Sping-Spring表达式语言SpEL
- 概述
- SpEL:字面量
- SpEL:引用 Bean、属性和方法
- 引用其他对象
- 引用其他对象的属性
- 调用其他方法,还可以链式操作
- 调用静态方法或静态属性
- SpEL支持的运算符号
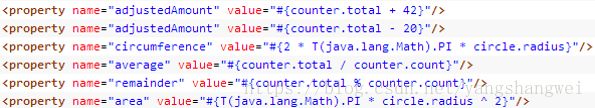
- 算数运算符:+, -, *, /, %, ^
- 加号还可以用作字符串连接
- 比较运算符: <, >, ==, <=, >=, lt, gt, eq, le, ge
- 逻辑运算符号: and, or, not, |
- if-else 运算符:?: (ternary), ?: (Elvis)
- if-else 的变体
- 正则表达式:matches
- 示例-基于xml的方式
- 示例-基于注解的方式
概述
Spring 表达式语言(简称SpEL):是一个支持运行时查询和操作对象图的强大的表达式语言。
语法类似于 EL:SpEL 使用 #{…} 作为定界符,所有在大框号中的字符都将被认为是 SpEL
SpEL 为 bean 的属性进行动态赋值提供了便利.
通过 SpEL 可以实现:
通过 bean 的 id 对 bean 进行引用
调用方法以及引用对象中的属性
计算表达式的值
正则表达式的匹配
SpEL:字面量
字面量的表示:
整数:
<property name="count" value="#{5}"/>
小数:
<property name="frequency" value="#{89.7}"/>
科学计数法:
<property name="capacity" value="#{1e4}"/>
String可以使用单引号或者双引号作为字符串的定界符号:
<property name=“name” value="#{'Chuck'}"/>
或
<property name='name' value='#{"Chuck"}'/>
Boolean:
<property name="enabled" value="#{false}"/>
如果仅仅是表示字面量,其实是没有必要使用Spring EL表达式的,这里仅仅演示一下而已,日常的开发中很少使用。
SpEL:引用 Bean、属性和方法
引用其他对象
但是我们更常用ref 来实现其他对象的引用
引用其他对象的属性
调用其他方法,还可以链式操作
调用静态方法或静态属性
通过 T() 调用一个类的静态方法,它将返回一个 Class Object,然后再调用相应的方法或属性:
SpEL支持的运算符号
算数运算符:+, -, *, /, %, ^
加号还可以用作字符串连接
比较运算符: <, >, ==, <=, >=, lt, gt, eq, le, ge
![]()
![]()
逻辑运算符号: and, or, not, |
if-else 运算符:?: (ternary), ?: (Elvis)
![]()
if-else 的变体
正则表达式:matches
![]()
示例-基于xml的方式
package com.xgj.spel;
/**
*
*
* @ClassName: Address
*
* @Description: 地址信息
*
* @author: Mr.Yang
*
* @date: 2018年4月7日 下午8:29:12
*/
public class Address {
private String city;
private String street;
public String getCity() {
return city;
}
public void setCity(String city) {
this.city = city;
}
public String getStreet() {
return street;
}
public void setStreet(String street) {
this.street = street;
}
@Override
public String toString() {
return "Address [city=" + city + ", street=" + street + ", getClass()=" + getClass() + ", hashCode()=" + hashCode() + ", toString()=" + super.toString() + "]";
}
}
package com.xgj.spel;
/**
*
*
* @ClassName: Car
*
* @Description: 车辆
*
* @author: Mr.Yang
*
* @date: 2018年4月7日 下午8:30:01
*/
public class Car {
private String brand;
private double price;
// 调用静态方法或静态属性:通过 T() 调用一个类的静态方法,它将返回一个 Class Object,然后再调用相应的方法或属性
private long weight;
public long getWeight() {
return weight;
}
public void setWeight(long weight) {
this.weight = weight;
}
public String getBrand() {
return brand;
}
public void setBrand(String brand) {
this.brand = brand;
}
public double getPrice() {
return price;
}
public void setPrice(double price) {
this.price = price;
}
@Override
public String toString() {
return "Car [brand=" + brand + ", price=" + price + ", weight=" + weight + "]";
}
}
package com.xgj.spel;
public class Boss {
private String name;
private Car car;
// 通过 Spring El 引用 Address的city
private String city;
// 通过 Car的price属性,确定info ,如果car.price>=500000 ,info 为CEO,否则为 Staff
private String info;
public String getName() {
return name;
}
public void setName(String name) {
this.name = name;
}
public Car getCar() {
return car;
}
public void setCar(Car car) {
this.car = car;
}
public String getCity() {
return city;
}
public void setCity(String city) {
this.city = city;
}
public String getInfo() {
return info;
}
public void setInfo(String info) {
this.info = info;
}
@Override
public String toString() {
return "Boss [name=" + name + ", car=" + car + ", city=" + city + ", info=" + info + "]";
}
}
配置文件:
<beans xmlns="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans"
xmlns:xsi="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance" xmlns:p="http://www.springframework.org/schema/p"
xsi:schemaLocation="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans/spring-beans.xsd">
<bean id="car" class="com.xgj.spel.Car"
p:brand="Bench"
p:price="700000"
p:weight="#{T(java.lang.Math).PI * 4567}" />
<bean id="address" class="com.xgj.spel.Address"
p:city="#{'NanJing'}"
p:street="RuanJianDaDao" />
<bean id="boss" class="com.xgj.spel.Boss"
p:name="Artisan"
p:city="#{address.city}"
p:car-ref="car"
p:info="#{car.price > 500000 ? 'CEO' : 'staff'}" />
beans>
测试类:
package com.xgj.spel;
import org.springframework.context.ApplicationContext;
import org.springframework.context.support.ClassPathXmlApplicationContext;
public class SpelTest {
public static void main(String[] args) {
String configLocation = "com/xgj/spel/beans_spel.xml";
ApplicationContext ctx = new ClassPathXmlApplicationContext(configLocation);
Car car = (Car) ctx.getBean("car");
System.out.println(car);
Boss boss = (Boss) ctx.getBean("boss");
System.out.println(boss);
}
}
结果:
2018-04-07 21:21:30,804 INFO [main] (AbstractApplicationContext.java:583) - Refreshing org.springframework.context.support.ClassPathXmlApplicationContext@4af6178d: startup date [Sat Apr 07 21:21:30 BOT 2018]; root of context hierarchy
2018-04-07 21:21:30,907 INFO [main] (XmlBeanDefinitionReader.java:317) - Loading XML bean definitions from class path resource [com/xgj/spel/beans_spel.xml]
Car [brand=Bench, price=700000.0, weight=14347]
Boss [name=Artisan, car=Car [brand=Bench, price=700000.0, weight=14347], city=NanJing, info=CEO]
示例-基于注解的方式
我们通过一个数据库的例子来演示。虽然可以通过Spring El 表达式从配置文件中加载一个参数值,比如
@Value("#{properties['jdbc.driverClassName']}")是不是容易出错…. Spring提供了更好的方式 context:property-placeholder。
package com.xgj.spel.annotation;
import org.springframework.beans.factory.annotation.Value;
import org.springframework.stereotype.Component;
/**
*
*
* @ClassName: MyDataSource
*
* @Description: 数据源 @Component标注
*
* @author: Mr.Yang
*
* @date: 2018年4月7日 下午9:26:32
*/
@Component
public class MyDataSource {
private String driverClass;
private String url;
private String username;
private String password;
public String getDriverClass() {
return driverClass;
}
/**
*
*
* @Title: setDriverClass
*
* @Description: @Value注解自动注入属性配置文件中对应属性的值
*
* @param driverClass
*
* @return: void
*/
@Value("${jdbc.driverClassName}")
public void setDriverClass(String driverClass) {
this.driverClass = driverClass;
}
public String getUrl() {
return url;
}
@Value("${jdbc.url}")
public void setUrl(String url) {
this.url = url;
}
public String getUsername() {
return username;
}
// @Value("$(jdbc.username)")
@Value("${jdbc.username}")
public void setUsername(String username) {
this.username = username;
}
public String getPassword() {
return password;
}
@Value("${jdbc.password}")
public void setPassword(String password) {
this.password = password;
}
@Override
public String toString() {
return "MyDataSource [driverClass=" + driverClass + ", url=" + url + ", username=" + username + ", password=" + password + "]";
}
}
<beans xmlns="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans"
xmlns:xsi="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance"
xmlns:p="http://www.springframework.org/schema/p"
xmlns:context="http://www.springframework.org/schema/context"
xsi:schemaLocation="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans/spring-beans.xsd
http://www.springframework.org/schema/context http://www.springframework.org/schema/context/spring-context-4.3.xsd">
<context:component-scan base-package="com.xgj.spel.annotation"/>
<context:property-placeholder location="classpath:mysql/db_mysql.properties"/>
beans>
db_mysql.properties
jdbc.driverClassName=com.mysql.jdbc.Driver
jdbc.url=jdbc:mysql://localhost:3306/artisan
jdbc.username=artisan
jdbc.password=artisanpackage com.xgj.spel.annotation;
import org.junit.Test;
import org.springframework.context.ApplicationContext;
import org.springframework.context.support.ClassPathXmlApplicationContext;
public class TestCase {
@Test
public void test() {
String configurationLocation = "com/xgj/spel/annotation/beans_anno.xml";
ApplicationContext ctx = new ClassPathXmlApplicationContext(configurationLocation);
MyDataSource myDataSource = (MyDataSource) ctx.getBean("myDataSource");
System.out.println(myDataSource);
System.out.println("driverClassName:" + myDataSource.getDriverClass());
System.out.println("url:" + myDataSource.getUrl());
System.out.println("username:" + myDataSource.getUsername());
System.out.println("password:" + myDataSource.getPassword());
}
}
运行结果
2018-04-07 23:37:11,409 INFO [main] (AbstractApplicationContext.java:583) - Refreshing org.springframework.context.support.ClassPathXmlApplicationContext@761df304: startup date [Sat Apr 07 23:37:11 BOT 2018]; root of context hierarchy
2018-04-07 23:37:11,552 INFO [main] (XmlBeanDefinitionReader.java:317) - Loading XML bean definitions from class path resource [com/xgj/spel/annotation/beans_anno.xml]
MyDataSource [driverClass=com.mysql.jdbc.Driver, url=jdbc:mysql://localhost:3306/artisan, username=artisan, password=artisan]
driverClassName:com.mysql.jdbc.Driver
url:jdbc:mysql://localhost:3306/artisan
username:artisan
password:artisan