CentOS7+Nginx+uWSGI+Flask部署
在linux上部署这套环境,折腾了十分的久,很多地方都不会,要反复的操作,还好,这些都不是问题,因为,我们最后,还是成功了,网上的部署方法很多,实际上我一步一步跟着做,也没奏效,最终都是零碎的去找原因,才OK的,下面介绍部署过程
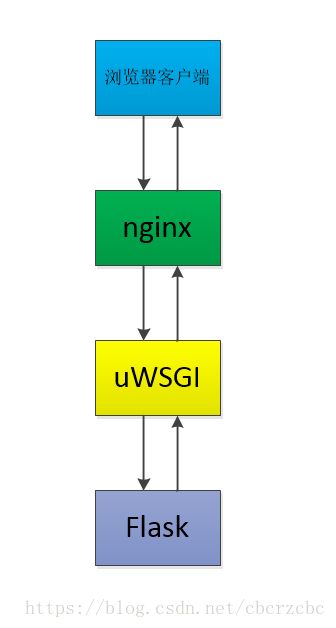
整个访问的流程是这样的,首先用户这边,用浏览器去访问我们flask的站点,由nginx受理,nginx接到请求后转发到uWSGI,由uWSGI来触发flask的应用,最终,将页面呈现到用户的浏览器上。
Linux环境:CentOS 7 1804
首先,我们安装了一个纯新的CentOS 7 1804版本的,我们先安装一些一些东西,一步一步调试
1、安装python-pip
[root@localhost ~]# yum -y install epel-release[root@localhost ~]# yum -y install python-pip2、升级pip的版本
[root@localhost ~]# python -m pip install --upgrade pip3、替换pip的国内源
替换国内源后,下载资源的速度会翻倍提升
创建一个隐藏目录,pip目录
[root@localhost ~]# mkdir -p .pip进入目录,并创建一个新的pip.conf文件,把配置写进去,保存
[root@localhost ~]# vi .pip/pip.confpip.conf的内容如下,替换的是清华大学的源:
[global]
index-url = https://pypi.tuna.tsinghua.edu.cn/simple4、安装uwsgi
直接pip安装uwsgi,可能会报错,因为缺少c组件和python-devel
所以,我们要先解决这两个依赖,再pip安装uwsgi
[root@localhost ~]# yum -y install gcc gcc-c++[root@localhost ~]# yum -y install python-devel[root@localhost ~]# pip install uwsgi5、准备flask项目的代码
安装好uwsgi后,我们就要准备flask项目的代码了,就拿hello world为例
先是pip安装一下flask框架
[root@localhost ~]# pip install flask创建flask的项目文件夹
[root@localhost ~]# mkdir flask
[root@localhost ~]# cd flask
[root@localhost flask]# vi run.py创建python文件 run.py ,内容如下:
from flask import Flask
application = Flask(__name__)
@application.route('/')
def hello_world():
return 'Hello World!'
if __name__ == '__main__':
application.run(host='0.0.0.0')6、配置uwsgi的配置文件,这个文件很重要,配置错了,会访问不了的
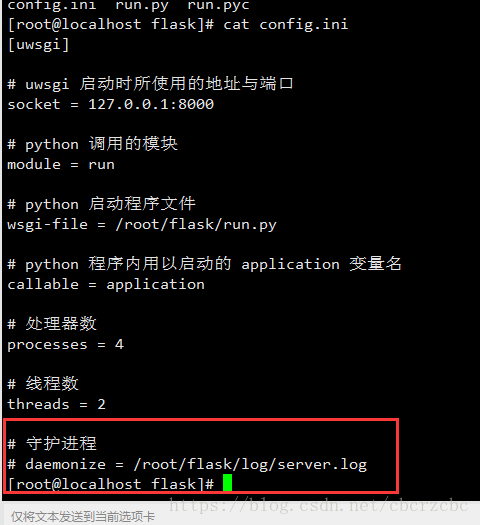
在flask项目下,创建一个config.ini,内容如下:
[uwsgi]
# uwsgi 启动时所使用的地址与端口
socket = 127.0.0.1:8000
# python 调用的模块
module = run
# python 启动程序文件
wsgi-file = /root/flask/run.py
# python 程序内用以启动的 application 变量名
callable = application
# 处理器数
processes = 4
# 线程数
threads = 2
# 守护进程
# daemonize = /root/flask/log/server.log7、安装Nginx
[root@localhost ~]# yum -y install nginx
配置nginx的配置文件
nginx的配置文件,在/etc/nginx/nginx.conf,可以直接配置它,也可以先把它备份一次,再进行配置
这里我就直接配置它了
# For more information on configuration, see:
# * Official English Documentation: http://nginx.org/en/docs/
# * Official Russian Documentation: http://nginx.org/ru/docs/
user nginx;
worker_processes auto;
error_log /var/log/nginx/error.log;
pid /run/nginx.pid;
# Load dynamic modules. See /usr/share/nginx/README.dynamic.
include /usr/share/nginx/modules/*.conf;
events {
worker_connections 1024;
}
http {
log_format main '$remote_addr - $remote_user [$time_local] "$request" '
'$status $body_bytes_sent "$http_referer" '
'"$http_user_agent" "$http_x_forwarded_for"';
access_log /var/log/nginx/access.log main;
sendfile on;
tcp_nopush on;
tcp_nodelay on;
keepalive_timeout 65;
types_hash_max_size 2048;
include /etc/nginx/mime.types;
default_type application/octet-stream;
# Load modular configuration files from the /etc/nginx/conf.d directory.
# See http://nginx.org/en/docs/ngx_core_module.html#include
# for more information.
include /etc/nginx/conf.d/*.conf;
server {
listen 80 default_server;
listen [::]:80 default_server;
server_name 192.168.10.139; # 这里配置你服务器的IP地址
root /usr/share/nginx/html;
# Load configuration files for the default server block.
include /etc/nginx/default.d/*.conf;
location / {
include uwsgi_params; # 引入uwsgi组件
uwsgi_pass 127.0.0.1:8000; # 定义uwsgi的转发端口
uwsgi_param UWSGI_CHDIR /root/flask; # 定义flask项目的路径
uwsgi_param UWSGI_SCRIPT run:application; # 定义flask项目的入口python文件和调用的函数
}
error_page 404 /404.html;
location = /40x.html {
}
error_page 500 502 503 504 /50x.html;
location = /50x.html {
}
}
# Settings for a TLS enabled server.
#
# server {
# listen 443 ssl http2 default_server;
# listen [::]:443 ssl http2 default_server;
# server_name _;
# root /usr/share/nginx/html;
#
# ssl_certificate "/etc/pki/nginx/server.crt";
# ssl_certificate_key "/etc/pki/nginx/private/server.key";
# ssl_session_cache shared:SSL:1m;
# ssl_session_timeout 10m;
# ssl_ciphers HIGH:!aNULL:!MD5;
# ssl_prefer_server_ciphers on;
#
# # Load configuration files for the default server block.
# include /etc/nginx/default.d/*.conf;
#
# location / {
# }
#
# error_page 404 /404.html;
# location = /40x.html {
# }
#
# error_page 500 502 503 504 /50x.html;
# location = /50x.html {
# }
# }
}
重启nginx服务
[root@localhost ~]# service nginx restart8、临时关闭防火墙firewalld和SELinux
这是为了方便才这么做的,实际上,我们不会关闭防火墙,而是针对业务,做对应的放行策略,这里只是方便测试
[root@localhost ~]# service firewalld stop[root@localhost ~]# setenforce 09、启动uwsgi
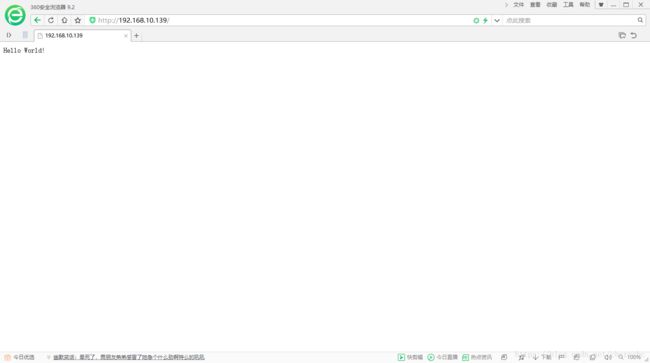
[root@localhost flask]# uwsgi config.ini10、测试一下,完全O98K
11、上线部署
直至上叙步骤,都只是半桶水的临时调试,综合多方面的考虑,我们并不能一昧的图方便,而关闭linux的防火墙,因此,我们要做放行策略
防火墙放行80端口,nginx访问web页面,默认是80,所以我们要放行80
[root@localhost ~]# firewall-cmd --zone=public --add-port=80/tcp --permanent
[root@localhost ~]# service firewalld restart将Nginx加到SELinux的允许名单
[root@localhost ~]# yum -y install policycoreutils-python
[root@localhost ~]# cat /var/log/audit/audit.log | grep nginx | grep denied | audit2allow -M mynginx
[root@localhost ~]# semodule -i mynginx.pp自启项目里的config.ini文件,启动uWSGI
还记得这里有个这个吧
我们在项目目录下,创建对应的文件
[root@localhost flask]# mkdir log
[root@localhost flask]# touch /root/flask/log/server.log然后,把config.ini的注释行,取消掉
这样,uwsgi的日志,就会写进server.log里面,方便我们随时调用日志查看
最后,配置开机自启动
开机自启动nginx服务和uwsgi
开机自启动nginx
[root@localhost ~]# systemctl enable nginx.service在计划任务中,添加开机自启动,让uwsgi自动执行配置文件
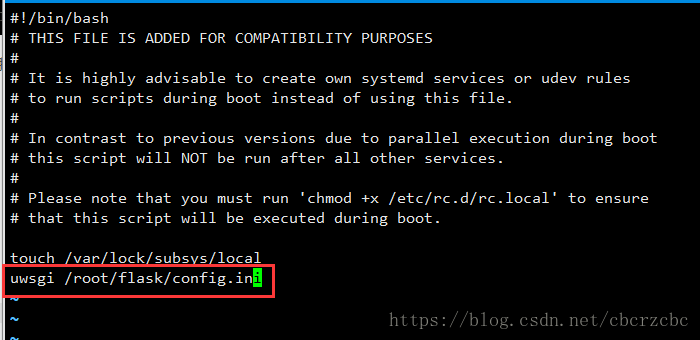
[root@localhost ~]# vi /etc/rc.d/rc.local加一行,写上uwsgi启动config.ini的命令
给rc.local添加执行权限
[root@localhost ~]# chmod +x /etc/rc.d/rc.local12、重启Linux机器
直接reboot重启,然后,去其他电脑试一下,浏览器能不能直接访问,如果可以,那就是大功告成了