Python学习——Anscombe’s quartet
Anscombe’s quartet
Anscombe’s quartet comprises of four datasets, and is rather famous. Why? You’ll find out in this exercise.
Part 1
For each of the four datasets…
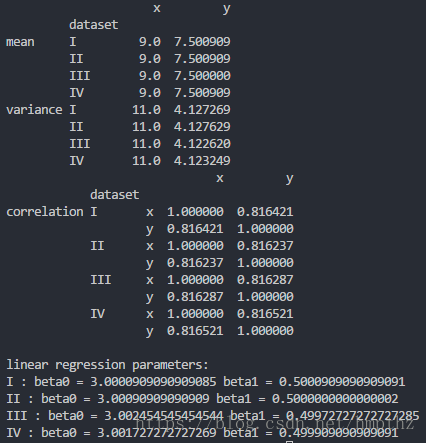
- Compute the mean and variance of both x and y
- Compute the correlation coefficient between x and y
- Compute the linear regression line: y=β0+β1x+ϵ y = β 0 + β 1 x + ϵ (hint: use statsmodels and look at the Statsmodels notebook)
Code:
import pandas as pd
import seaborn as sns
import statsmodels.api as sm
#mean, variance and correlation coefficient
anscombe = sns.load_dataset('anscombe')
df = anscombe.groupby('dataset')
mean_var = pd.concat([df.mean(), df.var()], keys=['mean', 'variance'])
corr = pd.concat([df.corr()], keys=['correlation'])
print(mean_var)
print(corr)
#linear regression
data_dict = dict(list(df))
array_x, array_y = {}, {}
for key, value in data_dict.items():
array_x[key] = value['x'].values
array_y[key] = value['y'].values
for key in array_x.keys():
x = sm.add_constant(array_x[key])
y = array_y[key]
est = sm.OLS(y, x).fit()
params = est.params
print(key, ': beta0 =', params[0], 'beta1 =', params[1])Output:
Part 2
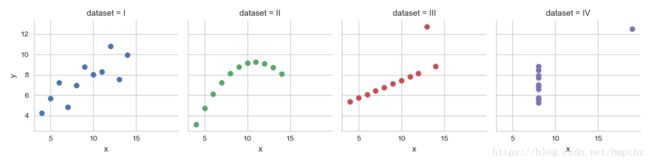
Using Seaborn, visualize all four datasets.
hint: use sns.FacetGrid combined with plt.scatter
Code:
sns.set(style='whitegrid')
g = sns.FacetGrid(anscombe, col="dataset", hue="dataset")
g.map(plt.scatter, 'x', 'y')
plt.show()Output: