optimizer特性之derived_merge
文章目录
- MySQL optimizer特性之derived_merge
- 1. 什么是derived table ?
- 2. 什么是derived_merge ?
- 3. derived_merge开启和关闭的区别
- 4. 无法利用derived_merge的情况
- 5. derived_merge引发的问题
- 6. 学以致用
MySQL optimizer特性之derived_merge
本文主要介绍如下内容
- 什么是派生表
- MySQL的查询优化器特性derived_merge
- 可以利用derived_merge的情况
- derived_merge存在的问题
- 了解derived_merge的目的
1. 什么是derived table ?
derived table中文译为派生表,关于派生表的含义,翻阅了MySQL的官方手册,并没有找到相对应的解释,不过在SQL92标准中有对它进行定义,原文如下
A derived table is a table derived directly or indirectly from one
or more other tables by the evaluation of a .
The values of a derived table are derived from the values of the
underlying tables when the is evaluated.
解释为:派生表为直接或者间接的通过一个查询表达式从一个或者多个表中得到的表。某种意义上来讲,MySQL中的视图也是派生表。
举个例子:在如下SQL语句中,表A即为派生表。
select * from (select * from tb_1) AS A where A.col_1=
2. 什么是derived_merge ?
derived_merge指的是一种查询优化技术,作用就是把派生表合并到外部的查询中,提高数据检索的效率。这个特性在MySQL5.7版本中被引入,可以通过如下SQL语句进行查看/开启/关闭等操作。
- 查看是否开启
mysql> show global variables like '%optimizer_switch%'\G
*************************** 1. row ***************************
Variable_name: optimizer_switch
Value: index_merge=on,index_merge_union=on,index_merge_sort_union=on,index_merge_intersection=on,engine_condition_pushdown=on,index_condition_pushdown=on,mrr=on,mrr_cost_based=on,block_nested_loop=on,batched_key_access=off,materialization=on,semijoin=on,loosescan=on,firstmatch=on,duplicateweedout=on,subquery_materialization_cost_based=on,use_index_extensions=on,condition_fanout_filter=on,derived_merge=on
1 row in set (0.00 sec)
derived_merge=on表示开启,如果是off的话表示关闭。
- 关闭derived_merge:
set session optimizer_switch='derived_merge=off'; //session
set global optimizer_switch='derived_merge=off'; //global
- 开启derived_merge:
set session optimizer_switch='derived_merge=on'; //session
set global optimizer_switch='derived_merge=on'; //global
3. derived_merge开启和关闭的区别
在关闭或者无法使用derived_merge特性时,MySQL处理派生表需要将其物化成临时表,然后外部查询再对临时表进行检索操作。可见如下操作
- 在关闭derived_merge时:
mysql>
mysql> set session optimizer_switch='derived_merge=off';
Query OK, 0 rows affected (0.00 sec)
mysql> explain select * from (select * from t1 where id < 1000 ) AS A where A.id < 10;
+----+-------------+------------+------------+-------+---------------+---------+---------+------+------+----------+-------------+
| id | select_type | table | partitions | type | possible_keys | key | key_len | ref | rows | filtered | Extra |
+----+-------------+------------+------------+-------+---------------+---------+---------+------+------+----------+-------------+
| 1 | PRIMARY | | NULL | ALL | NULL | NULL | NULL | NULL | 999 | 33.33 | Using where |
| 2 | DERIVED | t1 | NULL | range | PRIMARY | PRIMARY | 4 | NULL | 999 | 100.00 | Using where |
+----+-------------+------------+------------+-------+---------------+---------+---------+------+------+----------+-------------+
2 rows in set, 1 warning (0.00 sec)
mysql> show create table t1\G
*************************** 1. row ***************************
Table: t1
Create Table: CREATE TABLE `t1` (
`id` int(11) NOT NULL AUTO_INCREMENT,
`id_1` int(11) DEFAULT NULL,
`id_2` int(11) DEFAULT NULL,
`id_3` int(11) DEFAULT NULL,
`id_4` int(11) DEFAULT NULL,
`name` varchar(10) DEFAULT NULL,
`m_status` int(11) DEFAULT NULL,
PRIMARY KEY (`id`)
) ENGINE=InnoDB AUTO_INCREMENT=1783026 DEFAULT CHARSET=utf8mb4
1 row in set (0.00 sec)
- 在开启derived_merge时
mysql> explain select * from (select * from t1 where id < 1000 ) AS A where A.id < 10;
+----+-------------+-------+------------+-------+---------------+---------+---------+------+------+----------+-------------+
| id | select_type | table | partitions | type | possible_keys | key | key_len | ref | rows | filtered | Extra |
+----+-------------+-------+------------+-------+---------------+---------+---------+------+------+----------+-------------+
| 1 | SIMPLE | t1 | NULL | range | PRIMARY | PRIMARY | 4 | NULL | 9 | 100.00 | Using where |
+----+-------------+-------+------------+-------+---------------+---------+---------+------+------+----------+-------------+
1 row in set, 1 warning (0.01 sec)
通过对比执行计划可以看出两者的不同。通过开启profiling可以查看时间消耗对比
| 15 | 0.00020275 | set session optimizer_switch='derived_merge=off' |
| 16 | 0.00165350 | select * from (select * from t1 where id < 1000 ) AS A where A.id < 10 |
| 17 | 0.00018900 | set session optimizer_switch='derived_merge=on' |
| 18 | 0.00048125 | select * from (select * from t1 where id < 1000 ) AS A where A.id < 10 |
+----------+------------+--------------------------------------------------------------------------------+
如下是各个阶段的时间消耗
mysql> show profile for query 16;
+----------------------+----------+
| Status | Duration |
+----------------------+----------+
| starting | 0.000155 |
| checking permissions | 0.000012 |
| checking permissions | 0.000003 |
| Opening tables | 0.000018 |
| init | 0.000083 |
| System lock | 0.000008 |
| optimizing | 0.000005 |
| optimizing | 0.000046 |
| statistics | 0.000132 |
| preparing | 0.000027 |
| statistics | 0.000017 |
| preparing | 0.000008 |
| executing | 0.000008 |
| Sending data | 0.000009 |
| executing | 0.000002 |
| Sending data | 0.001045 |
| end | 0.000005 |
| query end | 0.000008 |
| closing tables | 0.000003 |
| removing tmp table | 0.000005 |
| closing tables | 0.000006 |
| freeing items | 0.000039 |
| cleaning up | 0.000012 |
+----------------------+----------+
23 rows in set, 1 warning (0.01 sec)
mysql> show profile for query 18;
+----------------------+----------+
| Status | Duration |
+----------------------+----------+
| starting | 0.000132 |
| checking permissions | 0.000014 |
| checking permissions | 0.000005 |
| Opening tables | 0.000019 |
| init | 0.000068 |
| System lock | 0.000007 |
| optimizing | 0.000021 |
| statistics | 0.000087 |
| preparing | 0.000020 |
| executing | 0.000003 |
| Sending data | 0.000046 |
| end | 0.000004 |
| query end | 0.000007 |
| closing tables | 0.000006 |
| freeing items | 0.000033 |
| cleaning up | 0.000012 |
+----------------------+----------+
16 rows in set, 1 warning (0.00 sec)
可以发现在开启derived_merge时,少了对派生表的处理,这些处理包括对派生查询表达式的prepare,optimize,数据检索,物化,到使用完之后的清除等,所以查询效率提高了很多。
其实更加明显的对比案例应该是派生表的查询无索引,而外部查询使用索引进行检索,这种情况下,利用到derived_merge和无法利用的效率会相差非常大。如下
| 20 | 0.00021500 | set session optimizer_switch='derived_merge=off' |
| 21 | 1.84053250 | select * from (select * from t1 where id_2 < 1000 ) AS A where A.id < 10 |
| 22 | 0.00021100 | set session optimizer_switch='derived_merge=on' |
| 23 | 0.00047275 | select * from (select * from t1 where id_2 < 1000 ) AS A where A.id < 10 |
+----------+------------+--------------------------------------------------------------------------------+
15 rows in set, 1 warning (0.00 sec)
相差了3893倍。
4. 无法利用derived_merge的情况
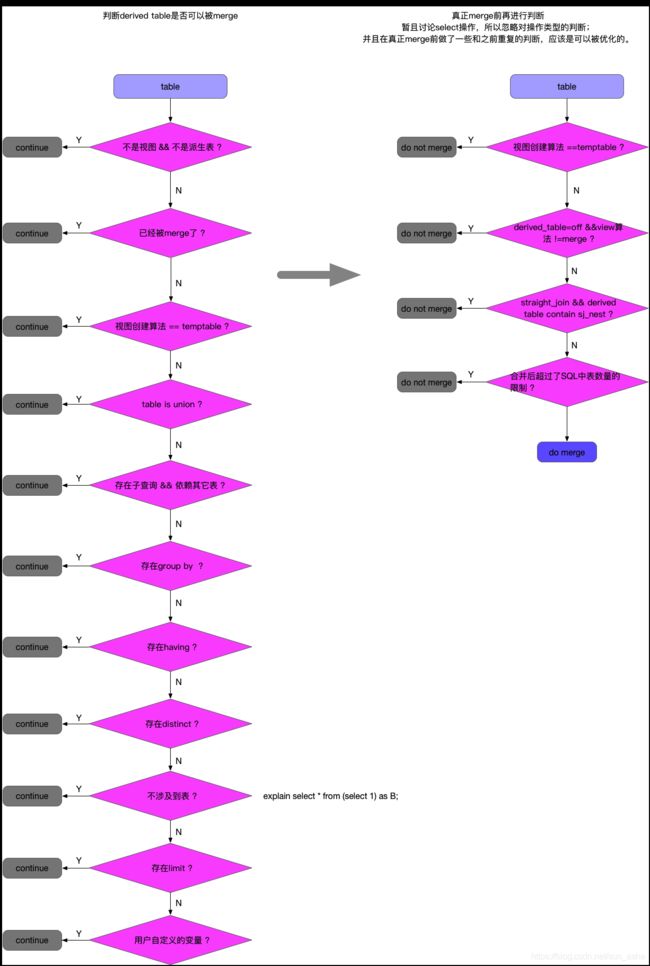
通过文字来描述什么情况下可以利用到derived_merge特性是一件比较绕口的事情,可以参照下图。
图中continue表示无法进行derived_merge
对于图中的描述,可以举几个简单的例子
- 示例1:派生表存在distinct操作,无法进行merge,如下:
mysql> set session optimizer_switch='derived_merge=on';
Query OK, 0 rows affected (0.00 sec)
mysql> explain select * from (select distinct id from t1 where id_2 < 1000 ) AS A where A.id < 10;
+----+-------------+------------+------------+------+---------------+------+---------+------+---------+----------+-------------+
| id | select_type | table | partitions | type | possible_keys | key | key_len | ref | rows | filtered | Extra |
+----+-------------+------------+------------+------+---------------+------+---------+------+---------+----------+-------------+
| 1 | PRIMARY | | NULL | ALL | NULL | NULL | NULL | NULL | 531747 | 33.33 | Using where |
| 2 | DERIVED | t1 | NULL | ALL | PRIMARY | NULL | NULL | NULL | 1595403 | 33.33 | Using where |
+----+-------------+------------+------------+------+---------------+------+---------+------+---------+----------+-------------+
2 rows in set, 1 warning (0.00 sec)
- 示例2:派生表中存在limit,无法进行merge
mysql> set session optimizer_switch='derived_merge=on';
Query OK, 0 rows affected (0.00 sec)
//无limit,可以进行merge
mysql> explain select * from (select * from t1 where id_2 < 1000 ) AS A where A.id < 10;
+----+-------------+-------+------------+-------+---------------+---------+---------+------+------+----------+-------------+
| id | select_type | table | partitions | type | possible_keys | key | key_len | ref | rows | filtered | Extra |
+----+-------------+-------+------------+-------+---------------+---------+---------+------+------+----------+-------------+
| 1 | SIMPLE | t1 | NULL | range | PRIMARY | PRIMARY | 4 | NULL | 9 | 33.33 | Using where |
+----+-------------+-------+------------+-------+---------------+---------+---------+------+------+----------+-------------+
1 row in set, 1 warning (0.00 sec)
//有limit,无法进行merge
mysql> explain select * from (select * from t1 where id_2 < 1000 limit 10) AS A where A.id < 10;
+----+-------------+------------+------------+------+---------------+------+---------+------+---------+----------+-------------+
| id | select_type | table | partitions | type | possible_keys | key | key_len | ref | rows | filtered | Extra |
+----+-------------+------------+------------+------+---------------+------+---------+------+---------+----------+-------------+
| 1 | PRIMARY | | NULL | ALL | NULL | NULL | NULL | NULL | 10 | 33.33 | Using where |
| 2 | DERIVED | t1 | NULL | ALL | NULL | NULL | NULL | NULL | 1595403 | 33.33 | Using where |
+----+-------------+------------+------------+------+---------------+------+---------+------+---------+----------+-------------+
2 rows in set, 1 warning (0.00 sec)
其它无法使用到derived merge的例子可以自己尝试。
5. derived_merge引发的问题
如下是官方文档的描述:
The optimizer now handles derived tables and views in the FROM clause in consistent fashion to
better avoid unnecessary materialization and to enable use of pushed-down conditions that produce
more efficient execution plans. However, for statements such as DELETE or UPDATE that modify
tables, using the merge strategy for a derived table that previously was materialized can result in an
ER_UPDATE_TABLE_USED error:
mysql> DELETE FROM t1
-> WHERE id IN (SELECT id
-> FROM (SELECT t1.id
-> FROM t1 INNER JOIN t2 USING (id)
-> WHERE t2.status = 0) AS t);
ERROR 1093 (HY000): You can't specify target table 't1'
for update in FROM clause
The error occurs when merging a derived table into the outer query block results in a statement that
both selects from and modifies a table. (Materialization does not cause the problem because, in effect, it
converts the derived table to a separate table.) To avoid this error, disable the derived_merge flag of
the optimizer_switch system variable before executing the statement:
SET optimizer_switch = 'derived_merge=off';
6. 学以致用
学习的目的是为了解决实际问题。
- 用途一:作为一个DBA,解决日常遇到的类似的慢语句。
- 用途二:当不确定的事情可以通过某种方法确定下来时,这件事情就可以被自动化,所以这部分内容被应用到了新的SQL优化组件中,判断用户在使用到派生表时,是否可以被merge,在数据库无法进行merge操作时,提示用户进行SQL改写。