8.2.3 Vue.js 源码剖析-模板编译和组件化
本文为拉勾网大前端高薪训练营第一期笔记
心得体会
从5月14日开始在拉勾网学习大前端高薪训练营,到现在8月6日,不知不觉快三个月了,又找到了过去顶着压力学习的感觉,一天不学就浑身难受,主要是进度赶着人走,再加上交作业的截止日期(虽然只是说早交加分,但是不知不觉还是会有压力)、串讲直播和小雪班主任的敲窗户式提醒,学习效果杠杠的。
从学习成果来讲,硕果累累,我之前只看文档不求甚解,这次Vue.js章节的源码剖析和讲解后的调试真的学到很多,不仅是Vue.js的原理,优化过程,更多的是一种学习的方法,码农本来就是追着前沿跑的职业,不进步就要被淘汰,看源码绝对是不可或缺的一种学习方法。更何况很多过时项目年久失修,文档更新不及时,都得靠看源码来找到使用方法和解决bug的途径。
从选题来讲,到目前学到的部分,ES新语法、前端工程化(主要是webpack)、Vue.js源码剖析,都是非常流行和实用的实践知识。
要说学习过程有什么困难的话,就是Vue.js源码部分比较复杂,经常听着听着走神漏了一句,还得倒回去重新听,恐怕要听好几遍,复习一下才能真正有一个清晰的认识。
8.2.3 Vue.js 源码剖析-模板编译和组件化
模板编译
- 模板编译的主要目的是将模板 (template) 转换为渲染函数 (render)
title
some content
- 渲染函数 render
render (h) {
return h('div', [
h('h1', { on: { click: this.handler} }, 'title'),
h('p', 'some content')
])
}
- 模板编译的作用
- Vue 2.x 使用 VNode 描述视图以及各种交互,用户自己编写 VNode 比较复杂
- 用户只需要编写类似 HTML 的代码 - Vue 模板,通过编译器将模板转换为返回 VNode 的
render 函数 - .vue 文件会被 webpack 在构建的过程中转换成 render 函数
体验模板编译的结果
- 带编译器版本的 Vue.js 中,使用 template 或 el 的方式设置模板
Vue模板编译过程
{{ msg }}
- 编译后 render 输出的结果
(function anonymous() {
with (this) {
return _c(
"div",
{ attrs: { id: "app" } },
[
_m(0),
_v(" "),
_c("p", [_v(_s(msg))]),
_v(" "),
_c("comp", { on: { myclick: handler } }),
],
1
);
}
});
- _c 是 createElement() 方法,定义的位置 instance/render.js 中
- 相关的渲染函数(_开头的方法定义),在 instance/render-helps/index.js 中
// instance/render-helps/index.js
target._v = createTextVNode target._m = renderStatic
// core/vdom/vnode.js
export function createTextVNode(val: string | number) {
return new VNode(undefined, undefined, undefined, String(val))
}
// 在 instance/render-helps/render-static.js
export function renderStatic(
index: number,
isInFor: boolean
): VNode | Array {
const cached = this._staticTrees || (this._staticTrees = []) let tree = cached[index]
// if has already-rendered static tree and not inside v-for,
// we can reuse the same tree.
if (tree && !isInFor) {
return tree
}
// otherwise, render a fresh tree.
tree = cached[index] = this.$options.staticRenderFns[index].call(this._renderProxy,
null,
this // for render fns generated for functional component templates
)
markStatic(tree, `__static__${index}`, false) return tree
}
- 把 template 转换成 render 的入口 src\platforms\web\entry-runtime-with-compiler.js
Vue Template Explorer
- vue-template-explorer
- Vue 2.6 把模板编译成 render 函数的工具
- vue-next-template-explorer
- Vue 3.0 beta 把模板编译成 render 函数的工具
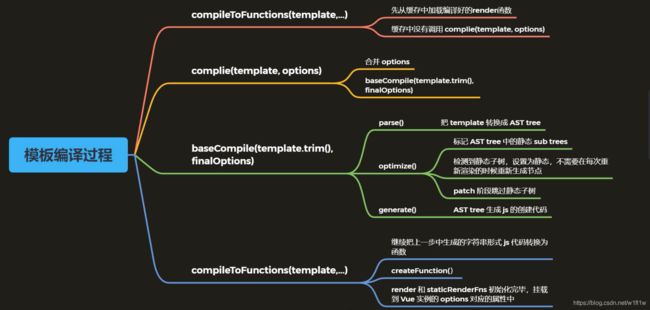
模板编译过程
- 解析、优化、生成
编译的入口
- src\platforms\web\entry-runtime-with-compiler.js
Vue.prototype.$mount = function (
// ......
// 把 template 转换成 render 函数
const { render, staticRenderFns } = compileToFunctions(template, {
outputSourceRange: process.env.NODE_ENV !== 'production',
shouldDecodeNewlines,
shouldDecodeNewlinesForHref,
delimiters: options.delimiters,
comments: options.comments
}, this)
options.render = render options.staticRenderFns = staticRenderFns
// ......
)
- 调试 compileToFunctions() 执行过程,生成渲染函数的过程
- compileToFunctions: src\compiler\to-function.js
- complie(template, options):src\compiler\create-compiler.js
- baseCompile(template.trim(), finalOptions):src\compiler\index.js
compileToFunctions()
把模板编译成字符串,new Function(str)转换成函数,如果有错误就保存下来,最后缓存转换出的函数
compile()
合并参数,调用baseCompile(),记录errors和tips
baseCompile()
- parse
- optimize
- generate
抽象语法树
- 简称AST(Abstract Syntax Tree)
- 使用对象的形式描述树形的代码结构
- 此处的抽象语法树是用来描述树形结构的HTML字符串
为什么要使用抽象语法树
- 模板字符串转换成AST后,可以通过AST对模板做优化处理
- 标记模板中的静态内容,在patch的时候直接跳过静态内容
- 在patch的过程中静态内容不需要对比和重新渲染
查看ast
astexplorer.net
@vue/compiler-core是vue3的解析器
vue-template-compiler是vue2.6的解析器
parse
- parse options
- parse html:使用simplehtmlparser开源库
- start开始标签,
- 创建ASTElement
- parse v-pre, v-if, v-for, v-once
- end结束标签
- chars文本内容
- comment注释标签
- start开始标签,
optimize
- 优化抽象语法树,检测子节点中是否是纯静态节点
- 一旦检测到纯静态节点
- 提升为常量,重新渲染的时候不在重新创建节点
- 在 patch 的时候直接跳过静态子树
// src\compiler\index.js
if (options.optimize !== false) {
optimize(ast, options)
}
// src\compiler\optimizer.js
/**
* Goal of the optimizer: walk the generated template AST tree
* and detect sub-trees that are purely static, i.e. parts of
* the DOM that never needs to change. *
* Once we detect these sub-trees, we can: *
* 1. Hoist them into constants, so that we no longer need to * create fresh nodes for them on each re-render;
* 2. Completely skip them in the patching process.
*/
export function optimize(root: ?ASTElement, options: CompilerOptions) {
if (!root) return
isStaticKey = genStaticKeysCached(options.staticKeys || '') isPlatformReservedTag = options.isReservedTag || no
// first pass: mark all non-static nodes.
// 标记非静态节点
markStatic(root)
// second pass: mark static roots.
// 标记静态根节点
markStaticRoots(root, false)
}
生成 - generate
AST生成js代码
// src\compiler\index.js
const code = generate(ast, options)
// src\compiler\codegen\index.js
export function generate(
ast: ASTElement | void,
options: CompilerOptions
): CodegenResult {
const state = new CodegenState(options)
const code = ast ? genElement(ast, state) : '_c("div")'
return {
render: `with(this){return ${code}}`,
staticRenderFns: state.staticRenderFns
}
}
// 把字符串转换成函数
// src\compiler\to-function.js
function createFunction(code, errors) {
try {
return new Function(code)
} catch (err) {
errors.push({ err, code }) return noop
}
}
总结
组件化回顾
- 一个Vue组件就是一个拥有预定义选项的一个Vue实例
- 一个组件可以组成页面上一个功能完备的区域,组件可以包含脚本、样式、模板
组件注册方式
- 全局组件
Vue.component('comp', { template: 'hello
'})
- 局部组件
var ComponentA = { /* ... */ }
var ComponentB = { /* ... */ }
var ComponentC = { /* ... */ }
new Vue({
el: '#app',
components: {
'component-a': ComponentA,
'component-b': ComponentB
}
})
- Vue.component() 入口
- 创建组件的构造函数,挂载到 Vue 实例的 vm.options.component.componentName =
Ctor
// src\core\global-api\index.js
// 注册 Vue.directive()、 Vue.component()、Vue.filter()
initAssetRegisters(Vue)
// src\core\global-api\assets.js
if (type === 'component' && isPlainObject(definition)) {
definition.name = definition.name || id
definition = this.options._base.extend(definition)
}
// ......
// 全局注册,存储资源并赋值
// this.options['components']['comp'] = Ctor
this.options[type + 's'][id] = definition
// src\core\global-api\index.js
// this is used to identify the "base" constructor to extend all plain- object
// components with in Weex's multi-instance scenarios.
Vue.options._base = Vue
// src\core\global-api\extend.js
Vue.extend()
- 组件构造函数的创建
const Sub = function VueComponent(options) {
this._init(options)
}
Sub.prototype = Object.create(Super.prototype)
Sub.prototype.constructor = Sub
Sub.cid = cid++
Sub.options = mergeOptions(
Super.options,
extendOptions
)
Sub['super'] = Super
// For props and computed properties, we define the proxy getters on
// the Vue instances at extension time, on the extended prototype. This
// avoids Object.defineProperty calls for each instance created.
if (Sub.options.props) {
initProps(Sub)
}
if (Sub.options.computed) {
initComputed(Sub)
}
// allow further extension/mixin/plugin usage
Sub.extend = Super.extend
Sub.mixin = Super.mixin
Sub.use = Super.use
// create asset registers, so extended classes
// can have their private assets too.
ASSET_TYPES.forEach(function (type) {
Sub[type] = Super[type]
})
// enable recursive self-lookup
if (name) {
Sub.options.components[name] = Sub
}
- 调试 Vue.component() 调用的过程
首次渲染过程
- Vue构造函数
- this._init()
- this.$mount()
- mountComponent()
- new Watch() 渲染Watcher
- updateComponent()
- vm._render() → createElement()
- vm._update()
组件创建和挂载组件
VNode 的创建过程
- 创建根组件,首次 _render() 时,会得到整棵树的 VNode 结构
- 整体流程:new Vue() --> $mount() --> vm._render() --> createElement() --> createComponent()
- 创建组件的 VNode,初始化组件的 hook 钩子函数
// 1. _createElement() 中调用 createComponent()
// src\core\vdom\create-element.js
else if ((!data || !data.pre) &&
{
isDef(Ctor = resolveAsset(context.$options, 'components', tag)))
// 查找自定义组件构造函数的声明
// 根据 Ctor 创建组件的 VNode
// component
vnode = createComponent(Ctor, data, context, children, tag)
// 2. createComponent() 中调用创建自定义组件对应的 VNode // src\core\vdom\create-component.js
export function createComponent(
Ctor: Class | Function | Object | void,
data: ?VNodeData,
context: Component,
children: ?Array < VNode >,
tag ?: string
): VNode | Array | void {
if(isUndef(Ctor)) {
return
}
// ......
// install component management hooks onto the placeholder node
// 安装组件的钩子函数 init/prepatch/insert/destroy
// 初始化了组件的 data.hooks 中的钩子函数
installComponentHooks(data)
// return a placeholder vnode
const name = Ctor.options.name || tag
// 创建自定义组件的 VNode,设置自定义组件的名字
// 记录this.componentOptions = componentOptions
const vnode = new VNode(
`vue-component-${Ctor.cid}${name ? `-${name}` : ''}`,
data, undefined, undefined, undefined, context,
{ Ctor, propsData, listeners, tag, children }, asyncFactory
)
return vnode
}
// 3. installComponentHooks() 初始化组件的 data.hook
function installComponentHooks(data: VNodeData) {
const hooks = data.hook || (data.hook = {})
// 用户可以传递自定义钩子函数
// 把用户传入的自定义钩子函数和 componentVNodeHooks 中预定义的钩子函数合并
for (let i = 0; i < hooksToMerge.length; i++) {
const key = hooksToMerge[i]
const existing = hooks[key]
const toMerge = componentVNodeHooks[key]
if (existing !== toMerge && !(existing && existing._merged)) {
hooks[key] = existing ? mergeHook(toMerge, existing) : toMerge
}
}
}
// 4. 钩子函数定义的位置(init()钩子中创建组件的实例)
// inline hooks to be invoked on component VNodes during patch
const componentVNodeHooks = {
init(vnode: VNodeWithData, hydrating: boolean): ?boolean {
if (
vnode.componentInstance && !vnode.componentInstance._isDestroyed && vnode.data.keepAlive
) {
// kept-alive components, treat as a patch
const mountedNode: any = vnode // work around flow
componentVNodeHooks.prepatch(mountedNode, mountedNode)
} else {
// 创建组件实例挂载到 vnode.componentInstance
const child = vnode.componentInstance = createComponentInstanceForVnode(
vnode,
activeInstance
)
// 调用组件对象的 $mount(),把组件挂载到页面
child.$mount(hydrating ? vnode.elm : undefined, hydrating)
}
},
prepatch(oldVnode: MountedComponentVNode, vnode: MountedComponentVNode) {
// ......
},
insert(vnode: MountedComponentVNode) {
// ......
},
destroy(vnode: MountedComponentVNode) {
// ......
}
}
//5 .创建组件实例的位置,由自定义组件的 init() 钩子方法调用
export function createComponentInstanceForVnode(
vnode: any, // we know it's MountedComponentVNode but flow doesn't
parent: any, // activeInstance in lifecycle state
): Component {
const options: InternalComponentOptions = {
_isComponent: true,
_parentVnode: vnode,
parent
}
// check inline-template render functions
const inlineTemplate = vnode.data.inlineTemplate
if (isDef(inlineTemplate)) {
options.render = inlineTemplate.render
options.staticRenderFns = inlineTemplate.staticRenderFns
}
// 创建组件实例
return new vnode.componentOptions.Ctor(options)
}
组件实例的创建和挂载过程
- Vue._update() --> patch() --> createElm() --> createComponent()
// src\core\vdom\patch.js
// 1. 创建组件实例,挂载到真实 DOM
function createComponent(vnode, insertedVnodeQueue, parentElm, refElm) {
let i = vnode.data
if (isDef(i)) {
const isReactivated = isDef(vnode.componentInstance) && i.keepAlive if (isDef(i = i.hook) && isDef(i = i.init)) {
// 调用 init() 方法,创建和挂载组件实例
// init() 的过程中创建好了组件的真实 DOM,挂载到了 vnode.elm 上
i(vnode, false /* hydrating */)
}
// after calling the init hook, if the vnode is a child component
// it should've created a child instance and mounted it. the child
// component also has set the placeholder vnode's elm.
// in that case we can just return the element and be done.
if (isDef(vnode.componentInstance)) {
// 调用钩子函数(VNode的钩子函数初始化属性/事件/样式等,组件的钩子函数)
initComponent(vnode, insertedVnodeQueue)
// 把组件对应的 DOM 插入到父元素中
insert(parentElm, vnode.elm, refElm)
if (isTrue(isReactivated)) {
reactivateComponent(vnode, insertedVnodeQueue, parentElm, refElm)
}
return true
}
}
}
// 2.
调用钩子函数,设置局部作用于样式
function initComponent(vnode, insertedVnodeQueue) {
if (isDef(vnode.data.pendingInsert)) {
insertedVnodeQueue.push.apply(insertedVnodeQueue, vnode.data.pendingInsert)
vnode.data.pendingInsert = null
}
vnode.elm = vnode.componentInstance.$el if (isPatchable(vnode)) {
// 调用钩子函数
invokeCreateHooks(vnode, insertedVnodeQueue)
// 设置局部作用于样式
setScope(vnode)
} else {
// empty component root.
// skip all element-related modules except for ref (#3455) registerRef(vnode)
// make sure to invoke the insert hook insertedVnodeQueue.push(vnode)
}
}
// 3. 调用钩子函数
function invokeCreateHooks(vnode, insertedVnodeQueue) {
// 调用 VNode 的钩子函数,初始化属性/样式/事件等
for (let i = 0; i < cbs.create.length; ++i) {
cbs.create[i](emptyNode, vnode)
}
i = vnode.data.hook // Reuse variable // 调用组件的钩子函数
if (isDef(i)) {
if (isDef(i.create)) i.create(emptyNode, vnode)
if (isDef(i.insert)) insertedVnodeQueue.push(vnode)
}
}