Android图片加载内存优化
Android图片加载内存优化
- 利用BitmapFactory.Options实现图片内存优化
- 通过设置options.inPreferredConfig控制内存占用
- 通过设置采样率options.inSampleSize来减少图片内存占用
- 通过设置 Options.inBitmap,使Bitmap 对象重复使用,节省内存
利用BitmapFactory.Options实现图片内存优化
通过设置options.inPreferredConfig控制内存占用
- 首先准备了一张1280x800的blue_bg.png图片,我们知道这张图片加载到内存默认占用的大小是1280x800x4 = 4096000byte
Bitmap bitmap = BitmapFactory.decodeResource(getResources(), R.drawable.blue_bg);
// 默认情况下 BitmapFactory 使用 Bitmap.Config.ARGB_8888 的存储方式来加载图片内容,而在这种存储模式下,每一个像素需要占用 4 个字节
// 1280x800x4 = 4096000 byte 核算大约4000kb = 4M
if (Build.VERSION.SDK_INT >= Build.VERSION_CODES.KITKAT) {
Log.d("zyl--","bitmap = " + bitmap.getAllocationByteCount() +", ="+bitmap.getByteCount());
}
- 我们知道可以通过设置options.inPreferredConfig,来设置图片加载时候占用的字节ALPHA_8(1byte),RGB_565(2),ARGB_4444(2),ARGB_8888(4)。
BitmapFactory.Options options = new BitmapFactory.Options();
options.inPreferredConfig = Bitmap.Config.RGB_565;
Bitmap bitmap = BitmapFactory.decodeResource(getResources(), R.drawable.blue_bg,options);
if (Build.VERSION.SDK_INT >= Build.VERSION_CODES.KITKAT) {
Log.d("zyl--","bitmap = " + bitmap.getAllocationByteCount() +", ="+bitmap.getByteCount());
}
- 经过日志分析,发现并没有生效,占用的内存并没有减少一半。大概的原因是
- 设备加载图片时候,不同android版本对图片编解码的支持不一样
- 图片的格式也决定了他不能支持通过Bitmap.Config.RGB_565模式去加载,所以会选择默认ARGB_8888模式去加载,所以我们的内存占用并没有减少。
- 这篇文章会有详细的介绍:文章链接
- 通过设置不同的inPreferredConfig值真的能减少Bitmap加载时占用的内存么?链接
- 我们增加一张one.jpg图片做对比,具体代码如下:
BitmapFactory.Options options = new BitmapFactory.Options();
options.inPreferredConfig = Bitmap.Config.RGB_565;
// options.inSampleSize = 2;
Bitmap bitmap = BitmapFactory.decodeResource(getResources(), R.drawable.blue_bg,options);
// 默认情况下 BitmapFactory 使用 Bitmap.Config.ARGB_8888 的存储方式来加载图片内容,而在这种存储模式下,每一个像素需要占用 4 个字节
// 1280x800x4 = 4096000 byte 核算大约4000kb = 4M
if (Build.VERSION.SDK_INT >= Build.VERSION_CODES.KITKAT) {
Log.d("zyl--","bitmap = " + bitmap.getAllocationByteCount() +", ="+bitmap.getByteCount());
}
Bitmap one = BitmapFactory.decodeResource(getResources(), R.drawable.one,options);
// 默认情况下 BitmapFactory 使用 Bitmap.Config.ARGB_8888 的存储方式来加载图片内容,而在这种存储模式下,每一个像素需要占用 4 个字节
// 1280x800x4 = 4096000 byte 核算大约4000kb = 4M
if (Build.VERSION.SDK_INT >= Build.VERSION_CODES.KITKAT) {
Log.d("zyl--","one = " + one.getAllocationByteCount() +", ="+one.getByteCount());
}
通过日志我们发现,jpg图片对于设置inPreferredConfig属性生效了,内存占用减少了一半。进一步证实了图片格式对于inPreferredConfig属性是否生效有一定影响。
通过设置采样率options.inSampleSize来减少图片内存占用
- 通过设置采样率options.inSampleSize来减少图片内存占用问题。inSampleSize 参数,可以实现 Bitmap 采样压缩,这个参数的含义是宽高维度上每隔 inSampleSize 个像素进行一次采集。
BitmapFactory.Options options = new BitmapFactory.Options();
// options.inPreferredConfig = Bitmap.Config.RGB_565;
options.inSampleSize = 2;
Bitmap bitmap = BitmapFactory.decodeResource(getResources(), R.drawable.blue_bg,options);
// 默认情况下 BitmapFactory 使用 Bitmap.Config.ARGB_8888 的存储方式来加载图片内容,而在这种存储模式下,每一个像素需要占用 4 个字节
// 1280x800x4 = 4096000 byte 核算大约4000kb = 4M
if (Build.VERSION.SDK_INT >= Build.VERSION_CODES.KITKAT) {
Log.d("zyl--","bitmap = " + bitmap.getAllocationByteCount() +", ="+bitmap.getByteCount());
}
通过日志分析,得到当采样率为2的时候,图片占用内存为
: bitmap = 1024000,
内存减少了1/4。
通过设置 Options.inBitmap,使Bitmap 对象重复使用,节省内存
- 实现点击切换图片的功能,代码如下:
public class MainActivity extends AppCompatActivity {
private int resIndex;
int[] resIds = {R.drawable.one, R.drawable.two};
@Override
protected void onCreate(Bundle savedInstanceState) {
super.onCreate(savedInstanceState);
setContentView(R.layout.activity_main);
TextView hello = findViewById(R.id.hello);
final ImageView iv = findViewById(R.id.iv);
hello.setOnClickListener(new View.OnClickListener() {
@RequiresApi(api = Build.VERSION_CODES.KITKAT)
@Override
public void onClick(View v) {
iv.setImageBitmap(getBitmap());
}
});
reuseBitmap = BitmapFactory.decodeResource(getResources(),R.drawable.one);
}
@RequiresApi(api = Build.VERSION_CODES.KITKAT)
private Bitmap getBitmap() {
return BitmapFactory.decodeResource(getResources(), resIds[resIndex++ % 2], options);
}
以上代码运行后,发现当我们切换图片时,内存情况如图:
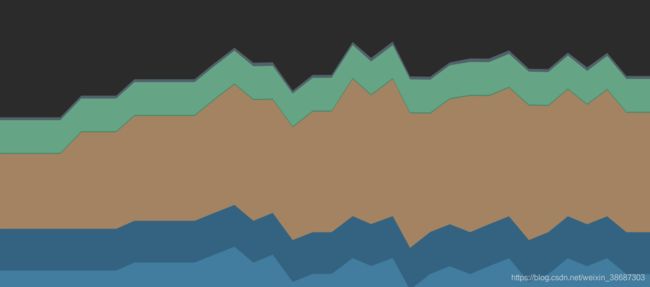
每次切换图片都需要通过 BitmapFactory 创建一个新的 Bitmap 对象。当方法执行完毕后,这个 Bitmap 又会被 GC 回收,这就造成不断地创建和销毁比较大的内存对象,从而导致频繁 GC(或者叫内存抖动)。像 Android App 这种面相最终用户交互的产品,如果因为频繁的 GC 造成 UI 界面卡顿,还是会影响到用户体验的。可以在 Android Studio Profiler 中查看内存情况。
- 使用Options.inBitmap,重复利用已经占用内存的 Bitmap 空间,解决内存抖动问题。
public class MainActivity extends AppCompatActivity {
private int resIndex;
int[] resIds = {R.drawable.one, R.drawable.two};
@Override
protected void onCreate(Bundle savedInstanceState) {
super.onCreate(savedInstanceState);
setContentView(R.layout.activity_main);
TextView hello = findViewById(R.id.hello);
final ImageView iv = findViewById(R.id.iv);
hello.setOnClickListener(new View.OnClickListener() {
@RequiresApi(api = Build.VERSION_CODES.KITKAT)
@Override
public void onClick(View v) {
// Intent intent = new Intent(MainActivity.this,MyActivity.class);
// startActivity(intent);
iv.setImageBitmap(getBitmap());
}
});
BitmapFactory.Options options = new BitmapFactory.Options();
//设置为true,使这块内存能够复用
options.inMutable =true;
reuseBitmap = BitmapFactory.decodeResource(getResources(),R.drawable.one,options);
}
/**
* 重用bitmap
*/
private Bitmap reuseBitmap;
@RequiresApi(api = Build.VERSION_CODES.KITKAT)
private Bitmap getBitmap() {
BitmapFactory.Options options = new BitmapFactory.Options();
options.inSampleSize = 1;
//为true 只解析bitmap的占用内存大小,不加载bitmap到内存中
options.inJustDecodeBounds = true;
BitmapFactory.decodeResource(getResources(), resIds[resIndex % 2], options);
if (canUseForInBitmap(reuseBitmap, options)) {
options.inMutable = true;
options.inBitmap = reuseBitmap;
}
//恢复设置
options.inJustDecodeBounds = false;
return BitmapFactory.decodeResource(getResources(), resIds[resIndex++ % 2], options);
}
static boolean canUseForInBitmap(
Bitmap candidate, BitmapFactory.Options targetOptions) {
if (Build.VERSION.SDK_INT >= Build.VERSION_CODES.KITKAT) {
// From Android 4.4 (KitKat) onward we can re-use if the byte size of
// the new bitmap is smaller than the reusable bitmap candidate
// allocation byte count.
int width = targetOptions.outWidth / targetOptions.inSampleSize;
int height = targetOptions.outHeight / targetOptions.inSampleSize;
int byteCount = width * height * getBytesPerPixel(candidate.getConfig());
return byteCount <= candidate.getAllocationByteCount();
}
// On earlier versions, the dimensions must match exactly and the inSampleSize must be 1
return candidate.getWidth() == targetOptions.outWidth
&& candidate.getHeight() == targetOptions.outHeight
&& targetOptions.inSampleSize == 1;
}
/**
* A helper function to return the byte usage per pixel of a bitmap based on its configuration.
*/
static int getBytesPerPixel(Bitmap.Config config) {
if (config == Bitmap.Config.ARGB_8888) {
return 4;
} else if (config == Bitmap.Config.RGB_565) {
return 2;
} else if (config == Bitmap.Config.ARGB_4444) {
return 2;
} else if (config == Bitmap.Config.ALPHA_8) {
return 1;
}
return 1;
}
}
