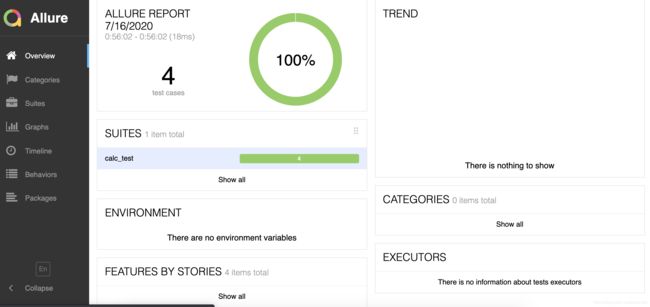
Python从0到1之pytest+Allure
pytest
是一个单元测试框架,简单易用,第三方库丰富,可以使用allure生成美观的测试报告
官网:https://docs.pytest.org/en/stable/
主流单元测试框架 unittest nose pytest
安装
安装pytest包
pip install -U pytest
配置
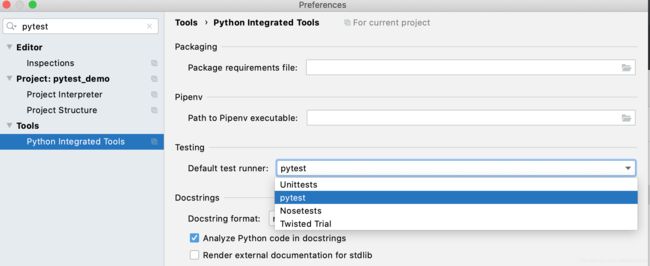
在Preferences 中的Tools->Python Interated Tools中配置Testing Default testing runner 为pytest,默认为unittest
在project interpreter中安装pytest

实战
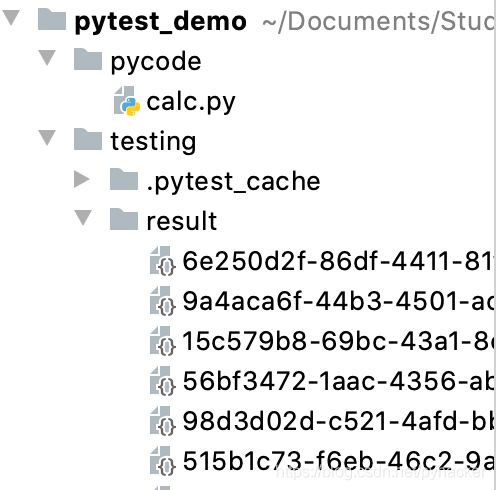
创建项目
在pycharm中创建pytest_demo项目,并创建pycode(代码)和testing(测试)目录,在pycode中创建calc.py,coding中创建calc_test.py,目录结构如下:
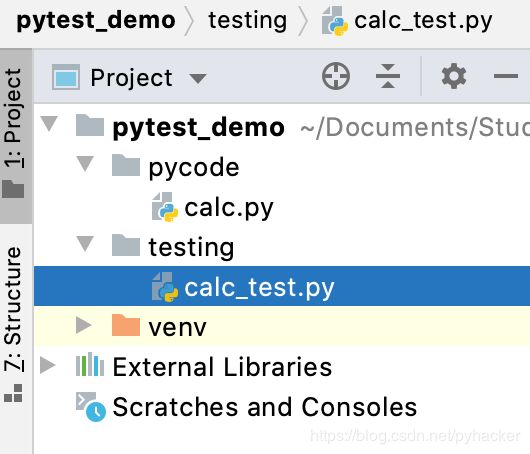
注意:不要使用code,test,pytest等关键字命名项目或者目录,否则会导致引用出错的问题
写代码
pytest 代码规范
- 文件名必须以test_开头
- 类名必须以Test开头,首字母大写,方法名test_开头
calc.py
class Calculator:
def add(self,a,b):
return a + b
def div(self,a,b):
return a / b
calc_test.py
from pycode.calc import Calculator
# 文件名必须以test_开头,类名必须以Test开头,首字母大写,方法名test_开头
class TestCalc:
def test_add(self):
calc = Calculator()
assert 2 == calc.add(1,1)
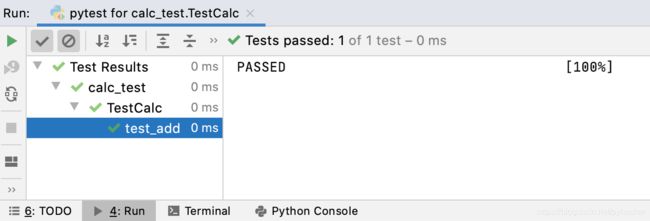
执行测试
在calc_test.py中右键绿色箭头,选择Run “pytest for …”
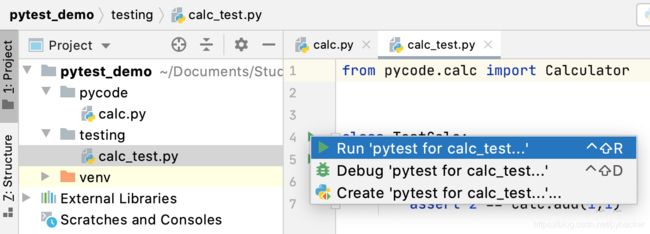
查看执行结果
参数化
待测试的输入和输出是一组数据,可以把测试数据组织起来,用不同的测试数据调用相同的测试方法(将可变数据处理成参数的形式来方便自动化测试过程中使用)
- 将变化的参数提取出来,以数据的形式传入到测试方法中
- 参数化会为每一条数据生成一条测用例,如果其中一条执行失败,不会影响其他用例的执行结果
calc_test.py
import pytest
from pycode.calc import Calculator
class TestCalc:
@pytest.mark.parametrize("a,b,c",[
(1,1,2),
(0.1,0.1,0.2),
(-1,-1,-2),
(100,50,200)
])
def test_add(self,a,b,c):
calc = Calculator()
assert c == calc.add(a,b)
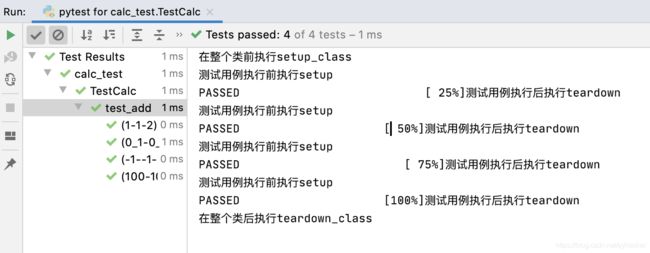
执行结果
四条用例都执行了
测试通过,展示测试进度
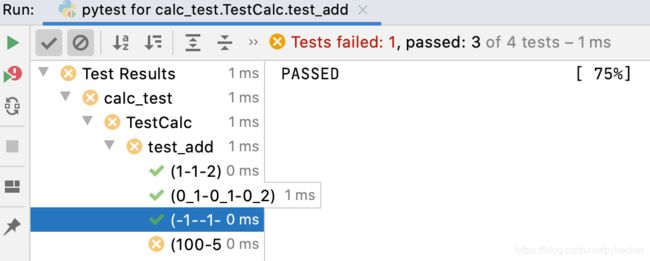
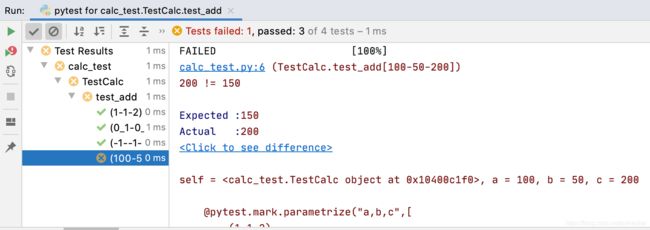
测试失败,提示失败原因
初始化和清除
在每条测试用例执行之前,执行setup()
在每条测试用例执行之后,执行teardown()
在整个测试类执行之前执行setup_class()
在整个测试类执行之后执行teardown_class()
import pytest
from pycode.calc import Calculator
class TestCalc:
# setup_class、teardown 是类级别的
def setup_class(self):
print("在整个类前执行setup_class")
self.calc = Calculator()
def teardown_class(self):
print("在整个类后执行teardown_class")
# setup、teardown是方法级别的
def setup(self):
print("测试用例执行前执行setup")
self.calc = Calculator()
def teardown(self):
print("测试用例执行后执行teardown")
@pytest.mark.parametrize("a,b,c",[
(1,1,2),
(0.1,0.1,0.2),
(-1,-1,-2),
(100,100,200)
])
def test_add(self,a,b,c):
assert c == self.calc.add(a,b)
Allure
Allure是一个轻量级,灵活的,支持多语言的测试报告工具
跨平台,奢华的报告框架
可以为开发和测试提供详尽的测试报告,测试步骤和日志
也可以为管理层提供high level 统计报告
Java语言开发,支持pytest、Javascript、PHP、ruby等
可以集成到Jenkins
官网:http://allure.qatools.ru/
安装Allure和Allure-pytest
brew install allure
pip install -U allure-pytest
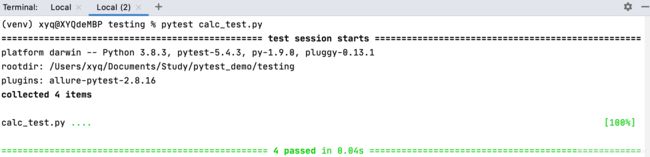
运行Allure
在calc_test.py上右键,选择open in terminal
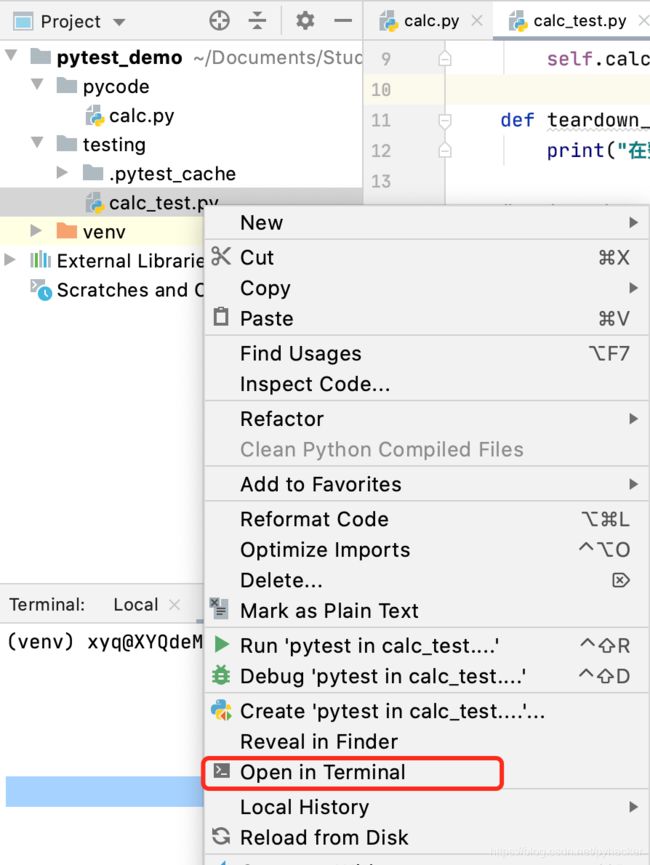
在terminal 中输入
pytest calc_test.py
收集结果
在pytest运行的时候收集结果
# --alluredir用于指定测试结果的存储路径
pytest calc_test.py -s -q --alluredir=./result/
获取报告
在线分析报告
allure serve ./result/
生成测报告文件
# --clean表示覆盖路径
allure generate ./result/ -o ./report/ --clean
# 打开报告文件,也可以直接打开html文件
allure open -h 127.0.0.1 -p 8883 ./report/
报告中添加文本
# 文本
allure.attach(str(data),attachment_type=allure.attachment_type.TEXT)
# HTML片段
allure.attach("首页",attachment_type=allure.attachment_type.HTML)
# 图片
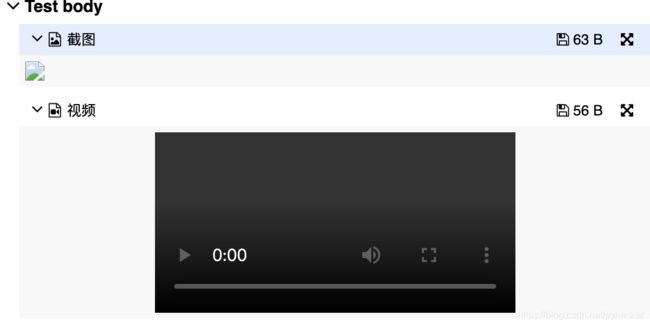
allure.attach("imagefile",name='截图',attachment_type=allure.attachment_type.PNG)
# 视频
allure.attach("videofile",name='视频',attachment_type=allure.attachment_type.MP4)
import pytest,sys,allure
sys.path.append("..")
from pycode.calc import Calculator
class TestCalc:
# setup_class、teardown 是类级别的
def setup_class(self):
print("在整个类前执行setup_class")
self.calc = Calculator()
def teardown_class(self):
print("在整个类后执行teardown_class")
# setup、teardown是方法级别的
def setup(self):
print("测试用例执行前执行setup")
self.calc = Calculator()
def teardown(self):
print("测试用例执行后执行teardown")
@pytest.mark.parametrize("a,b,c",[
(1,1,2),
(0.1,0.1,0.2),
(-1,-1,-2),
(100,100,200)
])
def test_add(self,a,b,c):
allure.attach("这是一个加法测试用例", name="文本类型",attachment_type=allure.attachment_type.TEXT)
allure.attach("HTML", name="HTML类型", attachment_type = allure.attachment_type.HTML)
assert c == self.calc.add(a,b)
def test_div(self):
allure.attach("/Users/xyq/Documents/Study/pytest_demo/testing/Python_notes.png", name='截图',attachment_type=allure.attachment_type.PNG)
allure.attach("/Users/xyq/Documents/Study/pytest_demo/testing/video.mp4", name='视频',attachment_type=allure.attachment_type.MP4)
assert 2 == self.calc.div(4,2)
数据驱动
数据驱动就是测试数据的改变从而驱动自动化测试的执行,最终引起测试结果的改变,说直白些就是参数化的应用