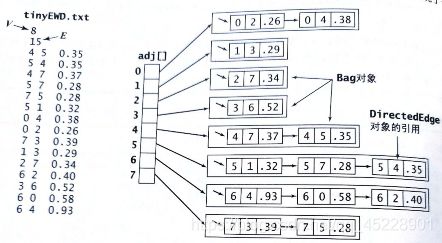
图3(最短路径)
最短路径
在一幅加权有向图中,顶点s到t的最短路径就是s到t路径中权重最小者。
- 解决边的权重非负的最短路径经典算法Dijkstra算法。
- 无环加权有向图的最短路径算法是一种快速算法,边的权重可为负数。
- 适用于一般情况的经典Bellman-Ford算法,图中可以含有环,边的权重也可以为负值。
最短路径的性质
- 路径是又向的。
- 权重不一定等价于距离。可能为时间、花费…
- 并不是所有顶点都可达。
- 负权重会使问题跟复杂。
- 最短路径不一定唯一
- 可能存在平行边和自环。
最短路径树
给定一个顶点s,计算结果为一颗最短路径树(SPT)。其结果包含了顶点s到所有可达顶点的路径。
加权有向图的数据结构
加权有向边数据类型
package com.t_graphs.SP;
/**
* 加权有向边数据类型
* @create 2020-03-31 18:57
*/
public class DirectedEdge {
private final int v; // 边起点
private final int w; // 边终点
private final double weight; // 边权重
/**
* 初始化顶点{@code v}到顶点{@code w}的有向边给定的{@code weight}。
* @throws IllegalArgumentException if {@code weight} is {@code NaN}
*/
public DirectedEdge(int v, int w, double weight) {
if (v < 0) throw new IllegalArgumentException("Vertex names must be nonnegative integers");
if (w < 0) throw new IllegalArgumentException("Vertex names must be nonnegative integers");
if (Double.isNaN(weight)) throw new IllegalArgumentException("Weight is NaN");
this.v = v;
this.w = w;
this.weight = weight;
}
/**.
* @return 有向边起点
*/
public int from() {
return v;
}
/**
* @return 有向边终点
*/
public int to() {
return w;
}
/**
* @return 有向边的权值
*/
public double weight() {
return weight;
}
/**
* @return 有向边的字符串表示形式
*/
public String toString() {
return v + "->" + w + " " + String.format("%5.2f", weight);
}
/**
* 测试
*/
public static void main(String[] args) {
DirectedEdge e = new DirectedEdge(12, 34, 5.67);
System.out.println(e);
}
}
加权有向图的数据结构
package com.t_graphs.SP;
import com.lb_linkedlist.Bag;
import edu.princeton.cs.algs4.In;
import java.util.NoSuchElementException;
/**
* 加权有向图的数据类型
* @create 2020-03-31 19:39
*/
public class EdgeWeightedDigraph {
private static final String NEWLINE = System.getProperty("line.separator");
private final int V; // 顶点总数
private int E; // 边总数
private Bag<DirectedEdge>[] adj; // 邻接表
private int[] indegree; // indegree[v] = 顶点v的入度
/**
* 用{@code V}顶点和0条边初始化一个空的边加权有向图。
*/
public EdgeWeightedDigraph(int V) {
if (V < 0) throw new IllegalArgumentException("Number of vertices in a Digraph must be nonnegative");
this.V = V;
this.E = 0;
this.indegree = new int[V];
adj = (Bag<DirectedEdge>[]) new Bag[V];
for (int v = 0; v < V; v++)
adj[v] = new Bag<>();
}
/**
* 从指定的输入流初始化边缘加权有向图。
* 格式为顶点数V,
* 后面是边数E,
* 后面是E对顶点和边权值,
* 每个条目之间用空格分隔。
*/
public EdgeWeightedDigraph(In in) {
if (in == null) throw new IllegalArgumentException("argument is null");
try {
this.V = in.readInt();
if (V < 0) throw new IllegalArgumentException("number of vertices in a Digraph must be nonnegative");
indegree = new int[V];
adj = (Bag<DirectedEdge>[]) new Bag[V];
for (int v = 0; v < V; v++) {
adj[v] = new Bag<>();
}
int E = in.readInt();
if (E < 0) throw new IllegalArgumentException("Number of edges must be nonnegative");
for (int i = 0; i < E; i++) {
int v = in.readInt();
int w = in.readInt();
validateVertex(v);
validateVertex(w);
double weight = in.readDouble();
addEdge(new DirectedEdge(v, w, weight));
}
}
catch (NoSuchElementException e) {
throw new IllegalArgumentException("invalid input format in EdgeWeightedDigraph constructor", e);
}
}
/**
* @return 顶点数
*/
public int V() {
return V;
}
/**
* @return 边总数
*/
public int E() {
return E;
}
// 抛出一个IllegalArgumentException,除非{@code 0 <= v < v}
private void validateVertex(int v) {
if (v < 0 || v >= V)
throw new IllegalArgumentException("vertex " + v + " is not between 0 and " + (V-1));
}
/**
* 将有向边{@code e}添加到这个边加权有向图中。
*/
public void addEdge(DirectedEdge e) {
int v = e.from();
int w = e.to();
validateVertex(v);
validateVertex(w);
adj[v].add(e); // 将边e加入尾部顶点v的邻接表中
indegree[w]++; // 头顶点入度+1
E++;
}
/**
* @return 将顶点{@code v}中的有向边关联作为一个iterable
*/
public Iterable<DirectedEdge> adj(int v) {
validateVertex(v);
return adj[v];
}
/**
* @return 顶点{@code v}的出度
*/
public int outdegree(int v) {
validateVertex(v);
return adj[v].size();
}
/**
* @return 顶点{@code v}的入度
*/
public int indegree(int v) {
validateVertex(v);
return indegree[v];
}
/**
* @return 加权有向图的所有边 ,作为一个iterable
*/
public Iterable<DirectedEdge> edges() {
Bag<DirectedEdge> list = new Bag<>();
for (int v = 0; v < V; v++) {
for (DirectedEdge e : adj(v)) {
list.add(e);
}
}
return list;
}
/**
* @return 返回此边加权有向图的字符串表示形式。
*/
public String toString() {
StringBuilder s = new StringBuilder();
// s.append(V + " " + E + NEWLINE);
s.append(V).append(" ").append(E).append(NEWLINE);
for (int v = 0; v < V; v++) {
s.append(v).append(": ");
for (DirectedEdge e : adj[v]) {
s.append(e).append(" ");
}
s.append(NEWLINE);
}
return s.toString();
}
/**
* 测试
*/
public static void main(String[] args) {
In in = new In(args[0]);
EdgeWeightedDigraph G = new EdgeWeightedDigraph(in);
System.out.println(G);
}
}
最短路径的数据结构
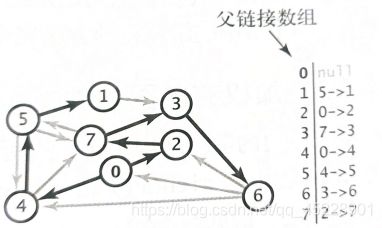
最短路径中的边。和深度优先、广度优先和Prim一样。使用一个有顶点索引的DirectedEdge对象的父链接数组edgeTo[],其中edgeTo[v]的值为树中连接v和它的父节点的边(从s到v的最短路径上的最后一条边)。
到达起点的距离。有顶点索引的数组distTo[],dist[v]为s到v的已知最短路径长度。
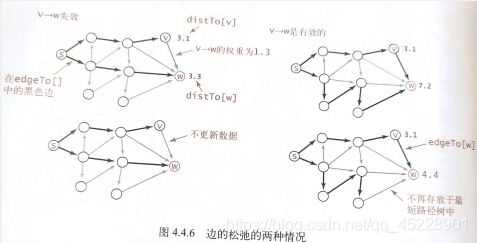
边的松弛。放松边v->w:检查从s到w的路径是否先s到v,再v到w。如果是,更细数据内容。
如果dist[v]与v到w的边(e.weight())的和不小于dist[w],则这条边失效并忽略。如果值更小,就更新数据。
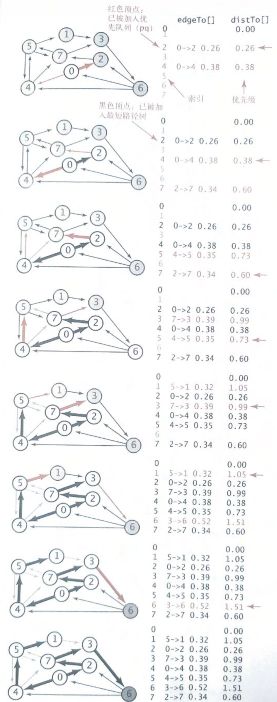
Dijkstra算法
package com.t_graphs.SP;
import com.t_graphs.MST.IndexMinPQ;
import com.z_stack.Stack;
/**
* @create 2020-04-01 9:39
*/
public class DijkstraSP {
private double[] distTo; // distTo[v] = s->v路径的最短距离
private DirectedEdge[] edgeTo; // edgeTo[v] = 最短s->v路径上的最后一条边
private IndexMinPQ<Double> pq; // 顶点优先队列
/**
* 计算从加权有向图{@code G}的源顶点{@code s}到其他顶点的最短路径树
*
* @throws IllegalArgumentException 如果边的权值是负的
*/
public DijkstraSP(EdgeWeightedDigraph G, int s) {
for (DirectedEdge e : G.edges()) { // 所有边的权值不能为负
if (e.weight() < 0)
throw new IllegalArgumentException("edge " + e + " has negative weight");
}
distTo = new double[G.V()];
edgeTo = new DirectedEdge[G.V()];
validateVertex(s);
for (int v = 0; v < G.V(); v++)
distTo[v] = Double.POSITIVE_INFINITY;
distTo[s] = 0.0;
// 按距离s的顺序放松顶点
pq = new IndexMinPQ<>(G.V());
pq.insert(s, distTo[s]);
while (!pq.isEmpty()) {
int v = pq.delMin(); // 取出优先队列最小值(广度优先搜索用的普通队列)
for (DirectedEdge e : G.adj(v)) // 以顶点v为起点的有向边
relax(e);
}
}
// 放松e边,如果改变则更新pq
private void relax(DirectedEdge e) {
int v = e.from(), w = e.to();
if (distTo[w] > distTo[v] + e.weight()) { // 已知的源顶点到w的最短路径并不是正确的最短路径
distTo[w] = distTo[v] + e.weight(); // 更新到w的最短路径
edgeTo[w] = e;
if (pq.contains(w)) pq.decreaseKey(w, distTo[w]); // 之前存在一条到w的最短路径,将其代替
else pq.insert(w, distTo[w]); // w不在优先队列,顶点w,distTo[w]加入优先队列
}
}
/**
* @return 从源顶点{@code s}到顶点{@code v}的最短路径长度;
* {@code Double.POSITIVE_INFINITY} 如果没有这样的路径
*/
public double distTo(int v) {
validateVertex(v);
return distTo[v];
}
/**
* @return {@code true} 如果从源顶点{@code s}能到达顶点{@code v}
*/
public boolean hasPathTo(int v) {
validateVertex(v);
return distTo[v] < Double.POSITIVE_INFINITY;
}
/**
* @param v the destination vertex
* @return 从源顶点{@code s}到顶点{@code v}的最短路径,作为边的迭代,如果没有这样的路径,则为{@code null}
*/
public Iterable<DirectedEdge> pathTo(int v) {
validateVertex(v);
if (!hasPathTo(v)) return null;
Stack<DirectedEdge> path = new Stack<>();
for (DirectedEdge e = edgeTo[v]; e != null; e = edgeTo[e.from()]) { // 从终点往起点找
path.push(e);
}
return path; // 遍历栈就可以从起点到终点
}
// throw an IllegalArgumentException unless {@code 0 <= v < V}
private void validateVertex(int v) {
int V = distTo.length;
if (v < 0 || v >= V)
throw new IllegalArgumentException("vertex " + v + " is not between 0 and " + (V - 1));
}
/**
* 测试
*/
public static void main(String[] args) {
}
}
一般加权有向图中的最短路径算法
负权重的环。加权有向图中一个总权重(换上所有边权重之和)为负的有向环。
假设从s可到达v。当路径上的某个顶点在负权重的环上,则最短路径是不存在的。
则一个定义明确觉可以解决的加权有向图的最短路径要满足:
1. 不可达的顶,最短路径为+∞。
2. 从起点可达,但有路径上有顶点在负权重换上。最短路径为-∞。
3. 对于其他顶点,计算最短路径。
命题X (ellman-Ford算法)。在任意含有V 个顶点的加权有向图中给定起点s,从s无法到达任何负权重环,以下算法能够解决其中的单点最短路径问题:将distTo[s] 初始化为0其他distTo[]元素初始化为无穷大。从源顶点开始以任意的顺序放松所有顶点。
证明。对于从s可达的任意顶点t,从s到t的一条最短路径: V0→V1→…→Vk,其中V0=s,Vk=t。因为负权重环是不可达的,这样的路径是存在的且k<=V-1。归纳法证明算法在第i轮之后能够得到s到vi的最短路径。最简单的情况( i=0)。假设对于i命题成立,那么s到vi的最短路径即为V0→V1→…→Vi,distTo[vi]是这条路径的长度。现在, 我们在第i轮中放松所有的点,包括vi,因此distTo[vi+1]不会大于distTo[vi]与边vi→vi+1的权重之和。在第i轮放松之后,distTo[vi+1] 必然等于distTo[vi]与边vi→vi+1的权重之和。它不可能更大,因为在第i轮中放松了所有顶点,包括Vi;它也不可能更小,因为它就V0→V1→…→Vi+1的长度,也就是最短路径了。因此,在i+1轮之后算法能够得到从s到Vi+1的最短路径。
package com.graphs.sp;
import com.dl_queue.Queue;
import com.stack.Stack;
import edu.princeton.cs.algs4.In;
import edu.princeton.cs.algs4.StdOut;
/**
* @create 2020-04-13 19:18
*/
public class BellmanFordSp {
private double[] distTo; // distTo[v] = s->v最短路径的距离
private DirectedEdge[] edgeTo; // edgeTo[v] = 最短s->v路径上的最后一条边
private boolean[] onQueue; // onQueue[v] = v当前在队列中吗?
private Queue<Integer> queue; // 要松弛的顶点队列
private int cost; // relax()调用的次数
private Iterable<DirectedEdge> cycle; // 负权重的环(如果没有,为null)
/**
* 计算从{@code s}到边缘加权有向图{@code G}中每个其他顶点的最短路径树。
*/
public BellmanFordSp(EdgeWeightedDigraph G, int s) {
distTo = new double[G.V()];
edgeTo = new DirectedEdge[G.V()];
onQueue = new boolean[G.V()];
for (int v = 0; v < G.V(); v++)
distTo[v] = Double.POSITIVE_INFINITY; // 正无穷
distTo[s] = 0.0;
// Bellman-Ford 算法
queue = new Queue<>();
queue.enqueue(s); // 源顶点入队列
onQueue[s] = true;
while (!queue.isEmpty() && !hasNegativeCycle()) {
int v = queue.dequeue();
onQueue[v] = false;
relax(G, v);
}
}
/**
* 放松顶点v,如果改变,将其他端点放到队列上
*/
private void relax(EdgeWeightedDigraph G, int v) {
for (DirectedEdge e : G.adj(v)) {
int w = e.to();
if (distTo[w] > distTo[v] + e.weight()) {
distTo[w] = distTo[v] + e.weight();
edgeTo[w] = e;
if (!onQueue[w]) { // 顶点w还不在队列中
queue.enqueue(w);
onQueue[w] = true;
}
}
if (++cost % G.V() == 0) { // 执行relax方法次数小于等于顶点数
findNegativeCycle();
if (hasNegativeCycle()) return; // 存在负权重环
}
}
}
/**
* @return 如果从源顶点{@code s}可以到达一个负权重环,则{@code true},
* 否则{@code false}
*/
public boolean hasNegativeCycle() {
return cycle != null;
}
/**
* @return 一个可以从源顶点{@code s}到达的负循环,如果没有这样的循环,则{@code null}。
*/
public Iterable<DirectedEdge> negativeCycle() {
return cycle;
}
/**
* 负权重环的检测方法
* 若存在负权重环,放松顶点到某个时(<=V)edgeTo()中会出现这个环。
* 要松弛的queue队列必然不会为空。
*/
private void findNegativeCycle() {
int V = edgeTo.length;
EdgeWeightedDigraph spt = new EdgeWeightedDigraph(V); //一个加权有向图
for (int v = 0; v < V; v++)
if (edgeTo[v] != null) // 已经到达过顶点v
spt.addEdge(edgeTo[v]);
EdgeWeightedDirectedCycle finder = new EdgeWeightedDirectedCycle(spt); // 检测有向环。
cycle = finder.cycle();
}
/**
* @return 从源顶点{@code s}到顶点{@code v}的最短路径长度
*/
public double distTo(int v) {
validateVertex(v);
if (hasNegativeCycle())
throw new UnsupportedOperationException("Negative cost cycle exists");
return distTo[v];
}
/**
* @return 存在从源 {@code s}到顶点{@code v}的路径{@code true}。
*/
public boolean hasPathTo(int v) {
validateVertex(v);
return distTo[v] < Double.POSITIVE_INFINITY;
}
/**
* @return 从源{@code s}到顶点{@code v}的最短路径
* 如果没有这样的路径,则为{@code null}
* @throws UnsupportedOperationException 存在从源顶点{@code s}可达的负权重环
*/
public Iterable<DirectedEdge> pathTo(int v) {
validateVertex(v);
if (hasNegativeCycle())
throw new UnsupportedOperationException("Negative cost cycle exists");
if (!hasPathTo(v)) return null;
Stack<DirectedEdge> path = new Stack<>();
for (DirectedEdge e = edgeTo[v]; e != null; e = edgeTo[e.from()]) {
path.push(e);
}
return path;
}
/**
* throw an IllegalArgumentException unless {@code 0 <= v < V}
*/
private void validateVertex(int v) {
int V = distTo.length;
if (v < 0 || v >= V)
throw new IllegalArgumentException("vertex " + v + " is not between 0 and " + (V-1));
}
/**
* Unit tests
*/
public static void main(String[] args) {
In in = new In(args[0]);
int s = Integer.parseInt(args[1]);
EdgeWeightedDigraph G = new EdgeWeightedDigraph(in);
BellmanFordSp sp = new BellmanFordSp(G, s);
// 打印-负权重环
if (sp.hasNegativeCycle()) {
for (DirectedEdge e : sp.negativeCycle())
StdOut.println(e);
}
// 打印最短路径
else {
for (int v = 0; v < G.V(); v++) {
if (sp.hasPathTo(v)) {
StdOut.printf("%d to %d (%5.2f) ", s, v, sp.distTo(v));
for (DirectedEdge e : sp.pathTo(v)) {
StdOut.print(e + " ");
}
StdOut.println();
}
else {
StdOut.printf("%d to %d no path\n", s, v);
}
}
}
}
}