【算法】B树的Java源码实现及Princeton版本源码理解
2019.02.24
文章目录
- 前言
- B树例子
- Princeton版本源码理解
- 哨兵
- 源码
- 基于Princeton的修改版本
- 相同的哨兵,不同的结点
- 源码
前言
想在业余时间做个小工具,设计是不使用数据库,而是用文件系统来存储数据。为了减少文件打开次数,提高索引效率,用B树构建内存索引。B的原理就不介绍了,提供如下链接供扩展阅读:
- Princeton算法课程slide:https://www.cs.princeton.edu/~rs/AlgsDS07/09BalancedTrees.pdf
- Princeton版本的B树Java实现(可直接使用,本文会添加配图说明和添加代码中文注释):
https://algs4.cs.princeton.edu/code/edu/princeton/cs/algs4/BTree.java.html - B树可视化:
https://www.cs.usfca.edu/~galles/visualization/BTree.html
网上很多博客都直接复制了Princeton版本的代码,但Princeton版源码生成的B树,叶子节点上都有哨兵,跟手绘出来的B树不太相同,所以撰写本文予以说明。同时,为了构建出与可视化出来更像的B树,我对Princeton版本源码略加修改,实现了自己的版本,在本文会有较多附图说明三者之间的区别。
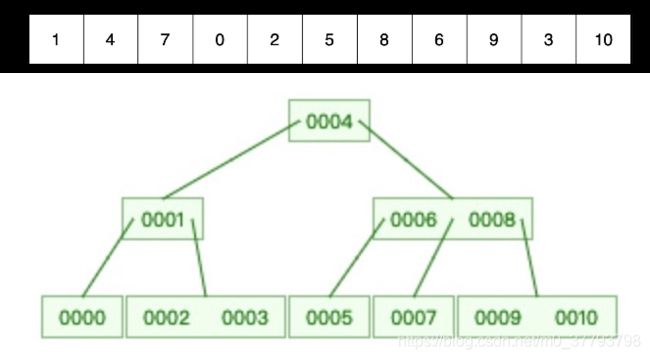
B树例子
Princeton版本源码理解
哨兵
Princeton版本的BTree实现,采用了哨兵,使得任意一个结点(包含key1, …, keyi, …, keym),keyi对应子结点内的所有key值都>=keyi,并且都小于key(i+1)。采用哨兵的数据结构有效地简化了代码。
对于上一节的B树例子,采用Princeton版本源码生成的B树如下图所示:

源码
public class PrincetonBTree<Key extends Comparable<Key>, Value> {
// max children per B-tree node = M-1
// (must be even and greater than 2)
private static final int M = 4;
private Node root; // root of the B-tree
private int height; // height of the B-tree
private int n; // number of key-value pairs in the B-tree
// helper B-tree node data type
private static final class Node {
private int m; // number of children
private Entry[] children = new Entry[M]; // the array of children
// create a node with k children
private Node(int k) {
m = k;
}
}
// internal nodes: only use key and next
// external nodes: only use key and value
// 因此,当索引key时,要获取value都只能在外部结点中获得
private static class Entry {
private Comparable key;
private final Object val;
private Node next; // helper field to iterate over array entries
public Entry(Comparable key, Object val, Node next) {
this.key = key;
this.val = val;
this.next = next;
}
}
/**
* Initializes an empty B-tree.
*/
public PrincetonBTree() {
root = new Node(0);
}
/**
* Returns true if this symbol table is empty.
* @return {@code true} if this symbol table is empty; {@code false} otherwise
*/
public boolean isEmpty() {
return size() == 0;
}
/**
* Returns the number of key-value pairs in this symbol table.
* @return the number of key-value pairs in this symbol table
*/
public int size() {
return n;
}
/**
* Returns the height of this B-tree (for debugging).
*
* @return the height of this B-tree
*/
public int height() {
return height;
}
/**
* Returns the value associated with the given key.
*
* @param key the key
* @return the value associated with the given key if the key is in the symbol table
* and {@code null} if the key is not in the symbol table
* @throws IllegalArgumentException if {@code key} is {@code null}
*/
public Value get(Key key) {
if (key == null) throw new IllegalArgumentException("argument to get() is null");
return search(root, key, height);
}
private Value search(Node x, Key key, int ht) {
Entry[] children = x.children;
// external node
if (ht == 0) {
for (int j = 0; j < x.m; j++) {
if (eq(key, children[j].key)) return (Value) children[j].val;
}
}
// internal node
else {
for (int j = 0; j < x.m; j++) {
if (j+1 == x.m || less(key, children[j+1].key))
return search(children[j].next, key, ht-1);
}
}
return null;
}
/**
* Inserts the key-value pair into the symbol table, overwriting the old value
* with the new value if the key is already in the symbol table.
* If the value is {@code null}, this effectively deletes the key from the symbol table.
*
* @param key the key
* @param val the value
* @throws IllegalArgumentException if {@code key} is {@code null}
*/
public void put(Key key, Value val) {
if (key == null) throw new IllegalArgumentException("argument key to put() is null");
Node node = insert(root, key, val, height);
n++;
if (node == null) return;
// need to split root
Node newRoot = new Node(2);
newRoot.children[0] = new Entry(root.children[0].key, null, root);
newRoot.children[1] = new Entry(node.children[0].key, null, node);
root = newRoot;
height++;
}
private Node insert(Node node, Key key, Value val, int height) {
int index;
Entry entry = new Entry(key, val, null);
// external node
if (height == 0) {
for (index = 0; index < node.m; index++) {
if (less(key, node.children[index].key)) break;
}
}
// internal node
else {
for (index = 0; index < node.m; index++) {
if ((index+1 == node.m) || less(key, node.children[index+1].key)) {
Node splitNode = insert(node.children[index++].next, key, val, height-1);
if (splitNode == null) return null;
entry.key = splitNode.children[0].key;
entry.next = splitNode;
break;
}
}
}
for (int i = node.m; i > index; i--)
node.children[i] = node.children[i-1];
node.children[index] = entry;
node.m++;
if (node.m < M) return null;
else return split(node);
}
// split node in half
private Node split(Node h) {
Node t = new Node(M/2);
h.m = M/2;
for (int j = 0; j < M/2; j++)
t.children[j] = h.children[M/2+j];
return t;
}
/**
* Returns a string representation of this B-tree (for debugging).
*
* @return a string representation of this B-tree.
*/
public String toString() {
return toString(root, height, "") + "\n";
}
private String toString(Node h, int ht, String indent) {
StringBuilder s = new StringBuilder();
Entry[] children = h.children;
if (ht == 0) {
for (int j = 0; j < h.m; j++) {
s.append(indent + children[j].key + " " + children[j].val + "\n");
}
}
else {
for (int j = 0; j < h.m; j++) {
if (j > 0) s.append(indent + "(" + children[j].key + ")\n");
s.append(toString(children[j].next, ht-1, indent + " "));
}
}
return s.toString();
}
// comparison functions - make Comparable instead of Key to avoid casts
private boolean less(Comparable k1, Comparable k2) {
return k1.compareTo(k2) < 0;
}
private boolean eq(Comparable k1, Comparable k2) {
return k1.compareTo(k2) == 0;
}
/**
* Unit tests the {@code BTree} data type.
*
* @param args the command-line arguments
*/
public static void main(String[] args) {
PrincetonBTree<Double, String> bTree = new PrincetonBTree<Double, String>();
bTree.put(1D, "test1");
bTree.put(4D, "test4");
bTree.put(7D, "test7");
bTree.put(0D, "test0");
bTree.put(2D, "test2");
bTree.put(5D, "test5");
bTree.put(8D, "test8");
bTree.put(6D, "test6");
bTree.put(9D, "test9");
bTree.put(3D, "test3");
bTree.put(10D, "test10");
System.out.println(bTree.get(-1D));
System.out.println(bTree.get(0D));
System.out.println(bTree.get(1D));
System.out.println(bTree.get(2D));
System.out.println(bTree.get(2.5D));
System.out.println(bTree.get(3D));
System.out.println(bTree.get(4D));
System.out.println(bTree.get(5D));
System.out.println(bTree.get(6D));
System.out.println(bTree.get(7D));
System.out.println(bTree.get(8D));
System.out.println(bTree.get(9D));
System.out.println(bTree.get(10D));
System.out.println(bTree.get(11D));
}
}
基于Princeton的修改版本
相同的哨兵,不同的结点
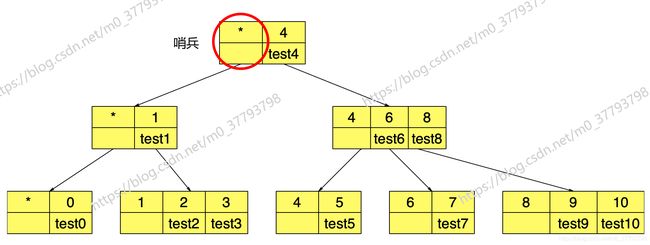
Princeton版本的BTree,显然,要查找key对应的value值,都必要索引到叶子结点才能得到,其原因是因为它区分了内部结点和外部结点。而在我修改的版本里,同样也采用了哨兵,但结点不区分内部与外部结点,除了哨兵没有value之外,所有非叶子结点既有value又有子结点。比如同样是查找4的value值,Princeton的B树要递归3次,而我修改的版本在根结点即可获得。
下图是对于同一个B树例子,用我修改的版本所生成的B树。对比三张图,可以明显地发现,Princeton版本的代码生成的B树跟我们手绘出来的是不一样的;而我修改的版本所生成的B树,和“B树例子”里是完成相同的,只是每个结点多了个哨兵。
源码
public class BTreeWithSentinel<Key extends Comparable, Value> {
private static final int M = 4;
private static final int M_WITH_SENTINEL = M + 1;
private Node root;
private int height;
BTreeWithSentinel() {
this.root = new Node(1);
this.root.keys[0] = new Entry(null, null, null);
this.height = 0;
}
public static final class Node {
Entry[] keys = new Entry[M_WITH_SENTINEL];
int size = 0;
Node(int size) {
this.size = size;
}
}
public static final class Entry {
Comparable key;
Object value;
Node next;
Entry(Comparable key, Object value, Node next) {
this.key = key;
this.value = value;
this.next = next;
}
}
public void put(Key key, Value value) {
Node newNode = insert(this.root, key, value, this.height);
if (newNode == null) {
return;
}
Node newRoot = new Node(2);
newRoot.keys[0] = new Entry(null, null, root);
newRoot.keys[1] = new Entry(newNode.keys[0].key, newNode.keys[0].value, newNode);
this.root = newRoot;
this.height++;
}
public Value get(Key key) {
return search(this.root, key);
}
public Value search(Node root, Key key) {
if (root == null) {
return null;
}
for (int i = 0; i < root.size; i++) {
if ((i+1) == root.size || less(key, (Key) root.keys[i+1].key)) {
return search(root.keys[i].next, key);
} else if (equal(key, (Key) root.keys[i+1].key)) {
return (Value) root.keys[i+1].value;
}
}
return null;
}
public Node insert(Node root, Key key, Value value, int height) {
Entry entry = new Entry(key, value, null);
int index = 1;
if (height == 0) {
for ( index = 1; index < root.size; index++) {
if (less(key, (Key) root.keys[index].key)) {
break;
}
}
} else {
for ( index = 0; index < root.size; index++) {
if ( (index + 1) == root.size || less(key, (Key) root.keys[index + 1].key)) {
Node newNode = insert(root.keys[index].next, key, value, height - 1);
if (newNode == null) {
return null;
}
entry = new Entry(newNode.keys[0].key, newNode.keys[0].value, newNode);
index++;
break;
}
}
}
for (int i = root.size; i > index; i--) {
root.keys[i] = root.keys[i - 1];
}
root.keys[index] = entry;
root.size++;
if (root.size < M_WITH_SENTINEL) return null;
else return splitNode(root);
}
public Node splitNode(Node node) {
Node newNode = new Node(ceilDiv(node.size, 2));
node.size = floorDiv(node.size, 2);
for (int i = 0; i < newNode.size; i++) {
newNode.keys[i] = node.keys[node.size + i];
}
return newNode;
}
private int ceilDiv(int foo, int bar) {
return Double.valueOf(Math.ceil((double) foo / bar)).intValue();
}
private int floorDiv(int foo, int bar) {
return Double.valueOf(Math.floor((double) foo / bar)).intValue();
}
private Boolean more(Key foo, Key bar) {
return foo.compareTo(bar) > 0;
}
private Boolean equal(Key foo, Key bar) {
return foo.compareTo(bar) == 0;
}
private Boolean less(Key foo, Key bar) {
return foo.compareTo(bar) < 0;
}
public static void main(String[] args) {
BTreeWithSentinel<Double, String> bTree = new BTreeWithSentinel<Double, String>();
bTree.put(1D, "test1");
bTree.put(4D, "test4");
bTree.put(7D, "test7");
bTree.put(0D, "test0");
bTree.put(2D, "test2");
bTree.put(5D, "test5");
bTree.put(8D, "test8");
bTree.put(6D, "test6");
bTree.put(9D, "test9");
bTree.put(3D, "test3");
bTree.put(10D, "test10");
System.out.println(bTree.get(-1D));
System.out.println(bTree.get(0D));
System.out.println(bTree.get(1D));
System.out.println(bTree.get(2D));
System.out.println(bTree.get(2.5D));
System.out.println(bTree.get(3D));
System.out.println(bTree.get(4D));
System.out.println(bTree.get(5D));
System.out.println(bTree.get(6D));
System.out.println(bTree.get(7D));
System.out.println(bTree.get(8D));
System.out.println(bTree.get(9D));
System.out.println(bTree.get(10D));
System.out.println(bTree.get(11D));
}
}