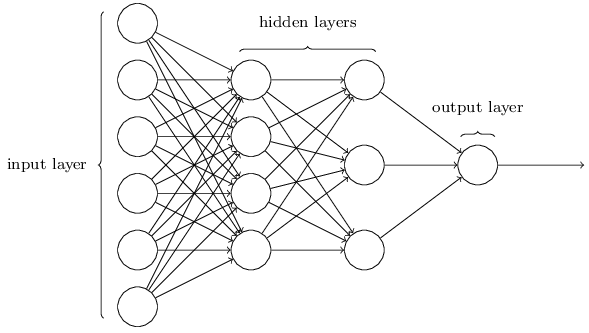
神经网络结构如下图所示(不失一般性,这里仅考虑二分类和回归问题):
假设训练数据共有$m$个,训练数据集可由矩阵$X=\begin{bmatrix}\begin{smallmatrix}\vdots&\vdots&\cdots&\vdots\\\vec{x}^{(1)}&\vec{x}^{(2)}&\cdots&\vec{x}^{(m)}\\\vdots&\vdots&\cdots&\vdots\end{smallmatrix}\end{bmatrix}$表示,X为p行m列的矩阵(p为特征数)。
假设从输入层到输出层依次记为第$0,1,2,...,L$层,每层的节点数记为$n_0,n_1,n_2,...,n_L$,可以看出$n_0=p$,$n_L=1$(这里仅考虑二分类和回归问题)
第$l$层($l=1,2,...,L$)的权重$W^{[l]}$为$n_l$行$n_{l-1}$列的矩阵,$b^{[l]}$为$n_l$行1列的矩阵
第$l$层($l=1,2,...,L$)使用激活函数前的值$Z^{[l]}$为$n_l$行$m$列的矩阵,使用激活函数后的值$A^{[l]}$为$n_l$行$m$列的矩阵
一、公式
1. Forward Propagation
线性部分:$Z^{[l]} = W^{[l]}A^{[l-1]} +b^{[l]}$(注:$A^{[0]}=X$)
非线性部分:$A^{[l]}=g(Z^{[l]})$($g$为激活函数)
- 本文隐藏层的激活函数使用relu,可减轻梯度消失问题
- 若为二分类问题,输出层的激活函数使用sigmoid;若为回归问题,输出层不使用激活函数,即$A^{[L]}=Z^{[L]}$
2. Loss Function
若为回归问题,损失函数可写为$\mathcal{J}=\frac{1}{2m}\sum\limits_{i = 1}^{m}(a^{[L] (i)}-y^{(i)})^2$,其中$a^{[L] (i)}$为第$i$个样本的预测值(即$A^{[L]}$的$i$列),$y^{(i)}$为第$i$个样本的真实值
若为二分类问题,损失函数可写为$\mathcal{J}=-\frac{1}{m} \sum\limits_{i = 1}^{m} [y^{(i)}\log\left(a^{[L] (i)}\right) + (1-y^{(i)})\log\left(1- a^{[L](i)}\right)]$
3. Backward Propagation
记$dA^{[l]}=\frac{\partial \mathcal{J} }{\partial A^{[l]}}$,则可推出以下公式:
- (1) $dZ^{[l]}=\frac{\partial \mathcal{J} }{\partial Z^{[l]}}=dA^{[l]}* g'(Z^{[l]})$,其中$g'$表示激活函数的导数
- (2) $dW^{[l]} = \frac{\partial \mathcal{J} }{\partial W^{[l]}} = \frac{1}{m} dZ^{[l]} A^{[l-1] T}$,其中$A^{[l-1] T}$表示$A^{[l-1]}$的转置
- (3) $db^{[l]} = \frac{\partial \mathcal{J} }{\partial b^{[l]}} = \frac{1}{m} \sum_{i = 1}^{m} dZ^{[l](i)}$,其中$dZ^{[l](i)}$为矩阵$dZ^{[l]}$的第$i$列
- (4) $dA^{[l-1]} = \frac{\partial \mathcal{J} }{\partial A^{[l-1]}} = W^{[l] T} dZ^{[l]}$,其中$W^{[l] T}$表示$W^{[l]}$的转置
4. Update Parameters
$W^{[l]} = W^{[l]} - \alpha \text{ } dW^{[l]}$,$b^{[l]} = b^{[l]} - \alpha \text{ } db^{[l]}$,$\alpha$为学习率
二、代码
1. Initialize Parameters
def initialize_parameters_deep(layer_dims): """ Arguments: layer_dims -- python array (list) containing the dimensions of each layer in our network Returns: parameters -- python dictionary containing your parameters 'W1', 'b1', ..., 'WL', 'bL': Wl -- weight matrix of shape (layer_dims[l], layer_dims[l-1]) bl -- bias vector of shape (layer_dims[l], 1) """ np.random.seed(3) parameters = {} L = len(layer_dims) # number of layers in the network(including the input layer) for l in range(1, L): parameters['W' + str(l)] = np.random.randn(layer_dims[l], layer_dims[l-1])*0.01 parameters['b' + str(l)] = np.zeros((layer_dims[l], 1)) return parameters
2. Forward Propagation
def sigmoid(Z): return 1/(1+np.exp(-Z)) def relu(Z): return np.maximum(0,Z) def linear_activation_forward(A_prev, W, b, activation): """ Implement the forward propagation for the LINEAR->ACTIVATION layer Arguments: A_prev -- activations from previous layer (or input data): (size of previous layer, number of examples) W -- weights matrix: numpy array of shape (size of current layer, size of previous layer) b -- bias vector, numpy array of shape (size of the current layer, 1) activation -- the activation to be used in this layer, stored as a text string: 'sigmoid' or 'relu' or 'none' Returns: A -- the output of the activation function, also called the post-activation value cache -- a python dictionary containing 'linear_cache' and 'activation_cache'; stored for computing the backward pass efficiently """ Z = np.dot(W, A_prev)+b linear_cache = (A_prev, W, b) activation_cache = Z A = sigmoid(Z) if activation=="sigmoid" else relu(Z) if activation=="relu" else np.array(Z,copy=True) cache = (linear_cache, activation_cache) return A, cache def L_model_forward(X, parameters, type): """ Implement forward propagation Arguments: X -- data, numpy array of shape (input size, number of examples) parameters -- output of initialize_parameters_deep() type -- problem type, stored as a text string: 'binary classification' or 'regression' Returns: AL -- last post-activation value caches -- list of caches containing: every cache of linear_activation_forward() (there are L of them, indexed from 0 to L-1) """ caches = [] A = X L = len(parameters) // 2 # number of layers in the neural network(excluding the input layer) ### hidden layer for l in range(1, L): A_prev = A A, cache = linear_activation_forward(A_prev, parameters['W'+str(l)], parameters['b'+str(l)], 'relu') caches.append(cache) ### output layer if type=="regression": AL, cache = linear_activation_forward(A, parameters['W'+str(L)], parameters['b'+str(L)], 'none') else: AL, cache = linear_activation_forward(A, parameters['W'+str(L)], parameters['b'+str(L)], 'sigmoid') caches.append(cache) return AL, caches
3. Loss Function
def compute_cost(AL, Y, type): """ Arguments: AL -- last post-activation value, shape (1, number of examples) Y -- true vector, shape (1, number of examples) type -- problem type, stored as a text string: 'binary classification' or 'regression' Returns: cost -- cross-entropy loss for classification and mean squared error for regression """ m = Y.shape[1] #number of examples if type=="regression": cost = np.sum(np.power(AL-Y,2))/(2*m) else: cost = -np.sum(Y*np.log(AL)+(1-Y)*np.log(1-AL))/m cost = np.squeeze(cost) # To make sure cost's shape is what expected (e.g., this turns [[10]] into 10) return cost
4. Backward Propagation
def relu_backward(dA, cache): """ Implement the backward propagation for a single RELU unit. Arguments: dA -- post-activation gradient, of any shape cache -- 'Z' where we store for computing backward propagation efficiently Returns: dZ -- Gradient of the cost with respect to Z """ Z = cache dZ = np.array(dA, copy=True) # just converting dz to a correct object dZ[Z <= 0] = 0 # When z <= 0, you should set dz to 0 as well return dZ def sigmoid_backward(dA, cache): """ Implement the backward propagation for a single SIGMOID unit. Returns: dZ -- Gradient of the cost with respect to Z """ Z = cache s = 1/(1+np.exp(-Z)) dZ = dA * s * (1-s) return dZ def linear_backward(dZ, cache): """ Implement the linear portion of backward propagation for a single layer (layer l) Arguments: dZ -- Gradient of the cost with respect to the linear output (of current layer l) cache -- tuple of values (A_prev, W, b) coming from the forward propagation in the current layer Returns: dA_prev -- Gradient of the cost with respect to the activation (of the previous layer l-1), same shape as A_prev dW -- Gradient of the cost with respect to W (current layer l), same shape as W db -- Gradient of the cost with respect to b (current layer l), same shape as b """ A_prev, W, b = cache m = A_prev.shape[1] dW = np.dot(dZ, A_prev.T)/m db = np.sum(dZ, axis=1, keepdims=True)/m dA_prev = np.dot(W.T, dZ) return dA_prev, dW, db def linear_activation_backward(dA, cache, activation): """ Implement the backward propagation for the LINEAR->ACTIVATION layer. Arguments: dA -- post-activation gradient for current layer l cache -- tuple of values (linear_cache, activation_cache) we store for computing backward propagation efficiently activation -- the activation to be used in this layer, stored as a text string: 'sigmoid' or 'relu' or 'none' Returns: dA_prev -- Gradient of the cost with respect to the activation (of the previous layer l-1), same shape as A_prev dW -- Gradient of the cost with respect to W (current layer l), same shape as W db -- Gradient of the cost with respect to b (current layer l), same shape as b """ linear_cache, activation_cache = cache dZ = sigmoid_backward(dA, activation_cache) if activation=="sigmoid" else relu_backward(dA, activation_cache) if activation=="relu" else np.array(dA,copy=True) dA_prev, dW, db = linear_backward(dZ, linear_cache) return dA_prev, dW, db def L_model_backward(AL, Y, caches, type): """ Implement the backward propagation Arguments: AL -- output of the forward propagation (L_model_forward()) Y -- true vector caches -- list of caches containing: every cache of linear_activation_forward() (there are L of them, indexed from 0 to L-1) type -- problem type, stored as a text string: 'binary classification' or 'regression' Returns: grads -- A dictionary with the gradients grads["dA" + str(l)] = ... grads["dW" + str(l)] = ... grads["db" + str(l)] = ... """ grads = {} L = len(caches) # the number of layers(excluding the input layer) m = AL.shape[1] Y = Y.reshape(AL.shape) # after this line, Y is the same shape as AL current_cache = caches[L-1] ### Initializing the backpropagation if type=='binary classification': dAL = -(np.divide(Y, AL) - np.divide(1 - Y, 1 - AL)) grads["dA" + str(L-1)], grads["dW" + str(L)], grads["db" + str(L)] = linear_activation_backward(dAL, current_cache, 'sigmoid') else: dAL = AL-Y grads["dA" + str(L-1)], grads["dW" + str(L)], grads["db" + str(L)] = linear_activation_backward(dAL, current_cache, 'none') # Loop from l=L-2 to l=0 for l in reversed(range(L-1)): # (l+1)th layer: (RELU -> LINEAR) gradients. # Inputs: "grads["dA" + str(l + 1)], current_cache". Outputs: "grads["dA" + str(l)] , grads["dW" + str(l + 1)] , grads["db" + str(l + 1)] current_cache = caches[l] dA_prev_temp, dW_temp, db_temp = linear_activation_backward(grads["dA" + str(l+1)], current_cache, 'relu') grads["dA" + str(l)] = dA_prev_temp grads["dW" + str(l + 1)] = dW_temp grads["db" + str(l + 1)] = db_temp return grads
5. Update Parameters
def update_parameters(parameters, grads, learning_rate): """ Update parameters using gradient descent Arguments: parameters -- python dictionary containing parameters grads -- python dictionary containing gradients, output of L_model_backward Returns: parameters -- python dictionary containing updated parameters parameters["W" + str(l)] = ... parameters["b" + str(l)] = ... """ L = len(parameters)//2 #number of layers in the neural network(excluding the input layer) ### Update rule for each parameter. Use a for loop. for l in range(L): parameters["W" + str(l+1)] = parameters["W" + str(l+1)]-learning_rate*grads["dW" + str(l+1)] parameters["b" + str(l+1)] = parameters["b" + str(l+1)]-learning_rate*grads["db" + str(l+1)] return parameters
6. Train Neural Network
import numpy as np def train(X, Y, type, parameters, learning_rate): """ Train a neural network Arguments: X -- data, numpy array of shape (input size, number of examples) Y -- true vector, of shape (1, number of examples) type -- problem type, stored as a text string: 'binary classification' or 'regression' parameters -- python dictionary containing parameters learning_rate -- learning rate of the gradient descent update rule Returns: parameters -- python dictionary containing updated parameters parameters["W" + str(l)] = ... parameters["b" + str(l)] = ... """ ### gradient descent AL, caches = L_model_forward(X, parameters, type) # Forward propagation grads = L_model_backward(AL, Y, caches, type) # Backward propagation parameters = update_parameters(parameters, grads, learning_rate) # Update parameters return parameters
7. Prediction
def predict(X, parameters, type): """ Predict through neural network Arguments: X -- data, numpy array of shape (input size, number of examples) parameters -- output of initialize_parameters_deep() type -- problem type, stored as a text string: 'binary classification' or 'regression' Returns: AL -- last post-activation value(prediction) """ A = X L = len(parameters) // 2 # number of layers in the neural network(excluding the input layer) ### hidden layer for l in range(1, L): A_prev = A A, _ = linear_activation_forward(A_prev, parameters['W'+str(l)], parameters['b'+str(l)], 'relu') ### output layer if type=="regression": AL, _ = linear_activation_forward(A, parameters['W'+str(L)], parameters['b'+str(L)], 'none') else: AL, _ = linear_activation_forward(A, parameters['W'+str(L)], parameters['b'+str(L)], 'sigmoid') return AL
三、应用
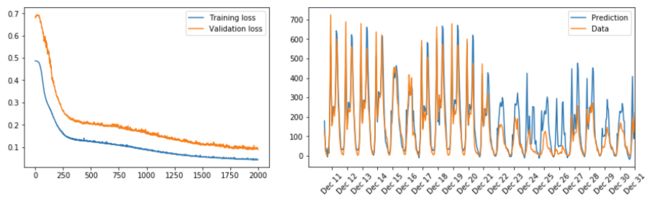
使用的数据为共享单车骑行数据,通过建立神经网络来预测共享单车的使用量
import sys import pandas as pd import matplotlib.pyplot as plt rides = pd.read_csv('Bike-Sharing-Dataset/hour.csv') ### Categorical variables dummy_fields = ['season', 'weathersit', 'mnth', 'hr', 'weekday'] for each in dummy_fields: dummies = pd.get_dummies(rides[each], prefix=each, drop_first=False) rides = pd.concat([rides, dummies], axis=1) fields_to_drop = ['instant', 'dteday', 'season', 'weathersit', 'weekday', 'atemp', 'mnth', 'workingday', 'hr'] data = rides.drop(fields_to_drop, axis=1) ### Numerical variables quant_features = ['casual', 'registered', 'cnt', 'temp', 'hum', 'windspeed'] scaled_features = {} #Store scalings in a dictionary so we can convert back later for each in quant_features: mean, std = data[each].mean(), data[each].std() scaled_features[each] = [mean, std] data.loc[:, each] = (data[each] - mean)/std ### Split data test_data = data[-21*24:] # Save test data for approximately the last 21 days data = data[:-21*24] # Now remove the test data from the data set target_fields = ['cnt', 'casual', 'registered'] features, targets = data.drop(target_fields, axis=1), data[target_fields] test_features, test_targets = test_data.drop(target_fields, axis=1), test_data[target_fields] train_features, train_targets = features[:-60*24], targets[:-60*24] val_features, val_targets = features[-60*24:], targets[-60*24:] # Hold out the last 60 days or so of the remaining data as a validation set ### Train layers_dims = [train_features.shape[1], 12, 1] learning_rate = 0.1 iterations = 2000 losses = {'train':[], 'validation':[]} parameters = initialize_parameters_deep(layers_dims) # Parameters initialization for ii in range(iterations): ### Go through a random batch of 128 records from the training data set batch = np.random.choice(train_features.index, size=128) X, y = train_features.ix[batch].values.T, train_targets.ix[batch]['cnt'].values.reshape((1,-1)) parameters = train(X, y, 'regression', parameters, learning_rate) ### Losses AL_train = predict(train_features.values.T, parameters, 'regression') AL_val = predict(val_features.values.T, parameters, 'regression') train_loss = compute_cost(AL_train, train_targets['cnt'].values.reshape((1,-1)), 'regression') val_loss = compute_cost(AL_val, val_targets['cnt'].values.reshape((1,-1)), 'regression') sys.stdout.write("\rProgress: {:2.1f}".format(100 * ii/float(iterations)) \ + "% ... Training loss: " + str(train_loss)[:5] \ + " ... Validation loss: " + str(val_loss)[:5]) sys.stdout.flush() losses['train'].append(train_loss) losses['validation'].append(val_loss) ### Plot Losses(left picture below) plt.plot(losses['train'], label='Training loss') plt.plot(losses['validation'], label='Validation loss') plt.legend() _ = plt.ylim() ### Predict and Plot(right picture below) fig, ax = plt.subplots(figsize=(8,4)) mean, std = scaled_features['cnt'] AL_test = predict(test_features.values.T, parameters, 'regression') predictions = AL_test*std + mean ax.plot(predictions[0], label='Prediction') ax.plot((test_targets['cnt']*std + mean).values, label='Data') ax.set_xlim(right=len(predictions)) ax.legend() dates = pd.to_datetime(rides.ix[test_data.index]['dteday']) dates = dates.apply(lambda d: d.strftime('%b %d')) ax.set_xticks(np.arange(len(dates))[12::24]) _ = ax.set_xticklabels(dates[12::24], rotation=45)