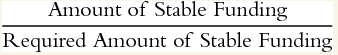Risk Management and Financial Institution Chapter 16 —— Basel II.5,Basel III, and Other Post-Crisis
typora-copy-images-to: Risk Management and Financial Institution
文章目录
- typora-copy-images-to: Risk Management and Financial Institution
- Risk Management and Financial Institution Chapter 16 —— Basel II.5,Basel III, and Other Post-Crisis Changes
- 16.1 Basel II.5
- 16.1.1 压力VaR
- 16.1.2 IRC incremental risk charge
- 16.1.3 The Comprehensive Risk Measure 综合风险计量
- 16.2 Basel III
- 16.2.1 资本金定义与要求
- 16.2.2 CCB 资本金留存缓冲
- 16.2.3 逆周期缓冲资本金
- 16.2.4 杠杆比率 leverage ratio
- 16.2.5 Liquidity Risk
- 16.2.6 Counterparty Credit Risk
- 16.2.7 G-SIBs ,SIFIs , and D-SIBs
- 16.3 Contingent Convertible Bond
- 16.4 Use of Standardized Approaches and SA-CCR
- 16.5 Dodd-Frank Act
- 16.6 其他国家的监管
Risk Management and Financial Institution Chapter 16 —— Basel II.5,Basel III, and Other Post-Crisis Changes
-
Basel III includes a series of rules concerned with increasing the amount of equity capital that banks have to keep for the risks being taken and tightening the definition of capital
-
An important new feature of Basel III is the specification of liquidity requirements that must be met by banks对流动性需求有了规定
16.1 Basel II.5
- 执行日期是2011年12月31日,更改内容包括:
- 压力VaR的计算
- new incremental risk charge
- 基于信用相关性的复杂风险测量工具
16.1.1 压力VaR
-
stressed VaR is determined by basing calculations on how market variables moved during a 250-day (12-month) period of stressed market conditions, rather than on how they moved during the past one to four years.
-
The two VaR measures are combined to calculate a total capital charge:
![]()
-
The parameters ms and mc are multiplicative factors that are determined by bank supervisors and are at minimum equal to three
-
这种方式至少把原先的VaR值翻倍了,甚至三倍的资本金要求都不罕见
-
A bank is now required to search for a one-year period that would be particularly stressful for its current portfolio
16.1.2 IRC incremental risk charge
-
一个bond 持有在trading book 以及 banking book 中的VaR 不同
-
IRC 要求使用99.9%置信区间,一年展望期来计算违约风险敏感的工具
-
The IRC requires banks to calculate a one-year 99.9% VaR for losses from credit-sensitive products in the trading book taking both credit rating changes and defaults into account
-
风险水平恒定假设会使得VaR值变小,巴塞尔委员会规定在计算IRC时,最小流动性区间为3个月
16.1.3 The Comprehensive Risk Measure 综合风险计量
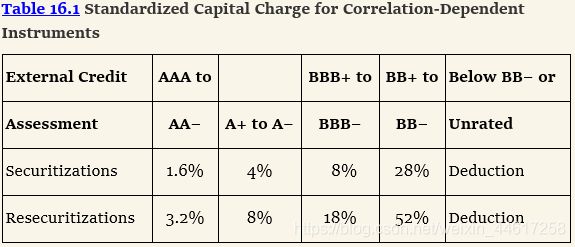
- 针对对于违约相关性敏感的金融工具而设计的计量方法,ABS 、 CDO
-
CRM 用于替代IRC以及SRC,关于相关性敏感的金融工具
-
对于再证券化收取的资本金要比直接证券化来得多
-
上图中Deduction的含义是100%收取的资本
16.2 Basel III
- six parts to the regulation:
- 资本金定义与要求
- CCB 资本金留存缓冲
- 逆周期缓冲资本
- 杠杆比率
- 流动性风险
- 对手信用风险
16.2.1 资本金定义与要求
-
Under Basel III, a bank’s total capital consists of:
- Tier 1 equity capital
- Additional Tier 1 capital
- Tier 2 capital
-
CET1——share capital and retained earnings,no deferred tax assets and goodwill
- 一类资本在固定收益养老金计划出现赤字的情况下要进行下调
- 但一类资本在固定收益养老金计划出现盈余时并不上调
- 证券化交易以及银行自身信用等级变化对留存收益的影响不计入一类资本
-
AT1—— items, such as non-cumulative preferred stock that were previously Tier 1 but are not common equity
-
Tier 2 capital—— includes debt that is subordinated to depositors with an original maturity of five years
-
普通股权资本又被称作为持续经营资本金,tier 2 是破产清算资本
-
资本金的要求如下:
- Tier 1 equity capital must be at least 4.5% of risk-weighted assets at all times
- Total Tier 1 capital (Tier 1 equity capital plus additional Tier 1 capital) must be at 6% of risk-weighted assets at all times
- Total capital (total Tier 1 plus Tier 2) must be at least 8% of risk-weighted assets at all times
-
巴塞尔协议III 对系统重要性银行的资本金有进一步的高要求
16.2.2 CCB 资本金留存缓冲
-
normal time
-
further amount of CET1 capital equal to 2.5%
-
防范金融风险时的资本不足
-
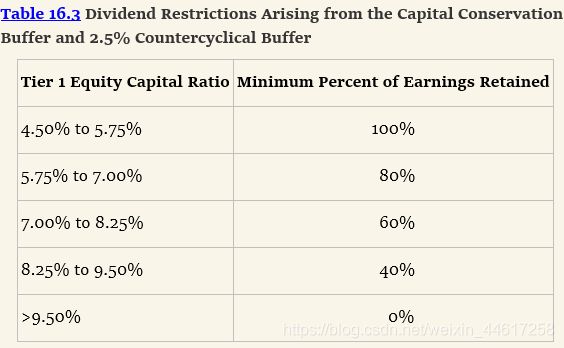
资本金充足率对银行分红的影响:
- 在普通时刻,CET1至少达到7%的风险加权资产比例
- 一类资产达到8.5%
- 总资本留存达到10.5%
- 导致的问题是:ROE无法提高,但是银行股票更安全了
16.2.3 逆周期缓冲资本金
- 与CCB类似,但是决定权在于各个国家自己的监管机构
- 比例范围是0 到 2.5%,而且必须是Tier 1 equity capital
- 逆周期缓冲资本金要求对股息派发的影响:
16.2.4 杠杆比率 leverage ratio
-
规定 minimum leverage ratio 为3%
-
计算方式是 capital / exposure ,其中capital 为 Tier 1,exposure 包括;
- on-balance-sheet exposures
- derivatives exposures
- securities financing
- off-balance-sheet items
-
中国的leverage ratio 设置为4%
-
引进杠杆比率的原因是巴塞尔委员会认为银行在计算风险加权资产上太自由,要求银行两个标准都要满足
-
不利的结果:当杠杆比率成为关键指标时,对于某些银行来说会持有风险更高的资产,因为杠杆比率不变,求回报率高
16.2.5 Liquidity Risk
-
流动性风险的产生原因:短期借债,长期资产的tendency,比如商业票据
-
Basel III has introduced requirements involving two liquidity ratios that are designed to ensure that banks can survive liquidity pressures. The ratios are:
- Liquidity Coverage Ratio (LCR); and
- Net Stable Funding Ratio (NSFR)
-
The LCR focuses on a bank’s ability to survive a 30-day period of liquidity disruptions. It is defined as:(流动性覆盖比率)
-
计算时的情景设定是银行的信用级别被下调3个级别、部分丧失存款、批发市场的资金来源全部丧失、资产折价比率提高(抵押品所获资金减少、抵押品的价值比率下降)
-
比率的要求是大于 100%
-
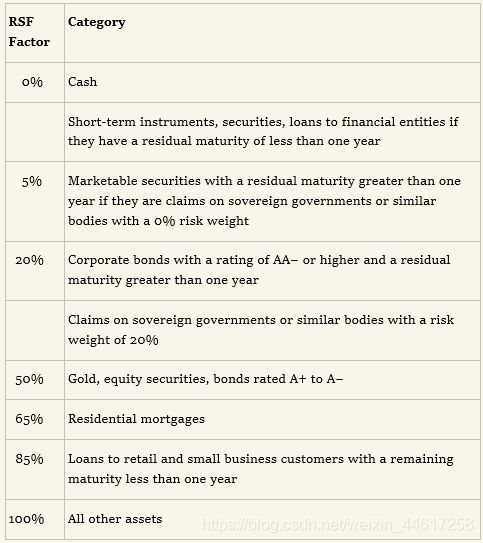
The NSFR focuses on liquidity management over a period of one year. It is defined as:
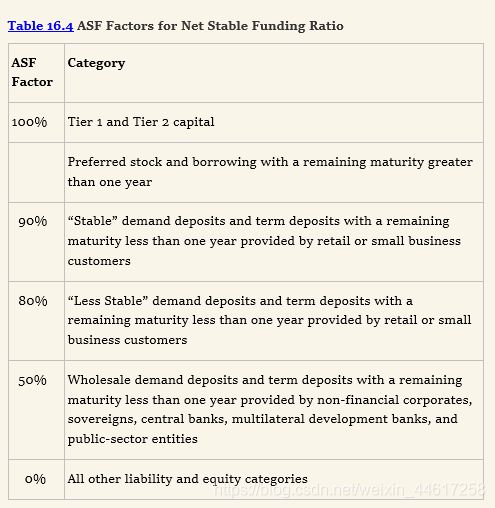
- 分子是每项可得资金 乘以 ASF 因子,再求和
- 分母计算与需要资金支持的表内外资产有关,每一项资金必须 乘以 RSF 因子
- 巴塞尔委员会要求的NSFR比例超过100%
16.2.6 Counterparty Credit Risk
-
CVA(credit value adjustment)—— expected loss because of the possibility of a default by the counterparty
-
Reported profit is reduced by the total of the CVAs for all counterparties
-
CVA的变化来源于两个方面:
- 交易所涉及市场变量的变化
- 对手信贷信用溢差的
-
巴塞尔III 要求CVA 成为市场风险资本的一部分
-
CVA可以比较容易的根据交易对手信用曲线平移
-
主要目的是考虑到信用溢差变化以及市场变化导致CVA变化的那些银行,并已经采取了对冲方式的重新计算监管资本,否则监管资本将因为对冲行为而增加
16.2.7 G-SIBs ,SIFIs , and D-SIBs
-
The term G-SIB stands for global systemically important bank
-
The popular view of SIFIs is that they are “too big to fail,”
-
巴塞尔委员会使用得分来评定系统性风险银行
-
对G-SIB的要求:
- G-SIBs are categorized according to whether the extra equity capital is 1%, 1.5%, 2%, 2.5%, or 3.5% of risk-weighted assets
16.3 Contingent Convertible Bond
-
CoCo bonds automatically get converted into equity when certain conditions are satisfied,与可转债相反
-
avoid for a bailout,also sometimes referred to as a bail in
-
关键在于制定转股的触发条件,以及转换率的问题
- Tier 1 capital ratio
- market value of equity to book value of assets
-
CoCos (prior to conversion) qualify as additional Tier 1 capital if the trigger, defined in terms of the ratio of Tier 1 equity capital to risk-weighted assets, is set at 5.125% or higher. Otherwise they qualify as Tier 2 capital
16.4 Use of Standardized Approaches and SA-CCR
-
2022年使用SA方法计算所有的资本
-
A bank’s total capital requirement will be the maximum of:
- that calculated as before using approved internal models
- a certain percentage of that given by the standardized approaches
-
SA-CCR方法计算EAD:
![]()
- RC is the replacement cost and PFE is potential future exposure
![]()
-
The variable D is the change in the V that could occur without any additional collateral being received
-
PFE计算时的要点:
- When the counterparty has posted excess collateral, risk is reduced and the reduction in risk increases as the amount of the excess collateral increases.
- When no collateral is posted, credit exposure reduces as V becomes more negative. The PFE add-on amount when V is slightly negative should be greater than when V is highly negative
16.5 Dodd-Frank Act
- 多得-弗兰克法案的内容:
- 成立金融稳定监管委员会及金融研究办公室
- 联邦存款保险公司的清算职权被扩大了
- FDIC的存款保险金额上限被增加到25万美元
- 大型对冲基金引入监管条款,披露其业务行为
- 对吸收存款的金融机构自营及类似交易进行限制
- 高风险交易必须要分离到独立资金的机构
- 标准的衍生品需要使用CCP来交易,增加市场透明度
- 要为系统重要性银行设定风险管理标准
- 加强对投资人的保护,完善证券的监管
- 评级机构的假设和评级方法必须透明,潜在的法律风险增加
- 外部信用评级不能再用于金融机构的监管过程
- 金融保护局成立,保证消费者获取清晰准确的信息
- 发行证券化产品的发行方必须持有5%比例的证券化产品
- 阻止过激的薪酬方案
- 按揭贷款的提供商应对借贷人的还款能力做合理的可信度鉴定
- 大型金融机构董事会至少应包含一名具有大型复杂金融机构风险管理经验的专家
- FDIC可以在金融机构破产时接管,并变卖其资产
- FSOC以及OFR两家机构负责识别系统性重要性金融机构
- 要求各个金融机构准备living will 准备遗嘱
16.6 其他国家的监管
- 多数国家监管机构认为,标准衍生品交易应该通过中央清算中心进行
- 关注系统风险性银行以及living will 都非常重要,抑制恐慌
- 雇员薪酬也很重要,更注重短期效应