合肥工业大学 程序设计艺术与方法实验报告( STL 的熟悉与使用 搜索算法的实现 计算几何算法的实现 动态规划算法的实现)
本实验报告包括四个实验内容:
1.STL 的熟悉与使用
2.搜索算法的实现
3.计算几何算法的实现
4.动态规划算法的实现
实验一、STL 的熟悉与使用
(1) 练习vector 和list 的使用。
定义一个空的vector,元素类型为int,生成10 个随机数插入到vector 中,用迭代
器遍历vector 并输出其中的元素值。在vector 头部插入一个随机数,用迭代器遍历vector
并输出其中的元素值。用泛型算法find 查找某个随机数,如果找到便输出,否则将此数
插入vector 尾部。用泛型算法sort 将vector 排序,用迭代器遍历vector 并输出其中的元
素值。删除vector 尾部的元素,用迭代器遍历vector 并输出其中的元素值。将vector 清
空。
定义一个list,并重复上述实验,并注意观察结果。
(2) 练习泛型算法的使用。
定义一个vector,元素类型为int,插入10 个随机数,使用sort 按升序排序,输出
每个元素的值,再按降叙排序,输出每个元素的值。练习用find 查找元素。用min 和
max 找出容器中的最小元素个最大元素,并输出。
(1)练习vector 和list 的使用。
vector:
源代码:
#includeList
源代码:
#include
//带头节点的双向循环链表
#include(1) 练习泛型算法的使用。
源代码:
#include实验二、搜索算法的实现
-
将书上的走迷宫代码上机运行并检验结果,并注意体会搜索的思想。
2.八皇后问题:在一个国际象棋棋盘上放八个皇后,使得任何两个皇后之间不相互攻击,求出所有的布棋方法。上机运行并检验结果。 -
骑士游历问题:在国际棋盘上使一个骑士遍历所有的格子一遍且仅一遍,对于任意给定的顶点,输出一条符合上述要求的路径。
4.倒水问题:给定2 个没有刻度容器,对于任意给定的容积,求出如何只用两个瓶装出L 升
的水,如果可以,输出步骤,如果不可以,请输出No Solution。 -
八皇后问题
1.1思路分析:
设立数组a[n],数组下标对应棋盘的行;数组存储的值为列;数组的每个下标(列)对应相应的行;
递归遍历所有的棋盘点,通过棋子是否在对角线或同一列判断是否能落子;
递归的同时输出满足条件的方法;
1.2解题详情
eightQueen()函数判断是否能落子
当queenCount == n 时,print()函数输出此种情况下落子情况。
#include - 骑士游历问题
2.1思路分析:
定义二位数组作为棋盘,初始化为0;
DFS算法遍历,判断是否已被访问或是否超界,若非法则回溯。
所有点被访问时输出路径。
2.2解题详情
二维数组chess[8][8]作为棋盘
dfs(int x, int y)函数根据走棋规则进行遍历;ifOut(int x, int y)函数判断是否出界;fVisited(int x, int y)函数判断是否被访问;
当所有点被访问时输出结果
#include倒水问题:
3.1思路分析:
1.若先将小桶水装满:将小桶装满水倒入大桶;若大桶中水未满,则重复过程直至大桶中水满;若大桶中水满则倒掉大桶中的水每次倒水后判断大桶中水是否满足要求,满足题目条件则结束程序;若运行至小桶没有水,大桶满水则表示no solution,程序结束;
2.若先将大桶水装满:过程同上;
3.比较1和2中哪一种情况下步骤最少,输出最少的步骤。
3.2实例演示
例: 容器A:3 ;容器B:5 待装水体积:4
A容器装满水倒入B容器中,此时: A:0 ;B:3
再将A容器装满水倒入B容器中,此时: A:1 ;B:5
B容器中水倒掉,A容器的水倒入B容器此时: A:0 ;B:1
再将A容器装满水倒入B容器中,此时: A:0 ;B:4
B容器中水的体积即为所求。将A,B容器互换重复以上操作。
#include实验三、计算几何算法的实现
(1) 将讲义第三章第三节中的凸包代码上机运行并检验结果。
(2) 完成讲义第三章的课后习题,上机运行并检验结果。
(3) 思考:
判线段相交时,如果有个线段的端点在另一条线段上,注意可能与另一条线段上的
端点重合,思考这样的情况怎么办。
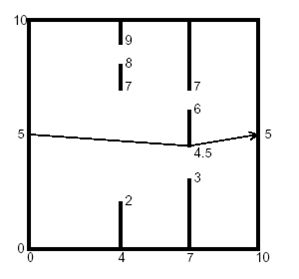
(4) 房间最短路问题:
给定一个内含阻碍墙的房间,求解出一条从起点到终点的最最短路径。房间的边界
固定在x=0,x=10,y=0 和y=10。起点和重点固定在(0,5)和(10,5)。房间里还有0 到8 个
墙,每个墙有两个门。输入给定的墙的个数,每个墙的x 位置和两个门的y 坐标区间,
输出最短路的长度。下图是个例子:
第三章课后习题(判断是否为多边形,求多边形面积)
1.1思路分析:
判断能否构成多边形,即判断是否存在两直线相交:两直线互相跨立;或一条线段的一个端点在另一条线段上
.求多边形面积:取一顶点与其它顶点相连,相邻的边做向量积再除以2;也就是求每个三角形的面积。
1.2解题详情
用poi[i].x poi[i].y表示第i个点(x,y); line[i].head line[i].tail表示第i条边从点head到点tail
inter(const line1& m, const line1& n)函数判断两直线是否相交
通过三角形两边矢量的叉乘求面积。
1.3源代码:
#include1.5思考:
若一线段端点在另一线段(除端点)上,则无法构成多边形;
若一线段端点与另一线段的端点重合,则可能构成多边形。但若三条线段端点重合则无法否成多边形。
房间最短路问题
2.1思路分析:
将起点,终点,每扇门的端点看成图的顶点。把这些点两两相连(若相连后线段与墙相交则不连)。即构成了图
问题转化成已知起点和终点的图求最短路问题。
2.2解题详情
judge(point p1, point p2)函数判断两点之间是否有墙隔开,也就是判断两直线是否相交。
floyd()函数求出图的最短路径。
2.3源代码:
#include实验四、动态规划算法的实现
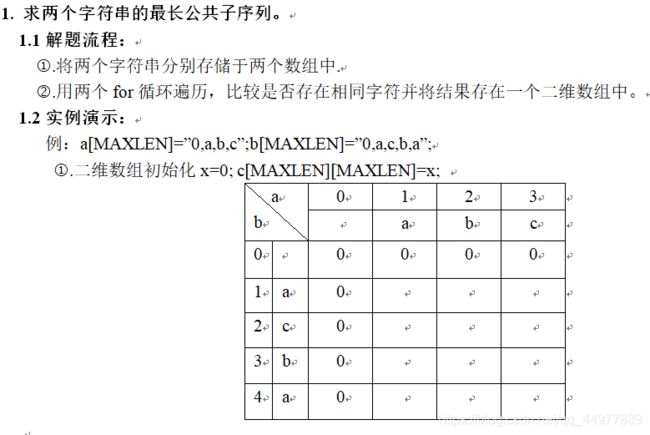
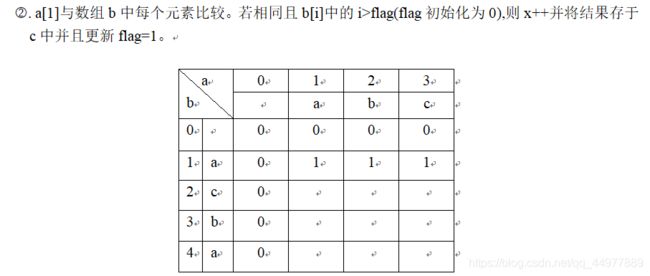
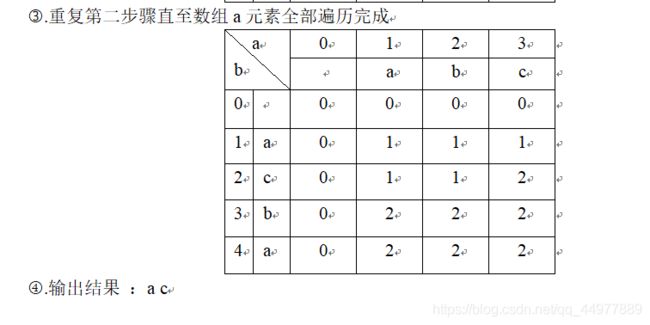
(1) 求两个字符串的最长公共子序列。
X 的一个子序列是相应于X 下标序列{1, 2, …, m}的一个子序列,求解两个序列的所有子序列中长度最大的,例如输入:pear, peach 输出:pea。
(2) 给定两个字符串a 和b,现将串a 通过变换变为串b,可用的操作为,删除串a 中的一个字符;在串a 的某个位置插入一个元素;将串a 中的某个字母换为另一个字母。对于任意的串a 和串b,输出最少多少次能够将串变为串b。
思考:输出变换的步骤。
(3) 输入一个矩阵,计算所有的子矩阵中和的最大值。
例如,输入
0 -2 -7 0
9 2 -6 2
-4 1 -4 1
-1 8 0 -2
输出为:15
思考:当矩阵很大时,比如100*100 的矩阵,你的程序还能够很快的得出结果吗,如果不能,请思考如何用动态规划的思想解决。
1.3源代码
#include - 串A变串B
2.1思路分析
定义一个二维数组D[i][j] 存储每一个对应的字符串A的前i个元素与字符串B的前j个元素的最小编辑距离D[i][j].
规律如下:D[i][j]=min(min(D[i-1][j]+1,D[i][j-1]+1),(A[j-1]==B[i-1]?D[i-1][j-1]: D[i-1][j-1]+1)); 从D[0][0]开始一直操作到了D [i][j]位置,其中删除操作肯定是str1比str2长,插入操作str1比str2短,我们所要做的是对D [i-1][j] 、D [i][j-1]、D [i-1][j-1]存的数进行比较,其中最小的就是当前str1和str2的编辑距离。
2.2源程序
#include 3.子矩阵最大和
3.1思路分析
将矩阵存入二维数组中,将二维数组第 i 行到第 j 行相同列的元素加起来,然后再当作一维数组来求解;
用b[i][j]记录第j列,0~i行的元素之和。那么当i>0时,要想得到第k列,从第i行到第j行的元素之和则通过计算 b[j][k]-b[i-1][k] 得到。当i==0时直接就是b[j][k]。
通过上述方法将二维转化为一维数组。再对这个一维数组用算法求子数组元素之和的最大值。不断的更新最大值,便是最终的结果。
#include 这里有完整的实验报告
CS·恰烂钱·恶心·DN 居然会根据下载量自动涨积分!!!
而且更改后又自动涨积分
祝~早日倒闭
资源连接点这里
既来之~
则赞之~