主要是需要满足hashmap 对key 的要求,即为hashcode和equals。因此重写这两个方法即可.
首先实现一个基础的树形数据结构。
/**
*
* @author yuyi
* @param
*/
public class Forest implements Serializable, Cloneable {
private static final long serialVersionUID = 1L;
protected Supplier> childInit = () -> new HashSet<>();
private Set roots = childInit.get();
protected HashMap map;
public Tree get(K key) {
return map.get(key);
}
/** 独立某个子树 */
public Tree aloneTree(K k1) {
Tree t = get(k1);
if (t == null)
return null;
if (t.par != null) {
t.parent().child.remove(k1);
t.par = null;
roots.add(k1);
}
return t;
}
/**
* 添加一个有序链
*
*
* 例如添加 1 2 3 则树为{k=1,son=[{k=2,son=[{key=3}]}]}
* 再次添加 1 4 则树为{k=1,son=[{k=2,son=[{key=3}]},{key=4}]}
* 再次添加 2 4 则树为{k=1,son=[{k=2,son=[{key=3},{key=4}]}]}
*
*
* @param ks
* 线性有序子树(即每层仅一个节点)
* @return
*/
@SuppressWarnings("unchecked")
public Forest appendChain(K... ks) {
assert ks != null && ks.length > 2 && ks[0] != null && ks[1] != null;
K k, pk = null;
int i = 0;
Tree curr = map.get(ks[i]), par = curr != null ? curr.parent() : null;
Set f = roots;
if (par != null) {
i = 1;
f = par.child;
}
for (; ks.length > i; i++) {
if (Objects.equals(k = ks[i], pk))
continue;
if ((curr = map.get(pk = k)) == null) {
curr = new Tree(k);
}
if (!f.contains(k)) {
if (par == null || !Objects.equals(curr.par, par)) {
if (curr.par == null)
roots.remove(k);
else
curr.parent().child.remove(k);
curr.par = par != null ? par.key : curr.par;
f.add(k);
map.put(k, curr);
}
}
par = curr;
f = curr.child;
}
return this;
}
public Forest appendChain(Iterator iterator) {
assert iterator != null;
Set f = roots;
Tree curr = null, par = null;
K k, pk = null;
while (iterator.hasNext()) {
if (Objects.equals(k = iterator.next(), pk))
continue;
if ((curr = map.get(k)) == null) {
curr = new Tree(k);
}
if (!f.contains(k)) {
if (par == null || !Objects.equals(curr.par, par)) {
if (curr.par == null)
roots.remove(k);
else
curr.parent().child.remove(k);
curr.par = par != null ? par.key : curr.par;
if (curr.par != null && roots == f) {
f = curr.parent().child;
}
f.add(k);
map.put(k, curr);
}
}
par = curr;
f = curr.child;
}
return this;
}
public void setRoots(Collection trees) {
trees.iterator().forEachRemaining(this::append);
}
public Forest merge(Forest forest) {
setRoots(forest.getRoots());
return this;
}
public Forest append(Forest.Tree tree) {
assert tree != null;
K k;
Tree curr, p;
if ((p = map.get(k = tree.par)) == null)
tree.par = null;
else
p.child.add(tree.key);
Iterator it = tree.toFirstRootList();
while (it.hasNext()) {
curr = it.next();
if ((p = map.get(k = curr.key)) == null) {
map.put(k, p = new Tree(k));
}
p.par = curr.par;
p.child.addAll(curr.child);
}
return this;
}
public Collection getRoots() {
return roots.stream().map(t -> map.get(t)).collect(Collectors.toList());
}
public int getAloneTreeSize() {
return roots.size();
}
public boolean containsKey(K key) {
return map.containsKey(key);
}
public Forest remove(K key) {
Tree t = map.get(key);
if (t == null)
return this;
if (t.par == null) {
roots.remove(t.key);
} else {
t.parent().child.remove(t.key);
}
Iterator it = t.toFirstRootList();
while (it.hasNext()) {
map.remove(it.next());
}
return this;
}
public static void main(String[] args) {
Forest tree = new Forest<>();
tree.appendChain("1", "2", "3", "4");
tree.appendChain("1", "1", "5", "6");
tree.appendChain("7", "8");
tree.appendChain("1", "7", "8", "9");
tree.appendChain("1", "8");
tree.appendChain("1", "8", "7", "6");
System.out.println(tree);
System.out.println(JSONObject.toJSONString(tree.getRoots()));
System.out.println(JSONObject.toJSONString(tree));
// System.out.println("--------------------------");
// System.out.println("toFirstRootList");
// tree.get("1").toFirstRootList().forEachRemaining(k -> System.out.println(k));
// System.out.println("toLevelRootList");
// tree.get("1").toLevelRootList().forEachRemaining(k -> System.out.println(k));
// System.out.println("toLeafNodeList");
// tree.get("1").toLeafNodeList().forEachRemaining(k -> System.out.println(k));
// System.out.println("toTreeNodeList");
// tree.get("1").toTreeNodeList().forEachRemaining(k -> System.out.println(k));
// System.out.println("toLevelList 2");
// tree.get("1").toLevelList(2).forEachRemaining(k -> System.out.println(k));
// System.out.println("toLevelList 1");
// tree.get("1").toLevelList(1).forEachRemaining(k -> System.out.println(k));
// System.out.println("toLevelList 0");
// tree.get("1").toLevelList(0).forEachRemaining(k -> System.out.println(k));
// System.out.println("toLevelList 3");
// tree.get("1").toLevelList(3).forEachRemaining(k -> System.out.println(k));
// System.out.println("toParentNodeList");
// tree.get("6").toParentNodeList().forEachRemaining(k ->
// System.out.println(k));
tree.append("1", (str) -> (Integer.valueOf(str) - 1 < 0 ? "0" : "" + (Integer.valueOf(str) - 1)));
tree.append("0", (str) -> (Integer.valueOf(str) - 1 < 0 ? "0" : "" + (Integer.valueOf(str) - 1)));
tree.append((str) -> (Integer.valueOf(str) - 1 < 0 ? "0" : "" + (Integer.valueOf(str) - 1)), "10", "11", "12",
"13", "14");
System.out.println(tree);
}
/**
* 树形节点
*
* @author yuyi
*/
public class Tree implements Serializable {
/**
* 先根遍历所有树根节点
*
* @author yuyi
*/
class FirstRootTreeNodeIterator extends FirstRootIterator {
protected void get() {
getflag = true;
do {
curr = null;
if (sons == null)
return;
if (!sons.hasNext()) {
do {
if (soniterators.isEmpty())
return;
sons = soniterators.pop();
} while (!sons.hasNext());
}
c = sons.next();
curr = map.get(c);
soniterators.push(sons);
sons = curr.child.iterator();
} while (!sons.hasNext());
}
}
/**
* 先根遍历叶子节点
*
* @author yuyi
*/
class FirstRootLeftNodeIterator extends FirstRootIterator {
FirstRootLeftNodeIterator() {
curr = null;
getflag = false;
}
protected void get() {
getflag = true;
do {
if (sons == null)
return;
if (!sons.hasNext()) {
do {
if (soniterators.isEmpty())
return;
sons = soniterators.pop();
} while (!sons.hasNext());
}
c = sons.next();
curr = map.get(c);
soniterators.push(sons);
sons = curr.child.iterator();
} while (sons.hasNext());
}
}
/**
* 先根遍历
*
* @author yuyi
*/
class FirstRootIterator implements Iterator {
protected Tree root = Tree.this, curr = root, por = root;
protected K c;
protected Iterator sons = Tree.this.child.iterator();
protected boolean getflag = true;
protected Stack> soniterators = new Stack<>();
@Override
public boolean hasNext() {
if (curr == null && !getflag) {
get();
}
return curr != null;
}
protected void get() {
getflag = true;
if (sons == null)
return;
if (!sons.hasNext()) {
do {
if (soniterators.isEmpty())
return;
sons = soniterators.pop();
} while (!sons.hasNext());
}
c = sons.next();
curr = map.get(c);
soniterators.push(sons);
sons = curr.child.iterator();
}
@Override
public Tree next() {
if (curr == null && !getflag) {
get();
}
getflag = false;
por = curr;
curr = null;
return por;
}
}
/**
* 水平遍历
*
* 逐层读取
*
*
* @author yuyi
*/
class LevelRootIterator extends FirstRootIterator {
protected Queue> soniterators = new LinkedList<>();
protected void get() {
getflag = true;
if (sons == null)
return;
if (!sons.hasNext()) {
do {
if (soniterators.isEmpty())
return;
sons = soniterators.poll();
} while (!sons.hasNext());
}
c = sons.next();
curr = map.get(c);
soniterators.add(curr.child.iterator());
}
}
/**
* 读取指定层节点
*
* @author yuyi
*/
class LevelNodeIterator extends LevelRootIterator {
@SuppressWarnings("unchecked")
protected Queue>[] soniteratorss = new Queue[] { new LinkedList<>(), new LinkedList<>() };
protected int level;
protected int currlevel = 0;
protected int parindex = 0;
LevelNodeIterator(int level) {
this.level = level;
if (level > currlevel) {
curr = null;
getflag = false;
soniteratorss[parindex].add(sons);
sons = null;
}
currlevel = 1;
}
protected void get() {
getflag = true;
if (level < currlevel)
return;
do {
curr = null;
while (sons == null || !sons.hasNext()) {
if ((soniterators = soniteratorss[parindex]).isEmpty()) {
if (level <= currlevel)
return;
soniterators = soniteratorss[parindex = 1 - parindex];
currlevel++;
}
sons = soniterators.poll();
}
curr = map.get(sons.next());
soniteratorss[1 - parindex].add(curr.child.iterator());
} while (currlevel != level);
}
}
/**
* 获取指定节点的父节点
*
* @author yuyi
*/
class ParentNodeIterator implements Iterator {
Tree curr = Tree.this;
@Override
public boolean hasNext() {
return curr != null;
}
@Override
public Forest.Tree next() {
Tree t = curr;
curr = curr.par != null ? map.get(curr.par) : null;
return t;
}
}
public Iterator toFirstRootList() {
return new FirstRootIterator();
}
public Iterator toLevelRootList() {
return new LevelRootIterator();
}
public Iterator toLevelList(int level) {
return new LevelNodeIterator(level);
}
public Iterator toParentNodeList() {
return new ParentNodeIterator();
}
public Iterator toTreeNodeList() {
return new FirstRootTreeNodeIterator();
}
public Iterator toLeafNodeList() {
return new FirstRootLeftNodeIterator();
}
private static final long serialVersionUID = 1L;
protected K key;
protected K par;
protected final Set child;
public K getKey() {
return key;
}
public Tree parent() {
return par == null ? null : map.get(par);
}
public List getChilds() {
return child.stream().map(map::get).collect(Collectors.toList());
}
public Tree(K key) {
this.key = key;
this.child = childInit.get();
}
@Override
public String toString() {
return String.format("{key=" + key + "%s}", child.isEmpty() ? "" : ",childs=" + getChilds());
}
}
public int size() {
return map.size();
}
public boolean empty() {
return map.isEmpty();
}
public void clear() {
map.clear();
}
public Forest() {
map = new HashMap<>();
}
public Forest(Supplier> childInit) {
this.childInit = childInit;
}
@Override
public String toString() {
return StringUtils.join(roots.stream().map(t -> map.get(t).toString()).iterator(), ",");
}
/**
* 无序添加
*
*
* @param ks
* @param getParent
* @return
*/
public Forest append(K k, Function getParent) {
if (k == null)
return this;
Tree curr = null, par = null, oldpar;
K pk;
if ((curr = map.get(k)) == null) {
curr = new Tree(k);
}
map.put(k, curr);
while ((pk = getParent.apply(k)) != null && !Objects.equals(pk, k)) {
par = map.get(pk);
if ((oldpar = curr.parent()) != null)
oldpar.child.remove(k);
else
roots.remove(k);
if (par != null) {
par.child.add(k);
return this;
}
par = new Tree(pk);
par.child.add(k);
curr.par = pk;
curr = par;
k = pk;
map.put(k, par);
}
roots.add(k);
return this;
}
/**
* 无序列表添加
*
* @param ks
* @param getParent
* @return
*/
@SuppressWarnings("unchecked")
public Forest append(Function getParent, K k, K... ks) {
assert getParent != null;
append(k, getParent);
Stream.of(ks).forEach(t -> append(t, getParent));
return this;
}
/**
* 无序列表添加
*
* @param ks
* @param getParent
* @return
*/
public Forest append(Collection list, Function getParent) {
assert list != null;
list.forEach(t -> append(t, getParent));
return this;
}
/**
*
* @param ks
* @param getParent
* @return
*/
public Forest append(Iterator iterator, Function getParent) {
assert iterator != null;
while (iterator.hasNext()) {
append(iterator.next(), getParent);
}
return this;
}
}
这个基础树,可以支持有根树的自动构造,只要插值满足值需要为(根节点,子根节点,三级根节点...叶子节点)即可。并提供了基础的子树遍历方法:先根遍历。逐层遍历等。
然后就可以在这个的基础上实现一个文件目录树
/**
* 文件目录树
*
* @author yuyi
*/
public class PathTree extends Forest {
private static final long serialVersionUID = 1L;
public static class FileNode {
FileNode(Path p) {
this.path = p;
filename = p.getFileName() == null ? p.toString() : p.getFileName().toString();
}
String filename;
Path path;
boolean isDirectory;
public String getFilename() {
return filename;
}
public void setFilename(String filename) {
this.filename = filename;
}
public Path getPath() {
return path;
}
public void setPath(Path path) {
this.path = path;
}
@Override
public String toString() {
return path.toString();
}
@Override
public int hashCode() {
return path == null ? 0 : path.hashCode();
}
@Override
public boolean equals(Object obj) {
return this == obj || obj != null && hashCode() == obj.hashCode();
}
}
public class PathTreeVisitor extends SimpleFileVisitor {
@Override
public FileVisitResult visitFile(Path file, BasicFileAttributes attrs) throws IOException {
appendChain(new FileNode(file.getParent()), new FileNode(file));
return super.visitFile(file, attrs);
}
@Override
public FileVisitResult postVisitDirectory(Path dir, IOException exc) throws IOException {
appendChain(new FileNode(dir.getParent()), new FileNode(dir));
return super.postVisitDirectory(dir, exc);
}
}
public void append(Path p) {
Path p1;
while ((p1 = p.getParent()) != null) {
appendChain(new FileNode(p1), new FileNode(p));
p = p1;
}
}
/**
* 读取某个文件目录下的所有文件并将其组织为树形结构存储
*
* @throws IOException
*/
public void read(Path path) {
assert Files.exists(path);
if (!Files.isDirectory(path))
throw new IllegalArgumentException(" path not`s Directory! ");
append(path);
try {
Files.walkFileTree(path, new PathTreeVisitor());
} catch (IOException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
public static void main(String[] args) {
PathTree pathtree = new PathTree();
pathtree.read(Paths.get("G:\\war3\\Warcraft3\\Maps"));
System.out.println(JSONObject.toJSONString(pathtree));
System.out.println(pathtree);
// pathtree.getRoots().forEach(p ->
// p.toFirstRootList().forEachRemaining(System.out::println));
}
}