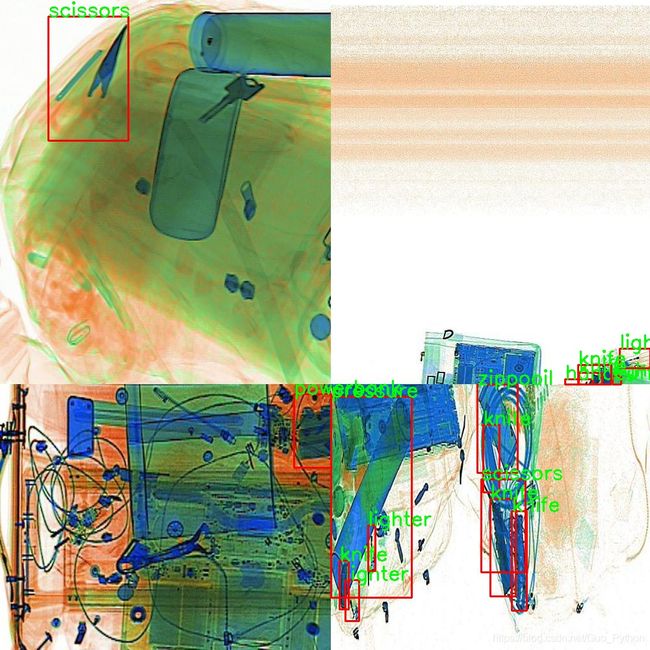
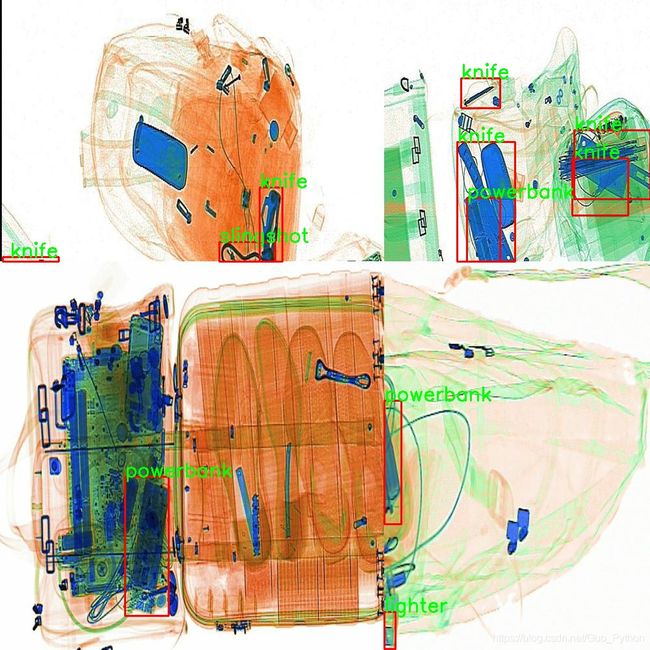
目标检测基础——mosaic数据增强
自从Yolo v4论文发表以后,新的数据增强方式mosaic备受关注。本文实现该数据增强方式:
先看看train.txt中的文件格式 img_path x1,y1,x2,y2,cls
/home/gp/dukto/Xray_match/data/train/JPEGImages/300059.jpg 91,263,219,324,2
/home/gp/dukto/Xray_match/data/train/JPEGImages/200408.jpg 274,99,358,139,1
/home/gp/dukto/Xray_match/data/train/JPEGImages/400329.jpg 370,356,467,439,2 588,107,720,160,0
/home/gp/dukto/Xray_match/data/train/JPEGImages/400566.jpg 115,52,201,199,0
/home/gp/dukto/Xray_match/data/train/JPEGImages/400327.jpg 151,184,236,292,2 159,210,418,298,0 313,110,382,216,4离线数据增强代码:
from PIL import Image, ImageDraw
import numpy as np
from matplotlib.colors import rgb_to_hsv, hsv_to_rgb
import math
from gen_xml import get_result, CreatXml
import xml.dom.minidom
def rand(a=0, b=1):
return np.random.rand()*(b-a) + a
def merge_bboxes(bboxes, cutx, cuty):
merge_bbox = []
for i in range(len(bboxes)):
for box in bboxes[i]:
tmp_box = []
x1,y1,x2,y2 = box[0], box[1], box[2], box[3]
if i == 0:
if y1 > cuty or x1 > cutx:
continue
if y2 >= cuty and y1 <= cuty:
y2 = cuty
if y2-y1 < 5:
continue
if x2 >= cutx and x1 <= cutx:
x2 = cutx
if x2-x1 < 5:
continue
if i == 1:
if y2 < cuty or x1 > cutx:
continue
if y2 >= cuty and y1 <= cuty:
y1 = cuty
if y2-y1 < 5:
continue
if x2 >= cutx and x1 <= cutx:
x2 = cutx
if x2-x1 < 5:
continue
if i == 2:
if y2 < cuty or x2 < cutx:
continue
if y2 >= cuty and y1 <= cuty:
y1 = cuty
if y2-y1 < 5:
continue
if x2 >= cutx and x1 <= cutx:
x1 = cutx
if x2-x1 < 5:
continue
if i == 3:
if y1 > cuty or x2 < cutx:
continue
if y2 >= cuty and y1 <= cuty:
y2 = cuty
if y2-y1 < 5:
continue
if (x2 >= cutx) and (x1 <= cutx):
x1 = cutx
if x2-x1 < 5:
continue
tmp_box.append(x1)
tmp_box.append(y1)
tmp_box.append(x2)
tmp_box.append(y2)
tmp_box.append(box[-1])
merge_bbox.append(tmp_box)
return merge_bbox
def get_random_data(annotation_line, input_shape, random=True, hue=.1, sat=1.5, val=1.5, proc_img=True):
'''random preprocessing for real-time data augmentation'''
h, w = input_shape
min_offset_x = 0.4
min_offset_y = 0.4
scale_low = 1-min(min_offset_x,min_offset_y)
scale_high = scale_low+0.2
image_datas = []
box_datas = []
index = 0
place_x = [0,0,int(w*min_offset_x),int(w*min_offset_x)]
place_y = [0,int(h*min_offset_y),int(w*min_offset_y),0]
for line in annotation_line:
# 每一行进行分割
line_content = line.split()
# 打开图片
image = Image.open(line_content[0])
image = image.convert("RGB")
# 图片的大小
iw, ih = image.size
# 保存框的位置
box = np.array([np.array(list(map(int,box.split(',')))) for box in line_content[1:]])
# image.save(str(index)+".jpg")
# 是否翻转图片
flip = rand()<.5
if flip and len(box)>0:
image = image.transpose(Image.FLIP_LEFT_RIGHT)
box[:, [0,2]] = iw - box[:, [2,0]]
# 对输入进来的图片进行缩放
new_ar = w/h
scale = rand(scale_low, scale_high)
if new_ar < 1:
nh = int(scale*h)
nw = int(nh*new_ar)
else:
nw = int(scale*w)
nh = int(nw/new_ar)
image = image.resize((nw,nh), Image.BICUBIC)
# 进行色域变换
hue = rand(-hue, hue)
sat = rand(1, sat) if rand()<.5 else 1/rand(1, sat)
val = rand(1, val) if rand()<.5 else 1/rand(1, val)
x = rgb_to_hsv(np.array(image)/255.)
x[..., 0] += hue
x[..., 0][x[..., 0]>1] -= 1
x[..., 0][x[..., 0]<0] += 1
x[..., 1] *= sat
x[..., 2] *= val
x[x>1] = 1
x[x<0] = 0
image = hsv_to_rgb(x)
image = Image.fromarray((image*255).astype(np.uint8))
# 将图片进行放置,分别对应四张分割图片的位置
dx = place_x[index]
dy = place_y[index]
new_image = Image.new('RGB', (w,h), (128,128,128))
new_image.paste(image, (dx, dy))
image_data = np.array(new_image)/255
index = index + 1
box_data = []
# 对box进行重新处理
if len(box)>0:
np.random.shuffle(box)
box[:, [0,2]] = box[:, [0,2]]*nw/iw + dx
box[:, [1,3]] = box[:, [1,3]]*nh/ih + dy
box[:, 0:2][box[:, 0:2]<0] = 0
box[:, 2][box[:, 2]>w] = w
box[:, 3][box[:, 3]>h] = h
box_w = box[:, 2] - box[:, 0]
box_h = box[:, 3] - box[:, 1]
box = box[np.logical_and(box_w>1, box_h>1)]
box_data = np.zeros((len(box),5))
box_data[:len(box)] = box
image_datas.append(image_data)
box_datas.append(box_data)
img = Image.fromarray((image_data*255).astype(np.uint8))
#for j in range(len(box_data)):
# thickness = 3
# left, top, right, bottom = box_data[j][0:4]
# draw = ImageDraw.Draw(img)
# for i in range(thickness):
# draw.rectangle([left + i, top + i, right - i, bottom - i],outline=(255,255,255))
#img.show()
# 将图片分割,放在一起
cutx = np.random.randint(int(w*min_offset_x), int(w*(1 - min_offset_x)))
cuty = np.random.randint(int(h*min_offset_y), int(h*(1 - min_offset_y)))
new_image = np.zeros([h,w,3])
new_image[:cuty, :cutx, :] = image_datas[0][:cuty, :cutx, :]
new_image[cuty:, :cutx, :] = image_datas[1][cuty:, :cutx, :]
new_image[cuty:, cutx:, :] = image_datas[2][cuty:, cutx:, :]
new_image[:cuty, cutx:, :] = image_datas[3][:cuty, cutx:, :]
# 对框进行进一步的处理
new_boxes = merge_bboxes(box_datas, cutx, cuty)
return new_image, new_boxes
def normal_(annotation_line, input_shape):
'''random preprocessing for real-time data augmentation'''
line = annotation_line.split()
image = Image.open(line[0])
box = np.array([np.array(list(map(int,box.split(',')))) for box in line[1:]])
iw, ih = image.size
image = image.transpose(Image.FLIP_LEFT_RIGHT)
box[:, [0,2]] = iw - box[:, [2,0]]
return image, box
if __name__ == "__main__":
with open("train.txt") as f:
lines = f.readlines()
for i in range(5000):
a = np.random.randint(0,len(lines))
line = lines[a:a+4]
try:
image_data, box_data = get_random_data(line,[416,416])
img = Image.fromarray((image_data*255).astype(np.uint8))
img_path = "imgs/%s.jpg" % i
img.save(img_path)
results = get_result(box_data)
xml_path = "xmls/%s.xml" % i
CreatXml(img_path, results, xml_path)
except:
continue
两个辅助函数的代码(本文以科大讯飞竞赛的数据为例说明):
#-*-coding:utf8-*-
import numpy as np
import sys
import cv2
import glob
import os
import xml.dom.minidom
import argparse
import random
def CreatXml(imgPath, results, xmlPath):
img = cv2.imread(imgPath)
imgSize = img.shape
imgName = imgPath.split('/')[-1]
impl = xml.dom.minidom.getDOMImplementation()
dom = impl.createDocument(None, 'annotation', None)
root = dom.documentElement
folder = dom.createElement('folder')
root.appendChild(folder)
name_folfer = dom.createTextNode('Unknown')
folder.appendChild(name_folfer)
filename = dom.createElement('filename')
root.appendChild(filename)
name_img = dom.createTextNode(os.path.splitext(imgName)[0])
filename.appendChild(name_img)
filepath = dom.createElement('path')
root.appendChild(filepath)
path_img = dom.createTextNode(imgPath)
filepath.appendChild(path_img)
source = dom.createElement('source')
root.appendChild(source)
database = dom.createElement('database')
database_name = dom.createTextNode('Unknown')
database.appendChild(database_name)
source.appendChild(database)
img_size = dom.createElement('size')
root.appendChild(img_size)
width = dom.createElement('width')
width_num = dom.createTextNode(str(int(imgSize[1])))
width.appendChild(width_num)
height = dom.createElement('height')
height_num = dom.createTextNode(str(int(imgSize[0])))
height.appendChild(height_num)
depth = dom.createElement('depth')
depth_num = dom.createTextNode(str(int(imgSize[2])))
depth.appendChild(depth_num)
img_size.appendChild(width)
img_size.appendChild(height)
img_size.appendChild(depth)
segmented = dom.createElement('segmented')
root.appendChild(segmented)
segmented_num = dom.createTextNode('0')
segmented.appendChild(segmented_num)
for i in range(len(results)):
img_object = dom.createElement('object')
root.appendChild(img_object)
label_name = dom.createElement('name')
namecls = dom.createTextNode(results[i]['name'])
label_name.appendChild(namecls)
pose = dom.createElement('pose')
pose_name = dom.createTextNode('Unspecified')
pose.appendChild(pose_name)
truncated = dom.createElement('truncated')
truncated_num = dom.createTextNode('0')
truncated.appendChild(truncated_num)
difficult = dom.createElement('difficult')
difficult_num = dom.createTextNode('0')
difficult.appendChild(difficult_num)
bndbox = dom.createElement('bndbox')
xmin = dom.createElement('xmin')
xmin_num = dom.createTextNode(str(int(results[i]['bbox'][0])))
xmin.appendChild(xmin_num)
ymin = dom.createElement('ymin')
ymin_num = dom.createTextNode(str(int(results[i]['bbox'][1])))
ymin.appendChild(ymin_num)
xmax = dom.createElement('xmax')
xmax_num = dom.createTextNode(str(int(results[i]['bbox'][2])))
xmax.appendChild(xmax_num)
ymax = dom.createElement('ymax')
ymax_num = dom.createTextNode(str(int(results[i]['bbox'][3])))
ymax.appendChild(ymax_num)
bndbox.appendChild(xmin)
bndbox.appendChild(ymin)
bndbox.appendChild(xmax)
bndbox.appendChild(ymax)
img_object.appendChild(label_name)
img_object.appendChild(pose)
img_object.appendChild(truncated)
img_object.appendChild(difficult)
img_object.appendChild(bndbox)
f = open(xmlPath, 'w')
dom.writexml(f, addindent=' ', newl='\n')
f.close()
def get_result(box_data):
classes = ['knife', 'scissors', 'lighter', 'zippooil', 'pressure',
'slingshot', 'handcuffs', 'nailpolish', 'powerbank',
'firecrackers']
results = []
for obj in box_data:
result = {}
obj = [int(i) for i in obj]
box = obj[:4]
name = classes[obj[-1]]
result["name"] = name
result["bbox"] = box
results.append(result)
return results
最终的效果如图所示:
博主在比赛中用到该数据增强,有涨点!!!