python基础(三)
python基础(三)
1. dict字典
在 python 中,字典是一系列键–值对,每个键都与一个值相关联,你可以使用键来访问与之相关联的值。python 中的任何对象都可以用作字典中的值。
(1) 访问字典中的值
#定义一个 fruits 字典,键为水果种类,值为个数
fruits = {'apple':2, 'banana':3, 'pear':1}
print(fruits['apple'])
#输出:2
(2) 修改字典
#增加新的键值对
fruits['cherry'] = 5
#此时 fruits = {'apple':2, 'banana':3, 'pear':1, 'cherry':5}
#删除已有键值对
del fruits #删除字典
fruits.clear() #删除所有键值对
del fruits['banana']
#此时 fruits = {'apple':2, 'pear':1, 'cherry':5}
#修改现有键值对
fruits['apple'] = 3
#此时 fruits = {'apple':3, 'pear':1, 'cherry':5}
(3) 字典特性
- 字典的值可以没有限制的取任何 python 的对象
- 不允许同一个键出现两次,如果同一个键被赋值两次,后一个值会被记住
- 键必须不可变,可以使用数字,字符串或元组充当,但是不能用列表充当
(4) 字典的方法
python 字典包含了一下内置函数:
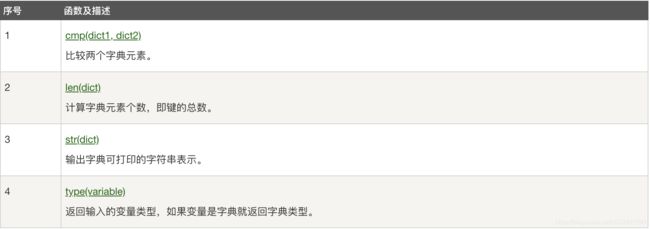
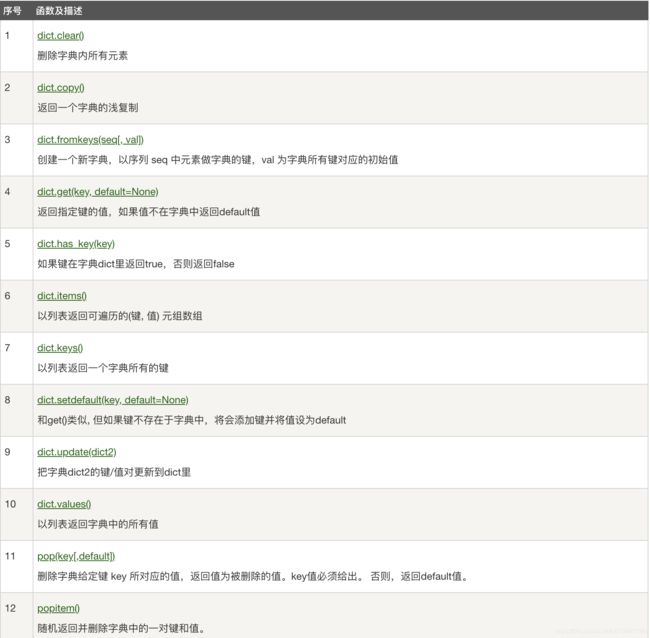
python 字典包含了一下内置方法:
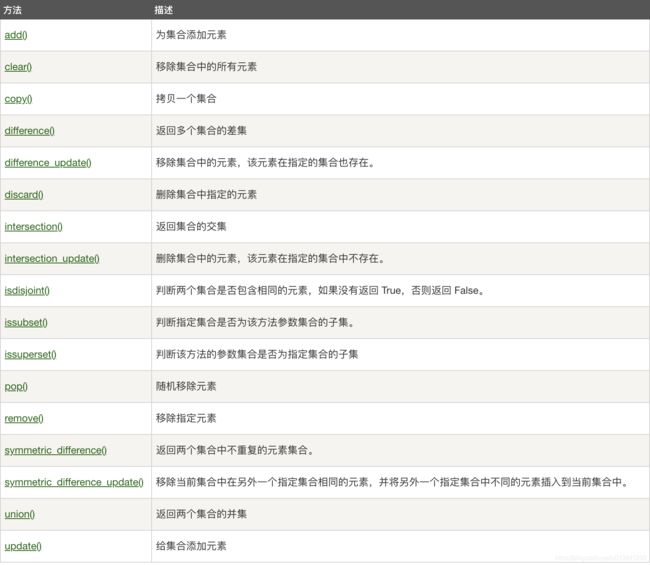
2. 集合
集合是一个无序的不重复元素序列,可以使用{}或set()来创建,但是空的集合只能用set()创建,因为{}表示一个空的字典。
#集合是一个不重复的序列
fruits = {'apple', 'banana', 'pear', 'apple', 'pear'}
print(fruits)
#{'apple', 'banana', 'pear'}
3. 判断语句
python 条件语句格式如下:
if condition1 :
.... #当 condition1 为真(True)时进入该片段
elif condition2 :
.... #当 condition1 为假(False)且 condition2 为真时进入该片段
else :
.... #当两个条件都为假时进入该片段
#example:
a = 80
if a < 60 :
print(‘fail’)
elif a >= 60 and a < 90 :#多条件
print('pass')
else :
print('great')
4. 三目表达式(原博客)
在很多别的语言中三目表达式为
rst = 5 > 3 ? 1 : 0
而在 python 中写法如下:
rst = 1 if 5 > 3 else 0
# 为真时的结果 if 条件 else 为假时的结果
5. 循环语句
(1) for 循环
python for 循环可以遍历任何序列的项目
fruits = ['apple', 'banana', 'pear']
for index in fruits :
print(index)
#通过序列索引迭代
for index in range(len(fruits)) :
print(index)
#增加 else 语句, for循环没有通过break跳出则执行else中的语句
for index in range(len(fruits)) :
if index == 'cherry' :
print('find cherry')
else :
print("can\'t find cherry")
#can't find cherry
(2) while 循环
while 循环用循环执行程序,即在某条件下循环执行某段程序
a = 0
while a < 10 :
a += 1
#当 a = 10 跳出循环
while ... :
else : #同 for else
(3) 循环控制语句
循环控制语句可以更改循环执行的循序,python 中有 break,continue,pass 三种
#break 在语句执行过程中终止循环,跳出整个循环
a = 0
while a < 5 :
if a == 3 :
break
else :
print(a)
a += 1
#输出为 0 1 2
#coninue 跳出本次循环,执行下一次循环
a = 0
while a < 5 :
if a == 3 :
a += 1
continue
else :
print(a)
a += 1
#输出为 0 1 2 4
#pass 是空语句,为了保持语句的完整性,不做任何事情
a = 0
while a < 5 :
if a == 3 :
pass
print(a * 2)
else :
print(a)
a += 1
#输出为 0 1 2 6 4