Nginx 模块开发
关注校招、实习信息

Nginx 模块概述
Nginx 模块有三种角色:
- 处理请求并产生输出的 Handler 模块;
- 处理由 Handler 产生的输出的 Filter(滤波器)模块;
- 当出现多个后台服务器时,Load-balancer (负载均衡器)模块负责选择其中一个后台服务器发送请求;
通常,服务器启动时,任何
Handler 模块都有可能去处理配置文件中的
location 定义。若出现多个
Handler 模块被配置成需要处理某一特定的
location 时,最终只有其中一个
Handler 模块是成功的。
Handler 模块有三种返回方式:
- 接收请求,并成功返回;
- 接收请求,但是出错返回;
- 拒绝请求,使默认的 Handler 模块处理该请求;
若
Handler 模块没有产生错误返回时,则会调用
Filter 模块。每个
location 配置里都可以添加多个
Filter 模块 ,因此响应可以被压缩和分块。
Filter 模块之间的处理顺序是在编译时就已经确定的。
Filter 模块采用“
CHAIN OF RESPONSIBILITY”链式的设计模式。当有请求到达时,请求依次经过这条链上的全部
Filter 模块,一个
Filter 被调用并处理,接下来调用下一个
Filter,直到最后一个
Filter 被调用完成,
Nginx 才真正完成响应流程。
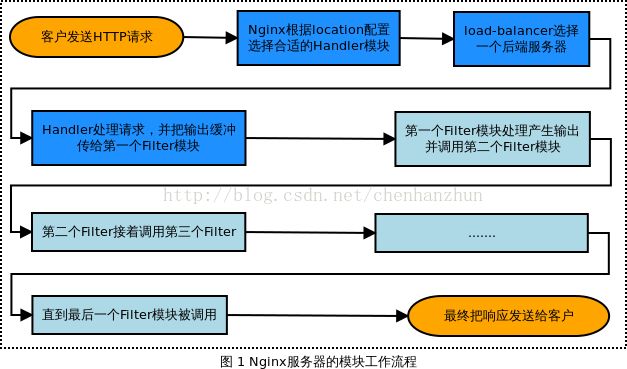
总结如下,典型的处理形式如下:
Client sends HTTP request → Nginx chooses the appropriate handler based on the location config →
(if applicable) load-balancer picks a backend server →
Handler does its thing and passes each output buffer to the first filter →
First filter passes the output to the second filter → second to third → third to fourth → etc.
→ Final response sent to client Nginx 模块的结构
模块的配置结构
模块最多可以定义三个配置结构:
main、
server、
location。绝大多数模块仅需要一个
location 配置。名称约定如下以
ngx_http__(main|srv|loc)_conf_t 为例的
dav module:
typedef struct {
ngx_uint_t methods;
ngx_flag_t create_full_put_path;
ngx_uint_t access;
} ngx_http_dav_loc_conf_t;
/* Nginx 模块的数据结构 */
#define NGX_MODULE_V1 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 1
#define NGX_MODULE_V1_PADDING 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0
struct ngx_module_s {
/* 模块类别由type成员决定,ctx_index表示当前模块在type类模块中的序号 */
ngx_uint_t ctx_index;
/* index 区别与ctx_index,index表示当前模块在所有模块中的序号 */
ngx_uint_t index;
/* spare 序列保留变量,暂时不被使用 */
ngx_uint_t spare0;
ngx_uint_t spare1;
ngx_uint_t spare2;
ngx_uint_t spare3;
/* 当前模块的版本 */
ngx_uint_t version;
/* ctx指向特定类型模块的公共接口,例如在HTTP模块中,ctx指向ngx_http_module_t结构体 */
void *ctx;
/* 处理nginx.conf中的配置项 */
ngx_command_t *commands;
/* type表示当前模块的类型 */
ngx_uint_t type;
/* 下面的7个函数指针是在Nginx启动或停止时,分别调用的7中方法 */
/* 在master进程中回调init_master */
ngx_int_t (*init_master)(ngx_log_t *log);
/* 初始化所有模块时回调init_module */
ngx_int_t (*init_module)(ngx_cycle_t *cycle);
/* 在worker进程提供正常服务之前回调init_process初始化进程 */
ngx_int_t (*init_process)(ngx_cycle_t *cycle);
/* 初始化多线程 */
ngx_int_t (*init_thread)(ngx_cycle_t *cycle);
/* 退出多线程 */
void (*exit_thread)(ngx_cycle_t *cycle);
/* 在worker进程停止服务之前回调exit_process */
void (*exit_process)(ngx_cycle_t *cycle);
/* 在master进程退出之前回调exit_master */
void (*exit_master)(ngx_cycle_t *cycle);
/* 保留字段,未被使用 */
uintptr_t spare_hook0;
uintptr_t spare_hook1;
uintptr_t spare_hook2;
uintptr_t spare_hook3;
uintptr_t spare_hook4;
uintptr_t spare_hook5;
uintptr_t spare_hook6;
uintptr_t spare_hook7;
};模块配置指令
模块指令存储在一个
ngx_command_t 类型的静态数组结构中,例如:
static ngx_command_t ngx_http_circle_gif_commands[] = {
{ ngx_string("circle_gif"),
NGX_HTTP_LOC_CONF|NGX_CONF_NOARGS,
ngx_http_circle_gif,
NGX_HTTP_LOC_CONF_OFFSET,
0,
NULL },
{ ngx_string("circle_gif_min_radius"),
NGX_HTTP_MAIN_CONF|NGX_HTTP_SRV_CONF|NGX_HTTP_LOC_CONF|NGX_CONF_TAKE1,
ngx_conf_set_num_slot,
NGX_HTTP_LOC_CONF_OFFSET,
offsetof(ngx_http_circle_gif_loc_conf_t, min_radius),
NULL },
...
ngx_null_command
};struct ngx_command_s {
/* 配置项名称 */
ngx_str_t name;
/* 配置项类型,type将指定配置项可以出现的位置以及携带参数的个数 */
ngx_uint_t type;
/* 处理配置项的参数 */
char *(*set)(ngx_conf_t *cf, ngx_command_t *cmd, void *conf);
/* 在配置文件中的偏移量,conf与offset配合使用 */
ngx_uint_t conf;
ngx_uint_t offset;
/* 配置项读取后的处理方法,必须指向ngx_conf_post_t 结构 */
void *post;
};type :该配置的类型,指定配置项的出现位置以及可携带参数的个数,下面规定只是其中一部分,更多信息可查看文件 core/ngx_conf_file.h:
NGX_HTTP_MAIN_CONF: directive is valid in the main config
NGX_HTTP_SRV_CONF: directive is valid in the server (host) config
NGX_HTTP_LOC_CONF: directive is valid in a location config
NGX_HTTP_UPS_CONF: directive is valid in an upstream config
NGX_CONF_NOARGS: directive can take 0 arguments
NGX_CONF_TAKE1: directive can take exactly 1 argument
NGX_CONF_TAKE2: directive can take exactly 2 arguments
…
NGX_CONF_TAKE7: directive can take exactly 7 arguments
NGX_CONF_FLAG: directive takes a boolean ("on" or "off")
NGX_CONF_1MORE: directive must be passed at least one argument
NGX_CONF_2MORE: directive must be passed at least two argumentschar *(*set)(ngx_conf_t *cf, ngx_command_t *cmd, void *conf);- cf :指向ngx_conf_t 结构的指针,该结构包括从配置指令传递的参数;
- cmd:指向当前ngx_command_t 结构;
- conf:指向模块配置结构;
为了方便实现对配置指令参数的读取,
Nginx 已经默认提供了对一些标准类型的参数进行读取的函数,可以直接赋值给
set 字段使用。下面是一部分已经实现的
set 类型函数,更多可参考文件
core/ngx_conf_file.h:
- ngx_conf_set_flag_slot : 把 "on" 或 "off" 解析为 1 或 0;
- ngx_conf_set_str_slot : 解析字符串并保存 ngx_str_t 类型;
- ngx_conf_set_num_slot: 解析一个数字并将其保存为int 类型;
- ngx_conf_set_size_slot: 解析数据大小 ("8k", "1m", etc.) 并将其保存为size_t;
conf :用于指示配置项所处内存的相对偏移量,仅在
type 中没有设置
NGX_DIRECT_CONF 和
NGX_MAIN_CONF 时才生效。对于
HTTP 模块,
conf 必须设置,它的取值如下:
- NGX_HTTP_MAIN_CONF_OFFSET:使用create_main_conf 方法产生的结构体来存储解析出的配置项参数;
- NGX_HTTP_SRV_CONF_OFFSET:使用 create_srv_conf 方法产生的结构体来存储解析出的配置项参数;
- NGX_HTTP_LOC_CONF_OFFSET:使用 create_loc_conf 方法产生的结构体来存储解析出的配置项参数;
offset :表示当前配置项在整个存储配置项的结构体中的偏移位置。
模块上下文
这是一个静态的
ngx_http_module_t 结构,它的名称是
ngx_http__module_ctx 。以下是该结构的定义,具体可查阅文件
http/ngx_http_config.h:
- preconfiguration
- postconfiguration
- creating the main conf (i.e., do a malloc and set defaults)
- initializing the main conf (i.e., override the defaults with what's in nginx.conf)
- creating the server conf
- merging it with the main conf
- creating the location conf
- merging it with the server conf
typedef struct{/* 可以把不需要调用的函数指针设置为 NULL */
/* 解析配置文件之前被调用 */
ngx_int_t (*preconfiguration)(ngx_conf_t *cf);
/* 完成配置文件的解析后被调用 */
ngx_int_t (*postconfiguration)(ngx_conf_t *cf);
/* 创建存储main级别的全局配置项的结构体(直属于http块) */
void *(*create_main_conf)(ngx_conf_t *cf);
/* 初始化main级别的配置项 */
char *(*init_main_conf)(ngx_conf_t *cf);
/* 创建存储srv级别的配置项的结构体(直属于server块) */
void *(*create_srv_conf)(ngx_conf_t *cf);
/* 合并main级别与srv级别下的同名配置项 */
char *(*merge_srv_conf)(ngx_conf_t *cf, void *prev, void *conf);
/* 创建存储loc级别的配置项的结构体(直属于location块) */
void *(*create_loc_conf)(ngx_conf_t *cf);
/* 合并srv级别与loc级别下的同名配置项 */
char *(*merge_loc_conf)(ngx_conf_t *cf, void *prev, void *conf);
}ngx_http_module_t;
在以上的结构内容中,大多数模块只使用最后两项:
ngx_http__create_loc_conf 和
ngx_http__merge_loc_conf ;例如:
static ngx_http_module_t ngx_http_circle_gif_module_ctx = {
NULL, /* preconfiguration */
NULL, /* postconfiguration */
NULL, /* create main configuration */
NULL, /* init main configuration */
NULL, /* create server configuration */
NULL, /* merge server configuration */
ngx_http_circle_gif_create_loc_conf, /* create location configuration */
ngx_http_circle_gif_merge_loc_conf /* merge location configuration */
};create_loc_conf 函数
该函数是传入一个
ngx_conf_t 结构的参数,返回新创建模块的配置结构,在这里是返回:
ngx_http_circle_gif_loc_conf_t
static void *
ngx_http_circle_gif_create_loc_conf(ngx_conf_t *cf)
{
ngx_http_circle_gif_loc_conf_t *conf;
conf = ngx_pcalloc(cf->pool, sizeof(ngx_http_circle_gif_loc_conf_t));
if (conf == NULL) {
return NGX_CONF_ERROR;
}
conf->min_radius = NGX_CONF_UNSET_UINT;
conf->max_radius = NGX_CONF_UNSET_UINT;
return conf;
}merge_loc_conf 函数
Nginx 为不同的数据类型提供了
merge 函数,可查阅
core/ngx_conf_file.h;
merge_loc_conf 函数定义如下:
static char *
ngx_http_circle_gif_merge_loc_conf(ngx_conf_t *cf, void *parent, void *child)
{
ngx_http_circle_gif_loc_conf_t *prev = parent;
ngx_http_circle_gif_loc_conf_t *conf = child;
ngx_conf_merge_uint_value(conf->min_radius, prev->min_radius, 10);
ngx_conf_merge_uint_value(conf->max_radius, prev->max_radius, 20);
if (conf->min_radius < 1) {
ngx_conf_log_error(NGX_LOG_EMERG, cf, 0,
"min_radius must be equal or more than 1");
return NGX_CONF_ERROR;
}
if (conf->max_radius < conf->min_radius) {
ngx_conf_log_error(NGX_LOG_EMERG, cf, 0,
"max_radius must be equal or more than min_radius");
return NGX_CONF_ERROR;
}
return NGX_CONF_OK;
}模块的定义
对任何开发模块,都需要定义一个
ngx_module_t 类型的变量来说明这个模块本身的信息,它告诉了
Nginx 这个模块的一些信息。这个变量是
ngx_http__module ;例如:更多例子可查找文件
core/ngx_conf_file.h;
ngx_module_t ngx_http__module = {
NGX_MODULE_V1,
&ngx_http__module_ctx, /* module context */
ngx_http__commands, /* module directives */
NGX_HTTP_MODULE, /* module type */
NULL, /* init master */
NULL, /* init module */
NULL, /* init process */
NULL, /* init thread */
NULL, /* exit thread */
NULL, /* exit process */
NULL, /* exit master */
NGX_MODULE_V1_PADDING
}; Handler 模块
Handler 模块必须提供一个真正的处理函数,这个函数负责处理来自客户端的请求。该函数既可以选择自己直接生成内容,也可以选择拒绝处理,并由后续的
Handler 去进行处理,或者是选择丢给后续的
Filter 模块进行处理。以下是该函数的原型:
typedef ngx_int_t (*ngx_http_handler_pt)(ngx_http_request_t *r);
Handler 模块处理过程中做了四件事情:
获取 location 配置、
生成合适的响应、
发送响应的 header 头部、
发送响应的 body 包体。
获取 location 配置
获取
location 配置 指向调用
ngx_http_get_module_loc_conf 函数即可,该函数传入的参数是
request 结构和 自定义的
module 模块。例如:
circle gif模块;
static ngx_int_t
ngx_http_circle_gif_handler(ngx_http_request_t *r)
{
ngx_http_circle_gif_loc_conf_t *circle_gif_config;
circle_gif_config = ngx_http_get_module_loc_conf(r, ngx_http_circle_gif_module);
...
}生成合适的响应
这里主要是 request 结构,其定义如下:更多可参考文件
http/ngx_http_request.h;
typedef struct {
...
/* the memory pool, used in the ngx_palloc functions */
ngx_pool_t *pool;
ngx_str_t uri;
ngx_str_t args;
ngx_http_headers_in_t headers_in;
...
} ngx_http_request_t;- uri 是 request 请求的路径,e.g. "/query.cgi".
- args 是请求串参数中问号后面的参数(e.g. "name=john").
- headers_in 包含有用的stuff,例如:cookies 和browser 信息。
发送响应的 header 头部
发送响应头部有函数
ngx_http_send_header(r) 实现。响应的
header 头部在
headers_out 结构中,定义如下:更多可参考文件 http/ngx_http_request.h;
typedef stuct {
...
ngx_uint_t status;
size_t content_type_len;
ngx_str_t content_type;
ngx_table_elt_t *content_encoding;
off_t content_length_n;
time_t date_time;
time_t last_modified_time;
..
} ngx_http_headers_out_t;r->headers_out.status = NGX_HTTP_OK;
r->headers_out.content_length_n = 100;
r->headers_out.content_type.len = sizeof("image/gif") - 1;
r->headers_out.content_type.data = (u_char *) "image/gif";
ngx_http_send_header(r);r->headers_out.content_encoding = ngx_list_push(&r->headers_out.headers);
if (r->headers_out.content_encoding == NULL) {
return NGX_ERROR;
}
r->headers_out.content_encoding->hash = 1;
r->headers_out.content_encoding->key.len = sizeof("Content-Encoding") - 1;
r->headers_out.content_encoding->key.data = (u_char *) "Content-Encoding";
r->headers_out.content_encoding->value.len = sizeof("deflate") - 1;
r->headers_out.content_encoding->value.data = (u_char *) "deflate";
ngx_http_send_header(r);发送响应的 body 包体
到此,该模块已经产生响应,并把它存储在内存中。发送包体的步骤是:首先分配响应特殊的缓冲区,然后分配缓冲区链接到
chain link,然后在
chain link 调用发送函数。
1、chain links 是 Nginx 使 Handler 模块在缓冲区中产生响应。在 chain 中每个 chain link 有一个指向下一个 link 的指针。首先,模块声明缓冲区 buffer 和 chain link:
ngx_buf_t *b;
ngx_chain_t out;b = ngx_pcalloc(r->pool, sizeof(ngx_buf_t));
if (b == NULL) {
ngx_log_error(NGX_LOG_ERR, r->connection->log, 0,
"Failed to allocate response buffer.");
return NGX_HTTP_INTERNAL_SERVER_ERROR;
}
b->pos = some_bytes; /* first position in memory of the data */
b->last = some_bytes + some_bytes_length; /* last position */
b->memory = 1; /* content is in read-only memory */
/* (i.e., filters should copy it rather than rewrite in place) */
b->last_buf = 1; /* there will be no more buffers in the request */out.buf = b;
out.next = NULL;return ngx_http_output_filter(r, &out);Handler 模块挂载
Handler 模块真正的处理函数通过两种方式挂载到处理过程中:按处理阶段挂载;按需挂载。
按处理阶段挂载
为了更精细地控制对于客户端请求的处理过程, Nginx 把这个处理过程划分成了11个阶段。依次列举如下:NGX_HTTP_POST_READ_PHASE:
/* 读取请求内容阶段 */
NGX_HTTP_SERVER_REWRITE_PHASE:
/* Server请求地址重写阶段 */
NGX_HTTP_FIND_CONFIG_PHASE:
/* 配置查找阶段: */
NGX_HTTP_REWRITE_PHASE:
/* Location请求地址重写阶段 */
NGX_HTTP_POST_REWRITE_PHASE:
/* 请求地址重写提交阶段 */
NGX_HTTP_PREACCESS_PHASE:
/* 访问权限检查准备阶段 */
NGX_HTTP_ACCESS_PHASE:
/* 访问权限检查阶段 */
NGX_HTTP_POST_ACCESS_PHASE:
/* 访问权限检查提交阶段 */
NGX_HTTP_TRY_FILES_PHASE:
/* 配置项try_files处理阶段 */
NGX_HTTP_CONTENT_PHASE:
/* 内容产生阶段 */
NGX_HTTP_LOG_PHASE:
/* 日志模块处理阶段 */NGX_HTTP_FIND_CONFIG_PHASE
NGX_HTTP_POST_ACCESS_PHASE
NGX_HTTP_POST_REWRITE_PHASE
NGX_HTTP_TRY_FILES_PHASE按需挂载
以这种方式挂载的 Handler 也被称为 content handler。当一个请求进来以后, Nginx 从 NGX_HTTP_POST_READ_PHASE 阶段开始依次执行每个阶段中所有 Handler。执行到 NGX_HTTP_CONTENT_PHASE 阶段时,如果这个 location 有一个对应的 content handler 模块,那么就去执行这个 content handler 模块真正的处理函数。否则继续依次执行 NGX_HTTP_CONTENT_PHASE 阶段中所有 content phase handlers,直到某个函数处理返回 NGX_OK 或者 NGX_ERROR。但是使用这个方法挂载上去的 handler 有一个特点是必须在 NGX_HTTP_CONTENT_PHASE 阶段才能被执行。如果你想自己的 handler 更早的阶段被执行,那就不要使用这种挂载方式。以下是例子:
circle gif ngx_command_t looks like this:
{ ngx_string("circle_gif"),
NGX_HTTP_LOC_CONF|NGX_CONF_NOARGS,
ngx_http_circle_gif,
0,
0,
NULL }static char *
ngx_http_circle_gif(ngx_conf_t *cf, ngx_command_t *cmd, void *conf)
{
ngx_http_core_loc_conf_t *clcf;
clcf = ngx_http_conf_get_module_loc_conf(cf, ngx_http_core_module);
clcf->handler = ngx_http_circle_gif_handler;
return NGX_CONF_OK;
}Handler 模块编写
Handler 模块编写步骤如下:- 编写模块基本结构:包括模块的定义,模块上下文结构,模块的配置结构等;
- 实现 handler 的挂载函数;根据模块的需求选择正确的挂载方式;
- 编写 handler 处理函数;模块的功能主要通过这个函数来完成;
Filter 模块
Filter 处理由 Handler 模块产生的响应,即仅处理由服务器发往客户端的 HTTP 响应,并不处理由客户端发往服务器的 HTTP 请求。 Filter 模块包括过滤头部( Header Filter)和过滤包体( Body Filter ), Filter 模块过滤头部处理 HTTP 的头部( HTTP headers), Filter 包体处理响应内容( response content)(即 HTTP 包体),这两个阶段可以对 HTTP 响应头部和内容进行修改。
Filter
模块
HTTP 响应
的方法如下
:定义在文件 src/http/ngx_http_core_module.h
typedef ngx_int_t (*ngx_http_output_header_filter_pt) (ngx_http_request_t *r);
typedef ngx_int_t (*ngx_http_output_body_filter_pt) (ngx_http_request_t *r, ngx_chain_t *chain);
所有 HTTP 过滤模块都需要实现上面的两个方法,在 HTTP 过滤模块组成的链表中,链表元素就是处理方法。HTTP 框架定义了链表入口:
extern ngx_http_output_header_filter_pt ngx_http_top_header_filter;
extern ngx_http_output_body_filter_pt ngx_http_top_body_filter;static ngx_http_output_header_filter_pt ngx_http_next_header_filter;
static ngx_http_output_body_filter_pt ngx_http_next_body_filter;
当执行发送 HTTP 头部或 HTTP 响应包体时,HTTP 框架是从 ngx_http_top_header_filter 和 ngx_http_top_body_filter 开始遍历 HTTP 头部过滤模块和 HTTP 包体过来模块。其源码实现在文件:src/http/ngx_http_core_module.c
/* 发送 HTTP 响应头部 */
ngx_int_t
ngx_http_send_header(ngx_http_request_t *r)
{
if (r->header_sent) {
ngx_log_error(NGX_LOG_ALERT, r->connection->log, 0,
"header already sent");
return NGX_ERROR;
}
if (r->err_status) {
r->headers_out.status = r->err_status;
r->headers_out.status_line.len = 0;
}
return ngx_http_top_header_filter(r);
}
/* 发送HTTP 响应包体 */
ngx_int_t
ngx_http_output_filter(ngx_http_request_t *r, ngx_chain_t *in)
{
ngx_int_t rc;
ngx_connection_t *c;
c = r->connection;
ngx_log_debug2(NGX_LOG_DEBUG_HTTP, c->log, 0,
"http output filter \"%V?%V\"", &r->uri, &r->args);
rc = ngx_http_top_body_filter(r, in);
if (rc == NGX_ERROR) {
/* NGX_ERROR may be returned by any filter */
c->error = 1;
}
return rc;
}Filter 模块相关结构
Filter 模块是采用链表形式的,其基本结构是
ngx_chain_t 和
ngx_buf_t;这两种结构定义如下:
typedef struct ngx_chain_s ngx_chain_t;
struct ngx_chain_s {
ngx_buf_t *buf;
ngx_chain_t *next;
};
struct ngx_buf_s {
u_char *pos; /* 当前buffer真实内容的起始位置 */
u_char *last; /* 当前buffer真实内容的结束位置 */
off_t file_pos; /* 在文件中真实内容的起始位置 */
off_t file_last; /* 在文件中真实内容的结束位置 */
u_char *start; /* buffer内存的开始分配的位置 */
u_char *end; /* buffer内存的结束分配的位置 */
ngx_buf_tag_t tag; /* buffer属于哪个模块的标志 */
ngx_file_t *file; /* buffer所引用的文件 */
/* 用来引用替换过后的buffer,以便当所有buffer输出以后,
* 这个影子buffer可以被释放。
*/
ngx_buf_t *shadow;
/* the buf's content could be changed */
unsigned temporary:1;
/*
* the buf's content is in a memory cache or in a read only memory
* and must not be changed
*/
unsigned memory:1;
/* the buf's content is mmap()ed and must not be changed */
unsigned mmap:1;
unsigned recycled:1; /* 内存可以被输出并回收 */
unsigned in_file:1; /* buffer的内容在文件中 */
/* 马上全部输出buffer的内容, gzip模块里面用得比较多 */
unsigned flush:1;
/* 基本上是一段输出链的最后一个buffer带的标志,标示可以输出,
* 有些零长度的buffer也可以置该标志
*/
unsigned sync:1;
/* 所有请求里面最后一块buffer,包含子请求 */
unsigned last_buf:1;
/* 当前请求输出链的最后一块buffer */
unsigned last_in_chain:1;
/* shadow链里面的最后buffer,可以释放buffer了 */
unsigned last_shadow:1;
/* 是否是暂存文件 */
unsigned temp_file:1;
/* 统计用,表示使用次数 */
/* STUB */ int num;
};Filter 过滤头部
header filter 包含三个基本步骤:
- 决定是否处理响应;
- 对响应进行处理;
- 调用下一个 filter;
例如下面的
"not modified" header filter:其中
headers_out 结构可参考文件
http/ngx_http_request.h;
static
ngx_int_t ngx_http_not_modified_header_filter(ngx_http_request_t *r)
{
time_t if_modified_since;
if_modified_since = ngx_http_parse_time(r->headers_in.if_modified_since->value.data,
r->headers_in.if_modified_since->value.len);
/* step 1: decide whether to operate */
if (if_modified_since != NGX_ERROR &&
if_modified_since == r->headers_out.last_modified_time) {
/* step 2: operate on the header */
r->headers_out.status = NGX_HTTP_NOT_MODIFIED;
r->headers_out.content_type.len = 0;
ngx_http_clear_content_length(r);
ngx_http_clear_accept_ranges(r);
}
/* step 3: call the next filter */
return ngx_http_next_header_filter(r);
}Filter 过滤包体
Filter 包体只能在 chain link缓冲区 buffer 中操作。模块必须决定是否修改输入缓冲区,或分配新的缓冲区替换当前缓冲区,或是在当前缓冲区之后还是之前插入新的缓冲区。很多模块接收多个缓冲区,导致这些模块在不完整的 chain 缓冲区中操作。 Filter 包体操作如下:static ngx_int_t ngx_http_chunked_body_filter(ngx_http_request_t *r, ngx_chain_t *in);/*
* Let's take a simple example.
* Suppose we want to insert the text "" to the end of every request.
* First, we need to figure out if the response's final buffer is included in the buffer chain we were given.
* Like I said, there's not a fancy API, so we'll be rolling our own for loop:
*/
ngx_chain_t *chain_link;
int chain_contains_last_buffer = 0;
chain_link = in;
for ( ; ; ) {
if (chain_link->buf->last_buf)
chain_contains_last_buffer = 1;
if (chain_link->next == NULL)
break;
chain_link = chain_link->next;
}
/*
* Now let's bail out if we don't have that last buffer:
*/
if (!chain_contains_last_buffer)
return ngx_http_next_body_filter(r, in);
/*
* Super, now the last buffer is stored in chain_link.
* Now we allocate a new buffer:
*/
ngx_buf_t *b;
b = ngx_calloc_buf(r->pool);
if (b == NULL) {
return NGX_ERROR;
}
/*
* And put some data in it:
*/
b->pos = (u_char *) "";
b->last = b->pos + sizeof("") - 1;
/*
* And hook the buffer into a new chain link:
*/
ngx_chain_t *added_link;
added_link = ngx_alloc_chain_link(r->pool);
if (added_link == NULL)
return NGX_ERROR;
added_link->buf = b;
added_link->next = NULL;
/*
* Finally, hook the new chain link to the final chain link we found before:
*/
chain_link->next = added_link;
/*
* And reset the "last_buf" variables to reflect reality:
*/
chain_link->buf->last_buf = 0;
added_link->buf->last_buf = 1;
/*
* And pass along the modified chain to the next output filter:
*/
return ngx_http_next_body_filter(r, in);
/*
* The resulting function takes much more effort than what you'd do with, say, mod_perl ($response->body =~ s/$//),
* but the buffer chain is a very powerful construct, allowing programmers to process data incrementally so that the client gets something as soon as possible.
* However, in my opinion, the buffer chain desperately needs a cleaner interface so that programmers can't leave the chain in an inconsistent state.
* For now, manipulate it at your own risk.
*/ Filter 模块挂载
Filters 模块和
Handler 模块一样,也是挂载到
post-configuration ,如下面代码所示:
static ngx_http_module_t ngx_http_chunked_filter_module_ctx = {
NULL, /* preconfiguration */
ngx_http_chunked_filter_init, /* postconfiguration */
...
};static ngx_int_t
ngx_http_chunked_filter_init(ngx_conf_t *cf)
{
ngx_http_next_header_filter = ngx_http_top_header_filter;
ngx_http_top_header_filter = ngx_http_chunked_header_filter;
ngx_http_next_body_filter = ngx_http_top_body_filter;
ngx_http_top_body_filter = ngx_http_chunked_body_filter;
return NGX_OK;
}ngx_int_t
ngx_http_send_header(ngx_http_request_t *r)
{
...
return ngx_http_top_header_filter(r);
}
ngx_int_t
ngx_http_output_filter(ngx_http_request_t *r, ngx_chain_t *in)
{
ngx_int_t rc;
ngx_connection_t *c;
c = r->connection;
rc = ngx_http_top_body_filter(r, in);
if (rc == NGX_ERROR) {
/* NGX_ERROR may be returned by any filter */
c->error = 1;
}
return rc;
}Filter 模块编写
Filter 模块编写步骤如下
- 编写基本结构:模块定义,上下文结构,基本结构;
- 初始化过滤模块:把本模块中处理的 HTTP 头部的 ngx_http_output_header_filter_pt 方法与处理HTTP 包体的ngx_http_output_body_filter_pt 方法插入到过滤模块链表首部;
- 实现处理 HTTP 响应的方法:处理 HTTP 头部,即 ngx_http_output_header_filter_pt 方法的实现,处理HTTP 包体的方法,即ngx_http_output_body_filter_pt 方法的实现;
- 编译安装;
开发 Nginx 新模块
把自己开发的模块编译到 N
ginx 中需要编写两个文件:
- "config",该文件会被 ./configure 包含;
- "ngx_http_
_module.c" ,该文件是定义模块的功能;
config 文件的编写如下:
/*
* "config" for filter modules:
*/
ngx_addon_name=ngx_http__module /* 模块的名称 */
HTTP_AUX_FILTER_MODULES="$HTTP_AUX_FILTER_MODULES ngx_http__module" /* 保存所有 HTTP 模块*/
NGX_ADDON_SRCS="$NGX_ADDON_SRCS $ngx_addon_dir/ngx_http__module.c" /* 指定新模块的源码路径 */
/*
* "config" for other modules:
*/
ngx_addon_name=ngx_http__module
HTTP_MODULES="$HTTP_MODULES ngx_http__module"
NGX_ADDON_SRCS="$NGX_ADDON_SRCS $ngx_addon_dir/ngx_http__module.c"
关于
"ngx_http__module.c" 文件的编写,可参考上面的
Handler 模块,同时可参考
Nginx 现有的模块:
src/http/modules/;
例如下面的
“Hello World ”
代码
:
#include
#include
#include
typedef struct
{
ngx_str_t hello_string;
ngx_int_t hello_counter;
}ngx_http_hello_loc_conf_t;
static ngx_int_t ngx_http_hello_init(ngx_conf_t *cf);
static void *ngx_http_hello_create_loc_conf(ngx_conf_t *cf);
static char *ngx_http_hello_string(ngx_conf_t *cf, ngx_command_t *cmd,
void *conf);
static char *ngx_http_hello_counter(ngx_conf_t *cf, ngx_command_t *cmd,
void *conf);
static ngx_command_t ngx_http_hello_commands[] = {
{
ngx_string("hello_string"),
NGX_HTTP_LOC_CONF|NGX_CONF_NOARGS|NGX_CONF_TAKE1,
ngx_http_hello_string,
NGX_HTTP_LOC_CONF_OFFSET,
offsetof(ngx_http_hello_loc_conf_t, hello_string),
NULL },
{
ngx_string("hello_counter"),
NGX_HTTP_LOC_CONF|NGX_CONF_FLAG,
ngx_http_hello_counter,
NGX_HTTP_LOC_CONF_OFFSET,
offsetof(ngx_http_hello_loc_conf_t, hello_counter),
NULL },
ngx_null_command
};
/*
static u_char ngx_hello_default_string[] = "Default String: Hello, world!";
*/
static int ngx_hello_visited_times = 0;
static ngx_http_module_t ngx_http_hello_module_ctx = {
NULL, /* preconfiguration */
ngx_http_hello_init, /* postconfiguration */
NULL, /* create main configuration */
NULL, /* init main configuration */
NULL, /* create server configuration */
NULL, /* merge server configuration */
ngx_http_hello_create_loc_conf, /* create location configuration */
NULL /* merge location configuration */
};
ngx_module_t ngx_http_hello_module = {
NGX_MODULE_V1,
&ngx_http_hello_module_ctx, /* module context */
ngx_http_hello_commands, /* module directives */
NGX_HTTP_MODULE, /* module type */
NULL, /* init master */
NULL, /* init module */
NULL, /* init process */
NULL, /* init thread */
NULL, /* exit thread */
NULL, /* exit process */
NULL, /* exit master */
NGX_MODULE_V1_PADDING
};
static ngx_int_t
ngx_http_hello_handler(ngx_http_request_t *r)
{
ngx_int_t rc;
ngx_buf_t *b;
ngx_chain_t out;
ngx_http_hello_loc_conf_t* my_conf;
u_char ngx_hello_string[1024] = {0};
ngx_uint_t content_length = 0;
ngx_log_error(NGX_LOG_EMERG, r->connection->log, 0, "ngx_http_hello_handler is called!");
my_conf = ngx_http_get_module_loc_conf(r, ngx_http_hello_module);
if (my_conf->hello_string.len == 0 )
{
ngx_log_error(NGX_LOG_EMERG, r->connection->log, 0, "hello_string is empty!");
return NGX_DECLINED;
}
if (my_conf->hello_counter == NGX_CONF_UNSET
|| my_conf->hello_counter == 0)
{
ngx_sprintf(ngx_hello_string, "%s", my_conf->hello_string.data);
}
else
{
ngx_sprintf(ngx_hello_string, "%s Visited Times:%d", my_conf->hello_string.data,
++ngx_hello_visited_times);
}
ngx_log_error(NGX_LOG_EMERG, r->connection->log, 0, "hello_string:%s", ngx_hello_string);
content_length = ngx_strlen(ngx_hello_string);
/* we response to 'GET' and 'HEAD' requests only */
if (!(r->method & (NGX_HTTP_GET|NGX_HTTP_HEAD))) {
return NGX_HTTP_NOT_ALLOWED;
}
/* discard request body, since we don't need it here */
rc = ngx_http_discard_request_body(r);
if (rc != NGX_OK) {
return rc;
}
/* set the 'Content-type' header */
/*
*r->headers_out.content_type.len = sizeof("text/html") - 1;
*r->headers_out.content_type.data = (u_char *)"text/html";
*/
ngx_str_set(&r->headers_out.content_type, "text/html");
/* send the header only, if the request type is http 'HEAD' */
if (r->method == NGX_HTTP_HEAD) {
r->headers_out.status = NGX_HTTP_OK;
r->headers_out.content_length_n = content_length;
return ngx_http_send_header(r);
}
/* allocate a buffer for your response body */
b = ngx_pcalloc(r->pool, sizeof(ngx_buf_t));
if (b == NULL) {
return NGX_HTTP_INTERNAL_SERVER_ERROR;
}
/* attach this buffer to the buffer chain */
out.buf = b;
out.next = NULL;
/* adjust the pointers of the buffer */
b->pos = ngx_hello_string;
b->last = ngx_hello_string + content_length;
b->memory = 1; /* this buffer is in memory */
b->last_buf = 1; /* this is the last buffer in the buffer chain */
/* set the status line */
r->headers_out.status = NGX_HTTP_OK;
r->headers_out.content_length_n = content_length;
/* send the headers of your response */
rc = ngx_http_send_header(r);
if (rc == NGX_ERROR || rc > NGX_OK || r->header_only) {
return rc;
}
/* send the buffer chain of your response */
return ngx_http_output_filter(r, &out);
}
static void *ngx_http_hello_create_loc_conf(ngx_conf_t *cf)
{
ngx_http_hello_loc_conf_t* local_conf = NULL;
local_conf = ngx_pcalloc(cf->pool, sizeof(ngx_http_hello_loc_conf_t));
if (local_conf == NULL)
{
return NULL;
}
ngx_str_null(&local_conf->hello_string);
local_conf->hello_counter = NGX_CONF_UNSET;
return local_conf;
}
/*
static char *ngx_http_hello_merge_loc_conf(ngx_conf_t *cf, void *parent, void *child)
{
ngx_http_hello_loc_conf_t* prev = parent;
ngx_http_hello_loc_conf_t* conf = child;
ngx_conf_merge_str_value(conf->hello_string, prev->hello_string, ngx_hello_default_string);
ngx_conf_merge_value(conf->hello_counter, prev->hello_counter, 0);
return NGX_CONF_OK;
}*/
static char *
ngx_http_hello_string(ngx_conf_t *cf, ngx_command_t *cmd, void *conf)
{
ngx_http_hello_loc_conf_t* local_conf;
local_conf = conf;
char* rv = ngx_conf_set_str_slot(cf, cmd, conf);
ngx_conf_log_error(NGX_LOG_EMERG, cf, 0, "hello_string:%s", local_conf->hello_string.data);
return rv;
}
static char *ngx_http_hello_counter(ngx_conf_t *cf, ngx_command_t *cmd,
void *conf)
{
ngx_http_hello_loc_conf_t* local_conf;
local_conf = conf;
char* rv = NULL;
rv = ngx_conf_set_flag_slot(cf, cmd, conf);
ngx_conf_log_error(NGX_LOG_EMERG, cf, 0, "hello_counter:%d", local_conf->hello_counter);
return rv;
}
static ngx_int_t
ngx_http_hello_init(ngx_conf_t *cf)
{
ngx_http_handler_pt *h;
ngx_http_core_main_conf_t *cmcf;
cmcf = ngx_http_conf_get_module_main_conf(cf, ngx_http_core_module);
h = ngx_array_push(&cmcf->phases[NGX_HTTP_CONTENT_PHASE].handlers);
if (h == NULL) {
return NGX_ERROR;
}
*h = ngx_http_hello_handler;
return NGX_OK;
}
写好上面的两个文件后,在编译 Nginx 时,步骤如下:
./configure --add-module=path/to/your/new/module/directory
make
make install
参考资料:
《
Emiller's Guide To Nginx Module Development》
《
nginx模块开发篇》
《
https://github.com/simpl/ngx_devel_kit》