Android采用ListView实现数据列表显示
(1)、首先设计界面,使用上面一个数据库项目,将数据库中的所有数据用ListView显示在屏幕上:新建一个布局文件item.xml
android:layout_width="120dp"
android:layout_height="wrap_content"
android:id="@+id/name"
/>
android:layout_width="150dp"
android:layout_height="wrap_content"
android:id="@+id/phone"
/>
android:layout_width="fill_parent"
android:layout_height="wrap_content"
android:id="@+id/amount"
/>
Main中:
android:layout_width="fill_parent"
android:layout_height="fill_parent"
android:id="@+id/listView"
>
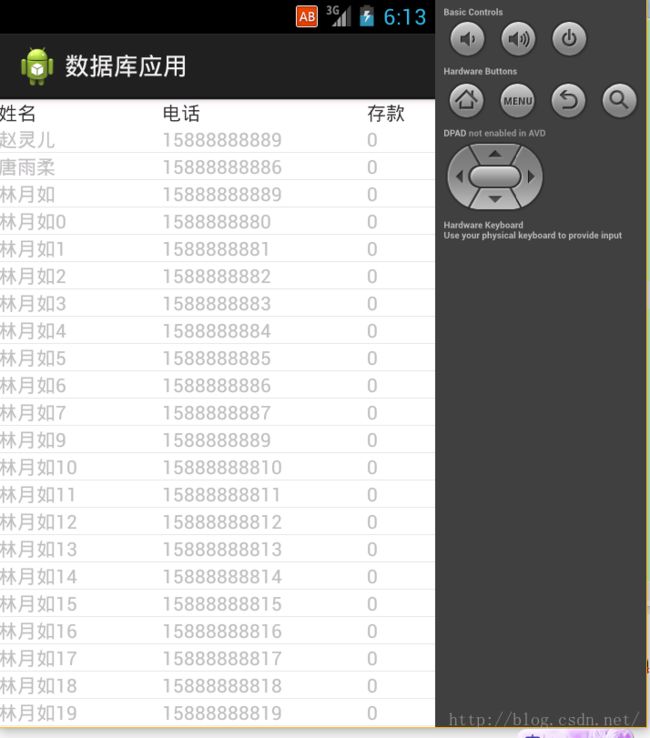
(2)、调用取得分页数据方法获得数据库中的内容,假设取得20条数据,返回一个集合。
(3)、接下来要在Activity当中使用适配器将数据与显示界面控件进行绑定,常用的适配器有SimpleAdapter与SimpleCursorAdapter,另外还有自定义适配器,首先创建适配器对象,内部有个参数,第一个是上下文对象,第二个是要绑定的数据,可以使用一个HashMap泛型进行存储,对persons进行迭代。放入泛型集合中。第三个参数是让我们指定数据绑定到哪一个条目上,我们希望绑定到item.xml这个界面上,第四个参数是(from参数),即指定把哪一项数据绑定到哪一个控件上,为String类型,第四个参数是控件位置(为int型),最后调用APIsetAdapter()进行绑定。
(4)、set方法的内部过程:首先adapter会调用getCount()方法用于得到数据总数,然后会根据每个条目的高度计算出在一个窗口里面应该显示多少个条目,假设每页显示7个条目,接下来进行迭代,使用for循环:
For(inti=0;i
接着调用getView(position,convertView,parent)方法用于每个条目的界面,最后进行界面显示的操作。
//convertView是原先缓存的页面,当翻到后面时,会使用以前的View对象进行缓存。
}
源代码:
private void show() {
List
List
for(Person person:persons){
HashMap
item.put("name",person.getName());
item.put("phone",person.getPhone());
item.put("amount",person.getAmount());
item.put("id",person.getId());
data.add(item);
}
SimpleAdapter adapter=newSimpleAdapter(getApplicationContext(), data,R.layout.item,newString[]{"name","phone","amount"}, newint[]{R.id.name,R.id.phone,R.id.amount});
listView.setAdapter(adapter);
}
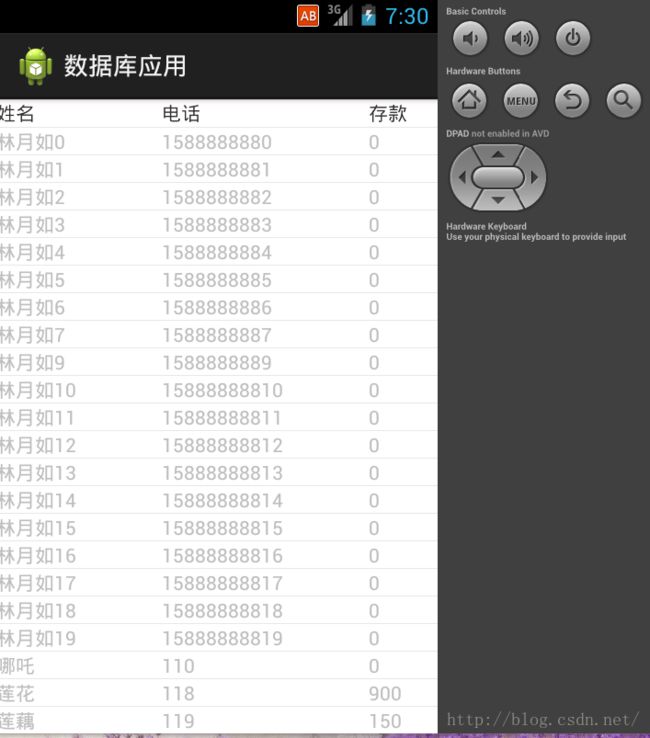
(5)、接下来将使用另外一种适配器实现此功能:SimpleCursorAdapter
private void show2() {
Cursorcursor=service.CursorgetScrollData(0, 40);
@SuppressWarnings("deprecation")
SimpleCursorAdapteradapter=new SimpleCursorAdapter(getApplicationContext(), R.layout.item, cursor,new String[]{"name","phone","amount"}, newint[]{R.id.name,R.id.phone,R.id.amount});
listView.setAdapter(adapter);
}
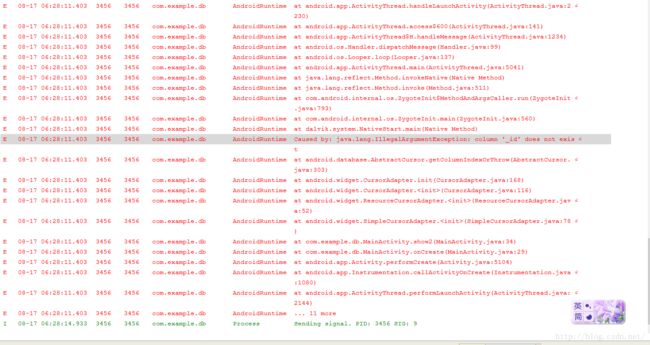
但运行后报错: Caused by:java.lang.IllegalArgumentException: column '_id' does not exist。
这时候打开CursorAdapter的最终父类源代码发现,想要使用这个类,必须包含一个叫’_id’的字段,否则就不能工作。
The Cursor must include a column named"_id" or this class will not work.
(6)、那么如何解决这个错误呢,有两种解决方案,第一种:在数据库中将主键名更改为_id,即可解决
第二种:如果不希望修改表结构,可以通过修改查询结果集实现,即修改sql语句的字段名:
public Cursor CursorgetScrollData(intoffset,int maxResult){
List
SQLiteDatabasedb=openHelper.getReadableDatabase();
Cursorcursor=db.rawQuery("SELECT persionidas _id,name,phone,amount FROM person order by persionid asc limit ?,?",new String[]{String.valueOf(offset),String.valueOf(maxResult)});
returncursor;
}
(7)、使用自定义适配器实现数据的绑定:
1、创建PersonAdapter继承BaseAdapter抽象类
2、这个抽象类里提供了一个getCount()方法用来统计数据的条数,而我们传进来的数据为List
3、创建一个int型的变量表示要绑定的条目界面,也通过构造器获得。
4、getView()方法用来获取界面,这里需要注意的是,当界面上出现一个条目时,安卓系统就会主动创建一个该条目的View对象,当翻过一页之后,已经创建的条目不会重新进行创建,系统会重用他们的View对象进行显示,即在这里实现了一个缓存的功能。
5、在这里需要使用到一个类LayoutInflater,可以使用一个XML文件生成类对象,属于系统内置服务,名为布局填充服务,需要使用上下文对象的getSystemService(Context.InflaterService)进行调用.
6、接着调用填充器的inflate(resource,null)方法,返回一个View类型的值。
7、接下来实现数据的绑定,调用该View属性的findViewById(),找到各自对应的控件。
8、接下来对控件赋值,需要用到position这参数值,表示该条目所绑定的数据在集合中的索引值。接着调用各自的setText方法。
源代码:
public class PersonAdapter extendsBaseAdapter {
privateList
privateint resource;//绑定的条目界面
privateLayoutInflater inflater;//布局填充器
publicPersonAdapter(List
this.persons= persons;
this.resource= resource;
inflater=(LayoutInflater)context.getSystemService(Context.LAYOUT_INFLATER_SERVICE);
}
@Override
publicint getCount() {//获取数据数量
intcount=persons.size();
returncount;
}
@Override
publicObject getItem(int position) {
returnpersons.get(position);
}
@Override
publiclong getItemId(int position) {
returnposition;
}
@Override
publicView getView(int position, View convertView, ViewGroup parent) {
if(convertView==null){
convertView=inflater.inflate(resource,null);//生成条目界面对象
}
TextViewnameView=(TextView) convertView.findViewById(R.id.name);
TextViewphoneView=(TextView) convertView.findViewById(R.id.phone);
TextViewamountView=(TextView) convertView.findViewById(R.id.amount);
Personperson=persons.get(position);
//数据绑定
nameView.setText(person.getName());
phoneView.setText(person.getPhone());
amountView.setText(person.getAmount().toString());
returnconvertView;
}
}
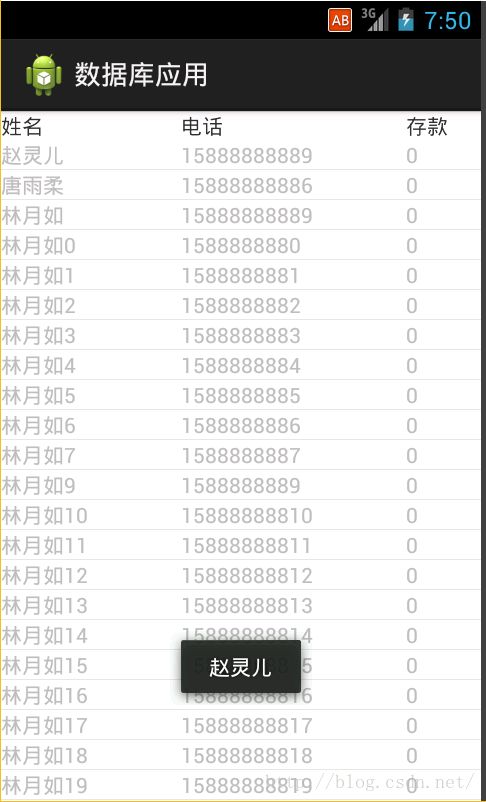
(9)、如果用户点击的某一条目,如何获得绑定的详细数据?
1、为listView设定一个条目点击事件setItemOnClickListener()
2、实现onItemClick(AdapterView parent,View view,int position,long id),第一个参数表示当前被点击条目所在的listView,第二个是代表当前所点击的View对象,第三个参数表示当前点击条目所绑定数据在集合中的索引值,最后一个id很少用到。
源代码:
public class ItemClick implementsOnItemClickListener {
@Override
publicvoid onItemClick(AdapterView parent, View view, int position,long id){
ListViewlview=(ListView) parent;
Personperson=(Person) lview.getItemAtPosition(position);
Toast.makeText(getApplicationContext(),person.getName().toString(), Toast.LENGTH_LONG).show();
}
}
(10)、如果返回值是Cursor类型的话:
ListView lview=(ListView) parent;
Cursorcursor=(Cursor) lview.getItemAtPosition(position);
intpersonid=cursor.getInt(cursor.getColumnIndex("_id"));
Toast.makeText(getApplicationContext(),personid+"", Toast.LENGTH_LONG).show();
(11)、然而做到这里,其实本程序的性能比不是很好,因为每一次翻页都会去查找控件,因此可以通过内部类进行优化:
public View getView(int position, ViewconvertView, ViewGroup parent) {
TextViewnameView=null;
TextViewphoneView=null;
TextViewamountView=null;
if(convertView==null){
convertView=inflater.inflate(resource,null);//生成条目界面对象
nameView=(TextView)convertView.findViewById(R.id.name);
phoneView=(TextView)convertView.findViewById(R.id.phone);
amountView=(TextView)convertView.findViewById(R.id.amount);
ViewCache cache=new ViewCache();
nameView=cache.nameView;
phoneView=cache.phoneView;
amountView=cache.amountView;
convertView.setTag(cache);
}else{
ViewCachecache=(ViewCache) convertView.getTag();
nameView=cache.nameView;
phoneView=cache.phoneView;
amountView=cache.amountView;
}
Personperson=persons.get(position);
//数据绑定
nameView.setText(person.getName());
phoneView.setText(person.getPhone());
amountView.setText(person.getAmount().toString());
returnconvertView;
}
private final class ViewCache{
publicTextView nameView;
publicTextView phoneView;
publicTextView amountView;
}