EPOLL的内核实现
1. select/poll的缺点
A. 每次调用时重复的从用户态读入参数
B. 每次调用时全量的扫描文件描述符
C. 每次调用开始,将进程加入到每个文件描述符的等待队列,在调用结束后又把进程从等待队列中删除。
D. 在不修改内核的情况下,select最多支持1024个文件描述符。
2. 文件系统中的一些重要结构
在linux中,进程通过file_struct结构与文件关联,而文件通过等待队列与进程关联,进而形成一种多对多的关系。
首先,文件对象struct file_struct
- struct files_struct {
- atomic_t count; //自动增量
- struct fdtable *fdt;
- struct fdtable fdtab;
- fd_set close_on_exec_init; //执行exec时需要关闭的文件描述符集合
- fd_set open_fds_init; //当前打开文件的文件描述符屏蔽字
- struct file *fd_array[NR_OPEN_DEFAULT];//文件对象数组
- spinlock_t file_lock;
- };
- struct file{
- ....
- struct file_operations *f_op;
- ...
- }
在struct file_operations对象中存储对文件对象可以进行各种操作的指针:
- struct file_operations {
- struct module *owner;
- loff_t(*llseek) (struct file *, loff_t, int);
- ssize_t(*read) (struct file *, char __user *, size_t, loff_t *);
- ssize_t(*aio_read) (struct kiocb *, char __user *, size_t, loff_t);
- ssize_t(*write) (struct file *, const char __user *, size_t, loff_t *);
- ssize_t(*aio_write) (struct kiocb *, const char __user *, size_t, loff_t);
- int (*readdir) (struct file *, void *, filldir_t);
- unsigned int (*poll) (struct file *, struct poll_table_struct *);
- int (*ioctl) (struct inode *, struct file *, unsigned int, unsigned long);
- int (*mmap) (struct file *, struct vm_area_struct *);
- int (*open) (struct inode *, struct file *);
- int (*flush) (struct file *);
- int (*release) (struct inode *, struct file *);
- int (*fsync) (struct file *, struct dentry *, int datasync);
- int (*aio_fsync) (struct kiocb *, int datasync);
- int (*fasync) (int, struct file *, int);
- int (*lock) (struct file *, int, struct file_lock *);
- ssize_t(*readv) (struct file *, const struct iovec *, unsigned long, loff_t *);
- ssize_t(*writev) (struct file *, const struct iovec *, unsigned long, loff_t *);
- ssize_t(*sendfile) (struct file *, loff_t *, size_t, read_actor_t, void __user *);
- ssize_t(*sendpage) (struct file *, struct page *, int, size_t, loff_t *, int);
- unsigned long (*get_unmapped_area) (struct file *, unsigned long,
- unsigned long, unsigned long,
- unsigned long);
- };
3. epoll模型
epoll自己保存传入的文件描述符,同时通过设备等待队列唤醒时调用“回调函数”实现事件的通知。
epoll模型将select/poll单个的操作拆分:
- int epoll_create(int size);
- int epoll_ctl(int epfd, int op, int fd ,struct epoll_event *event);
- int epoll_wait(int epfd, struct epoll_event *events, int maxevents, int timeout);
epoll_create闯将一个属于该文件系统的文件,并返回其文件描述符。struct eventpoll 保存了epoll文件节点的扩展信息,该结构保存在private_data域中,每个由epoll_create得到的文件描述符都分配了一个该结构体,让我们来看一下struct eventpll的内部结构:
- struct eventpoll {
- /* 用于维护自身的状态,可用于中断上下文 */
- spinlock_t lock;
- /*
- * 用户进程上下文中
- */
- struct mutex mtx;
- /* 进程等待队列,由 sys_epoll_wait()使用,调用epoll_wait时,休眠在这里 */
- wait_queue_head_t wq;
- /* 进程等待队列,由 file->poll()使用 ,epollfd本身被poll时,休眠在这里*/
- wait_queue_head_t poll_wait;
- /* 就绪文件描述符链表 */
- struct list_head rdllist;
- /* 红黑树头节点,该红黑树用于存储要监控的文件描述符 */
- struct rb_root rbr;
- /*
- * ready事件的临时存放链表
- */
- struct epitem *ovflist;
- /* 创建eventpoll descriptor的用户 */
- struct user_struct *user;
- };
epoll_ctl 接口加入该epoll描述符监听的套接字属于socket filesystem,每一个都对应一个epitem结构体,该结构以红黑树的方式存储,eventpoll中的rbr成员指向该红黑树的root节点,而有监听事件到来的套接字结构以双向连表的形式保存,其头结点对应eventpoll中的rdllist成员。
- struct epitem {
- /*红黑树节点 */
- struct rb_node rbn;
- /*就绪描述符链表节点 */
- struct list_head rdllink;
- /*
- * Works together "struct eventpoll"->ovflist in keeping the
- * single linked chain of items.
- */
- struct epitem *next;
- /* 本结构对应的文件描述符信息 */
- struct epoll_filefd ffd;
- /* Number of active wait queue attached to poll operations */
- int nwait;
- /* List containing poll wait queues */
- struct list_head pwqlist;
- /* The "container" of this item */
- struct eventpoll *ep;
- /* List header used to link this item to the "struct file" items list */
- struct list_head fllink;
- /* The structure that describe the interested events and the source fd */
- struct epoll_event event;
- };
上述结构中fllink是指向文件系统链表的立案表头,struct file 称为文件结构,一般代表一个打开的文件描述符。
而epoll_filefd结构则表明了epitem对应的文件描述符信息:
- struct epoll_filefd {
- struct file *file; //文件结构指针
- int fd;}; //对应的文件描述符
- struct epoll_event
- {
- uint32_t events; /*想要监听的事件 */
- epoll_data_t data; /* 用户数据变量,可以用来存放一些用户自定义的信息 */
- } __attribute__ ((__packed__));
- typedef union epoll_data
- {
- void *ptr; //指向自定义数据
- int fd;
- uint32_t u32;
- uint64_t u64;
- } epoll_data_t;
看完上面两个结构,让我们来看一下epoll_ctl的真身:
- SYSCALL_DEFINE4(epoll_ctl, int, epfd, int, op, int, fd,
- struct epoll_event __user *, event)
- {
- int error;
- struct file *file, *tfile;
- struct eventpoll *ep;
- struct epitem *epi;
- struct epoll_event epds;
- DNPRINTK(3, (KERN_INFO "[%p] eventpoll: sys_epoll_ctl(%d, %d, %d, %p)/n",
- current, epfd, op, fd, event));
- error = -EFAULT;
- if (ep_op_has_event(op) &&
- copy_from_user(&epds, event, sizeof(struct epoll_event)))
- goto error_return;
- /* Get the "struct file *" for the eventpoll file */
- error = -EBADF;
- file = fget(epfd);
- if (!file)
- goto error_return;
- /* Get the "struct file *" for the target file */
- tfile = fget(fd);
- if (!tfile)
- goto error_fput;
- /* The target file descriptor must support poll */
- error = -EPERM;
- if (!tfile->f_op || !tfile->f_op->poll)
- goto error_tgt_fput;
- /*
- * We have to check that the file structure underneath the file descriptor
- * the user passed to us _is_ an eventpoll file. And also we do not permit
- * adding an epoll file descriptor inside itself.
- */
- error = -EINVAL;
- if (file == tfile || !is_file_epoll(file))
- goto error_tgt_fput;
- /*
- * At this point it is safe to assume that the "private_data" contains
- * our own data structure.
- */
- ep = file->private_data;
- mutex_lock(&ep->mtx);
- /*
- * Try to lookup the file inside our RB tree, Since we grabbed "mtx"
- * above, we can be sure to be able to use the item looked up by
- * ep_find() till we release the mutex.
- */
- epi = ep_find(ep, tfile, fd);
- error = -EINVAL;
- switch (op) {
- case EPOLL_CTL_ADD:
- if (!epi) {
- epds.events |= POLLERR | POLLHUP;
- error = ep_insert(ep, &epds, tfile, fd);
- } else
- error = -EEXIST;
- break;
- case EPOLL_CTL_DEL:
- if (epi)
- error = ep_remove(ep, epi);
- else
- error = -ENOENT;
- break;
- case EPOLL_CTL_MOD:
- if (epi) {
- epds.events |= POLLERR | POLLHUP;
- error = ep_modify(ep, epi, &epds);
- } else
- error = -ENOENT;
- break;
- }
- mutex_unlock(&ep->mtx);
- error_tgt_fput:
- fput(tfile);
- error_fput:
- fput(file);
- error_return:
- DNPRINTK(3, (KERN_INFO "[%p] eventpoll: sys_epoll_ctl(%d, %d, %d, %p) = %d/n",
- current, epfd, op, fd, event, error));
- return error;
- }
代码的逻辑很简单,注释也很清楚。上面我们已经介绍了文件对象结构,因此我们这里主要关注剩下的流程,以添加一个监听事件为例:
- static int ep_insert(struct eventpoll *ep, struct epoll_event *event,struct file *tfile, int fd)
- {
- int error, revents, pwake = 0;
- unsigned long flags;
- struct epitem *epi;
- struct ep_pqueue epq;
- /* 不允许超过最大监听个数,每个用户均有一个监听上限*/
- if (unlikely(atomic_read(&ep->user->epoll_watches) >=
- max_user_watches))
- return -ENOSPC;
- if (!(epi = kmem_cache_alloc(epi_cache, GFP_KERNEL)))
- return -ENOMEM;
- /* Item initialization follow here ... */
- INIT_LIST_HEAD(&epi->rdllink);
- INIT_LIST_HEAD(&epi->fllink);
- INIT_LIST_HEAD(&epi->pwqlist);
- epi->ep = ep;
- ep_set_ffd(&epi->ffd, tfile, fd);
- epi->event = *event;
- epi->nwait = 0;
- epi->next = EP_UNACTIVE_PTR;
- /* Initialize the poll table using the queue callback */
- epq.epi = epi;
- init_poll_funcptr(&epq.pt, ep_ptable_queue_proc); //注册事件响应的回调函数
- /*
- * Attach the item to the poll hooks and get current event bits.
- * We can safely use the file* here because its usage count has
- * been increased by the caller of this function. Note that after
- * this operation completes, the poll callback can start hitting
- * the new item.
- */
- revents = tfile->f_op->poll(tfile, &epq.pt); //执行poll函数,对于socket来说,执行tcp_poll函数
- /*
- * We have to check if something went wrong during the poll wait queue
- * install process. Namely an allocation for a wait queue failed due
- * high memory pressure.
- */
- error = -ENOMEM;
- if (epi->nwait < 0)
- goto error_unregister;
- /* Add the current item to the list of active epoll hook for this file */
- spin_lock(&tfile->f_ep_lock);
- list_add_tail(&epi->fllink, &tfile->f_ep_links);
- spin_unlock(&tfile->f_ep_lock);
- /*
- * Add the current item to the RB tree. All RB tree operations are
- * protected by "mtx", and ep_insert() is called with "mtx" held.
- */
- ep_rbtree_insert(ep, epi);
- /* We have to drop the new item inside our item list to keep track of it */
- spin_lock_irqsave(&ep->lock, flags);
- /* If the file is already "ready" we drop it inside the ready list */
- if ((revents & event->events) && !ep_is_linked(&epi->rdllink)) {
- list_add_tail(&epi->rdllink, &ep->rdllist);
- /* Notify waiting tasks that events are available */
- if (waitqueue_active(&ep->wq))
- wake_up_locked(&ep->wq);
- if (waitqueue_active(&ep->poll_wait))
- pwake++;
- }
- spin_unlock_irqrestore(&ep->lock, flags);
- atomic_inc(&ep->user->epoll_watches);
- /* We have to call this outside the lock */
- if (pwake)
- ep_poll_safewake(&psw, &ep->poll_wait);
- DNPRINTK(3, (KERN_INFO "[%p] eventpoll: ep_insert(%p, %p, %d)/n",
- current, ep, tfile, fd));
- return 0;
- error_unregister:
- ep_unregister_pollwait(ep, epi);
- /*
- * We need to do this because an event could have been arrived on some
- * allocated wait queue. Note that we don't care about the ep->ovflist
- * list, since that is used/cleaned only inside a section bound by "mtx".
- * And ep_insert() is called with "mtx" held.
- */
- spin_lock_irqsave(&ep->lock, flags);
- if (ep_is_linked(&epi->rdllink))
- list_del_init(&epi->rdllink);
- spin_unlock_irqrestore(&ep->lock, flags);
- kmem_cache_free(epi_cache, epi);
- return error;
- }
- static void ep_ptable_queue_proc(struct file *file, wait_queue_head_t *whead,poll_table *pt)
- {
- struct epitem *epi = ep_item_from_epqueue(pt);
- struct eppoll_entry *pwq;
- if (epi->nwait >= 0 && (pwq = kmem_cache_alloc(pwq_cache, GFP_KERNEL))) {
- /* 为监听套接字注册一个等待回调函数,在唤醒时调用*/
- init_waitqueue_func_entry(&pwq->wait, ep_poll_callback);
- pwq->whead = whead;
- pwq->base = epi;
- add_wait_queue(whead, &pwq->wait);
- list_add_tail(&pwq->llink, &epi->pwqlist);
- epi->nwait++;
- } else {
- /* We have to signal that an error occurred */
- epi->nwait = -1;
- }
- }
让我们来看一下注册的ep_poll_callback:
- static int ep_poll_callback(wait_queue_t *wait, unsigned mode, int sync, void *key)
- {
- int pwake = 0;
- unsigned long flags;
- struct epitem *epi = ep_item_from_wait(wait);
- struct eventpoll *ep = epi->ep;
- DNPRINTK(3, (KERN_INFO "[%p] eventpoll: poll_callback(%p) epi=%p ep=%p/n",
- current, epi->ffd.file, epi, ep));
- /* 对eventpoll的spinlock加锁,因为是在中断上下文中*/
- spin_lock_irqsave(&ep->lock, flags);
- /* 没有事件到来
- * If the event mask does not contain any poll(2) event, we consider the
- * descriptor to be disabled. This condition is likely the effect of the
- * EPOLLONESHOT bit that disables the descriptor when an event is received,
- * until the next EPOLL_CTL_MOD will be issued.
- */
- if (!(epi->event.events & ~EP_PRIVATE_BITS))
- goto out_unlock;
- /*
- * If we are trasfering events to userspace, we can hold no locks
- * (because we're accessing user memory, and because of linux f_op->poll()
- * semantics). All the events that happens during that period of time are
- * chained in ep->ovflist and requeued later on.
- */
- if (unlikely(ep->ovflist != EP_UNACTIVE_PTR)) {
- if (epi->next == EP_UNACTIVE_PTR) {
- epi->next = ep->ovflist;
- ep->ovflist = epi;
- }
- goto out_unlock;
- }
- /* If this file is already in the ready list we exit soon */
- if (ep_is_linked(&epi->rdllink))
- goto is_linked;
- /* 加入ready queue*/
- list_add_tail(&epi->rdllink, &ep->rdllist);
- is_linked:
- /*
- * Wake up ( if active ) both the eventpoll wait list and the ->poll()
- * wait list.
- */
- if (waitqueue_active(&ep->wq))
- wake_up_locked(&ep->wq);
- if (waitqueue_active(&ep->poll_wait))
- pwake++;
- out_unlock:
- spin_unlock_irqrestore(&ep->lock, flags);
- /* We have to call this outside the lock */
- if (pwake)
- ep_poll_safewake(&psw, &ep->poll_wait);
- return 1;
- }
epoll_wait中调用下面的等待函数,一旦其被ep_poll_callback唤醒,则调用ep_send_events把事件复制到用户控件,进而epoll_wait返回。
- static int ep_poll(struct eventpoll *ep, struct epoll_event __user *events,
- int maxevents, long timeout)
- {
- int res, eavail;
- unsigned long flags;
- long jtimeout;
- wait_queue_t wait;
- /*
- * Calculate the timeout by checking for the "infinite" value ( -1 )
- * and the overflow condition. The passed timeout is in milliseconds,
- * that why (t * HZ) / 1000.
- */
- jtimeout = (timeout < 0 || timeout >= EP_MAX_MSTIMEO) ?
- MAX_SCHEDULE_TIMEOUT : (timeout * HZ + 999) / 1000;
- retry:
- spin_lock_irqsave(&ep->lock, flags);
- res = 0;
- if (list_empty(&ep->rdllist)) {
- /*
- * We don't have any available event to return to the caller.
- * We need to sleep here, and we will be wake up by
- * ep_poll_callback() when events will become available.
- */
- init_waitqueue_entry(&wait, current);
- wait.flags |= WQ_FLAG_EXCLUSIVE;
- __add_wait_queue(&ep->wq, &wait);
- for (;;) {
- /*
- * We don't want to sleep if the ep_poll_callback() sends us
- * a wakeup in between. That's why we set the task state
- * to TASK_INTERRUPTIBLE before doing the checks.
- */
- set_current_state(TASK_INTERRUPTIBLE);
- if (!list_empty(&ep->rdllist) || !jtimeout)
- break;
- if (signal_pending(current)) {
- res = -EINTR;
- break;
- }
- spin_unlock_irqrestore(&ep->lock, flags);
- jtimeout = schedule_timeout(jtimeout);
- spin_lock_irqsave(&ep->lock, flags);
- }
- __remove_wait_queue(&ep->wq, &wait);
- set_current_state(TASK_RUNNING);
- }
- /* Is it worth to try to dig for events ? */
- eavail = !list_empty(&ep->rdllist);
- spin_unlock_irqrestore(&ep->lock, flags);
- /*
- * Try to transfer events to user space. In case we get 0 events and
- * there's still timeout left over, we go trying again in search of
- * more luck.
- */
- if (!res && eavail &&
- !(res = ep_send_events(ep, events, maxevents)) && jtimeout)
- goto retry;
- return res;
- }
使用epoll的整个流程可以总结如下(copy来的):
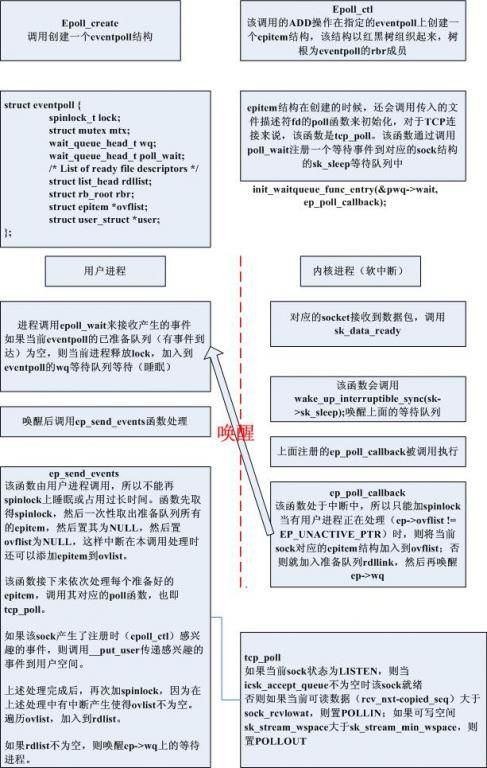
4. struct sock结构
该结构主要对应于一个socket描述符,通过上面的讲述再根据sock的结构,我们大致可以勾勒出一个事件到来到事件返回的全过程,涉及到Linux网络协议栈的等后面学习了再补充,当前仅贴出该数据结构:
- struct sock {
- struct sock_common __sk_common;
- #define sk_family __sk_common.skc_family
- #define sk_state __sk_common.skc_state
- #define sk_reuse __sk_common.skc_reuse
- #define sk_bound_dev_if __sk_common.skc_bound_dev_if
- #define sk_node __sk_common.skc_node
- #define sk_bind_node __sk_common.skc_bind_node
- #define sk_refcnt __sk_common.skc_refcnt
- unsigned char sk_shutdown : 2,
- sk_no_check : 2,
- sk_userlocks : 4;
- unsigned char sk_protocol;
- unsigned short sk_type;
- int sk_rcvbuf;
- socket_lock_t sk_lock;
- wait_queue_head_t *sk_sleep;
- struct dst_entry *sk_dst_cache;
- struct xfrm_policy *sk_policy[2];
- rwlock_t sk_dst_lock;
- atomic_t sk_rmem_alloc;
- atomic_t sk_wmem_alloc;
- atomic_t sk_omem_alloc;
- struct sk_buff_head sk_receive_queue;
- struct sk_buff_head sk_write_queue;
- int sk_wmem_queued;
- int sk_forward_alloc;
- unsigned int sk_allocation;
- int sk_sndbuf;
- int sk_route_caps;
- int sk_hashent;
- unsigned long sk_flags;
- unsigned long sk_lingertime;
- struct {
- struct sk_buff *head;
- struct sk_buff *tail;
- } sk_backlog;
- struct sk_buff_head sk_error_queue;
- struct proto *sk_prot;
- struct proto *sk_prot_creator;
- rwlock_t sk_callback_lock;
- int sk_err,
- sk_err_soft;
- unsigned short sk_ack_backlog;
- unsigned short sk_max_ack_backlog;
- __u32 sk_priority;
- struct ucred sk_peercred;
- int sk_rcvlowat;
- long sk_rcvtimeo;
- long sk_sndtimeo;
- struct sk_filter *sk_filter;
- void *sk_protinfo;
- struct timer_list sk_timer;
- struct timeval sk_stamp;
- struct socket *sk_socket;
- void *sk_user_data;
- struct page *sk_sndmsg_page;
- struct sk_buff *sk_send_head;
- __u32 sk_sndmsg_off;
- int sk_write_pending;
- void *sk_security;
- void (*sk_state_change)(struct sock *sk);//状态改变时调用
- void (*sk_data_ready)(struct sock *sk, int bytes);//有数据可读时调用,即读事件
- void (*sk_write_space)(struct sock *sk);//有数据可写时调用,即写事件
- void (*sk_error_report)(struct sock *sk);//套接字错误时调用
- int (*sk_backlog_rcv)(struct sock *sk,
- struct sk_buff *skb);
- void (*sk_destruct)(struct sock *sk);//套接字被释放时调用。
- };
5. epoll使用范例
- int epoll_create(int size); //size 表示要监听的文件描述符数量
- int epoll_ctl(int epfd, int op, int fd, struct epoll_event *event);
- int epoll_wait(int epfd, struct epoll_event* events, int maxevents, int timeout); // timeout = -1 阻塞; timeout = 0 立即返回
- typedef union epoll_data {
- void *ptr;
- int fd;
- __uint32_t u32;
- __uint64_t u64;
- } epoll_data_t;
- struct epoll_event {
- __uint32_t events; /* Epoll events */
- epoll_data_t data; /* User data variable */
- };
events可以是一下几个标志的集合:
EPOLLIN :表示对应的文件描述符可以读(包括对端SOCKET正常关闭);EPOLLOUT:表示对应的文件描述符可以写;
EPOLLPRI:表示对应的文件描述符有紧急的数据可读(这里应该表示有带外数据到来);
EPOLLERR:表示对应的文件描述符发生错误;
EPOLLHUP:表示对应的文件描述符被挂断;
EPOLLET: 将EPOLL设为边缘触发(Edge Triggered)模式,这是相对于水平触发(Level Triggered)来说的。
EPOLLONESHOT:只监听一次事件,当监听完这次事件之后,如果还需要继续监听这个socket的话,需要再次把这个socket加入到EPOLL队列里
而epoll_ctl的op参数可以为一下值:
EPOLL_CTL_ADD:注册新的fd到epfd中;
EPOLL_CTL_MOD:修改已经注册的fd的监听事件;
EPOLL_CTL_DEL:从epfd中删除一个fd;
随手附上一个简单的例子,不提供任何保证:
- #define MAX_CONNECTION 1024
- struct self_define_data{
- int data;
- };
- int main(int argc, char* argv[]){
- int listen_fd,client_fd,flag;
- struct sockaddr_in server,client;
- struct epoll_event ee,event_list[20];
- listen_fd = socket(AF_INET,SOCK_STREAM,0);
- /*
- flag = fcntl(listen_fd,F_GETFL,0);
- flag |= O_NONBLOCK;
- if(fcntl(listen_fd,F_SETFL,flag) < 0){
- perror("set non_block failed");
- return -1;
- }
- */
- ioctl(listen_fd,FIONBIO,&n);
- bzero(&server,sizeof(struct sockaddr_in));
- server.sin_family = AF_INET;
- inet_aton("127.0.0.1",&server.sin_addr);
- server.sin_port = htons(80);
- bind(listen_fd, (struct sockaddr*)&server, sizeof(struct sockaddr));
- listen(listen_fd,5);
- int ep = epoll_create(MAX_CONNECTION); // int cycle->connection
- if(-1 == ep){
- perror("epoll_create failed.");
- return -1;
- }
- struct self_define_data *self;
- self->data = 10;
- ee.events = EPOLLIN|EPOLLOUT|EPOLLET;
- ee.data.ptr = (void*)self;
- ee.data.fd = listen_fd;
- epoll_ctl(ep,EPOLL_CTL_ADD,listen_fd, &ee);
- while(1){
- int num = epoll_wait(ep,event_list,20,-1);
- for(int i = 0; i < num; i++){
- struct sef_define_data s = event_list[i].data.ptr;
- if(10 == s.data){
- uint32_t revent = event_list[i].events;//revent中包含返回的事件如EPOLLIN
- if(event_list[i].data.fd == listen_fd){
- client_fd = accept(listen_fd,(struct sockaddr*)&client,sizeof(struct sockaddr));
- //do someting
- if(client_fd < 0)
- break;
- close(client_fd);
- }
- }
- }
- }
- if(-1 == close(ep)){
- perror("epoll_close failed.");
- return -1;
- }
- return 0;
- }