简单的信号表示与matlab(含抽样频率
- 代码来自北邮MOOC《信号与系统》,仅做学习总结
离散信号的表示
- 单位样值信号
n = [-5:5];
x = [0 0 0 0 0 1 0 0 0 0 0];
% 画序列图,列宽为2
stem(n,x,'linewidth',2);
xlabel('n');
ylabel('x(n)');
- 有限长序列
x = [1 2 4 2 3];
n = -2:2;
stem(n,x);
xlabel('n');
ylabel('x(n)');
- 单边指数序列,text标注,power形成指数
n = 0:10;
x1 = power(0.8,n)
stem(n,x1,'linewidth',2)
xlabel('n');
ylabel('a^n');
axis([n(1) n(end) -1.5 1.5]);
text(7,1,2,'a = 0.8');
- 正弦序列
- x ( n ) = c o s ( n ω 0 + θ ) x(n)=cos(n\omega_0+\theta) x(n)=cos(nω0+θ)
- w0数字角频率
n = 0:31;
w0 = pi/8;
x = sin(w0*n);
stem(n,x,'linewidth',2);
xlabel('n');
ylabel('x(n)');
axis([0 max(n) -1.1 1.1]);
- 矩形脉冲序列 window 矩形窗
- R N ( n ) = u ( n ) − u ( n − N ) R_N(n)=u(n)-u(n-N) RN(n)=u(n)−u(n−N)
N = 11;
n = (0:N-1)';
w = window(@rectwin,N);
stem(n,w,'linewidth',2);
xlabel('n');
ylabel('R_N(n)');
ylim([0 1.5])
连续信号
- 复指数信号
- x ( t ) = e ( α + j ω ) t x(t) = e^{(\alpha+j\omega)t} x(t)=e(α+jω)t
- 转为实数信号画图
clear all;close all;
t0 = 0;
tf = 5;
dt = 0.01;
t = [t0:dt:tf];
alpha = -0.5;
w = 10;
x = exp((alpha+j*w)*t);
subplot(2,2,1);
plot(t,real(x),'linewidth',2)
xlim([t(1) t(end)])
grid on;
xlabel('t');ylabel('real part');
suplot(222);
plot(t,img(x),'linewidth',2)
suplot(223);
plot(t,abs(x),'linewidth',2)
suplot(224);
plot(t,angle(x),'linewidth',2)
- 相位解卷绕
- 相位图去掉了 2 π 2\pi 2π 的整倍数,图形分布在 ( − π , π ) (-\pi,\pi) (−π,π) ,称为卷绕
- unwrap: 解卷绕
x_ang = angle(x);
x_ang_unwrap = unwrap(x_ang)
plot(t,x_ang_unwrap);
grid on;
xlabel('t');ylabel('angle');
抽样信号
- NaN 不是一个数, 使用sinc
- S a ( t ) = s i n ( t ) t Sa(t) = \frac{sin(t)}{t} Sa(t)=tsin(t)
- S a ( t ) = s i n c { t π } Sa(t) = sinc\{\frac{t}{\pi}\} Sa(t)=sinc{πt}
t = linspace(-10,10,101);
x = sin(t)./t;
plot(t,x);
% sin(0)./0 Warning:Divided by a zero ans = NaN
- sinc(t/pi) 与 sinc(t)
t = linspace(-10,10,501);
x = sinc(t/pi);
subplot(211);
plot(t,x);grid on;
xlabel('t');ylabel('Sa(t)'); % 过零点pi的整倍数
y = sinc(t);
subplot(211);
plot(t,y);grid on;
xlabel('t');ylabel('sinc(t)');% 过零点整数
钢琴
- 钢琴键盘中央 “C” 对应的频率约为262Hz,请产生1秒钟的此频率信号,抽样频率8192Hz
- 正弦波模拟钢琴震动
x ( t ) = s i n ( 2 π f 0 t ) x ( n T ) = x ( t ) ∣ t = n T = s i n ( 2 π f 0 n T ) = s i n ( 2 π f 0 n 1 f s ) = s i n ( ω 0 n ) x(t) = sin(2\pi f_0 t) \\ x(nT) = x(t)|_{t=nT} \\ = sin(2\pi f_0nT)=sin(2\pi f_0n\frac{1}{f_s})=sin(\omega_0n) x(t)=sin(2πf0t)x(nT)=x(t)∣t=nT=sin(2πf0nT)=sin(2πf0nfs1)=sin(ω0n)
f0 = 262;
fs = 8192;
omega0 = 2*pi*f0/fs; % 1s数据
n = 0:fs-1;
x = sin(n*omega0);
sound(x,fs);
audiowrite('dou.wav',x,fs);
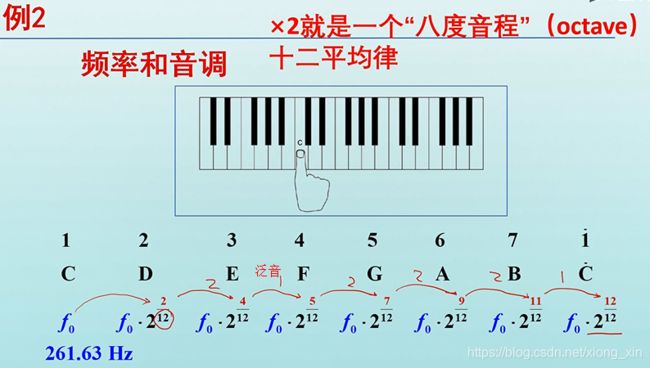
频率与音调
- 人耳对声波的频率是指数敏感的,某一组声音如果频率严格地按照 2 n 2^n 2n 的规律排列,它们听起来才是一个“等差音高序列”
- X2就是一个“八度音程“ (octave) 十二平均律
fs = 8192;
n = 0:fs/2-1
f1 = 262;
f2 = f1*power(2,2/12);
f3 = f1*power(2,4/12);
f4 = f1*power(2,5/12);
f5 = f1*power(2,7/12);
f6 = f1*power(2,9/12);
f7 = f1*power(2,11/12);
fh1 = f1*power(2,11/12);
x1 = sin(n*2*pi*f1/fs);
x2 = sin(n*2*pi*f2/fs);
x3 = sin(n*2*pi*f3/fs);
x4 = sin(n*2*pi*f4/fs);
x5 = sin(n*2*pi*f5/fs);
x6 = sin(n*2*pi*f6/fs);
x7 = sin(n*2*pi*f7/fs);
xh1 = sin(n*2*pi*fh1/fs);
x = [x1 x2 x3 x3 x5 x6 x7 xh1];
sound(x,fs);
% 简单的曲子
y = [x3 x3 x4 x5 x5 x4 x3];
sound(y,fs);
忙音信号
- “嘟、嘟、嘟……”的短促音(450Hz,响0.35s,断0.35s)
fs = 8000; % fs:抽样频率
Ts = 1/fs; % Ts:抽样间隔
f = 450;% 电话信号音的频率
T = 0.35;% 忙音通和断的时长
t = 0:Ts:T;% 抽样间隔
%电话信号音
x1 = sin(t*2*pi*f);
x2 = zeros(size(x1));
x = [x1 x2];
y = [x x x x];
sound(y,fs);
符号数学工具箱
- x ( t ) = s i n ( 2 π t / T ) x(t)=sin(2\pi t/T) x(t)=sin(2πt/T)
- subs 用于替换 T =5
syms t T;
w = 2*pi/T;
x = sin(w*t);
x1 = subs(x,'T',5);
ezplot(x1,[0 10]);
- 计算信号 x ( t ) = A s i n ( 2 π t / T ) x(t)=Asin(2\pi t/T) x(t)=Asin(2πt/T) 的平均值和平均功率
- int 积分从0到T
clear all
syms t T A;
w = 2*pi/T;
x = A*sin(w*t);
M = int(x,0,T)/T % 平均值
P = int(x^2,0,T)/T % 平均功率
- 对信号先分别创建再相乘,对于T = 4,用ezplot画出t在[0,4]内的信号,x(t)的基波周期用T表示
x ( t ) = c o s ( 2 π t / T ) s i n ( 2 π t / T ) x(t) = cos(2\pi t/T)sin(2\pi t/T) x(t)=cos(2πt/T)sin(2πt/T)
clear all
syms t T;
A = cos(2*pi*t/T);
B = sin(2*pi*t/T);
x = A*B;
x1 = subs(x,'T',4);
ezplot(x1,[0,4]);
- 有一线性时不变系统,当激励 x 1 ( t ) = u ( t ) x_1(t) = u(t) x1(t)=u(t) 时,零状态响应为 y 1 ( t ) = e − 2 t c o s ( 3 t ) u ( t ) y_1(t)=e^{-2t}cos(3t)u(t) y1(t)=e−2tcos(3t)u(t) ,试求当激励 x 2 ( t ) = δ ( t ) x_2(t)=\delta(t) x2(t)=δ(t) 时,零状态响应 y 2 ( t ) y_2(t) y2(t) 的表达式
- y 2 ( t ) = d y 1 ( t ) d t y_2(t)=\frac{dy_1(t)}{dt} y2(t)=dtdy1(t)
- u(t) 用 heaviside 表示
- simplify 表示化简
clear all;
syms t;
y1 = exp(-2*t)*cos(3*t)*heaviside(t);
y2 = diff(y1);
y3 = simplify(y2);
- 升余弦脉冲信号,画出波形图,并求其能量
x ( t ) = 1 2 [ 1 + c o s ( ω t ) ] [ u ( t + π / ω ) − u ( t − π / ω ) ] x(t)=\frac{1}{2}[1+cos(\omega t)][u(t+\pi/\omega)-u(t-\pi/\omega)] x(t)=21[1+cos(ωt)][u(t+π/ω)−u(t−π/ω)]
clear all;
syms t w;
x = (1+cos(w*t))/2;
E = int(x^2,t,-pi/w,pi/w);
x1 = subs(x,'w',pi);
ezplot(x1,[-1,1]);