剑指offer编程题
1.有序二维数组查找是否存在给定的值
class Solution {
public:
bool searchMatrix(vector<vector<int>>& matrix, int target) {
if(matrix.empty()) return false;
int row=matrix.size();
int col=matrix[0].size();
if(col==0) return false;
int r=0;
while(r1)>=0){
if(matrix[r][col-1]==target)
return true;
else if(matrix[r][col-1]>target)
col--;
else if(matrix[r][col-1]return false;
}
};
2.将字符串中的所有空格替换为%20
class Solution {
public:
void replaceSpace(char *str,int length) {
if(str==NULL) return ;
int count=0;
for(int i=0;iif(str[i]==' ') count++;
}
int previous=length;
length=length+count*2;
int after=length;
while(count--){
//previous--;
while(str[previous]!=' '){
str[after]=str[previous];
after--;previous--;
}
str[after--]='0';
str[after--]='2';
str[after--]='%';
}
}
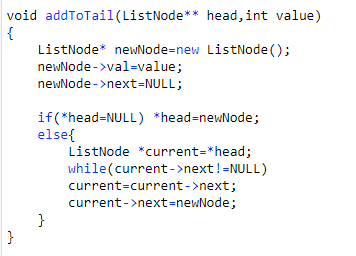
}; 3.在链表的末尾添加一个节点
4.在链表中找到第一个含有某值的节点并删除
void removeNode(ListNode** head,int value)
5.从尾到头打印节点
方法一:使用栈;
方法二:递归。
void recursive(ListNode* head)
{
if(head!=NULL)
{
if(head->next!=NULL)
{
recursive(head->next);
}
}
printf("%d\t",head->val);
}6.根据前序遍历和中序遍历重建二叉树
/**
* Definition for a binary tree node.
* struct TreeNode {
* int val;
* TreeNode *left;
* TreeNode *right;
* TreeNode(int x) : val(x), left(NULL), right(NULL) {}
* };
*/
class Solution {
public:
TreeNode* recursiveBuild(vector<int>& preorder, vector<int>& inorder) {
if(preorder.size()==0 || inorder.size()==0)
return NULL;
TreeNode* head=new TreeNode(preorder[0]);
//head->val=preorder[0];
if(preorder.size()==1 && inorder.size()==1)
return head;
vector<int> inleft,inright;//找到左右子树的中序遍历序列
int flag=0,count=0;
for(int i=0;iif(preorder[0]!=inorder[i] && flag==0){
inleft.push_back(inorder[i]);
count++;
}
if(preorder[0]==inorder[i]){
flag=1;
}
else{
inright.push_back(inorder[i]);
}
}
vector<int> preleft,preright;//找到左右子树的前序遍历序列
for(int i=1;iif(count--){
preleft.push_back(preorder[i]);
}
else{
preright.push_back(preorder[i]);
}
}
head->left=recursiveBuild(preleft,inleft);
head->right=recursiveBuild(preright,inright);
return head;
}
TreeNode* buildTree(vector<int>& preorder, vector<int>& inorder) {
//TreeNode* root;
TreeNode* root=recursiveBuild(preorder, inorder);
return root;
}
};
7.使用两个栈实现队列
class MyQueue {
private:
stack<int> in;
stack<int> out;
int front;
public:
/** Initialize your data structure here. */
MyQueue() {
}
/** Push element x to the back of queue. */
void push(int x) {
in.push(x);
}
/** Removes the element from in front of queue and returns that element. */
int pop() {
int l=in.size();
if(out.empty()){
for(int i=0;iint ans=out.top();
out.pop();
return ans;
}
/** Get the front element. */
int peek() {
int l=in.size();
if(out.empty()){
for(int i=0;ireturn out.top();
}
/** Returns whether the queue is empty. */
bool empty() {
return in.empty()&&out.empty();
}
};
/**
* Your MyQueue object will be instantiated and called as such:
* MyQueue obj = new MyQueue();
* obj.push(x);
* int param_2 = obj.pop();
* int param_3 = obj.peek();
* bool param_4 = obj.empty();
*/ 8.树的子结构
输入两棵二叉树A,B,判断B是不是A的子结构。(ps:我们约定空树不是任意一个树的子结构)
class Solution {
public:
bool ifTree2inTree1(TreeNode *p,TreeNode* q){
if(q==NULL) return true;
if(p==NULL) return false;
if(p->val!=q->val) return false;
else{
return ifTree2inTree1(p->left,q->left) && ifTree2inTree1(p->right,q->right);
}
}
bool HasSubtree(TreeNode* pRoot1, TreeNode* pRoot2)
{
bool result = false;
if(pRoot1!=NULL && pRoot2!=NULL){
if(pRoot1->val==pRoot2->val)
result=ifTree2inTree1(pRoot1,pRoot2);
if(!result)
result=HasSubtree(pRoot1->left,pRoot2);
if(!result)
result=HasSubtree(pRoot1->right,pRoot2);
}
return result;
}
};9.顺时针打印矩阵
class Solution {
public:
vector<int> printMatrix(vector<vector<int> > matrix) {
vector<int> ans;
if(matrix.size()==0) return ans;
int rows=matrix.size();
int columns=matrix[0].size();
int start=0;
while(columns>start*2 && rows>start*2){
//打印从左到右的一行
int length1=columns-start-1;
for(int i=start;i<=length1;i++){
ans.push_back(matrix[start][i]);
}
//打印从上到下的一列
int length2=rows-start-1;
if(startfor(int i=start+1;i<=length2;i++){
ans.push_back(matrix[i][length1]);
}
}
//打印从右到左的一行
if(startfor(int i=length1-1;i>=start;i--){
ans.push_back(matrix[length2][i]);
}
}
//打印从下到上的一列
if(start1 && startfor(int i=length2-1;i>=start+1;i--){
ans.push_back(matrix[i][start]);
}
}
start++;
}
return ans;
}
}; 10.包含min函数的栈
在栈里添加一个辅助栈,辅助栈里存放每次压入元素的最小元素(之前的最小元素和新压入栈元素两者的最小值),保持数据栈与辅助栈大小相等。当数据栈里最小元素被弹出时,辅助栈也弹出栈顶元素。
11.栈的压入、弹出序列
class Solution {
public:
bool IsPopOrder(vector<int> pushV,vector<int> popV) {
if(pushV.size()==0) return true;
stack<int> stackData;
int datalength=pushV.size();
int locPush=0,locPop=0;
for(int i=0;iwhile(stackData.empty() || stackData.top()!=popV[i]){
if(locPush==datalength) return false;
stackData.push(pushV[locPush]);
locPush++;
}
if(stackData.top()==popV[i]){
stackData.pop();
}
}
return true;
}
}; 12.按层打印二叉树
使用队列。
13.二叉搜索树的后序遍历序列
输入整数数组判断是否为某二叉搜索树的后序遍历序列。
class Solution {
public:
bool VerifySquenceOfBST(vector<int> sequence) {
if(sequence.size()==0)
return false;
int length=sequence.size();
int rootData=sequence[length-1];
vector<int> leftTree,rightTree;
int i;
for(i=0;i1;i++){
if(sequence[i]>rootData)
break;
}
for(int j=0;jfor(int j=i;j1;j++){
rightTree.push_back(sequence[j]);
if(sequence[j]return false;
}
bool left=true;
bool right=true;
if(i>0)
left=VerifySquenceOfBST(leftTree);
if(i1)
right=VerifySquenceOfBST(rightTree);
return (left&&right);
}
}; 14.二叉树中和为某一值的路径
class Solution {
public:
vector<vector<int> > ans;
int j=0;
void ifequal(vectorval;
trans.push_back(path[i]->val);
cout<val<<" ";
}
if(count==num)
{
for(int i=0;ival;
}
}
j++;
}
bool GetNodePath(TreeNode* pHead, TreeNode* pNode, vector 15.复杂链表的复制
输入一个复杂链表(每个节点中有节点值,以及两个指针,一个指向下一个节点,另一个特殊指针指向任意一个节点),返回结果为复制后复杂链表的head。
/*
struct RandomListNode {
int label;
struct RandomListNode *next, *random;
RandomListNode(int x) :
label(x), next(NULL), random(NULL) {
}
};
*/
class Solution {
public:
void cloneNodes(RandomListNode* pHead){
RandomListNode* pNode = pHead;
while(pNode != NULL){
RandomListNode* node = new RandomListNode(pNode->label);
node->next = pNode->next;
pNode->next = node;
node->random = NULL;
pNode = node->next;
}
}
void setRandomNodes(RandomListNode* pHead){
RandomListNode* pNode = pHead;
while(pNode != NULL){
RandomListNode* node = pNode->next;
if(pNode->random != NULL){
node->random = pNode->random->next;
}
pNode = node->next;
}
}
RandomListNode* reConnectNode(RandomListNode* pHead){
RandomListNode* pNode = pHead;
RandomListNode* newListNode = NULL;
RandomListNode* newListNodeHead = NULL;
if(pNode != NULL){
newListNodeHead = newListNode = pNode->next;
pNode->next = newListNode->next;
pNode = pNode->next;
}
while(pNode != NULL){
newListNode->next = pNode->next;
newListNode = newListNode->next;
pNode->next = newListNode->next;
pNode = pNode->next;
}
return newListNodeHead;
}
RandomListNode* Clone(RandomListNode* pHead)
{
cloneNodes(pHead);
setRandomNodes(pHead);
return reConnectNode(pHead);
}
};16.二叉搜索树与双向链表
输入一个二叉搜索树,将其转换为一个排序的双向链表。要求不能创建任何新的节点,只能调整树中节点指针的指向。