栈 力扣hot100热门面试算法题 面试基础 核心思路 背题 滑动窗口最大值 字符串解码 每日温度 柱状图中最大矩形 有效的括号 最小栈
栈
栈的核心思路:每个数都要进栈or队列,但是要及时维护栈or队列,当某元素没有存在的意义时就删掉,关键是思考栈尾什么时候有用与没用。
滑动窗口最大值
https://leetcode.cn/problems/sliding-window-maximum/
题解链接https://leetcode.cn/problems/sliding-window-maximum/solutions/3067170/dan-diao-dui-lie-by-ecstatic-allenmzl-y2xt
核心思路:
遍历每个数字:
- while(如果当前数比栈尾索引对应数字大,去除队尾元素);为什么去除呢,因为他没用了,他不可能成为最大值。
- 不管怎样,栈尾加入当前索引;因为即使当前元素比栈尾小,他也有可能成为最大值,因为窗口在滑动。
- 维护队列的对头是否在滑动窗口中;
- 当遍历指针走到第一个窗口的右边缘,开始记录ans[];
示例代码
class Solution {
public int[] maxSlidingWindow(int[] nums, int k) {
int n = nums.length;
int[] ans = new int[n-k+1];
Deque<Integer> q = new ArrayDeque<>();
for(int i = 0;i<n;i++){
//如果当前数比队尾索引对应数字大,去除队尾元素
while (!q.isEmpty() && nums[q.getLast()] <= nums[i]) {
q.removeLast();
}
//不论怎样,都加入当前元素的索引
q.addLast(i);
//同时维护队列的对头是否在滑动窗口中;
if (i - q.getFirst() >= k) {
q.removeFirst();
}
//当遍历指针走到第一个窗口的右边缘,开始记录ans[];
if (i >= k - 1) {
ans[i - k + 1] = nums[q.getFirst()];
}
}
return ans;
}
}
字符串解码
https://leetcode.cn/problems/min-stack/
核心思路
- 遍历输入字符串:
使用增强的 for 循环遍历字符串的每个字符。
- 处理字符:
如果字符是 '[':
- 将当前的
multi值压入stack_multi。 - 将当前的
res字符串压入stack_res。 - 重置
multi为 0 和res为新的StringBuilder实例。
如果字符是 ']':
-
从
stack_multi中弹出当前的重复次数cur_multi。 -
创建一个临时的
StringBuilder对象tmp,用于重复当前的res字符串cur_multi次。 -
将
tmp的内容与从stack_res中弹出的先前结果连接,并更新res。如果字符是数字(0-9):
更新 multi 的值,考虑到可能有多位数字。
如果字符是字母或其他字符:
直接将字符添加到 res 中。
- 返回结果:
遍历完成后,返回 res 的字符串表示。
示例代码
class Solution {
public String decodeString(String s) {
StringBuilder res = new StringBuilder();
//存储当前的重复次数。
int multi = 0;
//stack_multi 存储重复次数
Deque<Integer> stack_multi = new LinkedList<>();
//存储中间结果
Deque<String> stack_res = new LinkedList<>();
for(Character c : s.toCharArray()) {
if(c == '[') {
stack_multi.push(multi);
stack_res.push(res.toString());
multi = 0;
res = new StringBuilder();
}
else if(c == ']') {
StringBuilder tmp = new StringBuilder();
int cur_multi = stack_multi.pop();
for(int i = 0; i < cur_multi; i++) tmp.append(res);
res = new StringBuilder(stack_res.pop() + tmp);
}
else if(c >= '0' && c <= '9') multi = multi * 10 + (c-'0');
else res.append(c);
}
return res.toString();
}
}
每日温度
https://leetcode.cn/problems/daily-temperatures/
核心思路
每个数都要进栈or队列,但是要及时维护栈or队列,当某元素没有存在的意义时就删掉。
示例代码
class Solution {
public int[] dailyTemperatures(int[] temperatures) {
int[] ans= new int[temperatures.length];
Deque<Integer> st = new ArrayDeque<>();
for(int i = 0;i<=temperatures.length-1;i++){
int t = temperatures[i];
while(!st.isEmpty() && t > temperatures[st.peek()]){
int j = st.pop();
ans[j] = i-j;
}
st.push(i);
}
return ans;
}
}
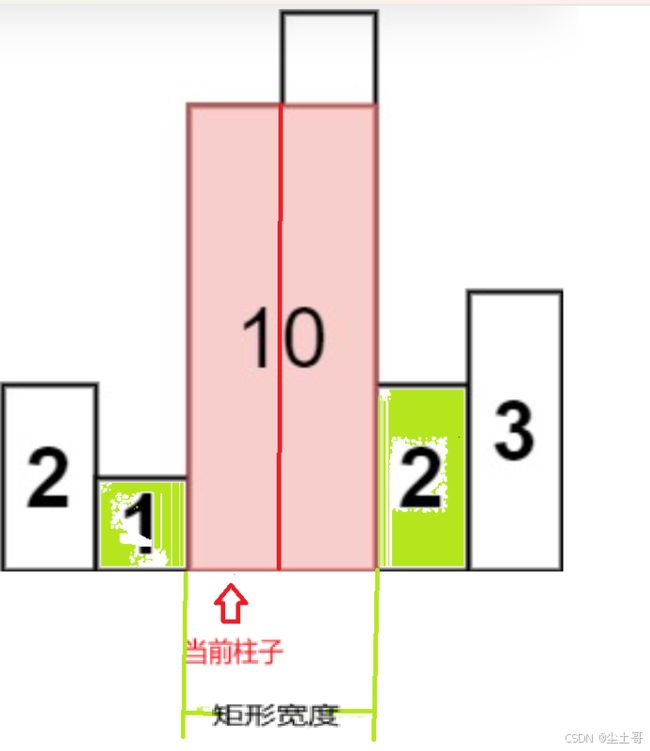
柱状图中最大矩形
https://leetcode.cn/problems/largest-rectangle-in-histogram/
核心思路
我们定义柱状图的每个高度都是一个柱子,
每个柱子都能形成一个以当前柱子为高度的矩形,此矩形的宽即 此柱子左右两边 第一个比当前柱子 矮的柱子 中间部分 的宽,
遍历每个柱子找到最大矩形;
示例代码
class Solution {
public int largestRectangleArea(int[] heights) {
int n = heights.length;
// 定义两个数组 ll 和 rr,分别存储每个柱子左边第一个小于该柱子的下标和右边第一个小于该柱子的下标
int[] ll = new int[n], rr = new int[n];
// 初始化 ll 和 rr 数组
// ll 初始化为 -1,表示如果没有更小的柱子,则左边界为 -1
// rr 初始化为 n,表示如果没有更小的柱子,则右边界为 n(数组外)
Arrays.fill(ll, -1);
Arrays.fill(rr, n);
// 定义一个栈,用于辅助计算左右边界
int[] st = new int[n];
int right = 0; // 栈指针,指向栈顶元素
// 计算每个柱子右边第一个小于它的柱子的下标 rr
for (int i = 0; i < n; i++) {
int t = heights[i]; // 当前柱子的高度
// 如果当前柱子的高度小于栈顶柱子的高度,则更新栈顶柱子的右边界
while (right > 0 && heights[st[right - 1]] > t) {
rr[st[--right]] = i; // 更新栈顶元素的右边界为当前下标 i
}
// 当前柱子的下标入栈
st[right++] = i;
}
// 清空栈指针,用于计算左边界
right = 0;
// 计算每个柱子左边第一个小于它的柱子的下标 ll
for (int i = n - 1; i >= 0; i--) {
int t = heights[i]; // 当前柱子的高度
// 如果当前柱子的高度小于栈顶柱子的高度,则更新栈顶柱子的左边界
while (right > 0 && heights[st[right - 1]] > t) {
ll[st[--right]] = i; // 更新栈顶元素的左边界为当前下标 i
}
// 当前柱子的下标入栈
st[right++] = i;
}
// 计算最大矩形面积
int ans = 0;
for (int i = 0; i < n; i++) {
// 当前柱子为高的矩形宽度为:rr[i] - ll[i] - 1
// 面积 = 高度 * 宽度
ans = Math.max(ans, heights[i] * (rr[i] - ll[i] - 1));
}
// 返回最大矩形面积
return ans;
}
}
有效的括号
https://leetcode.cn/problems/valid-parentheses/
核心思路
数组模拟栈,快多了
示例代码
class Solution {
public boolean isValid(String s) {
if (s.length() % 2 != 0) { // s 长度必须是偶数
return false;
}
HashMap<Character, Character> map = new HashMap<>();
map.put('}', '{');
map.put(']', '[');
map.put(')', '(');
int ll = 0;
char[] ch = new char[s.length()];
for (char c : s.toCharArray()) {
if (!map.containsKey(c)) { // c 是左括号
ch[ll++] = c; // 入栈
} else if (ll == 0 || ch[--ll] != map.get(c)) { // c 是右括号
return false; // 没有左括号,或者左括号类型不对
}
}
return ll == 0; // 所有左括号必须匹配完毕
}
}
最小栈
https://leetcode.cn/problems/min-stack/
核心思路
stack存一个pair,第二个数维护最小值
示例代码
class MinStack {
private final Deque<int[]> st = new ArrayDeque<>();
public MinStack() {
st.push(new int[]{0,Integer.MAX_VALUE});
}
public void push(int val) {
st.push(new int[]{val,Math.min(getMin(),val)});
}
public void pop() {
st.pop();
}
public int top() {
return st.peek()[0];
}
public int getMin() {
return st.peek()[1];
}
}