Nginx从安装到高级配置
文章目录
- 安装
- Nginx配置
- 配置文件
- Nginx虚拟主机
- 基于不同域名的虚拟主机
- 基于不同端口的虚拟主机
- 基于不同IP的虚拟主机
- 访问状态统计
- Nginx访问控制
- 基于授权的访问控制
- 基于客户端的访问控制
- Nginx反向代理
- Nginx+LAMP动静分离
- proxies模块
- Nginx优化
- 配置Nginx隐藏版本号
- 配置Nginx网页缓存时间
- 配置nginx实现连接超时
- 更改Nginx运行进程数
- Nginx网页压缩
- Nginx日志切割
- Nginx防盗链配置
安装
环境准备
yum -y install pcre-devel zlib-devel
useradd -M -s /sbin/nologin nginx
编译安装
./configure \
--prefix=/usr/local/nginx \
--user=nginx \
--group=nginx \
--with-http_stub_status_module
make && make install
# 创建软链接
ln -s /usr/local/nginx/sbin/nginx /usr/local/sbin/
检查配置文件语法
# 在创建了软链接后,可直接使用nginx命令
# -t 参数检查语法
[root@localhost nginx-1.12.2]# nginx -t
nginx: the configuration file /usr/local/nginx/conf/nginx.conf syntax is ok
nginx: configuration file /usr/local/nginx/conf/nginx.conf test is successful
配置文件路径为/usr/local/nginx/conf/nginx.conf
启动、停止Nginx
# 开启nginx
nginx
# 查看nginx状态
netstat -antp | grep nginx
tcp 0 0 0.0.0.0:80 0.0.0.0:* LISTEN 88282/nginx: master
# 停止nginx
nginx -s stop
# 重新加载nginx配置
nginx -s reload
同样也可以使用killall命令进行停止和重启
重载nginx:killall -s HUP nginx / killall -1 nginx
停止nginx:killall -s QUIT nginx / killall -3 nginx
说明:
只有第9种信号(SIGKILL)才可以无条件终止进程,其他信号进程都有权利忽略。 下面是常用的信号:
HUP 1 终端断线
INT 2 中断(同 Ctrl + C)
QUIT 3 退出(同 Ctrl + \)
TERM 15 终止
KILL 9 强制终止
CONT 18 继续(与STOP相反, fg/bg命令)
STOP 19 暂停(同 Ctrl + Z)
以上有关killall命令的参考博客:
https://www.cnblogs.com/rsky/p/4886043.html
使用nginx服务脚本
使用killall命令或者nginx -s的形式,多少会让人觉得有点不习惯。因为我们会更习惯于使用systemd或者service服务的形式去管理,那我们下面就把nginx服务写成服务脚本,让systemd和service能够去调用。
systemd服务脚本
新建/lib/systemd/system/nginx.service文件,写入:
[Unit]
Description=nginx # 描述信息
After=network.target # 在启动network.target服务之后启动
[Service]
Type=forking # systemd认为当该服务进程fork,且父进程退出后服务启动成功
PIDFile=/usr/local/nginx/logs/nginx.pid # PID文件位置
ExecStart=/usr/local/nginx/sbin/nginx # start的执行命令
ExecReload=/usr/bin/kill -s HUP $MAINPID # reload的执行命令
ExecStop=/usr/bin/kill -s QUIT $MAINPID # stop的执行命令
PrivateTmp=true # True表示给服务分配独立的临时空间
[Install]
WantedBy=multi-user.target # 单元被允许运行需要的弱依赖性单元
最后赋予脚本文件执行权限
chmod 754 /lib/systemd/system/nginx.service
service服务脚本
新建/etc/init.d/nginx文件,写入:
#!/bin/bash
# chkconfig: - 99 20
# description: Nginx Service Control Script
PROG="/usr/local/nginx/sbin/nginx" # program位置
PIDF="/usr/local/nginx/logs/nginx.pid" # pid文件位置
case "$1" in
start)
$PROG
;;
stop)
kill -s QUIT $(cat $PIDF)
;;
restart)
$0 stop
$0 start
;;
reload)
kill -s HUP $(cat $PIDF)
;;
*)
echo "Usage: $0 {start|stop|restart|reload}"
exit 1
esac
exit 0
最后赋予脚本文件执行权限并添加为系统服务
chmod +x /etc/init.d/nginx
chkconfig --add nginx
关于服务脚本,读者也参考了一些博客,都写得很好,拿出来给大家分享一下:
systemd:
https://www.cnblogs.com/wjb10000/p/5566801.html
https://www.jb51.net/LINUXjishu/350268.html
Nginx配置
Nginx配置包括全局配置、I/O时间配置和http配置这三块内容
格式为
key value;
以#开头的表示注释。
配置文件
全局配置
#user nobody; # 运行用户
worker_processes 1; # 工作进程数量
#error_log logs/error.log; # 错误日志文件的位置
#error_log logs/error.log notice; # 错误日志等级为notice
#error_log logs/error.log info; # 错误日志等级为info
#pid logs/nginx.pid; # pid文件的位置
I/O事件配置
使用"event{ }"界定标记
events {
# use epoll; 2.6及以上版本建议使用epoll模型以提高性能
worker_connections 1024; # 每个进程处理1024个连接
}
HTTP配置
使用"http{ }"界定标记,之后的虚拟主机、php解析等一系列设置大部分都在这里。
http {
include mime.types;
default_type application/octet-stream;
sendfile on;
keepalive_timeout 65;
server {
……省略部分内容……
}
}
Nginx虚拟主机
与apache类似,nginx也能配置虚拟主机,也可基于域名、基于端口、基于IP地址进行配置不同的虚拟主机
为了方便管理,可将虚拟主机的配置文件另写到一个文件中,而在主配置文件中的http模块中添加include将虚拟主机的配置文件包含进去。
如,我要将虚拟主机的配置写到nginx安装目录下的conf/vhosts.conf文件中。
http {
include mime.types;
default_type application/octet-stream;
include conf/vhosts.conf; # 在主配置中添加include
……省略部分内容……
这也是在开发当中的解耦思想,然后在conf/vhosts.conf文件中写入虚拟主机的配置。
基于不同域名的虚拟主机
根据上面提到的解耦的思路,我们把不同域名的虚拟主机的配置写到/usr/local/nginx/conf/vhosts.conf文件中。
server {
listen 80; # 监听端口
server_name www.testnginx1.com; # 主机域名
charset utf-8; # 字符编码utf-8
access_log logs/www.testnginx1.com.access.log main; # 访问日志位置
location / {
root /var/www/html/testnginx1; # testnginx1的根目录
index index.html; # 默认的首页
}
error_page 500 502 503 504/50x.html; # 当状态码定义的值时返回错误页面
location =50x.html{
root html; # 错误页面的根目录
}
}
server {
listen 80;
server_name www.testnginx2.com; # 配置不同域名的虚拟主机
charset utf-8;
access_log logs/www.testnginx2.com.access.log main;
location / {
root /var/www/html/testnginx2;
index index.html;
}
error_page 500 502 503 504/50x.html;
location =50x.html{
root html;
}
}
这样我们就可以给不同的网站设置不同的域名,nginx将通过不同的域名对访问请求进行区别,别忘记添加站点文件用于测试
[root@localhost ~]# ls /var/www/html/testnginx1/
index.html
[root@localhost ~]# ls /var/www/html/testnginx2/
index.html
配置完成后启动服务
[root@localhost conf]# systemctl start nginx
[root@localhost conf]# netstat -antp|grep nginx
tcp 0 0 0.0.0.0:80 0.0.0.0:* LISTEN 2859/nginx: master
若没有配置systemd或者service服务脚本,可以使用/usr/local/nginx/sbin/nginx的命令开启服务,开启服务后使用测试机上的curl命令或者使用浏览器进行测试
[root@localhost ~]# curl www.testnginx1.com
this is www.testnginx1.com # index.html里面的内容
[root@localhost ~]# curl www.testnginx2.com
this is www.testnginx2.com
PS:需要解析www.testnginx1.com,可以在测试机上修改/etc/hosts文件添加解析,或指定能解析到正确地址的DNS,可以参考我的博客:https://blog.csdn.net/weixin_43515220/article/details/103222415
添加域名解析到文件/etc/hosts:
192.168.218.4 www.testnginx1.com www.testnginx2.com
基于不同端口的虚拟主机
nginx还可以以不同的端口号来区分不同的网站,我们来继续修改vhosts.conf文件:
# 这里没有给server站点配置日志文件和错误页面,也没有设置server_name
server {
listen 8080;
charset utf-8;
location / {
root /var/www/html/port8080;
index index.html;
}
}
server {
listen 9090;
charset utf-8;
location / {
root /var/www/html/port9090;
index index.html;
}
}
修改完成后,添加站点文件
mkdir /var/www/html/port8080
echo "this is port8080" > /var/www/html/port8080/index.html
mkdir /var/www/html/port9090
echo "this is port9090" > /var/www/html/port9090/index.html
重启服务后,还使用curl进行测试
[root@localhost ~]# curl 192.168.218.4:8080
this is port8080
[root@localhost ~]# curl 192.168.218.4:9090
this is port9090
测试成功,我们再给站点配上域名试试。
# 为两个站点添加了server_name
server {
listen 8080;
server_name www.port8080.com;
charset utf-8;
location / {
root /var/www/html/port8080;
index index.html;
}
}
server {
listen 9090;
server_name www.port9090.com;
charset utf-8;
location / {
root /var/www/html/port9090;
index index.html;
}
}
然后我们再在/etc/hosts文件中添加对两个域名的解析,都解析到服务器IP地址192.168.218.4:
192.168.218.4 www.port8080.com www.port9090.com
重启服务后测试
[root@localhost conf]# curl www.port8080.com
this is www.testnginx1.com
[root@localhost conf]# curl www.port8080.com:8080
this is port8080
[root@localhost conf]# curl www.port9090.com
this is www.testnginx1.com
[root@localhost conf]# curl www.port9090.com:9090
this is port9090
我们会发现,在不加端口号的情况下,直接访问域名会转到咱们之前配置的www.testnginx1.com的网址。这是因为在不加端口号的情况下,默认会使用http协议的80端口,故直接访问www.port8080.com或者www.port9090.com会访问到80端口对应的网站。
基于不同IP的虚拟主机
在服务器有多张网卡的时候,有可能会有需要不同网站对应不同IP地址。
假如服务器的两个网卡的IP地址分别为:
192.168.218.4/24
192.168.218.101/24
那不同的IP即可对应不同的网站,我们直接来修改上面基于不同端口的虚拟主机的server配置:
# 在listen处添加IP地址
server {
listen 192.168.218.4:8080;
server_name www.port8080.com;
charset utf-8;
location / {
root /var/www/html/port8080;
index index.html;
}
}
server {
listen 192.168.218.101:9090;
server_name www.port9090.com;
charset utf-8;
location / {
root /var/www/html/port9090;
index index.html;
}
}
重启nginx服务后,我们直接访问IP和对应网站端口来进行测试:
[root@localhost conf]# curl 192.168.218.101:9090
this is port9090
[root@localhost conf]# curl 192.168.218.4:8080
this is port8080
测试成功。
访问状态统计
nginx内置的HTTP_STUB_STATUS状态统计模块,可用来反馈当前web访问情况。
配置编译时需加参数–with-http_stub_status_module
查看当前nginx是否包含HTTP_STUB_STATUS模块
[root@localhost ~]# nginx -V
nginx version: nginx/1.12.2
built by gcc 4.8.5 20150623 (Red Hat 4.8.5-16) (GCC)
configure arguments: --prefix=/usr/local/nginx --user=nginx --group=nginx --with-http_stub_status_module
再修改配置文件,我们直接在vhosts.conf里面的server实例进行修改
server {
listen 192.168.218.101:9090;
server_name www.port9090.com;
charset utf-8;
location / {
root /var/www/html/port9090;
index index.html;
}
# 添加/status网站位置
location /status {
stub_status on;
access_log off;
}
}
重启服务后,我们访问192.168.218.101:9090/status,可以看到192.168.218.101:9090的状态统计:
Nginx访问控制
基于授权的访问控制
与apache一样,nginx也可以实现基于用于授权的访问控制——要求用户输入用户名和密码。
实现步骤如下
使用工具htpasswd生成用户认证文件,如果没有该命令,则需要先安装:
yum -y install httpd-tools &>/dev/null
为用户nginxuser1生成用户认证文件
[root@localhost ~]# htpasswd -c /usr/local/nginx/passwd.db nginxuser1
New password:
Re-type new password:
Adding password for user nginxuser1
修改密码文件的权限为400,将所有者改为nginx,使得用户nginx可以读取
[root@localhost ~]# cd /usr/local/nginx/
[root@localhost nginx]# chmod 400 passwd.db
[root@localhost nginx]# chown nginx passwd.db
[root@localhost nginx]# ll -d passwd.db
-r-------- 1 nginx root 49 Dec 20 17:27 passwd.db
添加测试站点,修改配置文件,添加相应认证配置项
# 在location中加入认证
server {
listen 80;
charset utf-8;
location / {
root /var/www/html;
index index.html;
auth_basic "passwd";
auth_basic_user_file /usr/local/nginx/passwd.db;
}
}
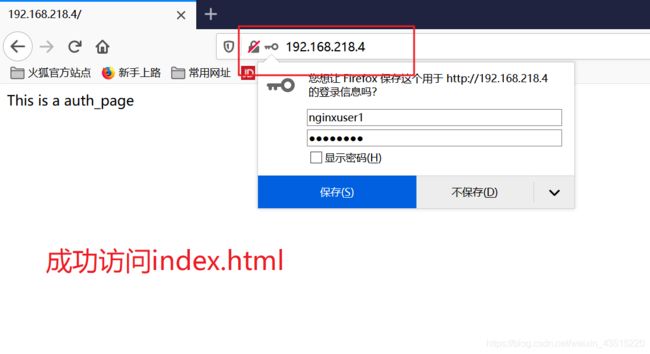
通过浏览器访问:
基于客户端的访问控制
基于客户端的访问控制是通过客户端IP地址,决定是否允许对页面的访问。
控制访问规则如下:
deny IP/IP段:拒绝某个IP或者IP段的客户端访问。
allow IP/IP段:允许某个IP或者IP段的客户端访问。
规则从上往下执行,如匹配则停止,不再继续匹配。
实现步骤如下
添加测试站点,在location中添加配置项
server {
listen 80;
charset utf-8;
location / {
root /var/www/html;
index index.html;
deny 192.168.218.5;
allow all;
}
}
分别使用192.168.218.5和其他的客户端对站点进行访问
客户端192.168.218.5没有权限访问
其他客户端可以访问
Nginx反向代理
nginx不仅能作为web服务器,还具有反向代理、负载均衡和缓存的功能
这里使用nginx将请求转发给apache服务器(192.168.218.4),返回apache的响应内容
使用apache部署测试站点(虚拟主机),可参考我的博客:
https://blog.csdn.net/weixin_43515220/article/details/103520797
在apache主页index中写入"this is apache server"
然后修改nginx的配置,使用proxies模块的proxy_pass指令进行转发
server {
listen 80;
location / {
proxy_pass http://192.168.218.4:8080;
}
}
proxy_pass为反向代理中最重要的指令,它能够根据URL、客户端参数或者它的处理逻辑将用户请求调度至上游服务器
启动服务,利用curl命令访问nginx服务器的80端口
curl 192.168.218.5
this is apache server
成功转发到apache服务器
Nginx+LAMP动静分离
nginx擅长处理高并发和静态资源,但并不擅长处理动态资源,而实际中可以利用nginx能够处理高并发的特性,将对静态资源的请求在本地进行处理,对动态资源的请求转发到apache服务器上去处理,这么做能够有效提高整个架构的效率。
首先搭建LAMP架构,来处理动态资源
接着修改 nginx配置文件,使用proxies模块的proxy_pass指令进行转发
server {
listen 80;
charset utf-8;
# 处理静态资源
location / {
root /usr/local/nginx/html;
index index.html;
}
# 转发到apache服务器,处理动态资源
location ~ \.php$ {
proxy_pass http://192.168.218.4;
}
}
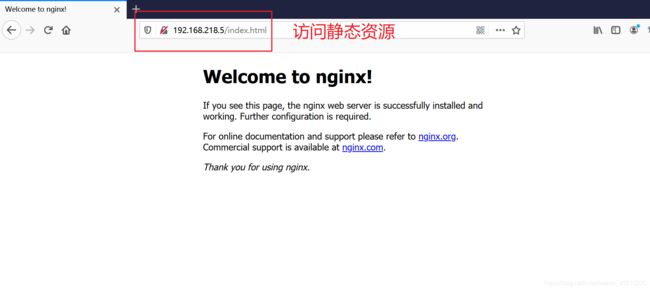
测试
访问静态资源
proxies模块
proxy_method get;
# 支持客户端的请求方法
proxy_http_version 1.0;
# nginx提供代理服务的http协议版本
反向代理和负载均衡都使用proxies模块,下面的博客我认为觉得写得不错
https://www.runoob.com/w3cnote/nginx-proxy-balancing.html
Nginx优化
配置Nginx隐藏版本号
在生产环境中,暴露nginx的版本号是非常不安全的,因为黑客可以利用nginx版本的漏洞对生产环境进行攻击。故隐藏nginx的版本号非常必要。
查看nginx版本号
[root@localhost ~]# nginx -v
nginx version: nginx/1.12.2
[root@localhost ~]# nginx -V
nginx version: nginx/1.12.2
built by gcc 4.8.5 20150623 (Red Hat 4.8.5-16) (GCC)
configure arguments: --prefix=/usr/local/nginx --user=nginx --group=nginx --with-http_stub_status_module
使用fiddler软件,可以在抓到的http包中的header查看到nginx的版本号
curl -I 127.0.0.1
HTTP/1.1 200 OK
Server: nginx/1.12.2
Date: Mon, 23 Dec 2019 16:16:28 GMT
Content-Type: text/html; charset=utf-8
Content-Length: 20
Last-Modified: Mon, 23 Dec 2019 15:55:08 GMT
Connection: keep-alive
ETag: "5e00e35c-14"
Accept-Ranges: bytes
修改配置文件隐藏版本号
在server配置中加入server_tokens配置项,值为off
server {
listen 80;
charset utf-8;
server_tokens off;
location / {
root /var/www/html;
index index.html;
}
}
使用curl -I查看
curl -I 127.0.0.1
HTTP/1.1 200 OK
Server: nginx
Date: Mon, 23 Dec 2019 16:15:09 GMT
Content-Type: text/html; charset=utf-8
Content-Length: 20
Last-Modified: Mon, 23 Dec 2019 15:55:08 GMT
Connection: keep-alive
ETag: "5e00e35c-14"
Accept-Ranges: bytes
可以看到header中已看不到版本号
修改源码设置版本号
我们可以在编译安装前对nginx的源码文件进行修改来隐藏或自定义版本信息
使用vim修改源码包中的src/core/nginx.h文件,把NGINX_VERSION和NGINX_VER的值进行修改
#define NGINX_VERSION "10.10.10"
#define NGINX_VER "IIS/" NGINX_VERSION
重新编译安装
./configure \
--prefix=/usr/local/nginx \
--user=nginx \
--group=nginx \
--with-http_stub_status_module
make && make install
开启服务后,使用fidder软件查看http的header
使用curl -I 命令查看
curl -I 127.0.0.1
HTTP/1.1 200 OK
Server: IIS/10.10.10
Date: Mon, 23 Dec 2019 16:23:09 GMT
Content-Type: text/html; charset=utf-8
Content-Length: 20
Last-Modified: Mon, 23 Dec 2019 15:55:08 GMT
Connection: keep-alive
ETag: "5e00e35c-14"
Accept-Ranges: bytes
配置Nginx网页缓存时间
当nginx将静态资源返回给客户端后,可设置缓存的时间,以方便在日后进行相同过内容的请求时直接返回,避免重复请求,加快了访问速度。
可在http段、server段、location段添加expires参数,设置缓存时间
/usr/local/nginx/conf/nginx.conf
worker_processes 1;
events {
worker_connections 1024;
}
http {
include mime.types;
default_type application/octet-stream;
include vhosts.conf;
# 设置缓存时间为4分钟
expires 4m;
……省略……
用fiddler软件抓包,看静态资源的缓存时间
配置nginx实现连接超时
为了避免同一个客户长时间占用连接,造成资源浪费,可设置响应的连接超时参数,实现控制连接访问时间。
Keepalive_timeout
设置连接保持时间,默认75秒,可在http段、server段、location段进行配置
Client_header_timeout
指定等待客户端发送请求头的超时时间
Client_body_timeout
设置请求体读超时时间
在http段添加超时参数
……省略部分内容……
http {
include mime.types;
default_type application/octet-stream;
include vhosts.conf;
expires 4m;
sendfile on;
keepalive_timeout 65;
client_header_timeout 20s;
client_body_timeout 15;
……省略部分内容……
使用fidder抓包查看connection
参考博客:
https://www.cnblogs.com/lemon-flm/p/8352194.html
更改Nginx运行进程数
我们都知道nginx的一大优点就是它处理高并发的能力,而在高并发的场景中,需要启动更多的nginx进程以保证快速响应,以处理用户的请求。
使用ps aux命令查看nginx运行进程的个数
ps aux | grep nginx
root 1403 0.0 0.0 20496 620 ? Ss 08:42 0:00 nginx: master process nginx
nginx 1404 0.0 0.0 23020 1400 ? S 08:42 0:00 nginx: worker process
root 1407 0.0 0.0 112660 968 pts/0 R+ 08:42 0:00 grep --color=auto nginx
修改配置文件的worker_processes参数,可指定运行进程数量
一般设为CPU的个数或者核数
在高并发情况下可设置为CPU个数或者核数的2倍
worker_processes参数在全局配置段中,修改为4,使用ps aux查看nginx进程
ps aux | grep nginx
root 1403 0.0 0.0 21168 1376 ? Ss 08:42 0:00 nginx: master process nginx
nginx 1456 0.0 0.0 23252 1524 ? S 08:45 0:00 nginx: worker process
nginx 1457 0.0 0.0 23252 1524 ? S 08:45 0:00 nginx: worker process
nginx 1458 0.0 0.0 23252 1524 ? S 08:45 0:00 nginx: worker process
nginx 1459 0.0 0.0 23252 1524 ? S 08:45 0:00 nginx: worker process
root 1461 0.0 0.0 112660 972 pts/0 R+ 08:45 0:00 grep --color=auto nginx
默认情况下,nginx的多个进程可能跑在一个CPU上,我们可以分配不同的进程给不同的CPU处理,充分利用硬件多核多CPU
假如服务器有4核,那么可以进行一下配置,将进程分配给不同CPU
worker_cpu_affinity 0001 0010 0100 1000
表示开启4个进程,二进制数表示的是第几个CPU
查看服务器CPU核数
cat /proc/cpuinfo |grep -c “physical”
Nginx网页压缩
nginx的ngx_http_gzip_module压缩模块提供对文件内容压缩的功能
允许nginx服务器将输出内容在发送给客户端之前进行压缩,以节约网站带宽,提高用户的访问体验,默认已经安装
压缩参数
gzip on|off
开启gzip压缩
可用位置:http,server,location
gzip_min_length 2k
大小超过2k则压缩,允许压缩的页面最小字节数
可用位置:http,server,location
gzip_buffers 4 16k
申请4个单位为16k的内存作为压缩结果流缓存,默认是申请与原始数据大小相同的内存空间来存储gzip压缩结果
可用位置:http,server,location
gzip_comp_level 2
指定gzip压缩比,1压缩比最小,处理最快;9压缩比最大,传输速度快,但处理速度最慢,使用默认即可
可用位置:http,server,location
gzip_types text/plain
压缩类型,对指定类型文件进行压缩
可用位置:http,server,location
gzip_vary on|off
让前端的缓存服务器缓存经过gzip压缩的页面
可用位置:http,server,location
gzip_proxied off|expired|no-cache|no-store|private|no_last_modified|no_etag|auth|any
响应报文在何种条件下启用压缩功能
expired,no-cache, no-store,private:响应报文首部Cache-Control值任何一个,启用压缩功能
可用位置:http, server, location
配置样例
server {
listen 80;
charset utf-8;
gzip on;
gzip_min_length 2k;
gzip_buffers 4 16k;
gzip_comp_level 4;
gzip_types image/png;
gzip_vary on;
gzip_proxied any;
location / {
root /var/www/html;
index index.html;
}
}
使用curl命令查看Content-Encoding
curl -I -H "Accept-Encoding: gzip,deflate" 127.0.0.1/test.png
HTTP/1.1 200 OK
Server: IIS/10.10.10
Date: Tue, 24 Dec 2019 09:34:51 GMT
Content-Type: image/png
Last-Modified: Tue, 24 Dec 2019 09:32:49 GMT
Connection: keep-alive
Vary: Accept-Encoding
ETag: W/"5e01db41-5915e"
Expires: Tue, 24 Dec 2019 09:38:51 GMT
Cache-Control: max-age=240
Content-Encoding: gzip
Nginx日志切割
nginx在处理高并发的时候,产生的日志量是非常大的,故nginx日志将需要管理员用科学的方法进行切割,以方便管理。
nginx本身不具备日志分割处理的功能,但可以通过nginx信号控制功能的脚本实现日志自动分割。
脚本主要思路
设置时间变量
设置保存日志路径
将目前的日志文件进行重命名
删除时间过长的日志文件
设置cron任务,定期执行脚本,自动分割日志
#!/bin/bash
date=$(date -d "-1 day" "+%Y%m%d")
logs_path="/var/log/nginx"
pid_path="/usr/local/nginx/logs/nginx.pid"
[ -d $logs_path ] || mkdir -p $logs_path
mv /usr/local/nginx/logs/access.log ${logs_path}/access.log-$date
kill -USR1 $(cat $pid_path)
find $logs_path -mtime +30| xargs rm -rf
然后利用crontab,可设置脚本在0点或自定义时间执行
Nginx防盗链配置
很多web服务器都有他们的防盗链机制,这里演示的是nginx对图片资源做防盗链
我们先使用nginx配置一个虚拟站点
server {
listen 80;
server_name www.test.com;
root html/test;
index index.html;
}
站点的网页文件为如下所示
引用了相同目录下的一张名为"baidu.png"的图片
<html>
<head>
<meta charset="utf-8">
<title>test_sitetitle>
head>
<body>
<h1>this is a test siteh1>
<img src="baidu.png" />
body>
html>
效果是这样的
目前我们还没有做防盗链配置,下面我们用另一服务器配置一个盗链网站,在站点的网页文件中这样配置:
<html>
<head>
<meta charset="utf-8">
<title>false_sitetitle>
head>
<body>
<h1>this is a false siteh1>
<img src="http://www.test.com/baidu.png" />
body>
html>
这里我们也引入一张图片,但是这里引用的图片却是nginx站点的图片,从www.test.com/baidu.png盗过来的
效果是这样的
下面我们到nginx上做防盗链配置
server {
listen 80;
server_name www.test.com;
root html/test;
index index.html;
location ~* \.(png|gif|jpg)$ {
valid_referers none blocked *.test.com;
if ($invalid_referer){
rewrite ^/ http://www.test.com/daoliankechi.png;
}
}
}
加入location语句,匹配所有去访问的资源为.png|gif|jpg结尾的请求
当referer不为nong、blocked、*.test.com时,将会跳转到daoliankechi.png
重启nginx服务
再次访问盗链网站www.false.com,效果是这样的
注意,使用location进行匹配时,需要注意location匹配的优先级
匹配具体文件的优先级从高到低依次为
location = 完整路径
location ^~ 完整路径
location ~* 完整路径
location ~ 完整路径
location 完整路径
location /
匹配目录的优先级从高到低依次为
location = 目录
location ^~ 目录
location ~ 目录
location ~* 目录
location 目录