地理空间索引:线段的GeoHash编码优化
在上一篇博客中,我们探讨了关于打网格寻找线段和多边形的GeoHash编码的框架,但是对直线而言还有更高效的编码算法,本文就探讨线段的GeoHash编码优化。
1. 线段的GeoHash编码问题
打网格的GeoHash编码方式需要在2维的网格上进行遍历,真正和线段相交的网格往往只占很少的部分,因此造成效率低下。我们优化的思路就是希望直接找到这些和线段相交的网格,如图所示。
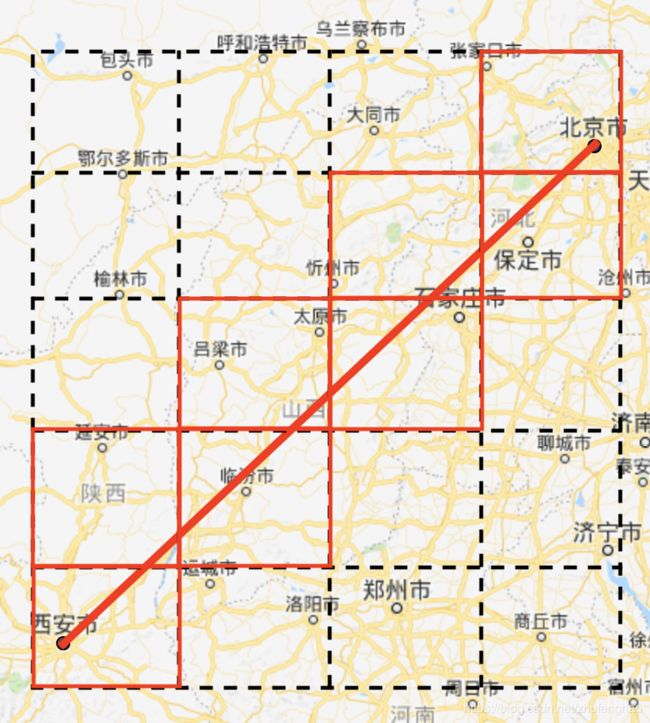
如果按照由西向东、由南向北的方向观察线段,线段和矩形网格相交具有如下特性:
- 线段的中间部分和矩形网格相交,总能找到一个入边,一个出边;
- 和线段依次相交的相邻矩形网格,前者的出边一定是后者的入边;
- 线段的首尾顶点一定落于网格内,首顶点所在的网格没有入边,尾顶点所在的网格没有出边;
- 特殊情况:如果线段与网格的边有重合,则网格的入边和出边重合,上述规律1和2则不再生效,线段与矩形网格相交的扩展方向和线段扩展方向一致。
2. 线段的GeoHash的编码思路
- 规定线段的方向为由西向东、由南向北,将线段的西南顶点作为起点并进行编码;
- 遍历起点所在的矩形网格的边,找到该网格的出边和下一个网格,将出边方向翻转(西 <=> 东,南 <=> 北)记为下一个网格的入边,特殊情况: 如果线段与网格的东西方向边有重合,则下一个网格朝北,如果与网格的南北方向边有重合,则下一个网格朝东;
- 重复上述操作,直到矩形网格找不到出边为止,所有相交的网格所代表的GeoHash编码就是该线段的编码。
这种思路是在GeoHash网格的基础上,优化了寻找与线段相交网格的方式,即按照一定的顺序直接找到依次相交网格,形象一点就像是“串糖葫芦”一般。
3. 代码实现
本处的代码依然继承上一篇博客定义好的点和线段的Python类,以及两条线段相交、线段与矩形相交的方法,这里不再重复。本处新添加了线段和网格边重合的方法is_lines_coincided。
def is_lines_coincided(line_ab, line_cd, eps=1e-6):
def between_range(num, num1, num2):
return min(num1, num2) < num < max(num1, num2)
len_ab = np.sqrt(line_ab.x * line_ab.x + line_ab.y * line_ab.y)
len_cd = np.sqrt(line_cd.x * line_cd.x + line_cd.y * line_cd.y)
if abs(dot_product(line_ab, line_cd)) != len_ab * len_cd: return False # parallel
if abs(line_ab.start.x - line_cd.start.x) < eps: # vertical
if between_range(line_ab.start.y, line_cd.start.y, line_cd.end.y) or \
between_range(line_ab.end.y, line_cd.start.y, line_cd.end.y):
return True
if abs(line_ab.start.y - line_cd.start.y) < eps: # horizontal
if between_range(line_ab.start.x, line_cd.start.x, line_cd.end.x) or \
between_range(line_ab.end.x, line_cd.start.x, line_cd.end.x):
return True
return False
接着定义西、北、东、南编号为1、2、3、4(编号0表示网格没有出边),并定义当前网格的出边和下一网格的入边翻转的方法,以及在线段与网格边有重合的特殊情况下,下一网格的入边的获取方法。
def reverse_direction(direction):
if direction == 1 or direction == 3: # west <=> east
direction = 4 - direction
elif direction == 2 or direction == 4: # south <=> north
direction = 6 - direction
return direction
def coincided_direction(direction):
if direction == 1 or direction == 3: # coincide west or east, to north
return 2
elif direction == 2 or direction == 4: # coincide south or north, to east
return 3
return direction
最后就是整体的线段编码方法了。
def geohash_to_rectangular(hashcode):
bbox = geohash.bbox(hashcode)
rectangular = [Point(bbox['w'], bbox['s']), Point(bbox['w'], bbox['n']),
Point(bbox['e'], bbox['s']), Point(bbox['e'], bbox['n'])]
return rectangular
def next_rectangular_direction(rectangular, line, previous):
rectangular = sorted(rectangular)
rectangular[3], rectangular[2] = rectangular[2], rectangular[3] # 0ws-1wn-2en-3es
for direction in xrange(1, 5):
side = Line(rectangular[direction - 1], rectangular[direction % 4])
if direction != previous and is_lines_intersected(line, side):
if is_lines_coincided(line, side): return coincided_direction(direction)
return direction
return 0
def next_direction_geohash(hashcode, direction, precision):
bbox = geohash.bbox(hashcode)
lng_delta, lat_delta = bbox['e'] - bbox['w'], bbox['n'] - bbox['s']
lat, lng = geohash.decode(hashcode)
if direction == 1: # west
lng -= lng_delta
elif direction == 2: # north
lat += lat_delta
elif direction == 3: # east
lng += lng_delta
elif direction == 4: # south
lat -= lat_delta
else:
raise Exception('Unknown direction %d' % direction)
return geohash.encode(lat, lng, precision)
def line_to_geohash(point1, point2, precision):
line = to_line(point1, point2)
start = min(line.start, line.end)
this_hash = geohash.encode(start.y, start.x, precision)
previous = 0
hash_list = []
while True:
hash_list.append(this_hash)
rectangular = geohash_to_rectangular(this_hash)
previous = reverse_direction(previous)
direction = next_rectangular_direction(rectangular, line, previous)
if direction == 0: break
this_hash = next_direction_geohash(this_hash, direction, precision)
previous = direction
return hash_list
4. 性能测试
import timeit
s = timeit.default_timer()
hashes = link_to_geohash(line, 8) # 本文
print timeit.default_timer() - s
>>> 0.0332131385803
s = timeit.default_timer()
hashes = link_to_geohash_previous(line, 8) # 上文
print timeit.default_timer() - s
>>> 0.571654081345