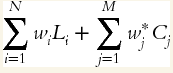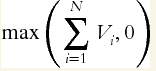Risk Management and Financial Institution Chapter 15 —— Basel I、II and Solvency II
typora-copy-images-to: Risk Management and Financial Institution
文章目录
- typora-copy-images-to: Risk Management and Financial Institution
- Risk Management and Financial Institution Chapter 15 —— Basel I、II and Solvency II
- 15.1 The Reasons for Regulating Banks
- 15.2 1988前的银行监管
- 15.3 1988 BIS Accord
- 15.3.1 The cooke Ratio
- 15.3.2 Capital Requirement
- 15.4 G30 Policy Recommendations
- 15.5 NETTING 净头寸计算
- 15.6 1996 Amendment 修正案
- 15.6.1 Back-Testing
- 15.7 Basel II
- 15.8 Credit Risk Capital Uner Basel II
- 15.8.1 SA 方法,标准法
- 15.8.2 Adjustments for collateral
- 15.8.3 IRB Approach
- 15.8.4 Exposure at Default
- 15.8.5 公司,主权以及银行Exposures
- 15.8.6 Retail Exposures
- 15.8.7 保证与信用衍生品
- 15.9 Operrational Risk Capital Under Basel II
- 15.10 Pillar 2 : Supervisory Review
- 15.11 Pillar 3 Market Discipline
- 15.12 Solvency II
Risk Management and Financial Institution Chapter 15 —— Basel I、II and Solvency II
15.1 The Reasons for Regulating Banks
- A major concern of governments is what is known as systemic risk
- Systemic risk is the risk that a default by one financial institution will create a “ripple effect” that leads to defaults by other financial institutions and threatens the stability of the financial system
15.2 1988前的银行监管
15.3 1988 BIS Accord
- first attempt to set international risk based standards
- too simple and somewhat arbitraty
15.3.1 The cooke Ratio
-
The Cooke ratio considers credit risk exposures that are both on-balance-sheet and off-balance-sheet. It is based on what is known as the bank’s total risk-weighted assets (also sometimes referred to as the risk-weighted amount). This is a measure of the bank’s total credit exposure
-
The total of the risk-weighted assets for N on-balance-sheet items equal
-
OECD国家权重比例不同
-
the total risk-weighted assets for a bank with N on-balance-sheet items and M off-balance-sheet items is:
- Li is the principal of the ith on-balance-sheet asset and wi is the risk weight for the asset; Cj is the credit equivalent amount for the jth derivative or other off-balance-sheet item and w*j is the risk weight of the counterparty for this jth item
15.3.2 Capital Requirement
-
The Accord required banks to keep capital equal to at least 8% of the risk-weighted assets
-
分为Tier 1 and Tier 2
-
要求4%以上的Tier 1,2%以上的普通股
-
Basel III 重新定义了Tier 1 and commonequity
15.4 G30 Policy Recommendations
- A brief summary of the important recommendations is as follows:
- 风险管理政策必须经过高管的明确定义批准,最理想是在董事会层面,经理层需要执行
- 衍生品头寸必须逐日盯市
- 衍生品的市场风险需要使用一致指标,比如VaR,limit需要提前设定
- 衍生品的压力测试需要使用,并决定潜在的极端损失
- 风险管理需要与交易行为相互独立
- 衍生品交易引起的信用风险需要以现存头寸的重置成本来评估
- 信用风险暴露需要可实行的netting来进行整合
- 设立limit的人需要与交易的人独立分割
- 仔细评估信用风险转移技巧,包括担保抵押以及触发降级,尤其是自身以及交易对手的现金流需求,当面临降级的时候
- 交易衍生品需要资质,经验,监管交易,管理back office都需要
- systems adequate
- dealer 必须说明用于风险管理衍生品交易以此来确认一致的收入确认
15.5 NETTING 净头寸计算
-
衍生品交易传统需要签署ISDA主协议
-
netting是主协议的一个条款
-
netting:in the event of a default all transactions are considered as a single transaction
-
netting 可以有效降低信用风险
- The credit equivalent amount was modified to:
15.6 1996 Amendment 修正案
-
要求对市场风险留存资本金
-
fair value accounting —— marking to market, refer to bank’s trading book
-
The Amendment introduced a capital charge for the market risk associated with all items in the trading book
-
SA 方法,不考虑相关性,所有交易分割处理
-
IMA 方法,internal model-based approach,VaR测量转换为资本留存
-
更多的银行喜欢使用IMA方法,因为分散化的优势
-
IMA 方法,考虑99%置信区间的10天的VaR
![]()
-
mc is a multiplicative factor and SRC is a specific risk charge
-
The variable VaRt-1 is the previous day’s value at risk and VaRavg is the average value at risk over the past 60 days
-
The minimum value for mc is 3
-
The second term, SRC, covers risks related to specific companies such as those concerned with movements in a company’s stock price or changes in a company’s credit spread 与信用相关的产品
-
corporate bond 使用与SRC,这样的证券有两种风险组成,利率风险以及信用风险
-
1996修正案 capital:
15.6.1 Back-Testing
-
1996修正案要求回测250天
- exception 小于 5 则 mc适用3
- 如果exception 5 到9 mc适用分别递升为3.4 、 3.5、3.65 、3.75 、 3.85
-
日内交易VaR值突破,那么更高的乘数应该予以考虑
15.7 Basel II
- 巴塞尔I 没有违约相关性模型
- The Basel II is based on three “pillars”:
- Minimum Capital Requirements
- Supervisory Review
- Market Discipline
-
Pillar 2 is concerned with the supervisory review process(定性与定量)Pillar 2 places more emphasis on early intervention when problems arise
-
market discipline, requires banks to disclose more information about the way they allocate capital and the risks they take
15.8 Credit Risk Capital Uner Basel II
- 三种方法:
- SA
- IRB (美国企业适用)
- Advanced IRB
15.8.1 SA 方法,标准法
-
OECD status of a bank or a country is no longer considered important under Basel II
-
The risk weight for mortgages in the Basel II standardized approach was 35% and that for other retail loans was 75%
15.8.2 Adjustments for collateral
-
抵押可以改变risk weights
- simple approach
- comprehensive approach(trading book必用)
-
simple approach, the risk weight of the counterparty is replaced by the risk weight of the collateral for the part of the exposure covered by the collateralThe exposure is calculated after netting.)
-
The minimum level for the risk weight applied to the collateral is 20%.11 A requirement is that the collateral must be revalued at least every six months and must be pledged for at least the life of the exposure
-
comprehensive approach, banks adjust the size of their exposure upward to allow for possible increases in the exposure and adjust the value of the collateral downward to allow for possible decreases in the value of the collateral(先对exposure进行计算,然后适用risk weight)
15.8.3 IRB Approach
- The value at risk is calculated using the one-factor Gaussian copula model of time to default
- where EADi is the exposure at default of the ith counterparty and LGDi is the loss given default for the ith counterparty
- PD: The probability that the counterparty will default within one year (expressed as a decimal)
- EAD: The exposure at default (in dollars)
- LGD: The loss given default or the proportion of the exposure that is lost if there is a default (expressed as a decimal)
15.8.4 Exposure at Default
- Effective Expected exposure 的1.4倍
15.8.5 公司,主权以及银行Exposures
![]()
- (Note that, when M = 1, MA is 1.0 and has no effect)
-
在IRB的方法下,银行提供PD ,而LGD ,EAD,M都由监管机构提供,PD的最低标准为0.03%
-
LGD is set at 45% for senior claims and 75% for subordinated claims
-
M is set at 2.5 in most circumstances
-
Under the Advanced IRB approach, banks supply their own estimates of the PD, LGD, EAD, and M for corporate, sovereign, and bank exposures
-
The two main factors influencing the LGD are the seniority of the debt and the collateral
-
The WCDR is the default rate that (theoretically) happens once every thousand years
15.8.6 Retail Exposures
- Foundation IRB and Advanced IRB approaches are merged and all banks using the IRB approach provide their own estimates of PD, EAD, and LGD. There is no maturity adjustment, MA. The capital requirement is therefore:
![]()
- For residential mortgages, ρ is set equal to 0.15
15.8.7 保证与信用衍生品
- As an alternative to using the credit substitution approach, the capital requirement can be calculated as the capital that would be required without the guarantee multiplied by 0.15 + 160 × PDg where PDg is the one-year probability of default of the guarantor
15.9 Operrational Risk Capital Under Basel II
-
计算操作风险资本的三种方式:
- BIA —— average annual gross income over the last three years multiplied by 0.15
- SA —— similar to the basic indicator approach except that a different factor is applied to the gross income from different business lines
- AMA —— operational risk capital is set equal to this loss minus the expected loss,允许使用认证风险转移的影响,比如说保险合约
-
选取三种方式的标准在于机构的复杂规模程度
15.10 Pillar 2 : Supervisory Review
-
关注监管流程,四个原则:
- 银行需要有流程评估其余风险状况相适应的资本充足率以及维持资本水平的策略
- 监管机构必须检验银行内部的资本金充足率评估系统,发现问题,及时采取适当措施
- 期望银行在运作时资本金持有率高于最低要求,并要求有超过其最低标准的能力
- 在发现问题的初期就应该介入,督促银行采取措施使资本金水平达标
-
巴塞尔协会要求透明度和可靠性,在监管的过程中
15.11 Pillar 3 Market Discipline
-
鼓励加大自身资本充足流程的披露
-
强制性程度在不同区域不同体现
-
监管部门要求的信息披露与审计报告不同,应当披露的信息如下:
- 银行什么部门实施了Basel II,对于不实施的部门做了什么调整
- 资本金构成产品的主要特征
- 构成一类资本的产品,以及其占比
- 二类资本的总数
- 信用、市场、操作风险需要的资本金构成
- 银行面临的其他风险的信息以及其他风险的测定
- 风险管理部门的结构以及运作方式
15.12 Solvency II
-
Whereas Solvency I calculates capital only for underwriting risks, Solvency II considers investment risks and operational risks as well
-
also have three pillars
-
Pillar 1 of Solvency II specifies a minimum capital requirement (MCR) and a solvency capital requirement (SCR)
-
The MCR is typically between 25% and 45% of the SCR
-
SCR 有两种计算方式,一种是标准法,一种是内部模型法
-
The internal models are required to satisfy three tests. The first is a statistical quality test. This is a test of the soundness of the data and methodology used in calculating VaR. The second is a calibration test. This is a test of whether risks have been assessed in accordance with a common SCR target criterion. The third is a use test. This is a test of whether the model is genuinely relevant to and used by risk managers