牛客多校9 - Groundhog Chasing Death(质因子分解+思维)
题目链接:点击查看
题目大意:给出 a , b , c , d , x , y ,求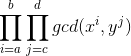
题目分析:因为涉及到了 gcd 的乘积运算,那么易知不同质因子的贡献是相互独立的,首先我们就可以先将 x 和 y 进行质因子分解,那么对于质因子 p 来说,设 cntx[ p ] 为 p 在 x 中出现的次数,cnty[ p ] 为 p 在 y 中出现的次数,不难看出,需要这两个数同时大于 0 才有贡献,如果其中一者为 0 的话,那么其表示的质因子就是 p^0 = 1 ,gcd 求出来显然也就是 1 了,对答案没有贡献
到此,cntx[ p ] 和 cnty[ p ] 都大于 0 ,那么质因子 p 的 gcd 就是 ![]() ,也就是
,也就是 ![]() ,这也就提醒我们可以对指数单独处理,最后求一下 p 的幂次再乘起来就是答案了
,这也就提醒我们可以对指数单独处理,最后求一下 p 的幂次再乘起来就是答案了
此时我们可以对指数稍微打表找一下规律,打表程序如下(可以自己更改一下 i 和 j 的取值范围,分别代表 [ a , b ] 和 [ c , d ] ):
for(int k=1;k<=5;k++)//质因子p在x中的个数
for(int t=1;t<=5;t++)//质因子p在y中的个数
{
printf("*****cntx:%d cnty:%d*****\n",k,t);
for(int i=1;i<=5;i++)//a~b
{
for(int j=1;j<=5;j++)//c~d
printf("%d ",min(i*k,j*t));
puts("");
}
}这里不卖关子了,直接说规律:
- 当 i 确定时,[ c , d ] 的一列可以分为两段:
- 前半段为等差数列
- 后半段为常数
- 当 j 确定时,[ a , b ] 的一行可以分为两段:
- 前半段为等差数列
- 后半段为常数
这样就可以将 ( b - a + 1 ) * ( d - c + 1 ) 的时间复杂度优化为 ( b - a + 1 ) 或者 ( d - c + 1 ) 了,因为知道了是等差数列,我们可以求出三项:第一项,第二项,最后一项,根据第一项和第二项得出公差,根据第一项、最后一项和公差计算出等差数列的长度,这样最后常数项的长度也能计算得出了
有个小坑就是,如果指数直接进行运算的话,会爆 long long ,可以用费马小定理降幂,一方面是保证指数在数据范围内,另一方面是加速快速幂的运算
因为我用了 map 参与质因子分解,所以总的时间复杂度为 ( b - a + 1 ) * logn * logn
代码:
#include
#include
#include
#include
#include
#include
#include
#include
#include
#include
#include