anchor机制讲解
在faster-rcnn中,有anchor这一知识点,我们在这篇博客中将主要讲解它。
先看以下内容:
faster rcnn结构及代码讲解
理论知识
前面提到经过Conv layers后,图片大小变成了原来的1/16,令feat_stride=16,假设最后输出特征图尺寸为60X40,那么可以理解为60X40个点,每一个点都可以作为一个窗口(Anchors)中心点,同时每一个窗口又有不同的尺寸(一般有9种尺寸),最终生成的窗口有60409个。在生成Anchors时,我们先定义一个base_anchor,大小为1616的box(因为特征图(6040)上的一个点,可以对应到原图(1000600)上一个1616大小的区域),源码中转化为[0,0,15,15](表示right, bottom, left, top四条边)的数组,参数ratios=[0.5, 1, 2]scales=[8, 16, 32]
先看[0,0,15,15],面积保持不变(表示right, bottom, left, top),长、宽比分别为[0.5, 1, 2]是产生的Anchors box
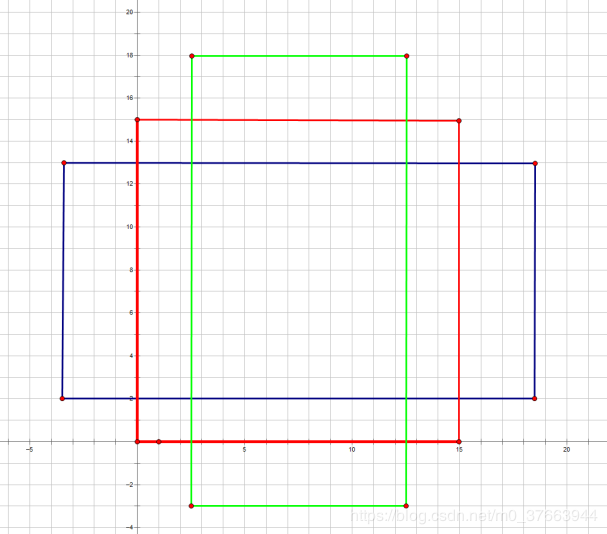
如果经过scales变化,即长、宽分别均为 (168=128)、(1616=256)、(1632=512),对应anchor box如图

综合以上两种变换,最后生成9个Anchor box在原图中。这只是其中一个点位的情况,一共有6040个,也就是60409。
源码讲解
以下为anchor机制主要结构(函数调用情况):
generate_anchors_pre_tf => generate_anchors
generate_anchors=>_ratio_enum,_scale_enum
_ratio_enum=>_whctrs,_mkanchors
_scale_enum=>_whctrs,_mkanchors
_whctrs:输入right, bottom, left, top四条边坐标;返回width, height, x center, y center中心坐标,长宽
_mkanchors:输入width, height, x center, y center中心坐标,长宽;返回right, bottom, left, top四条边坐标
以下代码参数设置height为Conv layers输出特征图高度60,width宽度40。其余参数使用默认。
# -*- coding: utf-8 -*-
"""
Created on Sun Dec 22 13:53:56 2019
@author: asus
"""
import tensorflow as tf
import numpy as np
#height=60 width=40
def generate_anchors_pre_tf(height, width, feat_stride=16, anchor_scales=(8, 16, 32), anchor_ratios=(0.5, 1, 2)):
shift_x = tf.range(width) * feat_stride # width shape=(40,)
shift_y = tf.range(height) * feat_stride # height shape=(60,)
#上诉两个步骤主要找到了特征图点在原图中的中心点位置
shift_x, shift_y = tf.meshgrid(shift_x, shift_y)
#meshgrid为网格矩阵,
#shift_x shape=(60, 40), shift_y shape=(60, 40)
sx = tf.reshape(shift_x, shape=(-1,))#shape=(2400,)
sy = tf.reshape(shift_y, shape=(-1,))#shape=(2400,)
shifts = tf.transpose(tf.stack([sx, sy, sx, sy]))#tf.stack -> shape=(4, 2400) shifts -> shape=(2400, 4)
K = tf.multiply(width, height)#shape=() K=2400
shifts = tf.transpose(tf.reshape(shifts, shape=[1, K, 4]), perm=(1, 0, 2))
#reshape -> shape=(1, 2400, 4) ,shifts shape=(2400, 1, 4), 特征图映射在原图上的2400个中心点位置
anchors = generate_anchors(ratios=np.array(anchor_ratios), scales=np.array(anchor_scales))
#根据anchor_ratios, anchor_scales产生anchors(3*3种变换),如下
"""
array([[ -84., -40., 99., 55.],
[-176., -88., 191., 103.],
[-360., -184., 375., 199.],
[ -56., -56., 71., 71.],
[-120., -120., 135., 135.],
[-248., -248., 263., 263.],
[ -36., -80., 51., 95.],
[ -80., -168., 95., 183.],
[-168., -344., 183., 359.]])
"""
A = anchors.shape[0] #9
anchor_constant = tf.constant(anchors.reshape((1, A, 4)), dtype=tf.int32)
#shape=(1, 9, 4) 表示一个基础图的9种处理
length = K * A #K=2400 A=9 shape=() length=21600
anchors_tf = tf.reshape(tf.add(anchor_constant, shifts), shape=(length, 4))
#anchor_constant shape=(1, 9, 4), shifts shape=(2400, 1, 4)
#add shape=(2400, 9, 4), anchors_tf shape=(21600, 4) 一张原图21600个achors
return tf.cast(anchors_tf, dtype=tf.float32), length
#大功告成
#全部使用默认参数anchor_scales=(8, 16, 32),控制大小 anchor_ratios=(0.5, 1, 2)控制比例
def generate_anchors(base_size=16, ratios=[0.5, 1, 2],
scales=2 ** np.arange(3, 6)):
"""
Generate anchor (reference) windows by enumerating aspect ratios X
scales wrt a reference (0, 0, 15, 15) window.
"""
base_anchor = np.array([1, 1, base_size, base_size]) - 1#array([ 0, 0, 15, 15])
ratio_anchors = _ratio_enum(base_anchor, ratios)
"""
array([[-3.5, 2. , 18.5, 13. ],
[ 0. , 0. , 15. , 15. ],
[ 2.5, -3. , 12.5, 18. ]])
"""
anchors = np.vstack([_scale_enum(ratio_anchors[i, :], scales)
for i in range(ratio_anchors.shape[0])])
return anchors
def _ratio_enum(anchor, ratios):
"""
Enumerate a set of anchors for each aspect ratio wrt an anchor.
"""
w, h, x_ctr, y_ctr = _whctrs(anchor)#(16, 16, 7.5, 7.5), (width, height, x center, y center)
size = w * h #(16*16)
size_ratios = size / ratios #array([512., 256., 128.])
ws = np.round(np.sqrt(size_ratios))# array([23., 16., 11.])
hs = np.round(ws * ratios)#array([12., 16., 22.])
anchors = _mkanchors(ws, hs, x_ctr, y_ctr)#输出窗口四条线#right, bottom, left, top,此时三种情况。
"""
array([[-3.5, 2. , 18.5, 13. ],
[ 0. , 0. , 15. , 15. ],
[ 2.5, -3. , 12.5, 18. ]])
"""
return anchors
#input
def _scale_enum(anchor, scales):
"""
Enumerate a set of anchors for each scale wrt an anchor.
"""
w, h, x_ctr, y_ctr = _whctrs(anchor)#(16, 16, 7.5, 7.5), (width, height, x center, y center)
#scales is array([ 8, 16, 32])
ws = w * scales
hs = h * scales
#ws,hs is array([128, 256, 512])
anchors = _mkanchors(ws, hs, x_ctr, y_ctr)
return anchors
def _whctrs(anchor):
"""
Return width, height, x center, and y center for an anchor (window).
"""
w = anchor[2] - anchor[0] + 1
h = anchor[3] - anchor[1] + 1
#right - left, top - bottom
x_ctr = anchor[0] + 0.5 * (w - 1)
y_ctr = anchor[1] + 0.5 * (h - 1)
return w, h, x_ctr, y_ctr
def _mkanchors(ws, hs, x_ctr, y_ctr):
"""
Given a vector of widths (ws) and heights (hs) around a center
(x_ctr, y_ctr), output a set of anchors (windows).
right, bottom, left, top
"""
ws = ws[:, np.newaxis]
hs = hs[:, np.newaxis]
anchors = np.hstack((x_ctr - 0.5 * (ws - 1),
y_ctr - 0.5 * (hs - 1),
x_ctr + 0.5 * (ws - 1),
y_ctr + 0.5 * (hs - 1)))
return anchors #right, bottom, left, top
上述代码最终返回的是right, bottom, left, top四条边。
我们可以看到最顶层的函数是generate_anchors_pre_tf,它由
以下函数generate_anchors_pre_tf调用
只看if语句里面的就行
def _anchor_component(self):
with tf.variable_scope('ANCHOR_' + self._tag) as scope:
# just to get the shape right
height = tf.to_int32(tf.ceil(self._im_info[0] / np.float32(self._feat_stride[0])))
width = tf.to_int32(tf.ceil(self._im_info[1] / np.float32(self._feat_stride[0])))
if cfg.USE_E2E_TF:
anchors, anchor_length = generate_anchors_pre_tf(
height,
width,
self._feat_stride,
self._anchor_scales,
self._anchor_ratios
)
else:
anchors, anchor_length = tf.py_func(generate_anchors_pre,
[height, width,
self._feat_stride, self._anchor_scales, self._anchor_ratios],
[tf.float32, tf.int32], name="generate_anchors")
anchors.set_shape([None, 4])
anchor_length.set_shape([])
self._anchors = anchors
self._anchor_length = anchor_length
self._anchors = anchors,self._anchor_length = anchor_length使最终的数据保存在类中。
参考文献:
https://blog.csdn.net/qq_41576083/article/details/82966489
https://www.cnblogs.com/wangyong/p/8513563.html