Java(八)GUI:3.JFrame常用的布局详细
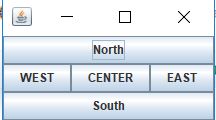
BorderLayout
·一个位置只能显示一个组件,相同位置的组件会被覆盖,只显示最上面(最后添加)的组件
·默认添加到BorderLayout.CENTER
· 这种布局管理器分为东、南、西、北、中心五个方位。北和南的组件可以在水平方向上拉伸;而东和西的组件可以在垂直方向上拉伸;中心的组件可同时在水平和垂直方向上同时拉伸,从而填充所有剩余空间。在使用BorderLayout的时候,如果容器的大小发生变化,其变化规律为:组件的相对位置不变,大小发生变化。例如容器变高了,则North、South 区域不变,West、Center、East区域变高;如果容器变宽了,West、East区域不变,North、Center、South区域变宽。不一定所有的区域都有组件,如果四周区域(West、East、North、South区域)没有组件,则由Center区域去补充,但是如果 Center区域没有组件,则保持空白。
·BorderLayout是RootPaneContainer(JInternalFrame、JDialog、JFrame、JWindow)的默认布局管理器。
class SimpleFrame extends JFrame
{
public SimpleFrame()
{
setLayout(new BorderLayout());
add(new JButton("North"),BorderLayout.NORTH);
add(new JButton("South"),BorderLayout.SOUTH);
add(new JButton("WEST"),BorderLayout.WEST);
add(new JButton("EAST"),BorderLayout.EAST);
add(new JButton("CENTER"));
pack();
}
}FlowLayout
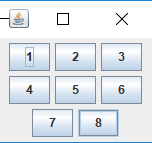
·该布局称为流式布局管理器,是从左到右,中间放置,一行放不下就换到另外一行。一行能放置多少组件取决于窗口的宽度。
·默认组件是居中对齐,可以通过FlowLayout(intalign)函数来指定对齐方式,默认情况下是居中(FlowLayout.CENTER)。FlowLayout为小应用程序(Applet)和面板(Panel)的默认布局管理器。
·其构造函数示例为:
FlowLayout() //生成一个默认的流式布局,组件在容器里居中,每个组件之间留下5个像素的距离。
FlowLayout(int alinment) //可以设定每行组件的对齐方式。
FlowLayout(int alignment , int horz , int vert) //设定对齐方式并设定组件水平和垂直的距离。
·当容器的大小发生变化时,用FlowLayout管理的组件会发生变化。其变化规律是:组件的大小不变,但是相对位置会发生变化。
class SimpleFrame extends JFrame
{
public SimpleFrame()
{
setLayout(new FlowLayout());
add(new JButton("1"));
add(new JButton("2"));
add(new JButton("3"));
add(new JButton("4"));
add(new JButton("5"));
add(new JButton("6"));
add(new JButton("7"));
add(new JButton("8"));
pack();
}
}class SimpleFrame extends JFrame
{
public SimpleFrame()
{
setLayout(new FlowLayout(FlowLayout.LEFT));
add(new JButton("1"));
add(new JButton("2"));
add(new JButton("3"));
add(new JButton("4"));
add(new JButton("5"));
add(new JButton("6"));
add(new JButton("7"));
add(new JButton("8"));
pack();
}
}GridLayout
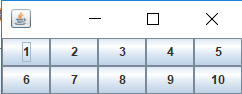
矩形网格形式对容器的组件进行布置,放置组件时,只能从左到右、由上到下的顺序填充,用户不能任意放置组件。
构造函数:
·GridLayout()
建立一个默认为一行的GridLayout
·GridLayout(int rows,int cols)
建立一个指定行(rows)和列(cols)的GridLayout
·GridLayout(int rows,int cols,int hgap,int vgap)
建立一个指定行(rows)和列(cols),且组件间水平间距为hgap、垂直间距为vgap的GridLayout
例:
import java.awt.GridLayout;
import javax.swing.JButton;
import javax.swing.JFrame;
public class SimpleFrame extends JFrame
{
public SimpleFrame()
{
setLayout(new GridLayout());
add(new JButton("1"));
add(new JButton("2"));
add(new JButton("3"));
add(new JButton("4"));
add(new JButton("5"));
add(new JButton("6"));
add(new JButton("7"));
add(new JButton("8"));
add(new JButton("9"));
add(new JButton("10"));
pack();
}
public static void main(String[] args) {
SimpleFrame simpleFrame = new SimpleFrame();
simpleFrame.setVisible(true);
}
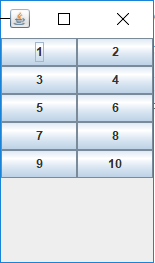
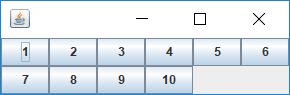
}rows与cols决定网格:
·按钮元素一定会全部展示出来
·rows与cols可以为0,但rows与cols不能同时为0,报错
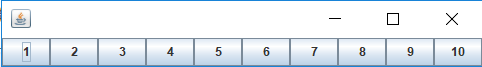
·当rows不为零时,不论列数是0还是非0,布局结果一定是rows个行数,但列数不一定是你的cols,是最小的大于等于(元素个数÷行数)的列数。
GridLayout(1,5):1行,自适应10列
GridLayout(8,5):8行,自适应2列。注意这还从左往右,从上往下排列的
·当行数rows为0时,列数cols不为0时,布局结果一定是cols个列数,但行数不一定是你的rows,是最小的大于等于(元素个数÷列数)的行数。
GridLayout(0,1):1列,自适应10行。
GridLayout(0,6):6列,自适应2行