Sofia-SIP辅助文档十 - Sofia SIP用户代理库 - "nua" - 高层用户代理模块
http://sofia-sip.sourceforge.net/refdocs/nua/index.html,翻译自官网的这张网页。
模块元信息
nua模块是一个用户代理库,主要提供基本的SIP用户代理功能。它的功能包括呼叫管理,消息和事件获取。
- 联系人:
- Pekka Pessi < [email protected]>
- 状态:
- Sofia SIP Core library
- 许可:
- LGPL
- 贡献者:
-
- Pekka Pessi
- Pasi Rinne-Rahkola
- Kai Vehmanen
- Martti Mela
- Pekka Pessi
概述
The NUA API提供给高层应用开发人员一套透明并且完全控制的底层SIP协议引擎。NUA提供的呼叫语义基于nta模块内的事务语义。使用NUA可以创建各类不同的SIP用户代理,例如终端、网关或者MCU。
nua引擎对开发人员而言隐藏了很多底层的信令和媒体管理操作。在一种完全透明的方式下可以使用各类媒体接口。
应用程序和用户代理库内的协议引擎可以分处不同的线程内。协议引擎和应用程序使用事件进行通信,主要通过应用程序提供的回调函数。回调函数在应用程序线程上下文环境下被调用,会向其传递su_root_t对象。
NUA User下的Sofia概念
介绍
Sofia软件包基于一些特定基本的观点和概念。它们中的很多在Sofia工具库(su)内实现,并且针对最重要的操作功能和工具提供统一的接口。
下面这些章节包括创建一个基于NUA库的可工作应用程序的所有概念的描述。对应用程序开发人员而言SU库内以及Sofia软件包其他库内的工具接口都非常有用,但开发人员必须非常小心地使用它们,因为不正确地使用NUA库将会改变Sofia软件包的行为。请至su库查看更多的SU功能细节描述。
事件循环 - root对象
The NUA为事件驱动系统使用了反应器模式(也可以称为发布器模式或通知者模式)。Sofia在编程模型中采用了任务作为基本的执行单元。程序可以要求当一个特定的事件发生时,事件循环调用一个回调函数。事件可以是IO操作,计时器,或者其他任务发来的异步消息。
在应用程序中root对象是一个代表任务的句柄。同样,root对象还可以代表任务的主事件循环。通过root对象,任务代码可访问到它自身的上下文信息以及线程同步特性对象,例如等待对象、定时器和消息。
使用NUA功能的应用程序创建一个root对象,以及一个处理NUA事件的回调函数。可以用su_root_create()函数创建root对象,在nua_create()函数中注册回调函数。
root对象的类型是su_root_t。
请查看
请查看nua_event_e章节获得更多的回调函数信息:http://sofia-sip.sourceforge.net/refdocs/nua/nua_8h.html#abca36033336ce16e538a279413d2ca51。
Magic
magic是可以绑定到任何对象的上下文指针术语。主事件循环负责调用回调函数,并且将这个指针传递给回调函数。Sofia栈维持这个上下文信息在通话和回调函数之间。应用程序可以使用上下文用来保存任何需要的信息。
内存处理
当为给定的任务分配很多内存块时,home-based内存管理非常有用。所有的内存分配均通过home内存,它维护着所有已分配内存的参考。当home内存被释放时,它将释放所有它参考的内存块。这将简化应用程序处理逻辑,因为应用程序不再需要保持监视每个已分配的内存块、不再需要再单独释放每块已分配的内存块。
使用NUA功能的应用程序可以使用su库提供的内存管理功能,但不使用这个功能也可以。
请参考
Tags
Tagging是Sofia软件包中的一项将参数打包给函数的机制。它允许将具备不固定类型的可变个数参数传递给函数。对应用程序开发人员而言,tagging以宏的形式出现用来封装参数。展开tagging宏后将得到一个包含tag(说明参数的类型)和值(不透明数据的指针)的结构体。Sofia软件包内的各个层检查是否该由他们自身来处理这些参数还是应当传递给更低一层处理。
下面这些tag有着特殊的含义:
- TAG_NULL() (与TAG_END()含义一致) tag列表的尾端
- TAG_SKIP() 空tag元素
- TAG_NEXT() 指向另一个tag列表的tag元素,并且结束当前tag列表
- TAG_ANY() 可接收任意tag的过滤器tag
- TAG_IF() 条件tag元素
可向NUA函数提供tag值列表,但在参数列表的尾端必须如下图所示的参数:
tag_type_t tag, tag_value_t value, ...);
参数列表中最后一个tag值必须是TAG_NULL()(或者TAG_END(),与TAG_NULL()一致)。
每个tag有两个版本:
NUTAG_
它接受一个值参数
NUTAG_
它接受一个引用参数。后者与tl_gets()函数一块使用可以获取tag列表内的tag值。
对SIP头来说,还有额外的tag版本:
SIPTAG_
这个tag版本接受C-语言类型的字符串作为参数。相应无_STR后缀版本接受解析过的结构体作为参数。
下面是一个包含tag值的NUA函数调用示例:
nua_unregister(op->op_handle,
TAG_IF(use_registrar, NUTAG_REGISTRAR(registrar)),
SIPTAG_CONTACT_STR("*"),
SIPTAG_EXPIRES_STR("0"),
TAG_NULL());
使用NUA功能的应用程序必须使用tag机制向函数传递参数。请参考nua_invite()函数的说明获得更多如何通过tag机制生成SIP消息的内容:http://sofia-sip.sourceforge.net/refdocs/nua/nua_8h.html#a8162fd7f0f1c693f2d49bb18f36acf52。
请参考
调试和日志
Sofia软件包具备可配置的调试和日志功能,基于头文件中定义的功能。调试和日志细节(例如输出内容等级以及输出文件名)可通过环境变量、配置文件中的指令以及源代码文件中的编译指令决定。
指令和环境变量包括:
- SOFIA_DEBUG 缺省调试等级(0..9)
- NUA_DEBUG NUA调试等级(0..9)
- NTA_DEBUG 事务引擎调试等级(0..9)
- TPORT_DEBUG 传输事件调试等级(0..9)
- TPORT_LOG 如果设置了,打印所有传输层使用的解析过的SIP消息
- TPORT_DUMP 保存传输层中所有未解析消息的转储文件名
预定义的调试输出等级:
- 0 非常严重的错误
- 1 严重错误,子系统层次最简化进度消息
- 2 非严重错误
- 3 告警,进度消息
- 5 信令协议动作(呼入包...)
- 7 媒体协议动作(呼入包...)
- 9 进入/退出函数,极细致的进度消息
使用NUA功能的应用程序也可以使用Sofia软件包提供的调试和日志服务。但不使用调试和日志服务也可以。
请查看
NUA概念
NUA Stack对象
Stack对象表示一个SIP stack和媒体引擎实例。它包括stack根对象的引用,用户代理特殊配置,以及SIP事务引擎的引用。
nua_create()函数用来创建一个NUA stack对象,nua_destroy() 函数删除它。nua_shutdown()函数优雅地释放nua引擎维护着的活动状态的会话。
NUA stack对象的类型是nua_t。
NUA Operation Handle操作句柄
Operation handle表示一个抽象的SIP call/会话。它包括SIP对话和媒体会话的信息,call的状态机,高层SDP offer-answer协议,注册,订阅,发布,和简单的SIP事务。Operation handle也可以包含NUA创建的SIP消息中使用的tags列表。
一个operation handle由应用程序通过函数nua_handle()显示创建用来发送消息,或由栈在收到INVITE或MESSAGE消息后创建。应用程序通过调用nua_handle_destroy()函数删除它。
指示或响应事件与某一个特定的operation handle相关。
NUA operation handle的类型是nua_handle_t。
栈线程和消息传递
栈线程与应用程序线程是分开的,它提供了实时的协议栈操作以便应用程序线程可以做其它事情。
栈线程和应用程序线程之间的通信是异步方式的。大部分的NUA API将引起一条发给栈线程处理的消息,同样当栈线程发生了一些事它将向应用程序线程发送一条消息。提供给应用程序线程的消息将通过回调函数发送,回调函数是在应用程序调用su_root_run()或su_root_step()函数时提供的。
SIP消息和头操作
使用SIPTAG_ tags操作SIP消息。每个SIP tag有三个版本:
- SIPTAG_
()接受解析过后的值作为参数。 - SIPTAG_
_STR()接受未解析的字串作为参数。 - SIPTAG_
_REF()接受一个引用作为参数,与tl_gets()函数一道使用从tag列表内取出tag值。 - SIPTAG_
__STR_REF()接受一个引用作为参数,与tl_gets()函数一道使用从tag列表内取出字串tag值。
例如一个名为Example的头,它会有如下这些tags:SIPTAG_EXAMPLE()、SIPTAG_EXAMPLE_STR()和SIPTAG_EXAMPLE_REF()。
当在NUA的函数中使用tags,一个对应的头会写入消息体内。如果在一个消息体内一个头只允许出现一次,最后给出的tags的值会替换已有的tags的值。传递一个空的tags值不会有任何作用。传递(void *)-1 tag值将使得从消息体内移出响应的头。
例如:
- 发送一个有Event:头和两个Accept:头的SUBSCRIBE消息:
nua_subscribe(nh,
SIPTAG_EVENT_STR("presence"),
SIPTAG_ACCEPT(accept1),
SIPTAG_ACCEPT(accept2),
TAG_END());
- 处理nua_r_subscribe消息时获取tag值:
sip_accept_t *ac = NULL;
sip_event_t *o = NULL;
tl_gets(tl,
SIPTAG_EVENT_REF(o), /* _REF takes a reference! */
SIPTAG_ACCEPT_REF(ac),
TAG_END());
SIP/NUA入门
这一节用消息序列图的方式描述了NUA/Sofia栈的基本使用场景。
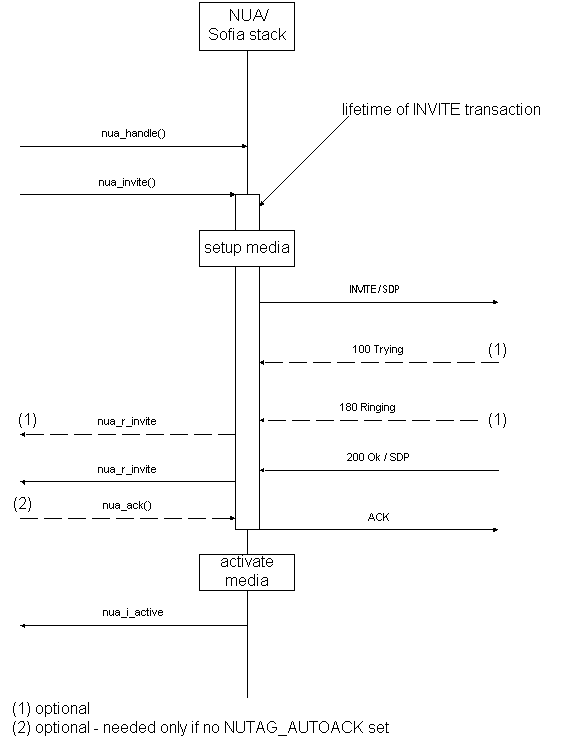
Outgoing Call
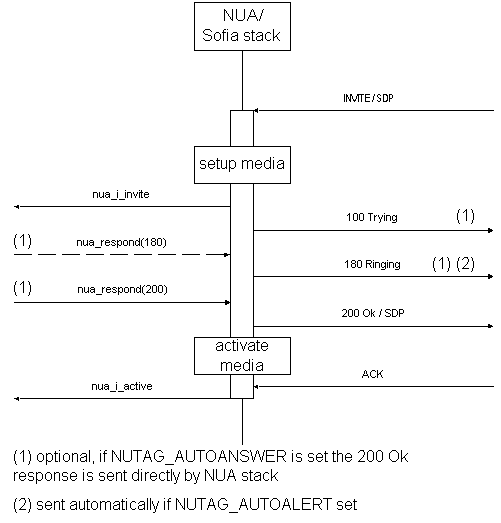
Incoming Call
Basic Outgoing Operation
Basic Incoming Operation
Outgoing Operation with Authentication
简单的应用程序
接下来的章节将用一个简单应用程序的代码展示如何使用NUA功能。展示的不是完整例子,但给出了使用NUA的所有相关细节。
在sourceforge.net网站上有一个完整的例子程序sofisip_cli.c,它可以作为学习用。
数据结构和定义
使用NUA功能的应用程序通常会定义一个存放上下文信息的数据空间。这些上下文信息的空间的指针类型会传给NUA。
/* type for application context data */ typedef struct application application; #define NUA_MAGIC_T application /* type for operation context data */ typedef union oper_ctx_u oper_ctx_t; #define NUA_HMAGIC_T oper_ctx_t
信息空间内容本身可用C结构体或联合体定义:
/* example of application context information structure */ typedef struct application { su_home_t home[1]; /* memory home */ su_root_t *root; /* root object */ nua_t *nua; /* NUA stack object */ /* other data as needed ... */ } application; /* Example of operation handle context information structure */ typedef union operation { nua_handle_t *handle; /* operation handle / struct { nua_handle_t *handle; /* operation handle / ... /* call-related information */ } call; struct { nua_handle_t *handle; /* operation handle / ... /* subscription-related information */ } subscription; /* other data as needed ... */ } operation;
NUA stack对象和句柄对应用程序开发人员而言是不透明的。同样,应用程序上下文也是完全对NUA stack模块透明的。传递给NUA函数的是一些指针,在后续这个指针会返回给应用程序提供的回调函数。在这个例子中应用程序上下文信息结构体还用来保存root对象和memory home对象。同时,还保存了NUA stack对象。
初始化和退出前清除
下面的代码展示了一个应用程序中初始化系统、进入处理消息的主循环以及主循环结束后清理系统阶段。
如果应用程序不只是响应接收到的SIP消息,它还想向NUA发送消息。这可以通过在另一线程内调用NUA函数来发送消息,或者应用程序有一个socket连接用来接收命令(请查看su_wait_create()和su_root_register()函数的文档)。
/* Application context structure */ application appl[1] = {{{{(sizeof appl)}}}}; /* initialize system utilities */ su_init(); /* initialize memory handling */ su_home_init(appl->home); /* initialize root object */ appl->root = su_root_create(appl); if (appl->root != NULL) { /* create NUA stack */ appl->nua = nua_create(appl->root, app_callback, appl, /* tags as necessary ...*/ TAG_NULL()); if (appl->nua != NULL) { /* set necessary parameters */ nua_set_params(appl->nua, /* tags as necessary ... */ TAG_NULL()); /* enter main loop for processing of messages */ su_root_run(appl->root); /* destroy NUA stack */ nua_destroy(appl->nua); } /* deinit root object */ su_root_destroy(appl->root); appl->root = NULL; } /* deinitialize memory handling */ su_home_deinit(appl->home); /* deinitialize system utilities */ su_deinit();
处理事件
在应用程序初始化阶段提供给nua_create()函数的回调函数,将用来处理从NUA stack得到的事件。回调函数的模式很简单,就是一个大型的switch/case语句,然后提供给不同的函数处理特定的消息。
void app_callback(nua_event_t event, int status, char const *phrase, nua_t *nua, nua_magic_t *magic, nua_handle_t *nh, nua_hmagic_t *hmagic, sip_t const *sip, tagi_t tags[]) { switch (event) { case nua_i_invite: app_i_invite(status, phrase, nua, magic, nh, hmagic, sip, tags); break; case nua_r_invite: app_r_invite(status, phrase, nua, magic, nh, hmagic, sip, tags); break; /* and so on ... */ default: /* unknown event -> print out error message */ if (status > 100) { printf("unknown event %d: %03d %s\n", event, status, phrase); } else { printf("unknown event %d\n", event); } tl_print(stdout, "", tags); break; } } /* app_callback */
发起通话
下面三个函数展示一个基本的SIP通话如何被创建。
The place_a_call()函数创建了一个operation handle并且调用nua_invite函数。
operation *place_a_call(char const *name, url_t const *url) { operation *op; sip_to_t *to; /* create operation context information */ op = su_zalloc(appl->home, (sizeof *op)); if (!op) return NULL; /* Destination address */ to = sip_to_create(NULL, url); if (!to) return NULL; to->a_display = name; /* create operation handle */ op->handle = nua_handle(appl->nua, op, SIPTAG_TO(to), TAG_END()); if (op->handle == NULL) { printf("cannot create operation handle\n"); return NULL; } nua_invite(op->handle, /* other tags as needed ... */ TAG_END()); } /* place_a_call */
当INVITE消息的响应消息收到后,app_r_invite()函数会被回调函数调用。这里假定自动回复确认被禁用了因此ACK响应消息必须显式发送。
void app_r_invite(int status, char const *phrase, nua_t *nua, nua_magic_t *magic, nua_handle_t *nh, nua_hmagic_t *hmagic, sip_t const *sip, tagi_t tags[]) { if (status == 200) { nua_ack(nh, TAG_END()); } else { printf("response to INVITE: %03d %s\n", status, phrase); } } /* app_r_invite */
当通话状态改变后,nua_i_state事件会被发送(app_i_state()函数由回调函数调用)。
void app_i_state(int status, char const *phrase, nua_t *nua, nua_magic_t *magic, nua_handle_t *nh, nua_hmagic_t *hmagic, sip_t const *sip, tagi_t tags[]) { nua_callstate_t state = nua_callstate_init; tl_gets(tags, NUTAG_CALLSTATE_REF(state), NUTAG__REF(state), state = (nua_callstate_t)t->t_value; printf("call %s\n", nua_callstate_name(state)); } /* app_i_state */
接听通话
当INVITE消息收到后,app_i_invite()函数会被回调函数调用。这个例子假定自动应答被禁用了因此响应消息必须显式发送。
void app_i_invite(int status, char const *phrase, nua_t *nua, nua_magic_t *magic, nua_handle_t *nh, nua_hmagic_t *hmagic, sip_t const *sip, tagi_t tags[]) { printf("incoming call\n"); nua_respond(nh, 200, "OK", SOA_USER_SDP(magic->sdp), TAG_END()); } /* app_i_invite */
当通话成功建立且媒体被激活,app_i_state()函数会被回调函数调用。
void app_i_active(int status, char const *phrase, nua_t *nua, nua_magic_t *magic, nua_handle_t *nh, nua_hmagic_t *hmagic, sip_t const *sip, tagi_t tags[]) { printf("call active\n"); } /* app_i_active */
结束通话
下面这三个函数展示一个基本SIP通话是如何被终止的。
terminate_call()函数会发送一个BYE消息。
void terminate_call(void) { nua_bye(op->handle, TAG_END()); } /* terminate call */
当BYE消息的响应收到后,app_r_bye()函数会被回调函数调用。函数将销毁通话句柄并且释放分配给operation上下文信息的空间。
void app_r_bye(int status, char const *phrase, nua_t *nua, nua_magic_t *magic, nua_handle_t *nh, nua_hmagic_t *hmagic, sip_t const *sip, tagi_t tags[]) { if (status < 200) return; printf("call released\n"); /* release operation handle */ nua_handle_destroy(hmagic->handle); op->handle = NULL; /* release operation context information */ su_free(appl->home, hmagic); } /* app_r_bye */
当BYE消息收到后,app_i_bye()函数会被回调函数调用。函数将销毁通话句柄并且释放分配给operation上下文信息的空间。
void app_i_bye(int status, char const *phrase, nua_t *nua, nua_magic_t *magic, nua_handle_t *nh, nua_hmagic_t *hmagic, sip_t const *sip, tagi_t tags[]) { printf("call released\n"); /* release operation handle */ nua_handle_destroy(hmagic->handle); op->handle = NULL; /* release operation context information */ su_free(appl->home, hmagic); } /* app_i_bye */
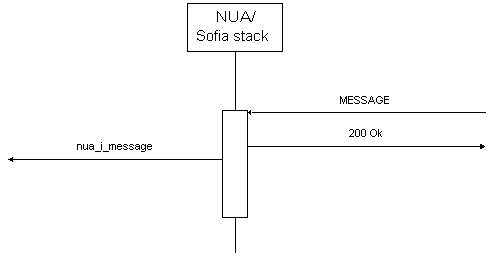
发送一条消息
下面函数将展示一个SIP MESSAGE消息是如何被发送的。
send_message()函数会发送SIP MESSAGE消息。
void send_message(void) { op_t *op; /* create operation context information */ op = su_zalloc(appl->home, sizeof(op_t)); if (op = NULL) { printf("cannot create operation context information\n"); return; } /* how we create destination_address? */ /* create operation handle */ op->handle = nua_handle(appl->nua, op, NUTAG_URL(destination_address), TAG_END()); if (op->handle == NULL) { printf("cannot create operation handle\n"); return; } /* send MESSAGE */ nua_message(op->handle, SIPTAG_CONTENT_TYPE_STR("text/plain"), SIPTAG_PAYLOAD_STR("Hello, world!"), /* other tags as needed ... */ TAG_END()); } /* send_message */
当MESSAGE消息的响应消息收到后,app_r_message()函数会被回调函数调用。
void app_r_message(int status, char const *phrase, nua_t *nua, nua_magic_t *magic, nua_handle_t *nh, nua_hmagic_t *hmagic, sip_t const *sip, tagi_t tags[]) { printf("response to MESSAGE: %03d %s\n", status, phrase); } /* app_r_message */
接收一条消息
下面函数将展示一个SIP MESSAGE消息如何被接收。
当一个SIP MESSAGE收到后,app_i_message()函数会被回调函数调用。
void app_i_message(int status, char const *phrase, nua_t *nua, nua_magic_t *magic, nua_handle_t *nh, nua_hmagic_t *hmagic, sip_t const *sip, tagi_t tags[]) { printf("received MESSAGE: %03d %s\n", status, phrase); printf("From: %s%s" URL_PRINT_FORMAT "\n", sip->sip_from->a_display ? sip->sip_from->a_display : "", sip->sip_from->a_display ? " " : "", URL_PRINT_ARGS(sip->sip_from->a_url)); if (sip->sip_subject) { printf("Subject: %s\n", sip->sip_subject->g_value); } if (sip->sip_payload) { fwrite(sip->sip_payload->pl_data, sip->sip_payload->pl_len, 1, stdout); fputs("\n", stdout); } } /* app_i_message */
创建一个Presence服务器
...
application_t *app;
operation_t *oper;
...
oper->app = app;
app->nua = nua_create(ssip->s_root,
app_callback,
app,
TAG_NULL());
...
oper->handle = nua_handle(app->nua, app,
NUTAG_URL(to->a_url),
SIPTAG_TO(to),
ta_tags(ta));
...
nua_notifier(oper->handle,
SIPTAG_EXPIRES_STR("3600"),
SIPTAG_EVENT_STR("presence"),
SIPTAG_CONTENT_TYPE_STR("application/pidf-partial+xml"),
NUTAG_SUBSTATE(nua_substate_pending),
TAG_END());
nua_notifier对象(presence server)创建后,nua_r_notifier事件会返回。回调函数中的status和phrase两个参数值会指出创建成功了。
一个订阅请求的授权会在回调函数中处理。
void app_callback(nua_event_t event, int status, char const *phrase, nua_t *nua, application_t *app, nua_handle_t *nh, oper_t *op, sip_t const *sip, tagi_t tags[]) { nea_sub_t *subscriber = NULL; switch (event) { case nua_i_subscription: tl_gets(tags, NEATAG_SUB_REF(subscriber), TAG_END()); nua_authorize(nua_substate_active); default: break; }
关闭
下面函数将展示一个应用程序如何关闭NUA stack。
shutdown()函数开始这么一个终止过程。
void shutdown(void) { nua_shutdown(appl->nua); } /* shutdown */
当NUA stack终止结束或失败都回触发回调函数调用app_r_shutdown()函数。
void app_r_shutdown(int status, char const *phrase, nua_t *nua, nua_magic_t *magic, nua_handle_t *nh, nua_hmagic_t *hmagic, sip_t const *sip, tagi_t tags[]) { printf("shutdown: %d %s\n", status, phrase); if (status < 200) { /* shutdown in progress -> return */ return; } /* end the event loop. su_root_run() will return */ su_root_break(magic->root); } /* app_r_shutdown */