【Java / python】高精度数运算(大数类)训练
- 前言
- 【HDU 1002】 A + B Problem II(大数相加)
- 【HDU 1042】 N!(大数阶乘)
- 【HDU 1047】 Integer Inquiry(大数加法)
- 【HDU 1063】 Exponentiation(实数高精度幂)
- 【HDU 1133】 Buy the Ticket(卡特兰数)
- 【HDU 1250】 Hat's Fibonacci(斐波那契数)
- 【HDU 1297】 Children’s Queue(大数+递推)
- 【HDU 1316】 How Many Fibs?(大数 + 斐波那契数列)
- 【HDU 1715】 大菲波数(斐波那契数列)
- 【HDU 1753】 大明A+B(大浮点数类)
- 【HDU 1865】 1sting(斐波那契数列)
- 【HDU 5666】 Segment(大数除法 + 取余)
- 【HDU 5686】 Problem B(斐波那契数列 + 大数)
前言
Java 知识点:
- 在JAVA中有两个类BigInteger和BigDecimal分别表示大整数类和大浮点数类,至于两个类的对象能表示最大范围不清楚,理论上能够表示无限大的数,只要计算机内存足够大。这两个类都在java.math.*包中,因此每次必须在开头处引用该包。
Ⅰ.基本函数:
1.valueOf(parament); 将参数转换为制定的类型
比如 int a=3;
BigInteger b=BigInteger.valueOf(a);
则b=3;
String s=”12345”;
BigInteger c=BigInteger.valueOf(s);
则c=12345;
2.add(); 大整数相加
BigInteger a=new BigInteger(“23”);
BigInteger b=new BigInteger(“34”);
a.add(b);
3.subtract(); 相减
4.multiply(); 相乘
5.divide(); 相除取整
6.remainder(); 取余
7.pow(); a.pow(b)=a^b
8.gcd(); 最大公约数
9.abs(); 绝对值
10.negate(); 取反数
11.mod(); a.mod(b)=a%b=a.remainder(b);
12.max(); min();
13.punlic int comareTo();
14.boolean equals(); 是否相等
15.BigInteger构造函数:
一般用到以下两种:
BigInteger(String val);
将指定字符串转换为十进制表示形式;
BigInteger(String val,int radix);
将指定基数的 BigInteger 的字符串表示形式转换为 BigInteger
Ⅱ.基本常量:
A=BigInteger.ONE 1
B=BigInteger.TEN 10
C=BigInteger.ZERO 0
Ⅲ.Java中高精度实数类 BigDecimal
BigDecimal add(BigDecimal augend) :加法
BigDecimal subtract(BigDecimal subtrahend) :减法
BigDecimal multiply(BigDecimal multiplicand) :乘法
BigDecimal divide(BigDecimal divisor) :除法
BigDecimal pow(int n) :乘幂
BigDecimal stripTrailingZeros() 移除小数所有尾部零,如果小数部分全是 0 则小数点也会移除
BigDecimal toPlainString() 返回字符串表示形式,不用科学计数法表示
toString() 会变成科学计数法输出
【HDU 1002】 A + B Problem II(大数相加)
原题链接: http://acm.hdu.edu.cn/showproblem.php?pid=1002
题意: 大整数类加法运算。
思路: 注意输出格式要求,例子之间换行,最后一个例子不用换行。
Code(Java):
import java.util.Scanner;
import java.math.*;
public class Main {
public static void main(String[] args) {
Scanner in = new Scanner(System.in);
int t = in.nextInt();
for(int i=1;i<=t;i++) {
BigInteger a = in.nextBigInteger();
BigInteger b = in.nextBigInteger();
System.out.println("Case " + i + ":");
System.out.println(a + " + " + b + " = " + a.add(b));
if(i!=t)
System.out.println();
}
}
}
Code(Python):
n = int(input())
for i in range(1,n+1):
s = input().split()
print("Case %d:" %(i))
print("%d + %d = %d" %(int(s[0]),int(s[1]),(int(s[0])+int(s[1]))))
if i!=n:
print()
【HDU 1042】 N!(大数阶乘)
原题链接: http://acm.hdu.edu.cn/showproblem.php?pid=1042
题意: 大整数类的阶乘
思路: 直接 Java 或 Python 暴力模拟。
Code(Java):
import java.util.Scanner;
import java.math.*;
public class Main {
public static void main(String[] args) {
Scanner in = new Scanner(System.in);
while(in.hasNext()) {
int n = in.nextInt();
BigInteger ans = BigInteger.ONE;
for(int i=1; i<=n; i++)
ans = ans.multiply(BigInteger.valueOf(i));
System.out.println(ans);
}
}
}
Code(Python):
while True:
try:
n=int(input())
ans=1
for i in range(1,n+1):
ans*=i
print(ans)
except:
break
【HDU 1047】 Integer Inquiry(大数加法)
原题链接: http://acm.hdu.edu.cn/showproblem.php?pid=1047
-
题意: 大数加法,首先输入测试组数,接着每组数据不断输入,直到输入 0 才停止输入。输出的每组之间要留一行空行,最后一组不用输出空行。
-
思路: 水题,直接 Java 输出即可,注意输出格式。
Code(Java):
import java.math.BigInteger;
import java.util.*;
public class Main {
public static void main(String[] args) {
Scanner cin = new Scanner(System.in);
int t = cin.nextInt();
while(t-- >0) {
BigInteger ans = BigInteger.ZERO;
while(cin.hasNextBigInteger()) {
BigInteger a = cin.nextBigInteger();
if(a.compareTo(BigInteger.ZERO)==0) {
System.out.println(ans);
if(t!=0) {
System.out.println();
break;
}
}
else ans = ans.add(a);
}
}
}
}
【HDU 1063】 Exponentiation(实数高精度幂)
原题链接: http://acm.hdu.edu.cn/showproblem.php?pid=1063
-
题意: 给你一个 0.0 ~ 99.999 的小数 R 和 0 ~ 25 的整数 n 让你求 R^n 高精度,最后输出结果要去掉整数部分前缀0和小数部分后缀 0,如果是整数的话不输出小数点,同时不能显示为科学计数法。
-
思路: 直接调用 Java 库函数即可。BigDecimal stripTrailingZeros() 移除小数所有尾部零的,若小数部分全是 0 ,则小数点也会移除;BigDecimal toPlainString() 返回字符串,直接显示,不用科学计数法表示。
Code(Java):
import java.util.*;
import java.math.*;
public class Main {
public static void main(String[] args) {
Scanner cin = new Scanner(System.in);
while(cin.hasNext()) {
BigDecimal r = cin.nextBigDecimal();
int n = cin.nextInt();
String str = r.pow(n).stripTrailingZeros().toPlainString();
while(str.charAt(0)=='0') //删掉前缀零
str = str.substring(1);
System.out.println(str);
}
}
}
【HDU 1133】 Buy the Ticket(卡特兰数)
原题链接: http://acm.hdu.edu.cn/showproblem.php?pid=1133
题意: 电影票每张50块,有m个人手里只有50块,n个人手里只有100块,售票厅开始没有钱。如果售票厅没有50块零钱,则持有100块的人买不了票。问,有多少种排队的方式,可以让每个人都买上票。
思路: 卡特兰数的变形题,这道题可以分为两种情况:
-
当m
-
当m>=n的时候:用0代表手里只有50块的人,1代表手里只有100块的人。
假设 m=4,n=3 的一个序列:0110100 ,显然第二个1的位置就开始不合法了。
那么,把所有的0换为1,所有的1换为0,变为:1001011,仍然不合法,但这里要说明的是:每一个不合法的序列都可以由另一个序列得到,所以 不能满足的条件的情况共有C(m+1,m+n)种。
合法的排列数 = 所有排列数 - 不合法的排列数,即 C(m,m+n) - C(m+1,m+n)
又因为每个人都是不同的,所以排列数公式为: F(N) = (C(m,m+n) - C(m+1,m+n)) * m! * n!
化简得:F(N) = (m+n)!*(m-n+1)/(m+1)
Code(Java):
import java.util.Scanner;
import java.math.*;
public class Main {
public static void main(String[] args) {
Scanner cin = new Scanner(System.in);
int t=1;
while(cin.hasNext()) {
int m = cin.nextInt();
int n = cin.nextInt();
if(m==0 && n==0)
break;
BigInteger ans = BigInteger.ONE;
if(m<n)
ans = BigInteger.ZERO;
else {
for(int i=1;i<=n+m;i++)
ans = ans.multiply(BigInteger.valueOf(i));
ans = ans.multiply(BigInteger.valueOf(m-n+1));
ans = ans.divide(BigInteger.valueOf(m+1));
}
System.out.println("Test #" + t + ":");
System.out.println(ans);
t++;
}
}
}
Code(Python):
t=1
while True:
s=input().split()
ans=1
if(int(s[0])==0 & int(s[1])==0):
break
if(s[0]<s[1]):
ans=0
else:
for i in range(1,int(s[0])+int(s[1])+1):
ans*=i
ans=ans*(int(s[0])-int(s[1])+1)/(int(s[0])+1)
print("Test #%d:"%t)
print(int(ans))
t=t+1
【HDU 1250】 Hat’s Fibonacci(斐波那契数)
原题链接: http://acm.hdu.edu.cn/showproblem.php?pid=1250
题意: 斐波那契数。
思路: 简单的大数相加问题。
Code(Java):
import java.util.Scanner;
import java.math.*;
public class Main {
public static void main(String[] args) {
BigInteger[] f = new BigInteger[20000];
f[0] = BigInteger.ONE;
f[1] = BigInteger.ONE;
f[2] = BigInteger.ONE;
f[3] = BigInteger.ONE;
for(int i=4; i<=10000; i++)
f[i] = f[i-1].add(f[i-2]).add(f[i-3]).add(f[i-4]);
Scanner cin = new Scanner(System.in);
while(cin.hasNext()) {
int n = cin.nextInt();
System.out.println(f[n-1]);
}
}
}
Code(Python):
a=[0]*10010
a[0]=1
a[1]=1
a[2]=1
a[3]=1
for i in range(4,10000):
a[i]=a[i-1]+a[i-2]+a[i-3]+a[i-4]
while True:
try:
n=int(input())
print(a[n-1])
except:
break
【HDU 1297】 Children’s Queue(大数+递推)
原题链接: http://acm.hdu.edu.cn/showproblem.php?pid=1297
题意: n个学生排队,要求女生不能单独站一起,即要么队伍中没有女生,要么两个及两个以上的女生站一起。求n个学生的男女排队方式有多少种。
思路: 用 f(n) 表示n个人的合法队列,而最后一个人要么是男要么是女的,所以可以分为两大类来分析:
- 如果合法队列的最后一个人是男,要使队列合法,那么前n-1个人组成的队列必须合法,这种情况一共有f(n-1)种。
- 如果合法队列的最后一个人是女,要使队列合法,第n-1个人必须是女生,再分析前n-2个人,有两种情况:
a. 前n-2个人组成的队列合法,则后面再加两个女生,也一定是合法的,这种情况有f(n-2)种。
b. 前n-2个人组成的队列不合法,但加上两个女生也可能变为合法队列,即第n-3个人是男,第n-2个人是女,而前面的队列合法,这样最后会有三个女的一起,即为合法队列,有f(n-4)种。
综上所述,一共有 f(n) = f(n-1) + f(n-2) + f(n-4) 种情况。
Code(Java):
import java.util.Scanner;
import java.math.*;
public class Main {
public static void main(String[] args) {
BigInteger[] f = new BigInteger[1050];
f[0] = BigInteger.valueOf(1);
f[1] = BigInteger.valueOf(2);
f[2] = BigInteger.valueOf(4);
f[3] = BigInteger.valueOf(7);
for(int i=4; i<=1025; i++)
f[i] = f[i-1].add(f[i-2]).add(f[i-4]);
Scanner cin = new Scanner(System.in);
while(cin.hasNext()) {
int n = cin.nextInt();
System.out.println(f[n-1]);
}
}
}
Code(Python):
f=[0]*1050
f[0]=1
f[1]=2
f[2]=4
f[3]=7
for i in range(4,1025):
f[i]=f[i-1]+f[i-2]+f[i-4]
while True:
try:
n=int(input())
print(f[n-1])
except:
break
【HDU 1316】 How Many Fibs?(大数 + 斐波那契数列)
原题链接: http://acm.hdu.edu.cn/showproblem.php?pid=1316
题意: 给一个区间,求区间内斐波那契数的数量。
思路: 直接暴力遍历,比较。
Code(Java):
import java.math.BigInteger;
import java.util.Scanner;
public class Main {
public static void main(String[] args) {
BigInteger[] f = new BigInteger[10010];
f[1] = new BigInteger("1");
f[2] = new BigInteger("2");
for(int i=3;i<=10000;i++)
f[i] = f[i-1].add(f[i-2]);
Scanner cin = new Scanner(System.in);
while(cin.hasNext()) {
int ans=0;
BigInteger a = cin.nextBigInteger();
BigInteger b = cin.nextBigInteger();
if(a.compareTo(BigInteger.ZERO)==0 && b.compareTo(BigInteger.ZERO)==0)
break;
for(int i=1;i<=10000;i++) {
if(a.compareTo(f[i])<=0 && b.compareTo(f[i])>=0)
ans++;
if(b.compareTo(f[i])<0)
break;
}
System.out.println(ans);
}
}
}
【HDU 1715】 大菲波数(斐波那契数列)
原题链接: http://acm.hdu.edu.cn/showproblem.php?pid=1715
题意: 求斐波那契数列
思路: 直接打表。
Code(Java):
import java.util.Scanner;
import java.math.*;
public class Main {
public static void main(String[] args) {
BigInteger[] f = new BigInteger[1050];
f[0] = BigInteger.ONE;
f[1] = BigInteger.ONE;
for(int i=2; i<=1030;i++)
f[i] = f[i-1].add(f[i-2]);
Scanner cin = new Scanner(System.in);
int n = cin.nextInt();
while(n-- >0) {
int x = cin.nextInt();
System.out.println(f[x-1]);
}
}
}
Code(Python):
a=[0 for i in range(1050)]
a[0]=a[1]=1
for i in range(2,1030):
a[i]=a[i-1]+a[i-2]
n=int(input())
for i in range(n):
x=int(input())
print(a[x-1])
【HDU 1753】 大明A+B(大浮点数类)
原题链接: http://acm.hdu.edu.cn/showproblem.php?pid=1753
题意: 大浮点数加法
思路: 注意下要求最简形式,可能会出现4.0或者1e5等形式:
- stripTrailingZeros():用来去掉末尾的0。
- toPlainString():转成普遍计数法输出,即不会使数字变成了科学计数法,例如 1e5。
Code(Java):
import java.util.Scanner;
import java.math.*;
public class Main {
public static void main(String[] args) {
Scanner cin = new Scanner(System.in);
while(cin.hasNext()) {
BigDecimal a = cin.nextBigDecimal();
BigDecimal b = cin.nextBigDecimal();
System.out.println(a.add(b).stripTrailingZeros().toPlainString());
}
}
}
【HDU 1865】 1sting(斐波那契数列)
原题链接: http://acm.hdu.edu.cn/showproblem.php?pid=1865
-
题意: 斐波那契数列
-
思路: 要注意的一点就是,会先输入一个n,表示实例个数,但输入后剩下一个换行符,而 nextLine() 会吸收掉剩下的换行符,所以,要用 next() 来输入字符串,因为其不会吸收换行符和空格。
Code(Java):
import java.util.Scanner;
import java.math.*;
public class Main {
public static void main(String[] args) {
BigInteger[] f = new BigInteger[101000];
f[0] = BigInteger.ONE;
f[1] = BigInteger.ONE;
for(int i=2; i<=1020;i++)
f[i] = f[i-1].add(f[i-2]);
Scanner cin = new Scanner(System.in);
int n = cin.nextInt();
// 这里多了一个换行符,故后面使用next() 来输入字符串
while(n-- >0) {
String s = cin.next();
System.out.println(f[s.length()]);
}
}
}
【HDU 5666】 Segment(大数除法 + 取余)
原题链接: http://acm.hdu.edu.cn/showproblem.php?pid=5666
-
题意: 给定 T 组数据,每组数据给定 q 和 P,问直线 x + y = q 在第一象限形成的三角形内部有多少个整数点,结果对P取模。
-
思路:
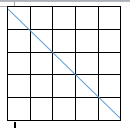
由图可知,三角形内部的整数点共有 1 + 2 + 3 + . . . + ( q − 2 ) 1+2+3+...+(q-2) 1+2+3+...+(q−2)可得出公式 ( q − 1 ) ( q − 2 ) 2 {(q-1)(q-2)\over 2} 2(q−1)(q−2)
Code(Java):
import java.math.*;
import java.util.*;
public class Main {
public static void main(String[] args) {
Scanner cin = new Scanner(System.in);
int t = cin.nextInt();
while(t-- >0) {
BigInteger q = cin.nextBigInteger();
BigInteger p = cin.nextBigInteger();
BigInteger a = q.subtract(BigInteger.ONE);
BigInteger b = q.subtract(BigInteger.valueOf(2));
System.out.println(a.multiply(b).divide(BigInteger.valueOf(2)).remainder(p));
}
}
}
【HDU 5686】 Problem B(斐波那契数列 + 大数)
原题链接: http://acm.hdu.edu.cn/showproblem.php?pid=5686
-
题意: 给一个长度 n ,长度为 n 的全 1 序列,相邻的两个 1 可以合并,问可以构成多少种不同的序列。
-
思路: 当我们要求 f[n] 时,可以考虑为前 n-1 个 1 的情况又加了一个 1 。此时有两种情况:当不使用第 n 个 1 进行合并时,就有 f[n-1] 个序列;当使用第 n 个 1 进行合并时,就有 f[n-2] 个序列。所以 f[n] = f[n-1] + f[n-2] 。
Code(Java):
import java.util.*;
import java.math.*;
public class Main {
static BigInteger[] f = new BigInteger[205];
public static void main(String[] args) {
Scanner cin = new Scanner(System.in);
f[1] = BigInteger.ONE;
f[2] = BigInteger.valueOf(2);
for(int i=3;i<=200;i++)
f[i] = f[i-1].add(f[i-2]);
while(cin.hasNext()) {
int n = cin.nextInt();
System.out.println(f[n]);
}
}
}