HashMap 和 HashTable 的区别
HashMap 和 HashTable 的区别(源码层)
1、HashMap 是非线程安全的,HashTable 是线程安全的。
2、HashMap 的键和值都允许有 null 值存在,而 HashTable 则不行。
3、因为线程安全的问题,HashMap 效率比 HashTable 的要高。
HashMap put(K key, V value) 方法的内部存储结构(jdk 1.7)
jdk 1.7 中 HashMap 内部采用 单向链表+数组的方式存储数据
1、HashMap
// DEFAULT_INITIAL_CAPACITY 初始化大小 16, DEFAULT_LOAD_FACTOR 扩容因子 0.75
public HashMap() {
this(DEFAULT_INITIAL_CAPACITY, DEFAULT_LOAD_FACTOR );
}
public HashMap(int initialCapacity, float loadFactor) {
if (initialCapacity < 0)
throw new IllegalArgumentException("Illegal initial capacity: " + initialCapacity);
if (initialCapacity > MAXIMUM_CAPACITY)
initialCapacity = MAXIMUM_CAPACITY;
if (loadFactor <= 0 || Float.isNaN(loadFactor))
throw new IllegalArgumentException("Illegal load factor: " + loadFactor);
this.loadFactor = loadFactor;
threshold = initialCapacity;
init();
}2、map 的初始化大小和扩容因子设置完成之后,map 准备就绪,调用 map.put() 方法向 map 中添加元素。在 put 方法中,如果当前 table(也就是 entry 数组)为空,就在 inflateTable 方法中初始化 table,
public V put(K key, V value) {
if (table == EMPTY_TABLE) {
inflateTable(threshold);
}
...
return null;
}3、在 inflateTable 方法中通过 roundUpToPowerOf2 方法计算当前要初始化的大小是否大于等于 MAXIMUM_CAPACITY(2的 30次方),如果大于等于就设置成 MAXIMUM_CAPACITY 的值,不大于就调用Integer.highestOneBit 方法计算初始化的大小。
highestOneBit 方法简单的说就是:
3.1、如果一个数是0, 则返回0;
3.2、如果是负数, 则返回 -2147483648;
3.3、如果是正数, 则返回的是比参数小的且最靠近参数的 2 的N次方;例如:参数是 17 则返回 16;参数是 15 则返回 8;
private void inflateTable(int toSize) {
// Find a power of 2 >= toSize
int capacity = roundUpToPowerOf2(toSize);
threshold = (int) Math.min(capacity * loadFactor, MAXIMUM_CAPACITY + 1);
table = new Entry[capacity];
initHashSeedAsNeeded(capacity);
}
private static int roundUpToPowerOf2(int number) {
// assert number >= 0 : "number must be non-negative";
return number >= MAXIMUM_CAPACITY
? MAXIMUM_CAPACITY
: ( number > 1) ? Integer.highestOneBit(( number - 1) << 1) : 1;
}4、初始化完成之后再回到 put 方法中,往下看会看到判断 key 值是否是空值,当 key 是空值的时候,调用 putForNullKey 处理。首先取出下标为0的元素,如果当前元素是空元素,就将当前key的 hashcode 设置为0,放在 table 下标为 0 的位置。
public V put(K key, V value) {
...
if (key == null)
return putForNullKey(value);
...
return null;
}
private V putForNullKey(V value) {
for (Entry e = table[0]; e != null; e = e.next) {
if (e.key == null) {
V oldValue = e.value;
e.value = value;
e.recordAccess(this);
return oldValue ;
}
}
modCount++;
addEntry(0, null, value , 0);
return null;
} 5、如果不是空的key,先计算 key 的 hash 值,然后调用 indexFor 方法根据 hash 值和 table 的长度计算出当前的 key 存储在 table 中的位置 i 。计算完位置之后,再取出位置 i 处是否已经有数据,如果有数据并且数据中也有相同的 hash 并且 key 也相同的时候,就将当前的值替换掉旧的值并返回旧的值。循环完之后没有相同的 hash key 的时候,就调用 addEntry 方法向 table 位置 i 处添加元素。添加规则是将当前 key 存放在位置 i 处链表的最顶部。
hash() 这个方法计算过程还没弄明白,希望弄明白的大神帮忙指点指点
public V put(K key, V value) {
....
int hash = hash(key); // 计算 key 的 hash 值,这一步是关键,暂时还没看明白计算方法
int i = indexFor(hash, table.length); // 计算得到的 hash 应该存放在 map entry 的哪个下标的位置
for (Entry e = table[i]; e != null; e = e .next) {
Object k;
if (e.hash == hash && ((k = e.key) == key || key.equals( k))) {
V oldValue = e.value;
e.value = value;
e.recordAccess(this);
return oldValue ;
}
}
modCount++;
addEntry(hash, key , value, i);
return null;
}
final int hash(Object k) {
int h = hashSeed;
if (0 != h && k instanceof String) {
return sun.misc.Hashing.stringHash32((String) k);
}
h ^= k.hashCode();
h ^= (h >>> 20) ^ (h >>> 12);
return h ^ (h >>> 7) ^ (h >>> 4);
}
static int indexFor(int h, int length ) {
return h & (length-1);
} 6、添加的时候判断当前位置 i 是否已经大于要扩容的极限(总长度 * 扩容因子),扩容是当前 table 大小的 2 倍。扩容之后重新"散列掩码值 ",然后循环旧 table,将每一个元素都重新计算存储在扩容之后新 table 中的哪个位置上。转换完之后,再计算下次要扩容的极限大小是多少。
void addEntry(int hash , K key, V value, int bucketIndex) {
if ((size >= threshold) && (null != table[bucketIndex])) {
// 扩容
resize(2 * table.length);
hash = (null != key) ? hash(key) : 0;
bucketIndex = indexFor(hash, table.length);
}
// 将新 put 进来的 key/value 放入扩容后的 map 对应的 table 中
createEntry(hash, key, value, bucketIndex);
}
// 扩容
void resize(int newCapacity) {
Entry[] oldTable = table ;
int oldCapacity = oldTable.length;
if (oldCapacity == MAXIMUM_CAPACITY) {
threshold = Integer.MAX_VALUE;
return;
}
Entry[] newTable = new Entry[newCapacity];
// initHashSeedAsNeeded 用来初始化哈希值
// transfer 循环旧的 map 中的数据,存放到扩容后的 map 中
transfer(newTable, initHashSeedAsNeeded(newCapacity));
table = newTable ;
threshold = (int)Math.min(newCapacity * loadFactor, MAXIMUM_CAPACITY + 1);
}
// 初始化哈希值
final boolean initHashSeedAsNeeded(int capacity) {
boolean currentAltHashing = hashSeed != 0;
boolean useAltHashing = sun.misc.VM.isBooted() &&
(capacity >= Holder.ALTERNATIVE_HASHING_THRESHOLD);
boolean switching = currentAltHashing ^ useAltHashing;
if (switching) {
hashSeed = useAltHashing
? sun.misc.Hashing.randomHashSeed(this)
: 0;
}
return switching;
}
// 循环旧的 map 中的数据,存放到扩容后的 map 中
void transfer(Entry[] newTable, boolean rehash) {
int newCapacity = newTable.length;
for (Entry e : table) {
while(null != e) {
Entry next = e.next;
if (rehash) {
e.hash = null == e.key ? 0 : hash(e.key);
}
int i = indexFor (e.hash, newCapacity);
e.next = newTable[i];
newTable[i] = e;
e = next ;
}
}
}
// 将新 put 进来的 key/value 放入扩容后的 map 对应的 table 中
void createEntry(int hash, K key, V value, int bucketIndex) {
Entry e = table[bucketIndex];
table[bucketIndex] = new Entry<>(hash, key, value, e);
size++;
} HashMap get(Object key) 方法的内部存储结构(jdk 1.7)
1、get 方法比较简单,进来之后先判断是否 key 是否是 null,是 null 就特殊处理,不是就常规处理并返回这个 key 对应的值。V 是泛型,声明 HashMap 的时候中的 value 类型。
public V get(Object key) {
if (key == null)
return getForNullKey();
Entry entry = getEntry(key );
return null == entry ? null : entry .getValue();
} 2、当 key 是 null 的情况,先判断当前 table 的 size 是否大于 0,大于 0 就继续,否则返回 null。然后再直接获取 hashMap 中 table(Entry) 下标为 0 的位置的链表,循环这个链表,依次判断每个元素的 key 是否为 null,为 null 就返回对应的值。
private V getForNullKey() {
if (size == 0) {
return null;
}
for (Entry e = table[0]; e != null; e = e.next) {
if (e.key == null)
return e.value;
}
return null;
} 3、key 不为 null 的情况,同样是先判断当前 table 的 size 是否大于 0,大于 0 就继续,否则返回 null。然后再计算要查找 key 的 hash 码,通过 hash 码和 table 的长度计算出这个 key 对应 table 的下标,得到下标之后取出 hashMap 中对应下标的 table(Entry) 链表,循环这个链表,依次判断每个元素的 key 是否与当前 key 相同 并且 hash 码也相同,相同就返回对应的值,不相同就返回 null。
final Entry getEntry(Object key) {
if (size == 0) {
return null;
}
int hash = (key == null) ? 0 : hash(key);
for (Entry e = table[indexFor(hash, table.length)];
e != null;
e = e.next) {
Object k;
if (e.hash == hash && ((k = e.key) == key || (key != null && key.equals(k))))
return e ;
}
return null;
}
HashMap put(K key, V value) 的内部存储结构(jdk 1.8)
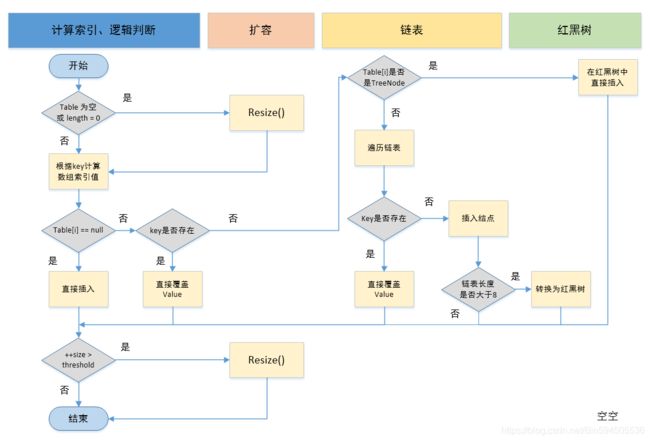
文末附 pu 方法的执行流程图
jdk 1.8 中 HashMap 内部采用 树+数组 的方式存储数据
1、HashMap
// 扩容因子
static final float DEFAULT_LOAD_FACTOR = 0.75f;
public HashMap() {
this.loadFactor = DEFAULT_LOAD_FACTOR; // all other fields defaulted
}2、put 方法,先计算 key 的 hash 值,调用 putVal() 方法进行设置值
public V put(K key, V value) {
return putVal(hash(key), key, value, false, true);
}3、首先看 hash(Object key) 方法,该方法用来计算 key 的 hash 值。可以看出 key 为空的时候 hash 为 0。(h = key.hashCode()) ^ (h >>> 16) 第一步 取 key 的 hash 值,第二步 h ^ (h >>> 16) 高位‘与’运算(底层的位移和异或运算效率要高于加减乘除取模等效率)因为 hashcode 对应的二进制是 32 位,无符号右移 16 位,那生成的就是16位0加原高位的16位值,就相当于把 int 对半分开了,异或计算也就变成了高16位和低16位进行异或,原高16位不变。这么干主要用于当hashmap 数组比较小的时候所有bit都参与运算了,防止hash冲突太大。
static final int hash(Object key) {
int h;
return (key == null) ? 0 : (h = key.hashCode()) ^ (h >>> 16);
}Hash 计算参考 https://blog.csdn.net/qq_38182963/article/details/78940047下面图示帮助理解(PS:图忘了出自哪个地方了,此处引用为了帮助理解,如果原博主介意的话请告知删除)
4、接下来看 putVal() 方法向 map 中添加数据,
final V putVal(int hash, K key, V value, boolean onlyIfAbsent, boolean evict) {
Node[] tab; Node p; int n, i;
// 第一次 put 进来的时候 tab 为空
if ((tab = table) == null || (n = tab.length) == 0)
n = (tab = resize()).length; // resize() 可以扩容也可以初始化 map
// n 是数组的长度 length,当length 总是 2 的 n 次方时,(n - 1) & hash 运算等价于对 length 取模,也就是 hash % length
// tab 是 map 中数组的大小,通过 & 计算,得到插入的下标,判断该下标是否已经存在元素数据
if ((p = tab[i = (n - 1) & hash]) == null)
// 如果当前位置为空,就放入新的 Node 数据,
tab[i] = newNode(hash, key, value, null);
else {
// hash 冲突了(对应下标的位置已经存在元素)
Node e; K k;
// hash 值相同并且 key 的地址和值也相同,说明 key 重复了
if (p.hash == hash && ((k = p.key) == key || (key != null && key.equals(k))))
// 将 p 赋值给 e 后面用来获取旧数据的操作
e = p;
// hash 值相同,如果以存在的值是个树类型的,则将给定的键值对和该值关联
else if (p instanceof TreeNode)
// 具体看下面第 6 步
e = ((TreeNode)p).putTreeVal(this, tab, hash, key, value);
// 如果key不相同,只是hash冲突,并且不是树,则是链表
else {
for (int binCount = 0; ; ++binCount) {
// 循环到链表的最后一个元素的时候,将新值追加到链表的末端
if ((e = p.next) == null) {
p.next = newNode(hash, key, value, null);
// 如果树的阀值大于等于7,也就是,链表长度达到了8(从0开始)
if (binCount >= TREEIFY_THRESHOLD - 1)
// 如果链表长度达到了8,且数组长度小于64,那么就重新散列,重新散列会拆分链表,使得链表变短提高性能,如果大于64,只能将链表变为红黑树
// 具体看下面第 5 步
treeifyBin(tab, hash);
break;
}
// 循环链表过程中有 key 和目标 key 相同的就直接结束
if (e.hash == hash && ((k = e.key) == key || (key != null && key.equals(k))))
break;
// 如果给定的 hash 值不同或者key不同
// 将 next 值赋给 p,为下次循环做铺垫
p = e;
}
}
// 通过上面的逻辑,如果 e 不是 null,表示:该元素存在了(也就是他们呢 key 相等)
if (e != null) { // existing mapping for key
V oldValue = e.value;
// 如果 onlyIfAbsent 是 true,就不要改变已有的值,这里我们是false。
if (!onlyIfAbsent || oldValue == null)
// 新值替换旧值
e.value = value;
// 什么都不操作
afterNodeAccess(e);
return oldValue;
}
}
// 如果e== null,需要增加 modeCount 变量,为迭代器服务。
++modCount;
// 数组长度大于扩容阀值
if (++size > threshold)
// 数组扩容
resize();
// HashMap 中什么都不做
afterNodeInsertion(evict);
return null;
} 接下来的5、6步(不分先后,这里只是和上面 putVal() 方法里面标注的步骤对应),是红黑树的构造、平衡(左旋、右旋)过程,由于是对树的操作,代码实现逻辑比较复杂难懂,楼主还没弄明白,所以不想了解的也可以跳过
5、在上一步中向链表中添加数据之后,如果此链表长度大于转换成树的限定值,就会调用 treeifyBin() 方法将此链表转换成树,下面详细分析 treeifyBin() 方法
static final int MIN_TREEIFY_CAPACITY = 64;
final void treeifyBin(Node[] tab, int hash) {
// n 是当前数组的长度,index hash 和 数组长度计算之后的下标位置,e 是链表中的节点每次取出一个转换成 TreeNode 用
int n, index; Node e;
// 当前数组为空 或者 数组的长度小于 64,就调用 resize() 方法扩容,扩容之后重新计算 hash
if (tab == null || (n = tab.length) < MIN_TREEIFY_CAPACITY)
resize();
// 数组长度大于 64 了就只能将链表转换成树
else if ((e = tab[index = (n - 1) & hash]) != null) {
// 经过下面代码分析,hd 是头节点, tl 是临时变量,每次都指向最后一个节点
TreeNode hd = null, tl = null;
// 通过循环将链表中的 Node 类型 转换成 TreeNode 类型,并还保持链表的结构
do {
// 将链表中的节点转换成树节点,replacementTreeNode() 方法内通过构造方法产生一个新的树节点
TreeNode p = replacementTreeNode(e, null);
if (tl == null)
hd = p;
else {
p.prev = tl;
tl.next = p;
}
tl = p;
} while ((e = e.next) != null);
// 将构造成 TreeNode 的链表 hd 赋值到数组中对应下标的位置并且数据不为空
if ((tab[index] = hd) != null)
// 将链表转换成树结构
hd.treeify(tab);
}
}
treeify 方法是 HashMap 内部静态常量类 TreeNode 中的方法
final void treeify(Node[] tab) {
TreeNode root = null;
// 这层循环的 TreeNode 链表
// this 是转换后的 TreeNode 链表中的第一个元素
for (TreeNode x = this, next; x != null; x = next) {
next = (TreeNode)x.next;
x.left = x.right = null;
// 如果根节点为空,说明 x 是循环的第一个节点
if (root == null) {
x.parent = null;
// 将 x 节点标记为黑色并设置为根节点
x.red = false;
root = x;
}
else {
// 已有根节点,需要把循环的节点设置为根节点的子节点
K k = x.key;
int h = x.hash;
Class kc = null;
// 这层循环的是构造成的树,当前节点的左右子节点都不为空的时候就往下循环。无限循环直到 break 退出
for (TreeNode p = root;;) {
// dir 左节点、右节点 的标记, ph 循环到的节点的 hash 值
int dir, ph;
K pk = p.key;
if ((ph = p.hash) > h)
dir = -1;
else if (ph < h)
dir = 1;
// 通过循环到的节点的 key 构造一个比较器,然后和要插入的节点的 key 进行比较
else if ((kc == null &&
(kc = comparableClassFor(k)) == null) ||
(dir = compareComparables(kc, k, pk)) == 0)
dir = tieBreakOrder(k, pk);
// p 是当前循环的节点
TreeNode xp = p;
// 判断 将插入节点设置成当前节点的左节点还是右节点
if ((p = (dir <= 0) ? p.left : p.right) == null) {
// 如果左节点或右节点不为空,就将要插入节点的父节点设置成当前循环到的节点
x.parent = xp;
// dir 小于等于 0 的时候,插入的节点设置成当前循环到的节点的左节点
if (dir <= 0)
xp.left = x;
else
// dir 大于 0 就设置成右节点
xp.right = x;
// 新插入一个节点之后,树之前的平衡被破坏,下面方法用来平衡树
root = balanceInsertion(root, x);
break;
}
}
}
}
// 确保树的根节点是第一个节点
moveRootToFront(tab, root);
}
// 从要插入的节点 x 开始遍历树进行平衡,这方法还没理解透彻,暂时不加注释了
static TreeNode balanceInsertion(TreeNode root,
TreeNode x) {
x.red = true;
for (TreeNode xp, xpp, xppl, xppr;;) {
if ((xp = x.parent) == null) {
x.red = false;
return x;
}
else if (!xp.red || (xpp = xp.parent) == null)
return root;
if (xp == (xppl = xpp.left)) {
if ((xppr = xpp.right) != null && xppr.red) {
xppr.red = false;
xp.red = false;
xpp.red = true;
x = xpp;
}
else {
if (x == xp.right) {
root = rotateLeft(root, x = xp);
xpp = (xp = x.parent) == null ? null : xp.parent;
}
if (xp != null) {
xp.red = false;
if (xpp != null) {
xpp.red = true;
root = rotateRight(root, xpp);
}
}
}
}
else {
if (xppl != null && xppl.red) {
xppl.red = false;
xp.red = false;
xpp.red = true;
x = xpp;
}
else {
if (x == xp.left) {
root = rotateRight(root, x = xp);
xpp = (xp = x.parent) == null ? null : xp.parent;
}
if (xp != null) {
xp.red = false;
if (xpp != null) {
xpp.red = true;
root = rotateLeft(root, xpp);
}
}
}
}
}
} 6、如果 hash 冲突的位置存在的已经是树,就执行下面方法向树中添加一个节点,大体执行流程和第 5 步中构造树的过程类似
final TreeNode putTreeVal(HashMap map, Node[] tab, int h, K k, V v) {
Class kc = null;
boolean searched = false;
TreeNode root = (parent != null) ? root() : this;
for (TreeNode p = root;;) {
int dir, ph; K pk;
if ((ph = p.hash) > h)
dir = -1;
else if (ph < h)
dir = 1;
else if ((pk = p.key) == k || (k != null && k.equals(pk)))
return p;
else if ((kc == null &&
(kc = comparableClassFor(k)) == null) ||
(dir = compareComparables(kc, k, pk)) == 0) {
if (!searched) {
TreeNode q, ch;
searched = true;
if (((ch = p.left) != null &&
(q = ch.find(h, k, kc)) != null) ||
((ch = p.right) != null &&
(q = ch.find(h, k, kc)) != null))
return q;
}
dir = tieBreakOrder(k, pk);
}
TreeNode xp = p;
if ((p = (dir <= 0) ? p.left : p.right) == null) {
Node xpn = xp.next;
TreeNode x = map.newTreeNode(h, k, v, xpn);
if (dir <= 0)
xp.left = x;
else
xp.right = x;
xp.next = x;
x.parent = x.prev = xp;
if (xpn != null)
((TreeNode)xpn).prev = x;
moveRootToFront(tab, balanceInsertion(root, x));
return null;
}
}
} HashMap get(Object key) 方法的内部存储结构(jdk 1.8)
1、首先调用 hash() 方法计算 key 的 hash 值,计算方法同 put() 方法的计算过程
public V get(Object key) {
Node e;
return (e = getNode(hash(key), key)) == null ? null : e.value;
} 2、get 的过程比较简单,在代码里说明
final Node getNode(int hash, Object key) {
Node[] tab; Node first, e; int n; K k;
// 数组不为空 并且 计算出的下标位置数据也不为空,就取出对应下标位置的数据元素
if ((tab = table) != null && (n = tab.length) > 0 &&
(first = tab[(n - 1) & hash]) != null) {
// 第一个元素的 hash 和查找的 hash 相同,并且 key 值和地址也都相等,说明找到了元素直接返回即可
if (first.hash == hash && ((k = first.key) == key || (key != null && key.equals(k))))
return first;
// 上面的条件都不成立,取出 first 的下一个元素进行遍历
if ((e = first.next) != null) {
// 下一个元素是树,就使用树的查找方法进行查找
if (first instanceof TreeNode)
return ((TreeNode)first).getTreeNode(hash, key);
// 是链表,就循环挨个往下查找,直到查找到目标元素为止
do {
if (e.hash == hash &&
((k = e.key) == key || (key != null && key.equals(k))))
return e;
} while ((e = e.next) != null);
}
}
return null;
}
未完待续。。。
putVal 方法执行流程(PS:图忘了出自哪个地方了,此处引用为了帮助理解,如果原博主介意的话请告知删除)