Android 入门第十讲01-服务(服务概述,创建和启动,播放音乐,启动服务的第二种方法,暂停音乐)
Android 入门第十讲01-服务(服务概述,创建和启动,播放音乐,启动服务的第二种方法,暂停音乐)
- 1.服务概述
- 2.服务的创建和启动
- 1.创建
- 2.启动
- 3.播放音乐
- 4.启动服务的第二种方法
- 5.暂停音乐
Android 入门第九讲03-动画(帧动画(点击开始,停止)+补间动画(透明度动画,缩放动画,位移动画,旋转动画,组合动画))
1.服务概述
- 定义:服务,是 Android 四大组件之一
- 作用:
1.提供需要在后台长期运行的服务 如:复杂计算,音乐播放,下载等。(本讲主讲)
就比如我们用的qq,在关掉以后,收到消息还是会弹出通知框,
2.跨进程访问。
我们 知道在两个不同的线程中,数据是可以共享的,但是在不同的两个进程中,就好比再两个不同的应用程序中是不能互相访问的,但是我们可以通过服务来实现跨进程访问
2.服务的创建和启动
1.创建
创建service

这里服务和activity有点类似,
第一是会创建一个服务的类

第二是会在Mainifest里注册

第三

不同的地方就是服务不能对界面UI进行操作
2.启动
启动service
第一步,添加一个按钮
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="utf-8"?>
<androidx.constraintlayout.widget.ConstraintLayout xmlns:android="http://schemas.android.com/apk/res/android"
xmlns:app="http://schemas.android.com/apk/res-auto"
xmlns:tools="http://schemas.android.com/tools"
android:layout_width="match_parent"
android:layout_height="match_parent"
tools:context=".MainActivity">
<Button
android:id="@+id/button"
android:layout_width="wrap_content"
android:layout_height="wrap_content"
android:text="启动服务"
app:layout_constraintBottom_toBottomOf="parent"
app:layout_constraintEnd_toEndOf="parent"
app:layout_constraintStart_toStartOf="parent"
app:layout_constraintTop_toTopOf="parent" />
</androidx.constraintlayout.widget.ConstraintLayout>
public class MainActivity extends AppCompatActivity {
@Override
protected void onCreate(Bundle savedInstanceState) {
super.onCreate(savedInstanceState);
setContentView(R.layout.activity_main);
Button button=findViewById(R.id.button);
button.setOnClickListener(new View.OnClickListener() {
@Override
public void onClick(View v) {
Intent intent=new Intent(MainActivity.this,MyService.class);
startService(intent);
}
});
}
}

第三步,在MyService的oncreat方法里打印日志,表示启动了服务
public class MyService extends Service {
public MyService() {
}
@Override
public IBinder onBind(Intent intent) {
// TODO: Return the communication channel to the service.
throw new UnsupportedOperationException("Not yet implemented");
}
@Override
public void onCreate() {
Log.i("MyService","成功的启动了服务");
super.onCreate();
}
@Override
public void onDestroy() {
super.onDestroy();
}
}
运行(成功打印了日志,也可以看到我们的界面没有任何的变化)
3.播放音乐
第一步, 先创建raw文件夹
第二步,导入音频文件
第三步,在service中添加播放音乐的代码
MyService代码
public class MyService extends Service {
MediaPlayer mMediaPlayer;
public MyService() {
}
@Override
public IBinder onBind(Intent intent) {
// TODO: Return the communication channel to the service.
throw new UnsupportedOperationException("Not yet implemented");
}
@Override
public void onCreate() {
if (mMediaPlayer == null) {
mMediaPlayer=MediaPlayer.create(this,R.raw.a1); //这里context 只需要传一个 this
}
//播放音乐
mMediaPlayer.start();
Log.i("MyService","成功的启动了服务");
super.onCreate();
}
@Override
public void onDestroy() {
super.onDestroy();
}
}

运行(可以看到,再点击启动服务以后,右下角录屏悬浮球音频监控波浪发生变化,说明有音乐播放)
4.启动服务的第二种方法
用这种方式启动服务的缺点就是,activity管不到service,也就是activity无法调用到service里面的方法,比如无法暂停音乐,所以这种方式启动服务只适用于启动以后不需要关闭的一些操作,如果我们需要在启动服务以后,改变其中某种操作的状态,就需要用到service的第二种启动方式
第一步,我们用bindservice来启动服务

第二步,创建一个MyServiceConnection内部类并且实现两种方法

我们再看到 MyService中 这个onBind方法,我们用第二种方法启动服务,一定会回调这个onBind方法,系统就会强制我们返回一个IBinder对象,然后通过activity拿到引用

第三步,重写MyBinder方法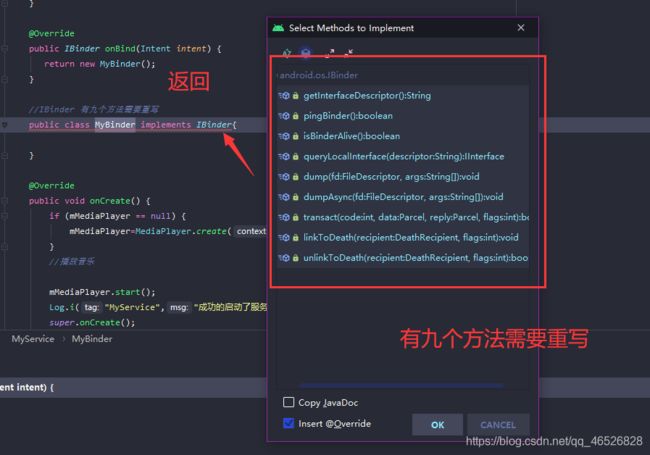
(因为IBinder接口需要重写九个方法,所以我们找一个已经实现IBinder接口的方法继承)
有点乱,统一 一下代码
activity代码
public class MainActivity extends AppCompatActivity {
MyService.MyBinder mMyBinder;
@Override
protected void onCreate(Bundle savedInstanceState) {
super.onCreate(savedInstanceState);
setContentView(R.layout.activity_main);
Button button=findViewById(R.id.button);
button.setOnClickListener(new View.OnClickListener() {
@Override
public void onClick(View v) {
Intent intent=new Intent(MainActivity.this,MyService.class);
bindService(intent,new MyServiceConnection(),BIND_AUTO_CREATE);
}
});
}
public class MyServiceConnection implements ServiceConnection{
//启动service时调用
@Override
public void onServiceConnected(ComponentName name, IBinder service) {
//IBinder 是一个接口
//拿到 mMyBinder -service里面一个类的引用
mMyBinder =(MyService.MyBinder)service;
}
@Override
public void onServiceDisconnected(ComponentName name) {
}
}
}
Myservice代码
public class MyService extends Service {
MediaPlayer mMediaPlayer;
public MyService() {
}
@Override
public IBinder onBind(Intent intent) {
return new MyBinder();
}
//Binder 已经实IBinder 接口
public class MyBinder extends Binder {
}
@Override
public void onCreate() {
if (mMediaPlayer == null) {
mMediaPlayer=MediaPlayer.create(this,R.raw.a1); //这里context 只需要传一个 this
}
//播放音乐
mMediaPlayer.start();
Log.i("MyService","成功的启动了服务");
super.onCreate();
}
}
运行(成功启动)
5.暂停音乐
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="utf-8"?>
<androidx.constraintlayout.widget.ConstraintLayout xmlns:android="http://schemas.android.com/apk/res/android"
xmlns:app="http://schemas.android.com/apk/res-auto"
xmlns:tools="http://schemas.android.com/tools"
android:layout_width="match_parent"
android:layout_height="match_parent"
tools:context=".MainActivity">
<Button
android:id="@+id/button"
android:layout_width="wrap_content"
android:layout_height="wrap_content"
android:text="启动服务"
app:layout_constraintBottom_toBottomOf="parent"
app:layout_constraintEnd_toEndOf="parent"
app:layout_constraintStart_toStartOf="parent"
app:layout_constraintTop_toTopOf="parent" />
<Button
android:id="@+id/button2"
android:layout_width="wrap_content"
android:layout_height="wrap_content"
android:text="暂停音乐"
app:layout_constraintBottom_toBottomOf="parent"
app:layout_constraintEnd_toEndOf="parent"
app:layout_constraintStart_toStartOf="parent"
app:layout_constraintTop_toBottomOf="@+id/button" />
</androidx.constraintlayout.widget.ConstraintLayout>
第二步,在Myservice 的 MyBinder 方法下添加暂停音乐的代码
public void stopmusic(){
//因为一开始没有播放音乐的时候,实际上就没有加载音频文件,所以点击暂停会报空指针
if (mMediaPlayer !=null) {
//暂停音乐
mMediaPlayer.pause();
}
}
第三步,添加点击事件,调用service中的mMyBinder类中暂停音乐的方法

Button button1=findViewById(R.id.button2);
button1.setOnClickListener(new View.OnClickListener() {
@Override
public void onClick(View v) {
mMyBinder.stopmusic();
}
});
运行
总结:在activity里面,有些与ui无关的操作,我们可以把它放到service里面来进行,或者是一些需要在后台长期运行的服务,都可以放到service里面来进行,service有两种启动方式,如果对service里面的操作不需要进一步修改,就可以用第一种方法,也比较简单,如果需要进一步改变操作的状态,就需要用到第二种方法 ,然后我们通过service里面的onBind方法,返回的IBand接口 ,我们拿到接口以后,就可以对它进行操作,但是接口本身里面是没有任何操作的,我们需要通过他的一个实现类,也就是上面的MyBinder,我们把需要控制的地方写到中间类MyBinder中,通过这个类来进行操作。
关于服务service的知识就讲到这里啦,谢谢您的服务,下一讲是小小白入门的最后一讲也是Android的四大组件之一-广播
Android 入门第十讲02-广播(广播概述,使用方法(系统广播,自定义广播,两个activity之间的交互和传值),EventBus使用方法,数据传递,线程切换,Android的系统广播大全)