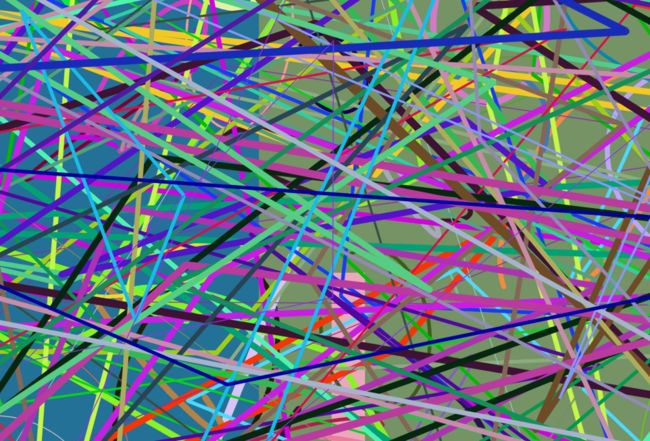
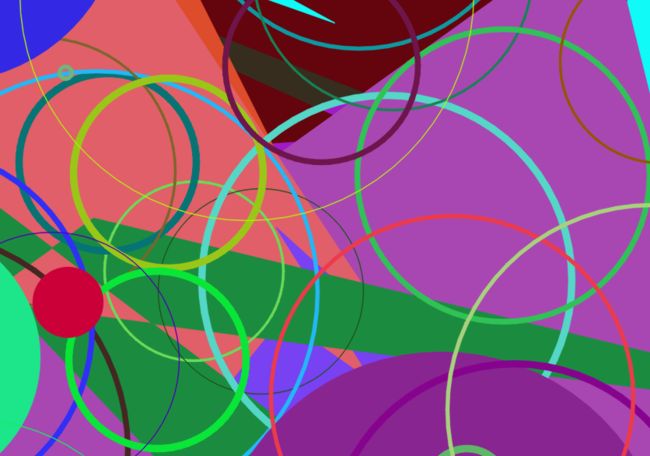
OpenCV学习(十一)之随机数生成器RNG
OpenCV中C++的RNG类可以压缩一个64位的i整数并可以得到scalar和array的随机数。目前的版本支持均匀分布随机数和Gaussian分布随机数。随机数的产生采用的是Multiply-With-Carry算法和Ziggurat算法。其构造函数的初始化可以传入一个64位的整型参数作为随机数产生器的初值。next可以取出下一个随机数,uniform函数可以返回指定范围的随机数,gaussian函数返回一个高斯随机数,fill则用随机数填充矩阵等等。
以下测试程序分别测试了RNG类中各个函数的用法以及解释了各个参数的意思,重点都在注释里。此外测试程序后半部分也大概介绍了c版本的随机数产生器,如cvRNG、cvRandArr、cvRandInt、cvRandReal等。由于理解还能力有限,个别函数还是不太清楚。
实验环境:VS2010 + OpenCV2.4.9.0
#include
#include "cv.h"
#include "highgui.h"
using namespace cv;
using namespace std;
int main(int argc,char** argv)
{
RNG rng;
// always produces 0
//RNG::uniform(int,int)
//因为只会去整数,所以只产生0
double a = rng.uniform(0,1);
//produces double from[0,1)
double a1 = rng.uniform((double)0,(double)1);
//produces float from[0,1)
double b = rng.uniform(0.f,1.f);
//produces double from[0,1)
double c = rng.uniform(0.,1.);
//may cause compiler error because of ambiguity:
//RNG:: uniform(0,(int)0.999999) ? or RNG::unigorm((double)0,0.999999)
//double d = rng.uniform(0,0.999999);所以先注释起来吧 O(∩_∩)O
cout << "a = " << a << endl;
cout << "a1 = " << a1 << endl;
cout << "b = " << b << endl;
cout << "c = " << c << endl;
//cout << "d = " << d << endl;
/*-------- returns the next random number sampled from the Gaussian distribution-------
* double RNG:: gaussian( double sigma)
* sigma – standard deviation(标准差) of the distribution
------------------------------------------------------------------------------------*/
double g = rng.gaussian(2);
cout << "g = " << g << endl;
/*-------- returns the next random number(还不理解这个“下一个”是指什么?) -------------------
* unsigned int RNG:: next()
* The method updates the state using the MWC algorithm and
returns the next 32-bit random number
------------------------------------------------------------------------------------*/
int n = rng.next();
cout << "n = " << n << endl;
/*-------- RNG::operator T returns the next random number of the specified type ---------
* RNG:: operator uchar()
* RNG:: operator schar()
* RNG:: operator ushort()
* RNG:: operator short int()
* RNG:: operator int()
* RNG:: operator unsigned int()
* RNG:: operator float()
* RNG:: operator double()
* 返回指定类型的下一个随机数。对于int型,返回可用数据类型范围内的随机数,对于float型,
返回[0,1)范围的随机数
------------------------------------------------------------------------------------*/
int n1 = rng.operator int();
cout << "n1 = " << n1 << endl;
float f = rng.operator float();
cout << "f = " << f << endl;
/*-------- RNG::operator () returns the next random number -----------------------
* unsigned int RNG:: operator() () == RNG::next() 两个函数相同
* unsigned int RNG:: operator() (unsigned int N) 注意括号
* return the result in the range [0,N)
------------------------------------------------------------------------------------*/
int o = rng.operator ()();
int o1 = rng.operator() (50);
cout << "o = " << o << endl << "o1 = " << o1 << endl;
/*---------------------- fills arrays with random numbers.------------------------
* void RNG:: fill( InputOutputArray mat, int distType, InputArray a,
InputArray b, bool saturateRange=false )函数原型
* mat – 2D or N-dimensional matrix; currently matrices with more than 4 channels
are not supported by the methods, use Mat::reshape() as a possible workaround
说明了输入矩阵的形式,目前尚不支持4通道以上的矩阵,如果超过了,需要调用reshape()函数
进行变更
* distribution type, RNG::UNIFORM or RNG::NORMAL 分布的类型(均匀或高斯)
* a – first distribution parameter; in case of the uniform distribution, this is an
inclusive lower boundary, in case of the normal distribution, this is a mean value
当为均匀分布时,a为下界(闭区间),当为高斯分布时,表示均值
* b – second distribution parameter; in case of the uniform distribution, this is a
non-inclusive upper boundary, in case of the normal distribution, this is a standard deviation
(diagonal of the standard deviation matrix or the full standard deviation matrix)
当为均匀分布时,a为上界(开区间),当为高斯分布时,表示标准差
* saturateRange – pre-saturation flag; for uniform distribution only; if true, the method will
first convert a and b to the acceptable value range (according to the mat datatype) and
then will generate uniformly distributed random numbers within the range [saturate(a),
saturate(b)) , if saturateRange=false, the method will generate uniformly distributed
random numbers in the original range [a, b) and then will saturate them, it means, for example,
that theRNG().fill(mat_8u, RNG::UNIFORM, -DBL_MAX, DBL_MAX) will likely produce array mostly
filled with 0’s and 255’s, since the range (0, 255) is significantly smaller than [-DBL_MAX, DBL_MAX)
意思是:此变量只针对均匀分布有效。当为真的时候,会先把产生随机数的范围变换到数据类型的范围,
再产生随机数;如果为假,会先产生随机数,再进行截断到数据类型的有效区间。请看以下fillM1和
fillM2的例子并观察结果
------------------------------------------------------------------------------------*/
Mat_fillM(3,3);
rng.fill(fillM,RNG::UNIFORM,1,1000);
cout << "filM = " << fillM << endl << endl;
Mat fillM1(3,3,CV_8U);
rng.fill(fillM1,RNG::UNIFORM,1,1000,TRUE);
cout << "filM1 = " << fillM1 << endl << endl;
//fillM1产生的数据都在[0,,255)内,且小于255;
//fillM2产生的数据虽然也在同样范围内,但是由于用了截断操作,所以很多数据都是255,
//因为CV_8U的有效范围就是0~255
//所以我认为最好的方式就是事先想好需要的数据类型和范围,再设置为FALSE(默认值)
Mat fillM2(3,3,CV_8U);
rng.fill(fillM2,RNG::UNIFORM,1,1000,FALSE);
cout << "filM2 = " << fillM2 << endl << endl;
/*------- uniformly-distributed random number or an array of random numbers----
* randu(dst, low, high)
* dst – output array of random numbers;
* low – inclusive lower boundary of the generated random numbers;
* high - exclusive upper boundary of the generated random numbers;
-----------------------------------------------------------------------------*/
Mat_randuM(3,3);
randu(randuM,Scalar(0),Scalar(255));
cout << "randuM = " << randuM << endl << endl;
/*---------------normally distributed random numbers-------------------
* randn(dst, mean, stddev)(也叫高斯分布)
* dst – output array of random numbers;
the array must be pre-allocated and have 1 to 4 channels;
* mean(均值) – mean value (expectation) of the generated random numbers
* stddev - standard deviation(标准差) of the generated random numbers; it can be either a vector
(in which case a diagonal standard deviation matrix is assumed) or a square matrix
-----------------------------------------------------------------------------*/
Mat_randnM(3,3);
randn(randnM,0,1);
cout << "randnM = " << randnM << endl << endl;
/*-----------------Shuffles the array elements randomly(产生随机打乱的矩阵)---------------
* randShuffle( InputOutputArray dst, double iterFactor=1., RNG* rng=0 )
* dst - input/output numerical 1D array;
* iterFactor - scale factor that determines the number of random swap operations;
* rng - optional random number generator used for shuffling; if it is zero,
theRNG()() is used instead;
* The function randShuffle shuffles the specified 1D array by randomly choosing
pairs of elements and swapping them. The number of such swap operations will be
dst.rows*dst.cols*iterFactor
-----------------------------------------------------------------------------*/
Mat_randShufM(4,1);
randShuffle(randShufM,1,0);
cout << "randShufM = " << randShufM << endl << endl;
//还不太会用...
/*------------------------下面介绍一下C版的随机数产生器的相关函数---------------*/
/*------- initializes a random number generator state(初始化随机数生成器状态)-----
* CvRNG cvRNG( int64 seed=-1) 函数原型
* seed – 64-bit value used to initiate a random sequence
64-bit的值用来初始化随机序列;
函数 cvRNG 初始化随机数生成器并返回其状态。
指向这个状态的指针可以传递给函数 cvRandInt, cvRandReal 和 cvRandArr;
在通常的实现中使用一个 multiply-with-carry generator
C++版本中的RNG已经代替了CvRNG
-----------------------------------------------------------------------------*/
//CvRNG rng1 = cvRNG(-1);
CvRNG cvRNG;
/*------- fills an array with random numbers and updates the RNG state-------
* void cvRandArr( CvRNG* rng, CvArr* arr, int dist_type,
CvScalar param1, CvScalar param2)函数原型
* rng – CvRNG state initialized by RNG()被 cvRNG 初始化的 RNG 状态
* arr – The destination array
* dist_type – Distribution type
- CV_RAND_UNI uniform distribution
- CV_RAND_NORMAL normal or Gaussian distribution
* param1 – The first parameter of the distribution. In the case of a uniform distribution it
is the inclusive lower boundary of the random numbers range. In the case of a normal
distribution it is the mean value of the random numbers
如果是均匀分布它是随机数范围的闭下边界;如果是正态分布它是随机数的平均值
* param2 – The second parameter of the distribution. In the case of a uniform distribution
it is the exclusive upper boundary of the random numbers range. In the case of a normal
distribution it is the standard deviation of the random numbers
如果是均匀分布它是随机数范围的开上边界;如果是正态分布它是随机数的标准差
-----------------------------------------------------------------------------*/
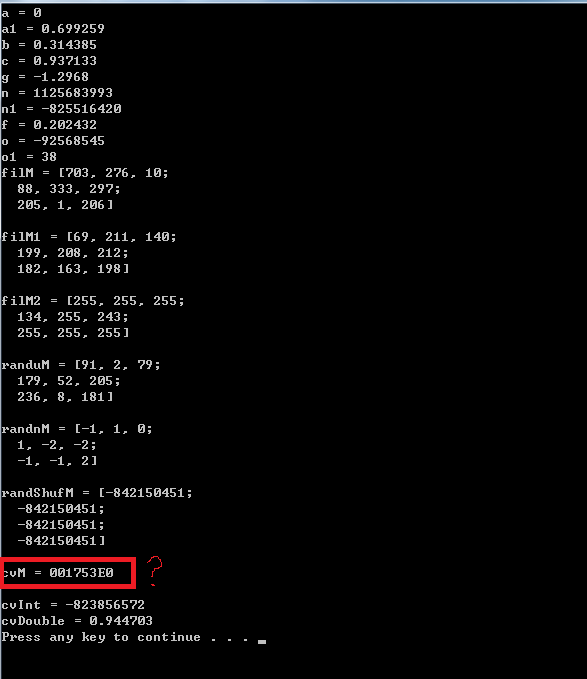
CvMat* cvM = cvCreateMat(3,3,CV_16U);
cvRandArr(&cvRNG,cvM,CV_RAND_UNI,cvScalarAll(0),cvScalarAll(255));
cout << "cvM = " << cvM << endl << endl;
//这里输出有点奇怪,明明定义的是矩阵,却输出的一串数字,不理解?
/*------- returns a 32-bit unsigned integer and updates RNG-------
* unsigned int cvRandInt( CvRNG* rng)函数原型
* rng – CvRNG state initialized by RNG()
函数 cvRandInt 返回均匀分布的随机 32-bit 无符号整型值并更新 RNG 状态;
它和 C 运行库里面的 rand() 函数十分相似,但是它产生的总是一个 32-bit 数而 rand()
返回一个 0 到 RAND_MAX(它是 2**16 或者 2**32, 依赖于操作平台)之间的数
-----------------------------------------------------------------------------*/
int cvInt = cvRandInt(&cvRNG);
cout << "cvInt = " << cvInt << endl;
/*------- returns a floating-point random number and updates RNG.-------
* double cvRandReal( CvRNG* rng)函数原型
* rng – RNG state initialized by RNG()
函数 cvRandReal 返回均匀分布的随机浮点数,范围在 0~1 之间 (不包括1)
-----------------------------------------------------------------------------*/
double cvDouble = cvRandReal(&cvRNG);
cout << "cvDouble = " << cvDouble << endl;
system("pause");
return 0;
}
同时也可以看到fillM1和fillM2之间的区别。
以下给出RNG类在OpenCV中源代码:
/*!
Random Number Generator
The class implements RNG using Multiply-with-Carry algorithm
*/
class CV_EXPORTS RNG
{
public:
enum { UNIFORM=0, NORMAL=1 };
RNG();//默认构造函数
// inline RNG::RNG() { state = 0xffffffff; }
RNG(uint64 state);//带参数的构造函数,接受一个64位无符号的值。
//inline RNG::RNG(uint64 _state) { state = _state ? _state : 0xffffffff; }
//! updates the state and returns the next 32-bit unsigned integer random number
unsigned next();
/*
inline unsigned RNG::next()
{
state = (uint64)(unsigned)state*CV_RNG_COEFF + (unsigned)(state >> 32);
return (unsigned)state;
}
#define CV_RNG_COEFF 4164903690U
用两个很大的无符号数相乘,乘积结果要转换为64位无符号数,转换的时候两个乘数应该向高精度看起,所以应该也先转换为64位再相乘。把state右移32位得到一个数,把这两个数相加。函数返回一个32位的无符号数,其值为截断前面求得的和。
*/
//以下几个函数是从类到uchar.schar,ushort,short,usinged的显示转换函数
operator uchar();//返回一个8位无符号类型的随机数,把next返回的数截断
//inline RNG::operator uchar() { return (uchar)next(); }
operator schar();//返回一个8为有符号类型的随机数。???会产生负数吗,返回的也是截断的next返回值。莫非是截断后得到的最高位作为符号位,这样也可能是随机的。???
//inline RNG::operator schar() { return (schar)next(); }
operator ushort();//返回一个无符号16为整数
//inline RNG::operator ushort() { return (ushort)next(); }
operator short();//返回一个有符号16为整数
// inline RNG::operator short() { return (short)next(); }
operator unsigned();//返回一个无符号32为整数
// inline RNG::operator unsigned() { return next(); }
//! returns a random integer sampled uniformly from [0, N).
unsigned operator ()(unsigned N);//重载括号操作符,带参数。在(0,N)之间返回一个整数,调用uniform成员函数
//inline unsigned RNG::operator ()(unsigned N) {return (unsigned)uniform(0,N);}
unsigned operator ()();//重载括号操作符,无参数。直接返回next结果。
// inline unsigned RNG::operator ()() {return next();}
//放在这个位置有点奇怪,为什么不和前边同类放一起呢?放回一个带符//号32为整数
operator int();
// inline RNG::operator int() { return (int)next(); }
//返回一个float型(具体多少位看平台)数。
operator float();
// inline RNG::operator float() { return next()*2.3283064365386962890625e-10f; }
//两个数按位或一下
operator double();
/*
inline RNG::operator double()
{
unsigned t = next();
return (((uint64)t << 32) | next())*5.4210108624275221700372640043497e-20;
}*/
//! returns uniformly distributed integer random number from [a,b) range
int uniform(int a, int b);//[a,b)内随机产生一个int型值,均匀分布
// inline int RNG::uniform(int a, int b) { return a == b ? a : (int)(next()%(b - a) + a); }
//! returns uniformly distributed floating-point random number from [a,b) range
float uniform(float a, float b); //[a,b)内随机产生一个float型值,均匀分布
// inline float RNG::uniform(float a, float b) { return ((float)*this)*(b - a) + a; }
//! returns uniformly distributed double-precision floating-point random number from [a,b) range
double uniform(double a, double b); //[a,b)内随机产生一个double型值,均匀分布
// inline double RNG::uniform(double a, double b) { return ((double)*this)*(b - a) + a; }
void fill( InputOutputArray mat, int distType, InputArray a, InputArray b, bool saturateRange=false );//这个函数实现很长,暂时略过。
//! returns Gaussian random variate with mean zero.
double gaussian(double sigma);//返回均值为0的高斯随机变量,
/*double RNG::gaussian(double sigma)
{
float temp;
randn_0_1_32f( &temp, 1, &state );
return temp*sigma;
}*/
uint64 state;//种子,next中需要这样一个初始值
};以下是一个以RNG的例子,画随机直线和在图像中添加字符:
#include
#include "cv.h"
#include "highgui.h"
using namespace std;
using namespace cv;
const char wndName[] = "randDraw";
const int randNumber = 100;
static Scalar randomColor(RNG& rng)
{
int rColor = (unsigned)rng;
//颜色是用RGB三通道表示,因此上面函数中颜色参数的类型都是Scalar类型
//将随机数的值取出分别作为RGB三个通道的颜色值
return Scalar(rColor & 0xFF,(rColor >> 8) & 0xFF,(rColor >> 16) & 0xFF);
}
int main(int argc,char** argv)
{
//抗锯齿,平滑线
//改为8就不是咯~
int lineType = CV_AA;
int width = 1000;
int height = 700;
int x1 = - width/2;
int x2 = 3 * width/2;
int y1 = - height/2;
int y2 = 3 * height/2;
const int DELAY = 10;
//0xFFFFFFFF表示初始的随机值
//RNG rng(0xFFFFFFFF);
RNG rng;
Mat image = Mat::zeros(height,width,CV_8UC3);
imshow(wndName,image);
waitKey(DELAY);
for(int i = 0;i < randNumber;i++)
{
Point pt1;
Point pt2;
pt1.x = rng.uniform(x1,x2);
pt1.y = rng.uniform(y1,y2);
pt2.x = rng.uniform(x1,x2);
pt2.y = rng.uniform(y1,y2);
/*----------------------draws a line segment connecting two points-----------
* void line( Mat& img, Point pt1, Point pt2, const Scalar& color,
int thickness=1, int lineType=8, int shift=0)函数原型
* lineType – Type of the line:
– 8 (or omitted) - 8-connected line.
– 4 - 4-connected line.
– CV_AA - antialiased line.
-----------------------------------------------------------------------------*/
line(image,pt1,pt2,randomColor(rng),rng.uniform(1,10),lineType);
}
imshow(wndName,image);
waitKey(0);
for(int i = 0;i < randNumber;i++)
{
Point org;
org.x = rng.uniform(x1,x2);
org.y = rng.uniform(y1,y2);
/*-------------------------draws a text string--------------------------------
* void putText(Mat& img, const string& text, Point org, int fontFace,
double fontScale, Scalar color,int thickness=1,
int lineType=8, bool bottomLeftOrigin=false )函数原型
* img – image
* text – Text string to be drawn
* org – Bottom-left corner of the text string in the image.
* font – CvFont structure initialized using InitFont() C版本的参数
* fontFace – Font type. One of FONT_HERSHEY_SIMPLEX, FONT_HERSHEY_PLAIN,
FONT_HERSHEY_DUPLEX, FONT_HERSHEY_COMPLEX, FONT_HERSHEY_TRIPLEX,
FONT_HERSHEY_COMPLEX_SMALL, FONT_HERSHEY_SCRIPT_SIMPLEX, or
FONT_HERSHEY_SCRIPT_COMPLEX, where each of the font ID’s can be
combined with FONT_HERSHEY_ITALIC to get the slanted letters
* fontScale – Font scale factor that is multiplied by the font-specific base size
* color – Text color
* thickness – Thickness of the lines used to draw a text
* lineType – Line type. See the line for details
* bottomLeftOrigin – When true, the image data origin is at the bottom-left corner;
Otherwise, it is at the top-left corner.如果为真,图像原点在左下角,否则在左上角
-----------------------------------------------------------------------------*/
putText(image,"OpenCV",org,rng.uniform(0,8),rng.uniform(0,10)*0.5 + 0.1,
randomColor(rng),rng.uniform(1,10),lineType,FALSE);
}
imshow(wndName,image);
waitKey(0);
return 0;
}
最后,再列出一个OpenCV自带Demo,我稍微对函数进行了注释。主要是为了练习使用随机数生成器和如何使用OpenCV画图。
#include
#include "cv.h"
#include "highgui.h"
using namespace std;
using namespace cv;
static void help()
{
cout << "This program demonstrates OpenCV drawing and text output functions" << endl
<< "Usage:" << endl
<<"./drawing" << endl;
}
static Scalar randomColor(RNG& rng)
{
int iColor = unsigned(rng);
//255 = 0xFF
return Scalar(iColor & 255,(iColor >> 8) & 255,(iColor >> 16) & 255);
}
int main(int argc,char** argv)
{
help();
char wndName[] = "Drawing Demo";
const int randomNumber = 100;
const int DELAY = 10;
int lineType = CV_AA;
int height = 700;
int width = 1000;
int x1 = - width/2;
int x2 = 3 * width/2;
int y1 = - height/2;
int y2 = 3 * height/2;
RNG rng(0xFFFFFFFF);
Mat image = Mat::zeros(height,width,CV_8UC3);
imshow(wndName,image);
waitKey(DELAY);
//draw line
for(int i = 0;i < randomNumber;i++)
{
Point pt1,pt2;
pt1.x = rng.uniform(x1,x2);
pt1.y = rng.uniform(y1,y2);
pt2.x = rng.uniform(x1,x2);
pt2.y = rng.uniform(y1,y2);
line(image,pt1,pt2,randomColor(rng),rng.uniform(1,10),lineType);
imshow(wndName,image);
if(waitKey(DELAY) >= 0)
return 0;
}
//draw rectangle
for(int i = 0;i < randomNumber;i++)
{
Point pt1,pt2;
pt1.x = rng.uniform(x1,x2);
pt1.y = rng.uniform(y1,y2);
pt2.x = rng.uniform(x1,x2);
pt2.y = rng.uniform(y1,y2);
int thickness = rng.uniform(-3,10);
/*----------------------draws a simple, thick, or filled up-right rectangle-----------
* C++: void rectangle(Mat& img, Point pt1, Point pt2, const Scalar& color,
int thickness=1, int lineType=8,int shift=0)
* C++: void rectangle(Mat& img, Rect rec, const Scalar& color, int thickness=1,
int lineType=8, int shift=0)
* img – image
* pt1 – Vertex of the rectangle
* pt2 – Vertex of the rectangle opposite to pt1
* rec – Alternative specification of the drawn rectangle
* color – Rectangle color or brightness (grayscale image)
* thickness – Thickness of lines that make up the rectangle. Negative values,
like CV_FILLED, mean that the function has to draw a filled rectangle
* lineType – Type of the line. See the line() description
* shift – Number of fractional bits in the point coordinates
-----------------------------------------------------------------------------*/
rectangle(image,pt1,pt2,randomColor(rng),MAX(thickness,-1),lineType);
imshow(wndName,image);
if(waitKey(DELAY) >= 0)
return 0;
}
//draw ellipse
for(int i = 0; i < randomNumber;i++)
{
Point center;
center.x = rng.uniform(x1,x2);
center.y = rng.uniform(y1,y2);
Size axes;
axes.width = rng.uniform(0,200);
axes.height = rng.uniform(0,200);
double angle = rng.uniform(0,180);
/*---------draws a simple or thick elliptic arc or fills an ellipse sector---------
* C++: void ellipse(Mat& img, Point center, Size axes, double angle,
double startAngle,double endAngle,const Scalar& color,
int thickness=1, int lineType=8, int shift=0)
* C++: void ellipse(Mat& img, const RotatedRect& box, const Scalar& color,
int thickness=1, int lineType=8)
* img – image
* center – Center of the ellipse 椭圆中心
* axes – Half of the size of the ellipse main axes 椭圆长轴的一半
* angle – Ellipse rotation angle in degrees 椭圆旋转的角度
* startAngle – Starting angle of the elliptic arc in degrees 弧度开始的角度
* endAngle – Ending angle of the elliptic arc in degrees 弧度结束的角度
* box – Alternative ellipse representation via RotatedRect or CvBox2D
This means that the function draws an ellipse inscribed in the rotated rectangle
* color – Ellipse color
* thickness – Thickness of the ellipse arc outline, if positive. Otherwise, this indicates that a
filled ellipse sector is to be drawn
* lineType – Type of the ellipse boundary. See the line() description
* shift – Number of fractional bits in the coordinates of the center and values of axes
-----------------------------------------------------------------------------*/
ellipse(image,center,axes,angle,angle - 100,angle + 200,randomColor(rng),rng.uniform(1,8),lineType);
imshow(wndName,image);
if(waitKey(DELAY) >= 0)
return 0;
}
//draw polylines
for(int i = 0;i < randomNumber;i++)
{
Point pt[2][3];
pt[0][0].x = rng.uniform(x1,x2);
pt[0][0].y = rng.uniform(y1,y2);
pt[0][1].x = rng.uniform(x1,x2);
pt[0][1].y = rng.uniform(y1,y2);
pt[0][2].x = rng.uniform(x1,x2);
pt[0][2].y = rng.uniform(y1,y2);
pt[1][0].x = rng.uniform(x1,x2);
pt[1][0].y = rng.uniform(y1,y2);
pt[1][1].x = rng.uniform(x1,x2);
pt[1][1].y = rng.uniform(y1,y2);
pt[1][2].x = rng.uniform(x1,x2);
pt[1][2].y = rng.uniform(y1,y2);
const Point* ppt[2] = {pt[0],pt[1]};
int npt[] = {3,3};
/*-------------------draws several polygonal curves----------------------------
* C++: void polylines(Mat& img, const Point** pts, const int* npts, int ncontours,
bool isClosed, const Scalar& color, int thickness=1,
int lineType=8, int shift=0 )
* C++: void polylines(InputOutputArray img, InputArrayOfArrays pts, bool isClosed,
const Scalar& color,int thickness=1, int lineType=8, int shift=0 )
* img – image
* pts – Array of polygonal curves 多边形曲线数组
* npts – Array of polygon vertex counters 顶点数组
* ncontours – Number of curves 曲线数量
* isClosed – Flag indicating whether the drawn polylines are closed or not
If they are closed,the function draws a line from the last vertex
of each curve to its first vertex 标志曲线是否闭合
* color – Polyline color
* thickness – Thickness of the polyline edges
* lineType – Type of the line segments. See the line() description
* shift – Number of fractional bits in the vertex coordinates
-----------------------------------------------------------------------------*/
polylines(image,ppt,npt,2,TRUE,randomColor(rng),rng.uniform(1,10),lineType);
imshow(wndName,image);
if(waitKey(DELAY) >= 0)
return 0;
}
//draw polygons with filled area
for(int i = 0;i < randomNumber;i++)
{
Point pt[2][3];
pt[0][0].x = rng.uniform(x1, x2);
pt[0][0].y = rng.uniform(y1, y2);
pt[0][1].x = rng.uniform(x1, x2);
pt[0][1].y = rng.uniform(y1, y2);
pt[0][2].x = rng.uniform(x1, x2);
pt[0][2].y = rng.uniform(y1, y2);
pt[1][0].x = rng.uniform(x1, x2);
pt[1][0].y = rng.uniform(y1, y2);
pt[1][1].x = rng.uniform(x1, x2);
pt[1][1].y = rng.uniform(y1, y2);
pt[1][2].x = rng.uniform(x1, x2);
pt[1][2].y = rng.uniform(y1, y2);
const Point* ppt[2] = {pt[0], pt[1]};
int npt[] = {3, 3};
/*--------------fills the area bounded by one or more polygons---------------
* C++: void fillPoly( Mat& img, const Point** pts, const int* npts, int ncontours,
const Scalar& color, int lineType=8, int shift=0, Point offset=Point() )
* img – image
* pts – Array of polygons where each polygon is represented as an array of points
* npts – Array of polygon vertex counters
* ncontours – Number of contours that bind the filled region
* color – Polygon color
* lineType – Type of the polygon boundaries. See the line() description
* shift – Number of fractional bits in the vertex coordinates
* offset – Optional offset of all points of the contours
-----------------------------------------------------------------------------*/
fillPoly(image, ppt, npt, 2, randomColor(rng), lineType);
imshow(wndName, image);
if(waitKey(DELAY) >= 0)
return 0;
}
//draw circle
for(int i = 0;i < randomNumber;i++)
{
Point center;
center.x = rng.uniform(x1,x2);
center.y = rng.uniform(y1,y2);
/*-----------------------------draw a circle----------------------------------
* C++: void circle(Mat& img, Point center, int radius, const Scalar& color,
int thickness=1, int lineType=8,int shift=0)
* img – Image where the circle is drawn
* center – Center of the circle
* radius – Radius of the circle
* color – Circle color
* thickness – Thickness of the circle outline, if positive.
Negative thickness means that a
* filled circle is to be drawn
* lineType – Type of the circle boundary. See the line() description
* shift – Number of fractional bits in the coordinates of the center and
in the radius value
-----------------------------------------------------------------------------*/
circle(image,center,rng.uniform(0,300),randomColor(rng),rng.uniform(-1,9),lineType);
imshow(wndName,image);
if(waitKey(DELAY) >= 0)
return 0;
}
//put text on the image
for(int i = 0;i < randomNumber;i++)
{
Point org;
org.x = rng.uniform(x1,x2);
org.y = rng.uniform(y1,y2);
putText(image,"Testing text rendering",org,rng.uniform(0,8)/*font type*/,
rng.uniform(0,100)*0.05 + 0.1/*font scale*/,
randomColor(rng),rng.uniform(1,10)/*thickness*/,lineType);
imshow(wndName,image);
if(waitKey(DELAY) >= 0)
return 0;
}
/*------------------calculates the width and height of a text string--------------
* C++: Size getTextSize( const string& text, int fontFace, double fontScale,
int thickness, int* baseLine)
* text – Input text string
* fontFace – Font to use. See the putText() for details
* fontScale – Font scale. See the putText() for details
* thickness – Thickness of lines used to render the text
* baseLine – Output parameter - y-coordinate of the baseline relative
to the bottom-most text point.
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------------*/
//string text = " OpenCV Forever!" ;
//int fontFace = FONT_HERSHEY_COMPLEX;
//double fontScale = 2;
//int thickness = 3;
//int baseline=0;
//baseline += thickness;
//Size textSize = getTextSize(text, fontFace,
// fontScale, thickness, &baseline);
Size textSize = getTextSize("OpenCV Forever!",FONT_HERSHEY_COMPLEX,3,5,0);
Point org((width - textSize.width)/2,(height - textSize.height)/2);
Mat image2;
for(int i = 0;i < 255;i += 2)
{
image2 = image - Scalar::all(i);
putText(image2,"OpenCV Forever!",org,FONT_HERSHEY_COMPLEX,
3,Scalar(i,i,255),5,lineType);
imshow(wndName,image2);
if(waitKey(DELAY) >= 0)
return 0;
}
waitKey();
return 0;
} 测试结果很有意思。顿时让我对OpenCV又爱上了几分。。。