Hololens 开发笔记(11)——Spatial Mapping
Hololens 作为一款混合现实设备,其与传统 VR/AR 设备最大的区别是,能够和现实世界进行交互。
以一个立方体为例,当我们没有使用 Spatial Mapping 时,我们只能在空间中移动它,而不能把它放置在现实世界的物体上,例如放置在一个椅子上。当我们使用了 Spatial Mapping 后,Hololens 会先扫描出所在房间的三维信息,扫描完毕后你就可以将物体放置在扫描后的空间物体上。
创建一个新的 Unity 项目 SpatialDemo,初始化项目:
- 导入 MRTK 包
- 应用项目设置为 MR 项目
- 使用
HoloLensCamera替代默认相机 - 添加
CursorWithFeedback - 创建一个空 GameObject,名为
Manager,为其添加子 gameObject:InputManager - 设置 InputManager 的
SimpleSinglePointerSelector脚本的 Cursor 属性为添加的 CursorWithFeedback - 添加一个 Cube,位置如下
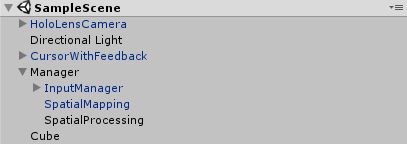
最终 Hierarchy 结构如下:
一、Spatial Mapping
(1)添加 MRTK 工具包下的 SpatialMapping 预制体到 Manager 对象下。
修改 Spatial Mapping Manager 的 Surface Material 属性值为 MRTK 包中的 SpatialUnderstandingSurface,其他参数使用默认值即可,该属性为空间扫描时所使用的材质。
(2)在 Manager 下新建一个 GameObject,名为 SpatialProcessing。
(3)为 SpatialProcessing 添加以下两个 MRTK 包中的脚本:
SurfaceMeshesToPlanes.csRemoveSurfaceVertices.cs
(4)新建脚本 SpatialProcessing.cs,并将其添加到 SpatialProcessing 上。
// Copyright (c) Microsoft Corporation. All rights reserved.
// Licensed under the MIT License. See LICENSE in the project root for license information.
using System.Collections.Generic;
using UnityEngine;
namespace HoloToolkit.Unity.SpatialMapping.Tests
{
public class SpatialProcessing : Singleton<SpatialProcessing>
{
[Tooltip("How much time (in seconds) that the SurfaceObserver will run after being started; used when 'Limit Scanning By Time' is checked.")]
public float scanTime = 30.0f;
[Tooltip("Material to use when rendering Spatial Mapping meshes while the observer is running.")]
public Material defaultMaterial;
[Tooltip("Optional Material to use when rendering Spatial Mapping meshes after the observer has been stopped.")]
public Material secondaryMaterial;
[Tooltip("结束处理所需要的最小floor数量")]
public uint minimumFloors = 1;
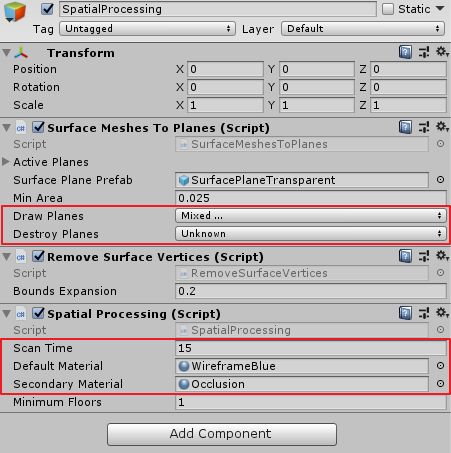
/// Surface Meshes To Planes脚本能够将扫描的网格转换为实体。- Draw Planes 为需要转换的类型。
- Destory Planes 为需要丢弃的类型。
- 我这里这两个参数都使用了默认值,即保留了 Wall、Floor、Ceiling、Table 类型的网格数据。
Remove Surface Vertices脚本能够把与实体重合的网格删除。SpatialProcessing脚本用于处理网格数据。- Scan Time : 扫描过多少秒开始转换
- Default Material: 扫描时使用的材质,这里使用 MRTK 包中的
WireframeBlue。 - secondaryMaterial: 停止扫描时使用的材质,这里使用 MRTK 包中的
Occlusion,注意路径是HoloToolKit/SpatialMapping/Materials/Occlusion.mat。 - minimumFloors: 结束处理所需要的最小 floor 数量。
(5)为 Cube 添加 MRTK 包下的 TapToPlace.cs 脚本。
(6)使用真机运行程序,不要忘记添加 SpatialPerception 权限:
程序启动后,会先扫描空间信息:
当扫描结束后,我们就可以把 Cube 放在实际的物体上,比如墙壁上:
二、Spatial UnderStanding
不知道你在运行上面的程序时,有没有尝试过,在扫描结束后你走动到之前没有扫描到的地方,这时候就无法将Cube放置在实际的物体上了。
这也很好理解,程序在启动的一段时间内扫描空间数据,扫描结束后将其转换为(房屋)模型,你实际上放到的是在(房屋)模型上(不信你先扫描一个椅子,扫描结束后将椅子移走,Cube 只能放在椅子原来的位置上)。而我们之前没有扫描到的地方,自然没有(房屋)模型,因此无法放置。
Hololens 为我们提供了 Spatial UnderStanding 的功能,能够让 Hololens 实时扫描空间数据,实时更新(房屋)模型。当然这样会占用较大的 CPU 资源。
MRTK 工具包为我们提供了 SpatialUnderstanding,直接将其拖入 Manager 下即可。
重新运行程序,我们发现是在实时扫描的,扫描到的部分被蓝色网格所覆盖。
查看下开启 SpatialUnderstanding 的 CPU 使用情况:
三、Anchor
如果我们查看 Cube 上的 TapToPlace 脚本的源码的话,我们会发现它内部调用了 WorldAnchorManager 来实现锚点的管理。
因此理论上我们给任一 GameObject 添加上 WorldAnchorManager 脚本,就能够实现锚点管理。但是遗憾的是,不知道是不是我打开姿势不对,还是什么原因,即时添加了 WorldAnchorManager 脚本,仍然无法实现锚点的效果,有实现的小伙伴可以留言告诉我下。
因此,我只能放弃使用官方提供的 WorldAnchorManager,使用在《Hololens 开发笔记(10)——World Anchor》 中的方法,自己实现锚点效果。
使用如下代码覆盖 TapToPlace 脚本即可:
// Copyright (c) Microsoft Corporation. All rights reserved.
// Licensed under the MIT License. See LICENSE in the project root for license information.
using System.Collections.Generic;
using UnityEngine;
using HoloToolkit.Unity.InputModule;
using UnityEngine.XR.WSA.Persistence;
using System.Linq;
using UnityEngine.XR.WSA;
namespace HoloToolkit.Unity.SpatialMapping
{
/// Placement position in front of the user
private static Vector3 GetPlacementPosition(Vector3 headPosition, Vector3 gazeDirection, float defaultGazeDistance)
{
RaycastHit hitInfo;
if (SpatialMappingRaycast(headPosition, gazeDirection, out hitInfo))
{
return hitInfo.point;
}
return GetGazePlacementPosition(headPosition, gazeDirection, defaultGazeDistance);
}
/// Whether it found a hit or not
private static bool SpatialMappingRaycast(Vector3 origin, Vector3 direction, out RaycastHit spatialMapHit)
{
if (SpatialMappingManager.Instance != null)
{
RaycastHit hitInfo;
if (Physics.Raycast(origin, direction, out hitInfo, 30.0f, SpatialMappingManager.Instance.LayerMask))
{
spatialMapHit = hitInfo;
return true;
}
}
spatialMapHit = new RaycastHit();
return false;
}
/// Placement position in front of the user
private static Vector3 GetGazePlacementPosition(Vector3 headPosition, Vector3 gazeDirection, float defaultGazeDistance)
{
if (GazeManager.Instance.HitObject != null)
{
return GazeManager.Instance.HitPosition;
}
return headPosition + gazeDirection * defaultGazeDistance;
}
}
}
运行程序,将 Cube 放置在椅子上,重新运行程序,Cube 会被还原到椅子上。
PS:注意去除
is Being Placed选项,不然程序每次启动 Cube 都会处于可移动状态。