动手学深度学习Pytorch版Task01
线性回归
一.基本要素
1.模型
一般为一公式,表示输入和输出之间的数学关系。
2.数据集
就是很多很多数据样本
3.损失函数
在模型训练中,我们需要衡量价格预测值与真实值之间的误差。通常我们会选取一个非负数作为误差,且数值越小表示误差越小。一个常用的选择是平方函数。公式表达如下
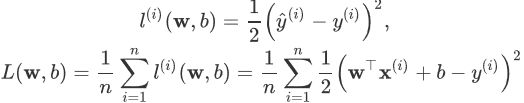
4.优化函数(随机梯度下降)
当模型和损失函数形式较为简单时,上面的误差最小化问题的解可以直接用公式表达出来。这类解叫作解析解(analytical solution)。本节使用的线性回归和平方误差刚好属于这个范畴。然而,大多数深度学习模型并没有解析解,只能通过优化算法有限次迭代模型参数来尽可能降低损失函数的值。这类解叫作数值解(numerical solution)。
在求数值解的优化算法中,小批量随机梯度下降(mini-batch stochastic gradient descent)在深度学习中被广泛使用。它的算法很简单:先选取一组模型参数的初始值,如随机选取;接下来对参数进行多次迭代,使每次迭代都可能降低损失函数的值。在每次迭代中,先随机均匀采样一个由固定数目训练数据样本所组成的小批量(mini-batch)B,然后求小批量中数据样本的平均损失有关模型参数的导数(梯度),最后用此结果与预先设定的一个正数的乘积作为模型参数在本次迭代的减小量。
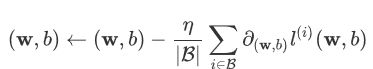
学习率: η代表在每次优化中,能够学习的步长的大小
批量大小: B是小批量计算中的批量大小batch size
矢量计算(torch实现)
import torch
import time
# init variable a, b as 1000 dimension vector
n = 1000
a = torch.ones(n)
b = torch.ones(n)# define a timer class to record time
class Timer(object):
"""Record multiple running times."""
def __init__(self):
self.times = []
self.start()
def start(self):
# start the timer
self.start_time = time.time()
def stop(self):
# stop the timer and record time into a list
self.times.append(time.time() - self.start_time)
return self.times[-1]
def avg(self):
# calculate the average and return
return sum(self.times)/len(self.times)
def sum(self):
# return the sum of recorded time
return sum(self.times)接下来就可以试验了
timer = Timer()
c = torch.zeros(n)
for i in range(n):
c[i] = a[i] + b[i]
'%.5f sec' % timer.stop()timer.start()
d = a + b
'%.5f sec' % timer.stop()结果后者明显比前者快
线性回归模型的实现(pytorch实现)
import torch
from torch import nn
import numpy as np
torch.manual_seed(1)
print(torch.__version__)
torch.set_default_tensor_type('torch.FloatTensor')生成数据集
num_inputs = 2
num_examples = 1000
true_w = [2, -3.4]
true_b = 4.2
features = torch.tensor(np.random.normal(0, 1, (num_examples, num_inputs)), dtype=torch.float)
labels = true_w[0] * features[:, 0] + true_w[1] * features[:, 1] + true_b
labels += torch.tensor(np.random.normal(0, 0.01, size=labels.size()), dtype=torch.float)读取数据集
mport torch.utils.data as Data
batch_size = 10
# combine featues and labels of dataset
dataset = Data.TensorDataset(features, labels)
# put dataset into DataLoader
data_iter = Data.DataLoader(
dataset=dataset, # torch TensorDataset format
batch_size=batch_size, # mini batch size
shuffle=True, # whether shuffle the data or not
num_workers=2, # read data in multithreading
)for X, y in data_iter:
print(X, '\n', y)
break定义模型
class LinearNet(nn.Module):
def __init__(self, n_feature):
super(LinearNet, self).__init__() # call father function to init
self.linear = nn.Linear(n_feature, 1) # function prototype: `torch.nn.Linear(in_features, out_features, bias=True)`
def forward(self, x):
y = self.linear(x)
return y
net = LinearNet(num_inputs)
print(net)# ways to init a multilayer network
# method one
net = nn.Sequential(
nn.Linear(num_inputs, 1)
# other layers can be added here
)
# method two
net = nn.Sequential()
net.add_module('linear', nn.Linear(num_inputs, 1))
# net.add_module ......
# method three
from collections import OrderedDict
net = nn.Sequential(OrderedDict([
('linear', nn.Linear(num_inputs, 1))
# ......
]))
print(net)
print(net[0])初始化模型参数
from torch.nn import init
init.normal_(net[0].weight, mean=0.0, std=0.01)
init.constant_(net[0].bias, val=0.0) # or you can use `net[0].bias.data.fill_(0)` to modify it directly for param in net.parameters():
print(param)定义损失函数
loss = nn.MSELoss() # nn built-in squared loss function
# function prototype: `torch.nn.MSELoss(size_average=None, reduce=None, reduction='mean')`定义优化函数
import torch.optim as optim
optimizer = optim.SGD(net.parameters(), lr=0.03) # built-in random gradient descent function
print(optimizer) # function prototype: `torch.optim.SGD(params, lr=, momentum=0, dampening=0, weight_decay=0, nesterov=False)训练
num_epochs = 3
for epoch in range(1, num_epochs + 1):
for X, y in data_iter:
output = net(X)
l = loss(output, y.view(-1, 1))
optimizer.zero_grad() # reset gradient, equal to net.zero_grad()
l.backward()
optimizer.step()
print('epoch %d, loss: %f' % (epoch, l.item()))
# result comparision
dense = net[0]
print(true_w, dense.weight.data)
print(true_b, dense.bias.data)softmax与分类模型
1.主要概念
主要为这一公式
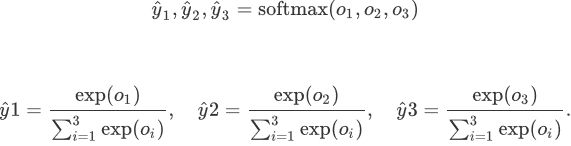
2.交叉熵损失函数
平方损失估计
![]()
交叉熵
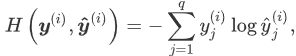
函数定义

softmax实现
import torch
import torchvision
import numpy as np
import sys
sys.path.append("/home/kesci/input")
import d2lzh1981 as d2l
print(torch.__version__)
print(torchvision.__version__)获取训练集数据和测试集数据
batch_size = 256
train_iter, test_iter = d2l.load_data_fashion_mnist(batch_size, root='/home/kesci/input/FashionMNIST2065')模型参数初始化
num_inputs = 784
print(28*28)
num_outputs = 10
W = torch.tensor(np.random.normal(0, 0.01, (num_inputs, num_outputs)), dtype=torch.float)
b = torch.zeros(num_outputs, dtype=torch.float)
W.requires_grad_(requires_grad=True)
b.requires_grad_(requires_grad=True)多层感知机
表达公式
具体来说,给定一个小批量样本X∈Rn×d,其批量大小为n,输入个数为d。假设多层感知机只有一个隐藏层,其中隐藏单元个数为h。记隐藏层的输出(也称为隐藏层变量或隐藏变量)为H,有H∈Rn×h。因为隐藏层和输出层均是全连接层,可以设隐藏层的权重参数和偏差参数分别为Wh∈Rd×h和 bh∈R1×h,输出层的权重和偏差参数分别为Wo∈Rh×q和bo∈R1×q。
我们先来看一种含单隐藏层的多层感知机的设计。其输出O∈Rn×q的计算为
激活函数
共有三种
1.Relu函数
2.sigmoid函数
3.tanh函数
多层感知机pytorch实现
import torch
from torch import nn
from torch.nn import init
import numpy as np
import sys
sys.path.append("/home/kesci/input")
import d2lzh1981 as d2l
print(torch.__version__)初始化模型和各个参数
num_inputs, num_outputs, num_hiddens = 784, 10, 256
net = nn.Sequential(
d2l.FlattenLayer(),
nn.Linear(num_inputs, num_hiddens),
nn.ReLU(),
nn.Linear(num_hiddens, num_outputs),
)
for params in net.parameters():
init.normal_(params, mean=0, std=0.01)训练
[23]:
batch_size = 256
train_iter, test_iter = d2l.load_data_fashion_mnist(batch_size,root='/home/kesci/input/FashionMNIST2065')
loss = torch.nn.CrossEntropyLoss()
optimizer = torch.optim.SGD(net.parameters(), lr=0.5)
num_epochs = 5
d2l.train_ch3(net, train_iter, test_iter, loss, num_epochs, batch_size, None, None, optimizer)