子线程优雅调用父线程RequestScope作用域Bean问题的探究
一、前言
最近我们组在做项目分层模块化项目调研,就产生一个问题如何在开启的线程中不破坏使用习惯情况下使用请求线程里面的RequestScope作用域的bean,感觉这个问题比较有意思就研究并整理下一下,以便备忘,下面从最基础知识将起,一步步引入问题和解决方法
二、ThreadLocal原理
众所周知如果一个变量定义为了threadlocal变量,那么访问这个变量的每个线程都独有一个属于自己的变量,这变量值只有当前线程才能访问使用,各个线程直接相互不干扰,那原理究竟如何那?
2.1 ThreadLocal类
通常代码里面经常使用threadlocal的set和get方法,下面就讲解下这两个方法,首先set方法:
public void set(T value) {
//获取当前线程
Thread t = Thread.currentThread();
//当前线程作为key,去查找对应的线程变量,找到则设置
ThreadLocalMap map = getMap(t);
if (map != null)
map.set(this, value);
else
//第一次调用则创建当前线程对应的map
createMap(t, value);
}
getMap(t)所做的就是获取线程自己的变量threadLocals,可知threadlocal变量是绑定到了线程的成员变量里面,那么threadLocals是什么结构那?其实是ThreadLocalMap类型,不关心里面细节的话我们可以认为他是个map.
ThreadLocalMap getMap(Thread t) {
return t.threadLocals;
}
createMap(t, value)里面做了啥那?其实就是线程第一次设置threalocal.set时候创建线程的成员变量threadLocals,并把值初始化到map.
void createMap(Thread t, T firstValue) {
t.threadLocals = new ThreadLocalMap(this, firstValue);
}
下面看下get方法:
public T get() {
//获取当前线程的成员变量值为map,如果map不为空则获取当前线程对应的threadlocal变量的值,并返回
Thread t = Thread.currentThread();
ThreadLocalMap map = getMap(t);
if (map != null) {
ThreadLocalMap.Entry e = map.getEntry(this);
if (e != null) {
@SuppressWarnings("unchecked")
T result = (T)e.value;
return result;
}
}
//map为空则给实例化当前线程的t.threadLocals成员变量,并且初始化threadlocal值为null
return setInitialValue();
}
总结:
(1)、 每个线程都有一个名字为threadLocals的成员变量,该变量类型为ThreadLocalMap,不深究的话可以简单认为是一个特殊的map,其中key为我们定义的ThreadLocal变量的this引用,value则为我们set时候的值
(2)、 对于下面定义ThreadLocal
当线程A首次调用threadLocal.set(new Integer(666));时候会创建线程A的成员变量threadLocals,并且把threadLocal做为key,new Integer(666)作为value放入threadLocals中。然后当线程A调用threadLocal.get()时候那么首先获取到成员变量threadLocals,然后以key等于threadLocal去threadLocals中获取对应的值为new Integer(666)。
2.2 ThreadLocal不支持继承特性
运行一下代码:
public static ThreadLocal threadLocal = new ThreadLocal();
public static void main(String args[]) {
threadLocal.set(new Integer(666));
Thread thread = new MyThread();
thread.start();
System.out.println("main = " + threadLocal.get());
}
static class MyThread extends Thread {
@Override
public void run() {
System.out.println("MyThread = " + threadLocal.get());
}
}
结果为:
main = 666
MyThread = null
也就是说ThreadLocal不支持在子线程中获取父线程中的设置的值,这个根据代码来看很正常,因为子线程get时候当前线程为thread,而设置线程变量是在main线程,两者是不同的线程
三、InheritableThreadLocal原理
为了解决2.2的问题InheritableThreadLocal应运而生。
3.1 InheritableThreadLocal类
public class InheritableThreadLocal extends ThreadLocal {
protected T childValue(T parentValue) {
return parentValue;
}
ThreadLocalMap getMap(Thread t) {
return t.inheritableThreadLocals;
}
void createMap(Thread t, T firstValue) {
t.inheritableThreadLocals = new ThreadLocalMap(this, firstValue);
}
}
可知InheritableThreadLocal继承了ThreadLocal,并重写了三个方法,好下面在重新走下set和get方法
如下代码第一次调用set的时候,map为空,所以调用createMap,
public void set(T value) {
Thread t = Thread.currentThread();
ThreadLocalMap map = getMap(t);
if (map != null)
map.set(this, value);
else
createMap(t, value);
}
而ThreadLocal的createMap实例化了当前线程的threadLocals成员变量,InheritableThreadLocal重写的createMap则实例化了inheritableThreadLocals变量,这是其一。
如下代码调用get方法时候与set方法对应InheritableThreadLocal重写了getMap方法,目的是获取当前线程的inheritableThreadLocals成员变量,而不是threadLocals。
public T get() {
Thread t = Thread.currentThread();
ThreadLocalMap map = getMap(t);
if (map != null) {
ThreadLocalMap.Entry e = map.getEntry(this);
if (e != null) {
@SuppressWarnings("unchecked")
T result = (T)e.value;
return result;
}
}
//map为空则给实例化当前线程的t.threadLocals成员变量,并且初始化threadlocal值为null
return setInitialValue();
}
到了这里我们知道了inheritableThreadLocal改变在于set和get操作的都是当前线程的inheritableThreadLocals成员变量,替代了ThreadLocals操作threadLocals,这样看来似乎两者没啥区别,但是还有一个重写的函数我们没有分析到那就是childValue。
打开Thread.java类的构造函数:
public Thread() {
init(null, null, "Thread-" + nextThreadNum(), 0);
}
private void init(ThreadGroup g, Runnable target, String name,
long stackSize, AccessControlContext acc) {
.....
if (parent.inheritableThreadLocals != null)
//拷贝父线程的inheritableThreadLocals当当前线程的inheritableThreadLocals
this.inheritableThreadLocals =
ThreadLocal.createInheritedMap(parent.inheritableThreadLocals);
.....
}
创建线程时候在构造函数里面会调用init方法,前面讲到了inheritableThreadLocal类get,set的是inheritableThreadLocals,所以这里parent.inheritableThreadLocals != null,调用了createInheritedMap个方法。
static ThreadLocalMap createInheritedMap(ThreadLocalMap parentMap) {
return new ThreadLocalMap(parentMap);
}
下面函数所做的事情就是把父线程的inheritableThreadLocals成员变量的值复制到ThreadLocalMap对象
private ThreadLocalMap(ThreadLocalMap parentMap) {
Entry[] parentTable = parentMap.table;
int len = parentTable.length;
setThreshold(len);
table = new Entry[len];
for (int j = 0; j < len; j++) {
Entry e = parentTable[j];
if (e != null) {
@SuppressWarnings("unchecked")
ThreadLocal所以把上节代码修改为
public static ThreadLocal threadLocal = new InheritableThreadLocal();
public static void main(String args[]) {
threadLocal.set(new Integer(666));
Thread thread = new MyThread();
thread.start();
System.out.println("main = " + threadLocal.get());
}
static class MyThread extends Thread {
@Override
public void run() {
System.out.println("MyThread = " + threadLocal.get());
}
}
结果为:
MyThread = 666
main = 666
现在可以从子线程中正常的获取到线程变量值了,但是我们使用场景并不是那么简单我们使用的是requestscope的bean,所以下节将下RequestContextListener的原理以及遇到的问题。
四、RequestContextListener原理
spring中配置bean的作用域时候我们一般配置的都是Singleton,但是有些业务场景则需要三个web作用域,分别为request、session和global session,如果你想让你Spring容器里的某个bean拥有web的某种作用域,则除了需要bean级上配置相应的scope属性,还必须在web.xml里面配置如下:
<listener-class>org.springframework.web.context.request.RequestContextListenerlistener-class>
listener>
主要看RequestContextListener的两个方法public void requestInitialized(ServletRequestEvent
requestEvent)和public void requestDestroyed(ServletRequestEvent requestEvent)。
当web请求过来时候:
public void requestInitialized(ServletRequestEvent requestEvent) {
.......
HttpServletRequest request = (HttpServletRequest) requestEvent.getServletRequest();
ServletRequestAttributes attributes = new ServletRequestAttributes(request);
request.setAttribute(REQUEST_ATTRIBUTES_ATTRIBUTE, attributes);
LocaleContextHolder.setLocale(request.getLocale());
//设置属性到threadlocal变量
RequestContextHolder.setRequestAttributes(attributes);
}
public static void setRequestAttributes(RequestAttributes attributes) {
setRequestAttributes(attributes, false);
}
public static void setRequestAttributes(RequestAttributes attributes, boolean inheritable) {
if (attributes == null) {
resetRequestAttributes();
}
else {
//默认inheritable=false
if (inheritable) {
inheritableRequestAttributesHolder.set(attributes);
requestAttributesHolder.remove();
}
else {
requestAttributesHolder.set(attributes);
inheritableRequestAttributesHolder.remove();
}
}
}
所以知道默认inheritable为FALSE,我们的属性值都放到了requestAttributesHolder里面,而他是:
private static final ThreadLocal requestAttributesHolder =
new NamedThreadLocal("Request attributes");
private static final ThreadLocal inheritableRequestAttributesHolder =
new NamedInheritableThreadLocal("Request context");
NamedThreadLocal
NamedInheritableThreadLocal
当请求结束时候调用:
public void requestDestroyed(ServletRequestEvent requestEvent) {
ServletRequestAttributes attributes =
(ServletRequestAttributes) requestEvent.getServletRequest().getAttribute(REQUEST_ATTRIBUTES_ATTRIBUTE);
ServletRequestAttributes threadAttributes =
(ServletRequestAttributes) RequestContextHolder.getRequestAttributes();
if (threadAttributes != null) {
// We're assumably within the original request thread...
if (attributes == null) {
attributes = threadAttributes;
}
//请求结束则清除当前线程的线程变量。
LocaleContextHolder.resetLocaleContext();
RequestContextHolder.resetRequestAttributes();
}
if (attributes != null) {
attributes.requestCompleted();
}
}
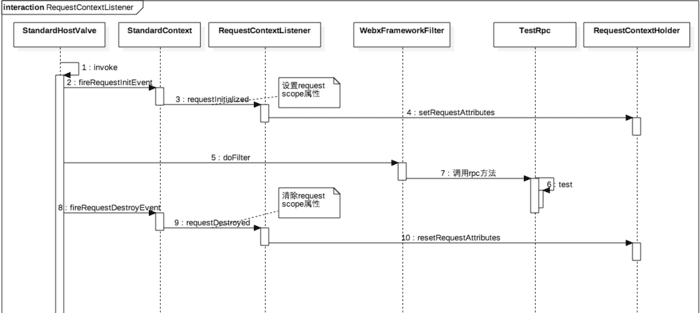
这个listener调用逻辑如何那,如下:
也就是说每次发起一个web请求在tomcat中context(具体应用)处理前,host匹配后都会去设置下RequestContextHolder属性,让requestAttributesHolder不为空,在请求结束时候会清除。
总结:默认情况下放入RequestContextHolder里面的属性子线程访问不到。spring的request作用域的bean是使用threadlocal实现的。
五、根据需求对RequestContextListener进行改造
需求模拟,配置如下bean
"pvgInfo" class="com.test.privilege.PrivilegeInfo"
scope="request">
"aesKey" value="666" />
然后在Rpc里面autowired该bean,然后在rpc方法里面访问pvgInfo,然后方法里面在开启一个线程去获取pvgInfo里面设置的值。
@WebResource("/testService")
public class TestRpc {
@Autowired
private PrivilegeInfo pvgInfo;
@ResourceMapping("test")
public ActionResult test(ErrorContext context) {
ActionResult result = new ActionResult();
String aseKey = pvgInfo.getAesKey();
pvgInfo.setAesKey("888");
System.out.println("aseKey---" + aseKey);
Thread myThread = new Thread(new Runnable() {
public void run() {
System.out.println("hellobegin");
System.out.println(pvgInfo.getAesKey());
System.out.println("helloend");
}
});
myThread.start();
try {
//防止主线程结束后清除线程变量
myThread.join();
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
return result;
}
}
直接调用Rpc返回结果为:
明显子线程获取父线程线程变量时候抛异常了。
下面分析下调用这个rpc方法时候时序图为:
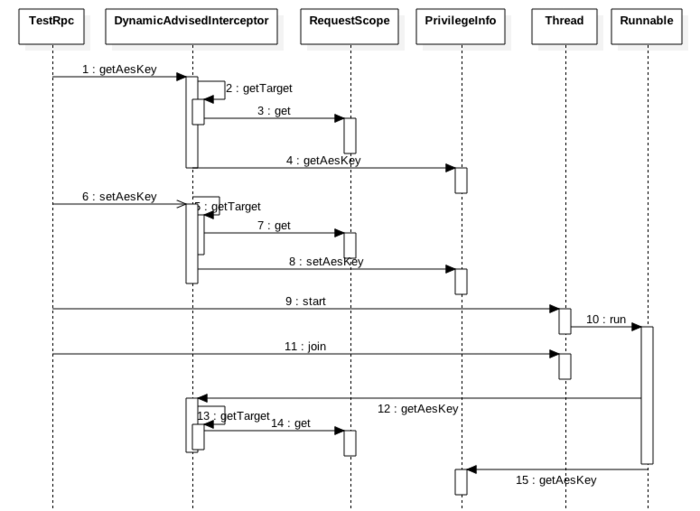
下面看下test方法内发生了啥:
下面重点看RequestScope的get方法:
public Object get(String name, ObjectFactory objectFactory) {
//获取RequestContextListener.requestInitialized设置的属性值
RequestAttributes attributes = RequestContextHolder.currentRequestAttributes();(1)
Object scopedObject = attributes.getAttribute(name, getScope());
if (scopedObject == null) {
scopedObject = objectFactory.getObject();(2)
attributes.setAttribute(name, scopedObject, getScope());(3)
}
return scopedObject;
}
public static RequestAttributes currentRequestAttributes() throws IllegalStateException {
//获取RequestContextListener.requestInitialized设置的属性值,为null则抛出异常,所以如果在非web项目中普通线程中调用会抛异常,这是因为他没有在RequestContextListener.requestInitialized设置过。
RequestAttributes attributes = getRequestAttributes();
if (attributes == null) {
if (jsfPresent) {
attributes = FacesRequestAttributesFactory.getFacesRequestAttributes();
}
if (attributes == null) { (4)
throw new IllegalStateException("No thread-bound request found: " +
"Are you referring to request attributes outside of an actual web request, " +
"or processing a request outside of the originally receiving thread? " +
"If you are actually operating within a web request and still receive this message, " +
"your code is probably running outside of DispatcherServlet/DispatcherPortlet: " +
"In this case, use RequestContextListener or RequestContextFilter to expose the current request.");
}
}
return attributes;
}
//获取RequestContextListener.requestInitialized设置的属性值
public static RequestAttributes getRequestAttributes() {
RequestAttributes attributes = requestAttributesHolder.get();(5)
if (attributes == null) {
attributes = inheritableRequestAttributesHolder.get();
}
return attributes;
}
可知时序图访问rpc方法时候在RequestContextListener.requestInitialized里面调用RequestContextHolder.setRequestAttributess设置了设置了requestAttributesHolder,所以在test方法内第一次调用getAesKey()方法时候,RequestScope.get()方法里面第一步时候获取到了attributes,但是属性里面却没有pvginfo对象,所以会创建个,然后放入attributes.然后返回,然后在cgib代理里面调用pvginfo的getAesKey方法。
调用setAesKey时候RequestScope.get()则是直接从attributes里面获取返回,然后在cglib代理里面调用pvginfo的setAesKey方法设置。
在子线程中调用getAesKey方法时候,RequestScope.get()方法里面第一步时候获取attributes时候,由于(5)是threadlocal,所以根据第二节讲的threadlocal原理知道返回的attributesnull.所以(4)出抛出了异常。
从第三节讲的如果是inheritthreadlocal,则子线程克继承父线程pvginfo信息,而前面正好介绍了
RequestContextHolder里面:
private static final ThreadLocal
new NamedThreadLocal
private static final ThreadLocal inheritableRequestAttributesHolder =
new NamedInheritableThreadLocal("Request context");
有一个inheritableRequestAttributesHolder是继承了inheritthreadlocal。
在回头看RequestContextListener.requestInitialized里面调用RequestContextHolder.setRequestAttributess设置了设置了requestAttributesHolder,而setRequestAttributess还有个 public static void setRequestAttributes(RequestAttributes attributes, boolean inheritable) 用来指定使用这两个变量的哪一个,那如果我们重写RequestContextListener的requestInitialized方法为:
public class InheritableRequestContextListener extends RequestContextListener {
private static final String REQUEST_ATTRIBUTES_ATTRIBUTE =
InheritableRequestContextListener.class.getName() + ".REQUEST_ATTRIBUTES";
@Override
public void requestInitialized(ServletRequestEvent requestEvent) {
if (!(requestEvent.getServletRequest() instanceof HttpServletRequest)) {
throw new IllegalArgumentException(
"Request is not an HttpServletRequest: " + requestEvent.getServletRequest());
}
HttpServletRequest request = (HttpServletRequest) requestEvent.getServletRequest();
ServletRequestAttributes attributes = new ServletRequestAttributes(request);
request.setAttribute(REQUEST_ATTRIBUTES_ATTRIBUTE, attributes);
LocaleContextHolder.setLocale(request.getLocale());
//传入true标示使用inheritableRequestAttributesHolder而不是requestAttributesHolder
RequestContextHolder.setRequestAttributes(attributes, true);
}
}
根据第三届原理知道这样应该是可以行的,其实如果使用的不是webx框架而是springmvc确实是可行的,但是我们使用的是webx框架发现还是抛出了和上面一样的异常,为啥那?请看第六届`
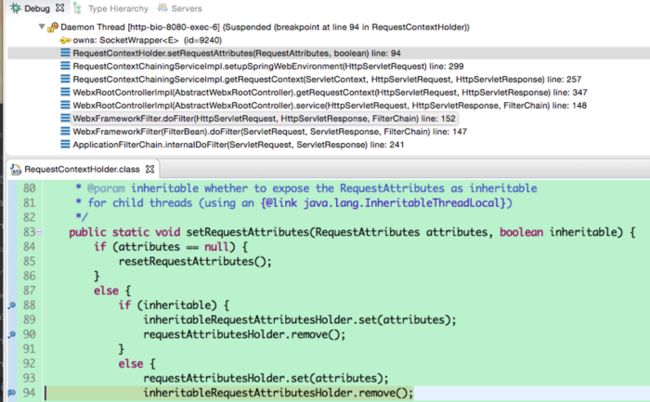
六、Webx的改造
对代码进行debug发现RequestContextHolder.setRequestAttributess被调用了两次,其中一次是在RequestContextListener.requestInitialized里面,这个正常,并且inheritable=true
public static void setRequestAttributes(RequestAttributes attributes) {
setRequestAttributes(attributes, false);
}
public static void setRequestAttributes(RequestAttributes attributes, boolean inheritable) {
if (attributes == null) {
resetRequestAttributes();
}
else {
//inheritable=true
if (inheritable) {
inheritableRequestAttributesHolder.set(attributes);
requestAttributesHolder.remove();
}
else {
requestAttributesHolder.set(attributes);
inheritableRequestAttributesHolder.remove();
}
}
}
然后发现第二次webx竟然也调用这个方法但是传递的inheritable=FALSE,艾玛,我们前面的工作白做了。
具体看下是RequestContextChainingServiceImpl的setupSpringWebEnvironment
那么这个值哪里来的那?
咨询千臂后查找了如下:
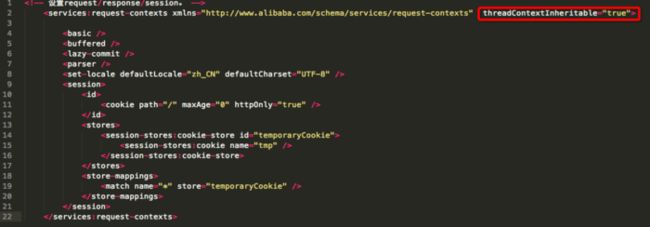
默认为FALSE,那么如何进行设置那,从这xsd知道webx.xml里面应该有标签设置。
然后看下webx.xml里面有个
根据经验搜索类RequestContextChainingService*,找到了RequestContextChainingServiceDefinitionParser。
protected void doParse(Element element, ParserContext parserContext, BeanDefinitionBuilder builder) {
parseBeanDefinitionAttributes(element, parserContext, builder);
//sort为RequestContextChainingService的成员变量
builder.addPropertyValue("sort", defaultIfNull(trimToNull(element.getAttribute("sort")), "true"));
List factoryList = createManagedList(element, parserContext);
for (Element subElement : subElements(element)) {
factoryList.add(parseConfigurationPointBean(subElement, requestContextsConfigurationPoint, parserContext,
builder));
}
//factories为RequestContextChainingService的成员变量
builder.addPropertyValue("factories", factoryList);
}
但是唯独没有在bean定义中填入threadContextInheritable的,目前没法配置这个变量(webx没有提供),咨询webx维护人员后,建议debug时候添加threadContextInheritable到builder测试下,然后在debug 下display中执行
builder.addPropertyValue("threadContextInheritable",true)后,上面Rpc代码输出为:
aseKey--666
hellobegin
888
helloend
至此达到了想要的结果,然后让webx维护人员帮搞了个snapshot版本的webx包,其实就是在parse里面添加一行:
然后在webx.xml配置如下:
七、总结
其实子线程中使用父线程中threadlocal方法有很多方式,比如创建线程时候传入线程变量的拷贝到线程中,或者在父线程中构造个map作为参数传递给子线程,但是这些都改变了我们的使用习惯,所以研究了本文方法。
欢迎关注微信公众号:技术原始积累 获取更多技术干货