SpringCloud | SpringCloud Feign的前世今生【源码深入分析】
微信公众号:吉姆餐厅ak
学习更多源码知识,欢迎关注。
概述
springCloud feign主要对netflix feign进行了增强和包装,本篇从源码角度带你过一遍装配流程,揭开feign底层的神秘面纱。
主要包括feign整合ribbon,hystrix,sleuth,以及生成的代理类最终注入到spring容器的过程。篇幅略长,耐心读完,相信你会有所收获。
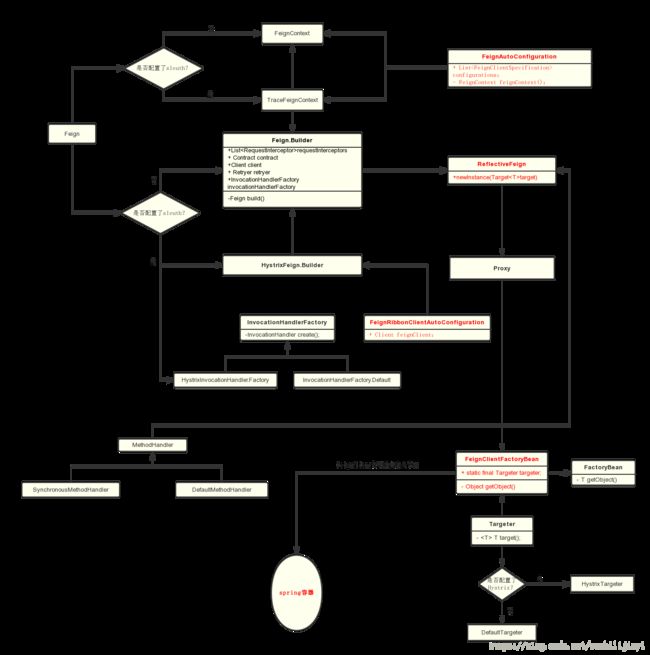
Feign架构图
一些核心类及大致流程:
大体步骤:
一、注册FeignClient配置类和FeignClient BeanDefinition
二、实例化Feign上下文对象FeignContext
三、创建 Feign.builder 对象
四、生成负载均衡代理类
五、生成默认代理类
六、注入到spring容器
源码分析
主要围绕上面6个步骤详细分析。
一、注册FeignClient配置类和FeignClient BeanDefinition
从启动类注解开始,来看下@EnableFeignClients注解:
@EnableFeignClients
public class MyApplication {
}
这是在启动类开启feign装配的注解,跟进该注解,看看做了什么:
@Import(FeignClientsRegistrar.class)
public class FeignClientsRegistrar implements ImportBeanDefinitionRegistrar,
ResourceLoaderAware, BeanClassLoaderAware {
// patterned after Spring Integration IntegrationComponentScanRegistrar
// and RibbonClientsConfigurationRegistgrar
private final Logger logger = LoggerFactory.getLogger(FeignClientsRegistrar.class);
private ResourceLoader resourceLoader;
private ClassLoader classLoader;
public FeignClientsRegistrar() {
}
@Override
public void setResourceLoader(ResourceLoader resourceLoader) {
this.resourceLoader = resourceLoader;
}
@Override
public void setBeanClassLoader(ClassLoader classLoader) {
this.classLoader = classLoader;
}
@Override
public void registerBeanDefinitions(AnnotationMetadata metadata,
BeanDefinitionRegistry registry) {
//1、先注册默认配置
registerDefaultConfiguration(metadata, registry);
//2、注册所有的feignClient beanDefinition
registerFeignClients(metadata, registry);
}
//...
}
我们分别来看一下上面registerBeanDefinitions中的两个方法:
1) 注册默认配置方法:registerDefaultConfiguration:
private void registerDefaultConfiguration(AnnotationMetadata metadata,
BeanDefinitionRegistry registry) {
Map defaultAttrs = metadata
.getAnnotationAttributes(EnableFeignClients.class.getName(), true);
if (defaultAttrs != null && defaultAttrs.containsKey("defaultConfiguration")) {
String name;
if (metadata.hasEnclosingClass()) {
name = "default." + metadata.getEnclosingClassName();
}
else {
name = "default." + metadata.getClassName();
}
// name 默认以 default 开头,后续会根据名称选择配置
registerClientConfiguration(registry, name,
defaultAttrs.get("defaultConfiguration"));
}
}
上述方法为读取启动类上面@EnableFeignClients注解中声明feign相关配置类,默认name为default,一般情况下无需配置。用默认的FeignAutoConfiguration即可。
上面有个比较重要的方法:注册配置registerClientConfiguration,启动流程一共有两处读取feign的配置类,这是第一处。根据该方法看一下:
private void registerClientConfiguration(BeanDefinitionRegistry registry, Object name,
Object configuration) {
BeanDefinitionBuilder builder = BeanDefinitionBuilder
.genericBeanDefinition(FeignClientSpecification.class);
builder.addConstructorArgValue(name);
builder.addConstructorArgValue(configuration);
registry.registerBeanDefinition(
name + "." + FeignClientSpecification.class.getSimpleName(),
builder.getBeanDefinition());
}
上面将bean配置类包装成FeignClientSpecification,注入到容器。该对象非常重要,包含FeignClient需要的重试策略,超时策略,日志等配置,如果某个服务没有设置,则读取默认的配置。
2、扫描FeignClient
该方法主要是扫描类路径,对所有的FeignClient生成对应的BeanDefinition:
public void registerFeignClients(AnnotationMetadata metadata,
BeanDefinitionRegistry registry) {
//...
//获取扫描目录下面所有的bean deanDefinition
for (String basePackage : basePackages) {
Set candidateComponents = scanner
.findCandidateComponents(basePackage);
for (BeanDefinition candidateComponent : candidateComponents) {
if (candidateComponent instanceof AnnotatedBeanDefinition) {
// verify annotated class is an interface
AnnotatedBeanDefinition beanDefinition = (AnnotatedBeanDefinition) candidateComponent;
AnnotationMetadata annotationMetadata = beanDefinition.getMetadata();
Assert.isTrue(annotationMetadata.isInterface(),
"@FeignClient can only be specified on an interface");
Map attributes = annotationMetadata
.getAnnotationAttributes(
FeignClient.class.getCanonicalName());
String name = getClientName(attributes);
//这里是第二处
registerClientConfiguration(registry, name,
attributes.get("configuration"));
//注册feignClient
registerFeignClient(registry, annotationMetadata, attributes);
}
}
}
}
可以看到上面又调用了registerClientConfiguration注册配置的方法,这里是第二处调用。这里主要是将扫描的目录下,每个项目的配置类加载的容器当中。
注册到容器中,什么时候会用到呢?具体又如何使用呢?别着急,后面会有介绍。
我们先会回到继续主流程,继续看注册feignClient的方法,跟进registerFeignClient:
private void registerFeignClient(BeanDefinitionRegistry registry,
AnnotationMetadata annotationMetadata, Map attributes) {
String className = annotationMetadata.getClassName();
//声明代理类名称
BeanDefinitionBuilder definition = BeanDefinitionBuilder
.genericBeanDefinition(FeignClientFactoryBean.class);
//logger.info("TEX do some replacement");
//attributes.put("value", ((String)attributes.get("value")).replace('_','-'));
validate(attributes);
definition.addPropertyValue("url", getUrl(attributes));
definition.addPropertyValue("path", getPath(attributes));
String name = getName(attributes);
definition.addPropertyValue("name", name);
definition.addPropertyValue("type", className);
definition.addPropertyValue("decode404", attributes.get("decode404"));
definition.addPropertyValue("fallback", attributes.get("fallback"));
definition.setAutowireMode(AbstractBeanDefinition.AUTOWIRE_BY_TYPE);
String alias = name + "FeignClient";
AbstractBeanDefinition beanDefinition = definition.getBeanDefinition();
beanDefinition.setPrimary(true);
BeanDefinitionHolder holder = new BeanDefinitionHolder(beanDefinition, className,
new String[] { alias });
//将bean definition加入到spring容器
BeanDefinitionReaderUtils.registerBeanDefinition(holder, registry);
}
划重点,上面出现了一行相当关键代码:
BeanDefinitionBuilder definition = BeanDefinitionBuilder.genericBeanDefinition(FeignClientFactoryBean.class);
springCloud FeignClient其实是利用了spring的代理工厂来生成代理类,所以这里将所有的feignClient的描述信息BeanDefinition设定为FeignClientFactoryBean类型,该类又继承FactoryBean,很明显,这是一个代理类。
在spring中,FactoryBean是一个工厂bean,用作创建代理bean,所以得出结论,feign将所有的feignClient bean包装成FeignClientFactoryBean。扫描方法到此结束。
代理类什么时候会触发生成呢?
在spring刷新容器时,当实例化我们的业务service时,如果发现注册了FeignClient,spring就会去实例化该FeignClient,同时会进行判断是否是代理bean,如果为代理bean,则调用FeignClientFactoryBean的T getObject() throws Exception;方法生成代理bean。
先来隆重介绍一下FeignClientFactoryBean,后面四步都基于此类。
先看一下代理feignClient代理生成入口:getObject方法:
@Override
public Object getObject() throws Exception {
// 二、实例化Feign上下文对象FeignContext
FeignContext context = applicationContext.getBean(FeignContext.class);
// 三、生成builder对象,用来生成feign
Feign.Builder builder = feign(context);
// 判断生成的代理对象类型,如果url为空,则走负载均衡,生成有负载均衡功能的代理类
if (!StringUtils.hasText(this.url)) {
String url;
if (!this.name.startsWith("http")) {
url = "http://" + this.name;
}
else {
url = this.name;
}
url += cleanPath();
// 四、生成负载均衡代理类
return loadBalance(builder, context, new HardCodedTarget<>(this.type,
this.name, url));
}
//如果指定了url,则生成默认的代理类
if (StringUtils.hasText(this.url) && !this.url.startsWith("http")) {
this.url = "http://" + this.url;
}
String url = this.url + cleanPath();
// 五、生成默认代理类
return targeter.target(this, builder, context, new HardCodedTarget<>(
this.type, this.name, url));
}
getObject()逻辑比较多,每一行都会做一些初始化配置,来逐步分析。
二、实例化Feign上下文对象FeignContext
上述方法中第一行便是实例化FeignContext:
FeignContext context = applicationContext.getBean(FeignContext.class);
获取FeignContext对象,如果没有实例化,则主动实例化,如下:
@Configuration
@ConditionalOnClass(Feign.class)
public class FeignAutoConfiguration {
@Autowired(required = false)
private List configurations = new ArrayList<>();
@Bean
public HasFeatures feignFeature() {
return HasFeatures.namedFeature("Feign", Feign.class);
}
@Bean
public FeignContext feignContext() {
FeignContext context = new FeignContext();
//将feign的配置类设置到feign的容器当中
context.setConfigurations(this.configurations);
return context;
}
}
可以看到feign的配置类设置到feign的容器当中,而集合中的元素 正是上面我们提到的两处调用registerClientConfiguration方法添加进去的,前后呼应。
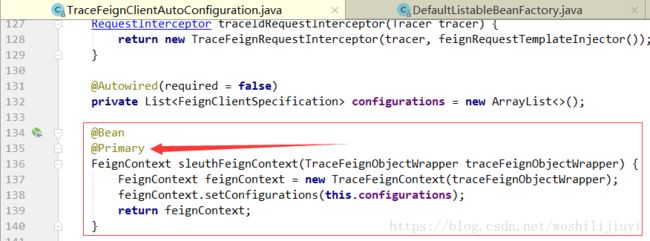
然而,当我们引入了sleuth之后,获取的feignContext确是TraceFeignClientAutoConfiguration中配置的实例sleuthFeignContext:
可以看到上面创建了一个TraceFeignContext实例,因为该对象继承FeignContext,同时又加了@Primary注解,所以在上面第2步中通过类型获取:
applicationContext.getBean(FeignContext.class);,最终拿到的是TraceFeignContext。
三、构造FeignBuilder
继续跟进该方法:
Feign.Builder builder = feign(context);
protected Feign.Builder feign(FeignContext context) {
Logger logger = getOptional(context, Logger.class);
if (logger == null) {
logger = new Slf4jLogger(this.type);
}
// 1、构造 Feign.Builder
Feign.Builder builder = get(context, Feign.Builder.class)
// required values
.logger(logger)
.encoder(get(context, Encoder.class))
.decoder(get(context, Decoder.class))
.contract(get(context, Contract.class));
// 2、设置重试策略,log等组件
//设置log级别
Logger.Level level = getOptional(context, Logger.Level.class);
if (level != null) {
builder.logLevel(level);
}
//设置重试策略
Retryer retryer = getOptional(context, Retryer.class);
if (retryer != null) {
builder.retryer(retryer);
}
//feign的错误code解析接口
ErrorDecoder errorDecoder = getOptional(context, ErrorDecoder.class);
if (errorDecoder != null) {
builder.errorDecoder(errorDecoder);
}
//超时时间设置,连接超时时间:connectTimeout默认10s,请求请求超时时间:readTimeout默认60s
Request.Options options = getOptional(context, Request.Options.class);
if (options != null) {
builder.options(options);
}
//拦截器设置,可以看出拦截器也是可以针对单独的feignClient设置
Map requestInterceptors = context.getInstances(
this.name, RequestInterceptor.class);
if (requestInterceptors != null) {
builder.requestInterceptors(requestInterceptors.values());
}
if (decode404) {
builder.decode404();
}
return builder;
}
上述代码有两处逻辑,分别来看:
1、Feign.Builder builder = get(context, Feign.Builder.class) ,又会有以下三种情况:
1)单独使用Feign,没有引入 sleuth、hystrix:
通过加载FeignClientsConfiguration的配置创建Feign的静态内部类:Feign.Builder
@Bean
@Scope("prototype")
@ConditionalOnMissingBean
public Feign.Builder feignBuilder(Retryer retryer) {
return Feign.builder().retryer(retryer);
}
2)引入了hystrix,没有引入sleuth:
通过加载FeignClientsConfiguration的配置创建HystrixFeign的静态内部类:HystrixFeign.Builder
@Configuration
@ConditionalOnClass({ HystrixCommand.class, HystrixFeign.class })
protected static class HystrixFeignConfiguration {
@Bean
@Scope("prototype")
@ConditionalOnMissingBean
@ConditionalOnProperty(name = "feign.hystrix.enabled", matchIfMissing = false)
public Feign.Builder feignHystrixBuilder() {
return HystrixFeign.builder();
}
}
3)同时引入hystrix 和 sleuth:
加载TraceFeignClientAutoConfiguration的配置创建:HystrixFeign.Builder:
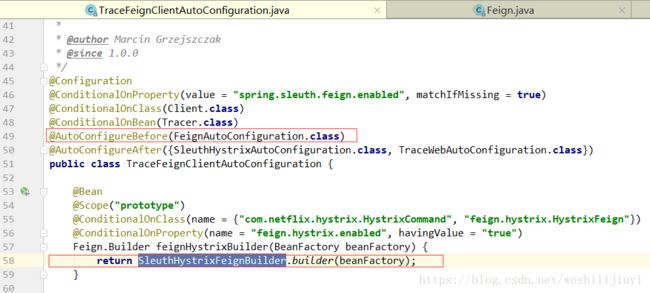
注意:
TraceFeignClientAutoConfiguration的配置类加载一定是在FeignClientsConfiguration之前(先加载先生效),而FeignClientsConfiguration加载是通过FeignAutoConfiguration完成的,所以上图中引入了条件注解:
@AutoConfigureBefore({FeignAutoConfiguration.class})
- 创建创建的
builder对象和第二种情况一下,只是做了一层包装:
final class SleuthFeignBuilder {
private SleuthFeignBuilder() {}
static Feign.Builder builder(Tracer tracer, HttpTraceKeysInjector keysInjector) {
return HystrixFeign.builder()
//各组件`client,retryer,decoder`进行增强,装饰器模式。
.client(new TraceFeignClient(tracer, keysInjector))
.retryer(new TraceFeignRetryer(tracer))
.decoder(new TraceFeignDecoder(tracer))
.errorDecoder(new TraceFeignErrorDecoder(tracer));
}
}
2、设置重试策略,log等组件
Feign.builder在获取之后又分别指定了重试策略,日志级别,错误代码code等,在上一步中调用SleuthFeignBuilder.build()时已经设置过默认值了,这里为什么要重复设置呢?
我们跟进去get()方法,一探究竟:
protected T get(FeignContext context, Class type) {
//根据name,也就是服务名称来生成builder
T instance = context.getInstance(this.name, type);
if (instance == null) {
throw new IllegalStateException("No bean found of type " + type + " for "
+ this.name);
}
return instance;
}
public T getInstance(String name, Class type) {
//这里获取AnnotationConfigApplicationContext容器
AnnotationConfigApplicationContext context = getContext(name);
if (BeanFactoryUtils.beanNamesForTypeIncludingAncestors(context,
type).length > 0) {
return context.getBean(type);
}
return null;
}
private Map contexts = new ConcurrentHashMap<>();
protected AnnotationConfigApplicationContext getContext(String name) {
if (!this.contexts.containsKey(name)) {
synchronized (this.contexts) {
if (!this.contexts.containsKey(name)) {
//这里创建容器createContext(name)
this.contexts.put(name, createContext(name));
}
}
}
return this.contexts.get(name);
}
重点来了,上述代码将FeignContext做了缓存,每个服务对应一个FeignContext,服务名作为key。
继续跟进createContext(name)方法:
protected AnnotationConfigApplicationContext createContext(String name) {
//注意:这里的容器并不是spring的容器,而是每次都重新创建一个
AnnotationConfigApplicationContext context = new AnnotationConfigApplicationContext();
//加载每个服务对应的配置类
if (this.configurations.containsKey(name)) {
for (Class configuration : this.configurations.get(name)
.getConfiguration()) {
context.register(configuration);
}
}
//加载启动类@EnableFeignClients注解指定的配置类
for (Map.Entry entry : this.configurations.entrySet()) {
if (entry.getKey().startsWith("default.")) {
for (Class configuration : entry.getValue().getConfiguration()) {
context.register(configuration);
}
}
}
//注册默认的配置类:FeignClientsConfiguration
context.register(PropertyPlaceholderAutoConfiguration.class,
this.defaultConfigType);
context.getEnvironment().getPropertySources().addFirst(new MapPropertySource(
this.propertySourceName,
Collections. singletonMap(this.propertyName, name)));
if (this.parent != null) {
// Uses Environment from parent as well as beans
context.setParent(this.parent);
}
//刷新容器
context.refresh();
return context;
}
可以看到上述AnnotationConfigApplicationContext容器并非spring容器,只是利用了spring刷新容器的方法来实例化配置类,以服务名作为key,配置隔离。
重点来了,上面加载配置的顺序为:先加载每个服务的配置类,然后加载启动类注解上的配置类,最后加载默认的配置类。这样做有什么好处?
spring刷新容器的方法也是对所有的bean进行了缓存,如果已经创建,则不再实例化。所以优先选取每个FeignClient的配置类,最后默认的配置类兜底。
所以这也证明了sleuth的配置一定在feign的配置类之前加载。
至此,FeignBuilder构造流程结束。
四、生成负载均衡代理类
再贴一下生成代理类的入口:
//判断url是否为空
if (!StringUtils.hasText(this.url)) {
//......
return loadBalance(builder, context, new HardCodedTarget<>(this.type,
this.name, url));
}
//......
return targeter.target(this, builder, context, new HardCodedTarget<>(
this.type, this.name, url));
这里有个重要判断:判断FeignClient声明的url是否为空,来判断具体要生成的代理类。如下:
这么做有什么意义?
1)如果为空,则默认走Ribbon代理,也就是这个入口,会有加载ribbon的处理。
@FeignClient("MyFeignClient")
2)如果不为空,指定url,则走默认生成代理类的方式,也就是所谓的硬编码。
@FeignClient(value = "MyFeignClient",url = "http://localhost:8081")
这样处理方便开发人员进行测试,无需关注注册中心,直接http调用,是个不错的开发小技巧。
生产环境也可以用上述第二种方式,指定域名的方式。
我们跟进loadBalance方法:
protected T loadBalance(Feign.Builder builder, FeignContext context,
HardCodedTarget target) {
//获得FeignClient
Client client = getOptional(context, Client.class);
if (client != null) {
builder.client(client);
return targeter.target(this, builder, context, target);
}
throw new IllegalStateException(
"No Feign Client for loadBalancing defined. Did you forget to include spring-cloud-starter-ribbon?");
}
Client client = getOptional(context, Client.class);这里会从FeignContext上下文中获取Client对象,该对象有三种实例,具体是哪个实现呢?
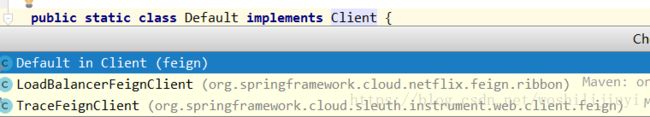
这里又会有三种情况:
1)没有整合ribbon、sleuth:
获取默认的Client:Default实例。
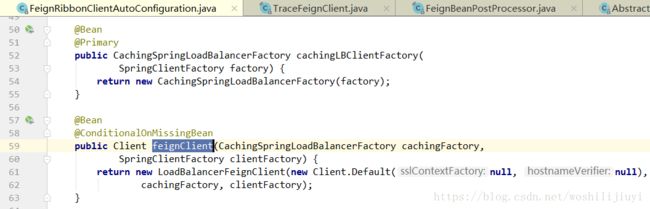
2)整合了ribbon,没有整合sleuth:
获取LoadBalanceFeignClient实例。
3)整合了ribbon 和 sleuth:
会获取TraceFeignClient实例,该实例是对LoadBalanceFeignClient的一种包装,实现方式通过BeanPostProcessor实现:FeignBeanPostProcessor中定义了包装逻辑:
@Override
public Object postProcessBeforeInitialization(Object bean, String beanName)
throws BeansException {
return this.traceFeignObjectWrapper.wrap(bean);
}
通过wrap方法最终返回TraceFeignClient实例。
继续回到主流程,先来看下Targeter接口:
interface Targeter {
T target(FeignClientFactoryBean factory, Feign.Builder feign, FeignContext context,
HardCodedTarget target);
}
该对象定义在FeignClientFactoryBean静静态代码块中:
private static final Targeter targeter;
static {
Targeter targeterToUse;
//判断类路径是否引入了hystrixFeign
if (ClassUtils.isPresent("feign.hystrix.HystrixFeign",
FeignClientFactoryBean.class.getClassLoader())) {
targeterToUse = new HystrixTargeter();
}
else {
targeterToUse = new DefaultTargeter();
}
targeter = targeterToUse;
}
这里会初始化Targeter,该类是生成feign代理类的工具类,有两种实现,正是上面的HystrixTargeter,DefaultTargeter。
因为我们引入了hystrix,所以Targeter实现类为HystrixTargeter。我们继续跟进targeter.target方法:
public T target(Target target) {
return build().newInstance(target);
}
上面通过build()方法获取生成代理类的工具类ReflectiveFeign,再通过newInstance正式创建代理类。
继续跟进:
public Feign build() {
SynchronousMethodHandler.Factory synchronousMethodHandlerFactory =
new SynchronousMethodHandler.Factory(client, retryer, requestInterceptors, logger,
logLevel, decode404);
ParseHandlersByName handlersByName =
new ParseHandlersByName(contract, options, encoder, decoder,
errorDecoder, synchronousMethodHandlerFactory);
return new ReflectiveFeign(handlersByName, invocationHandlerFactory);
}
这里会创建Feign的方法工厂synchronousMethodHandlerFactory,Feign通过该工厂为每个方法创建一个methodHandler,每个methodHandler中包含Feign对应的配置:retryer、requestInterceptors等。
继续跟进newInstance方法:
public T newInstance(Target target) {
//创建所有的 MethodHandler
Map nameToHandler = targetToHandlersByName.apply(target);
Map methodToHandler = new LinkedHashMap();
List defaultMethodHandlers = new LinkedList();
for (Method method : target.type().getMethods()) {
if (method.getDeclaringClass() == Object.class) {
continue;
//判断是否启用默认handler
} else if(Util.isDefault(method)) {
DefaultMethodHandler handler = new DefaultMethodHandler(method);
defaultMethodHandlers.add(handler);
methodToHandler.put(method, handler);
} else {
methodToHandler.put(method, nameToHandler.get(Feign.configKey(target.type(), method)));
}
}
//创建InvocationHandler,接收请求,转发到methodHandler
InvocationHandler handler = factory.create(target, methodToHandler);
//生成代理类
T proxy = (T) Proxy.newProxyInstance(target.type().getClassLoader(), new Class[]{target.type()}, handler);
//将默认方法绑定到代理类
for(DefaultMethodHandler defaultMethodHandler : defaultMethodHandlers) {
defaultMethodHandler.bindTo(proxy);
}
return proxy;
}
InvocationHandler最终创建的实例为HystrixInvocationHandler,核心方法如下:
HystrixCommand整个流程:Feign调用方发起请求,发送至hystrix的HystrixInvocationHandler,通过服务名称,找到对应方法的methodHandler,methodHandler中封装了loadBalanceClient、retryer、RequestInterceptor等组件,如果引入了sleuth,这几个组件均是sleuth的包装类。然后通过以上组件构造http请求完成整个过程。
五、生成默认代理类
理解了第四步的逻辑,生成默认代理类就很容易理解了,唯一不同点就是client的实现类为loadBalanceClient。
注意:不管是哪种代理类,最终发起请求还是由
Feign.Default中的execute方法完成,默认使用HttpUrlConnection实现。
六、注入spring容器
总结:通过spring refresh()方法,触发FeignClientFactoryBean.getObject()方法获得了代理类,然后完成注入spring容器的过程。该实现方式同Dubbo的实现方式类似,有兴趣的可以自行研究噢。