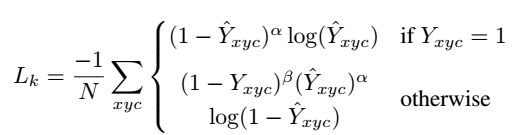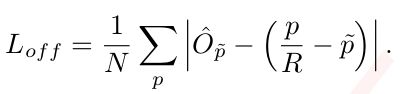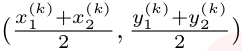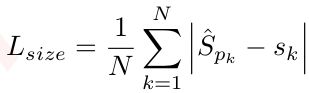centernet理解+demo代码分析
因为毕业设计打算要用centernet网络,所以,对centernet的demo的ctdet_detector进行了详细的功能分析。
本篇论文的参考:
1.原文:https://arxiv.org/pdf/1904.07850.pdf
2.代码:https://github.com/xingyizhou/CenterNet
3.原理参考:https://blog.csdn.net/c20081052/article/details/89358658
4.代码分析参考:https://blog.csdn.net/FSALICEALEX/article/details/94839011
食用方法:建议对照3和本文先阅读一遍原文
--------------------------------------------------------做有意的事儿的华丽分割线------------------------------------------------------------------
Part One 论文原文阅读
三种可选择的网络结构:
1)Resnet-18,可实现124fps,AP28.1%的检测效果
2)DLA-34,可实现52fps,37.4%AP的检测效果
3)Hourglass-104,可实现1.4fps,45.1%AP的检测效果
思想:把对框的检测变成对框的中心点的检测,将框的检测转变成关键点检测。将图片输入到神经网络中,得到heatmap,heatmap的peak(峰值点)就是中心点,利用peaks附近的特征预测长宽。没有NMS抑制。
损失函数:
heatmap的Focal loss,偏置offset的L1 loss,wh的L1 loss
(1)Focal loss
Q1:什么是heatmap???
![]()
![]() ,WH为图片尺寸,R为output_stride,C在本文的目标检测中为80。
,WH为图片尺寸,R为output_stride,C在本文的目标检测中为80。![]() 为关键点。
为关键点。![]() 代表为背景。
代表为背景。
Q2:如何把ground truth转换成heatmap?
Gaussian kernel:![]() ,(x,y)为ground_truth中的关键点,
,(x,y)为ground_truth中的关键点,![]() ,R为4在本文中,下采样output_stride。
,R为4在本文中,下采样output_stride。![]() 为尺寸自适应标准差。If two Gaussians of the same class overlap, we take the element-wise maximum.
为尺寸自适应标准差。If two Gaussians of the same class overlap, we take the element-wise maximum.
Q3:α、β、N是什么?
α=2、β=4是超参数。N是代表关键点的个数。The normalization by N is chosen as to normalize all positive focal loss instances to 1.
Q4:这个损失函数的作用就是使预测的关键点位置更准确。
(2)偏置offset的L1 loss
Q1:这个损失函数的作用是什么?
To recover the discretization error caused by the output stride。应该是在把512-128的过程中,heatmap是整数值,为了弥补这个整数后的误差,对于所有类都共享相同的偏差。
Q2:各参数的意义?
![]() 是局部偏置(local offset),网络预测的偏置值。P是关键点坐标,R是output_stride:4,
是局部偏置(local offset),网络预测的偏置值。P是关键点坐标,R是output_stride:4,![]() ,这个符号是向下取整符号吧。
,这个符号是向下取整符号吧。
(3)wh的L1 loss
For each object k :object size![]() 。
。
L1 loss:
Q1:参数的含义?
![]() 是预测的尺寸。(we use a single size prediction ___ for all object categories)
是预测的尺寸。(we use a single size prediction ___ for all object categories)
Q2:归一化方法?
we don't normalize the scale and directly use the raw pixel coordinates.we instead scale the loss by a constant ![]()
The overall training object is
Q3:该损失函数的作用?
回归框尺寸的大小。
点到框
a.For each category,提取heatmap上的peaks。
b.该peaks的值大于等于周围的其他8个点。
c.取值最大的前100个点。
不需要非极大值抑制,在peaks选择时已经相当于一个充分的nms了。
具体代码分析:
Demo:
from __future__ import absolute_import
from __future__ import division
from __future__ import print_function
import _init_paths
#这部分的作用是把lib加入到根目录下,有单独列出来解析
import os
import cv2
from opts import opts
from detectors.detector_factory import detector_factory
image_ext = ['jpg', 'jpeg', 'png', 'webp']#可检测的图片格式
video_ext = ['mp4', 'mov', 'avi', 'mkv']#可检测的视频格式
time_stats = ['tot', 'load', 'pre', 'net', 'dec', 'post', 'merge']#统计的时间的名称
def demo(opt):
os.environ['CUDA_VISIBLE_DEVICES'] = opt.gpus_str
opt.debug = max(opt.debug, 1)
#下面两步就是确定检测算子,是2d检测,3d检测还是人关键点检测,本人选用的是ctdet 2d检测。
Detector = detector_factory[opt.task]
detector = Detector(opt)
#判断是否为摄像头或者视频
if opt.demo == 'webcam' or \
opt.demo[opt.demo.rfind('.') + 1:].lower() in video_ext:
cam = cv2.VideoCapture(0 if opt.demo == 'webcam' else opt.demo)
detector.pause = False
while True:
_, img = cam.read()
cv2.imshow('input', img)
ret = detector.run(img)
time_str = ''
for stat in time_stats:
time_str = time_str + '{} {:.3f}s |'.format(stat, ret[stat])
print(time_str)
if cv2.waitKey(1) == 27:
return # esc to quit
#否:是图片
else:
#判断是否文件夹(一系列图片序列)
if os.path.isdir(opt.demo):
image_names = []
ls = os.listdir(opt.demo)
for file_name in sorted(ls):
ext = file_name[file_name.rfind('.') + 1:].lower()
if ext in image_ext:
image_names.append(os.path.join(opt.demo, file_name))
else:
#单张图片
image_names = [opt.demo]
for (image_name) in image_names:
#下面重点分析这个run函数(感觉检测的过程就是一次前向传播过程)
ret = detector.run(image_name)
time_str = ''
for stat in time_stats:
time_str = time_str + '{} {:.3f}s |'.format(stat, ret[stat])
print(time_str)
if __name__ == '__main__':
#对opt对象用opts().init()初始化
opt = opts().init()
#运行检测demo
demo(opt)
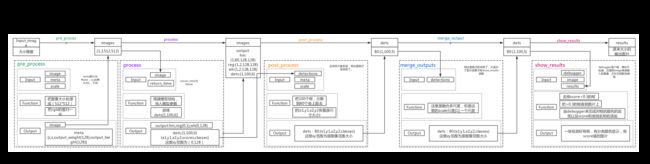
base_detector的run函数
这个几个主要的函数已经在上面的框图分析的比较清楚了。但有一说一,我没太懂这个debugger的操作。
def run(self, image_or_path_or_tensor, meta=None):
load_time, pre_time, net_time, dec_time, post_time = 0, 0, 0, 0, 0
merge_time, tot_time = 0, 0
debugger = Debugger(dataset=self.opt.dataset, ipynb=(self.opt.debug==3),
theme=self.opt.debugger_theme)
start_time = time.time()
pre_processed = False
#--------------------------------------------------------------
#这里的作用是判断输入的是什么格式的,第一个是ndarray,第二个是图片路径形式,第三个应该是字典路径的形式?最终得到的形式应该是ndarray的形式。
if isinstance(image_or_path_or_tensor, np.ndarray):
image = image_or_path_or_tensor
elif type(image_or_path_or_tensor) == type (''):
image = cv2.imread(image_or_path_or_tensor)
else:
image = image_or_path_or_tensor['image'][0].numpy()
pre_processed_images = image_or_path_or_tensor
pre_processed = True
loaded_time = time.time()
load_time += (loaded_time - start_time)
#---------------------------------------------------------------------------------------
detections = []
#这个是判断尺度,但是在ctdet中尺度为[1]
for scale in self.scales:
scale_start_time = time.time()
#前面有列到,pre_processed 为None,not pre_processed 为真,执行下面的语句
if not pre_processed:
#进行预处理,函数的作用输入输出见框图
images, meta = self.pre_process(image, scale, meta)
else:
# import pdb; pdb.set_trace()
images = pre_processed_images['images'][scale][0]
meta = pre_processed_images['meta'][scale]
meta = {k: v.numpy()[0] for k, v in meta.items()}
images = images.to(self.opt.device)
torch.cuda.synchronize()
pre_process_time = time.time()
pre_time += pre_process_time - scale_start_time
#--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
#进行process,详见框图
output, dets, forward_time = self.process(images, return_time=True)
torch.cuda.synchronize()
net_time += forward_time - pre_process_time
decode_time = time.time()
dec_time += decode_time - forward_time
if self.opt.debug >= 2:
self.debug(debugger, images, dets, output, scale)
dets = self.post_process(dets, meta, scale)
torch.cuda.synchronize()
post_process_time = time.time()
post_time += post_process_time - decode_time
detections.append(dets)
results = self.merge_outputs(detections)
torch.cuda.synchronize()
end_time = time.time()
merge_time += end_time - post_process_time
tot_time += end_time - start_time
if self.opt.debug >= 1:
self.show_results(debugger, image, results)
return {'results': results, 'tot': tot_time, 'load': load_time,
'pre': pre_time, 'net': net_time, 'dec': dec_time,
'post': post_time, 'merge': merge_time}base_detector中的pre_process
def pre_process(self, image, scale, meta=None):
height, width = image.shape[0:2]
#注意这里的int(图像原始尺寸)
new_height = int(height * scale)
new_width = int(width * scale)
#fix_res 为True,执行下列语句
if self.opt.fix_res:
#(128,128)
inp_height, inp_width = self.opt.input_h, self.opt.input_w
c = np.array([new_width / 2., new_height / 2.], dtype=np.float32)
s = max(height, width) * 1.0
else:
inp_height = (new_height | self.opt.pad) + 1
inp_width = (new_width | self.opt.pad) + 1
c = np.array([new_width // 2, new_height // 2], dtype=np.float32)
s = np.array([inp_width, inp_height], dtype=np.float32)
#以下三步的作用是把原尺寸变成[512,512]
trans_input = get_affine_transform(c, s, 0, [inp_width, inp_height])
resized_image = cv2.resize(image, (new_width, new_height))
inp_image = cv2.warpAffine(
resized_image, trans_input, (inp_width, inp_height),
flags=cv2.INTER_LINEAR)
#下面的作用是把rgb值进行归一化
inp_image = ((inp_image / 255. - self.mean) / self.std).astype(np.float32)
#把shape变成(1,3,512,512)的形式
images = inp_image.transpose(2, 0, 1).reshape(1, 3, inp_height, inp_width)
#flip_test的值为False,跳过下一行
if self.opt.flip_test:
images = np.concatenate((images, images[:, :, :, ::-1]), axis=0)
#把numpy转换成向量,创建字典
images = torch.from_numpy(images)
meta = {'c': c, 's': s,
'out_height': inp_height // self.opt.down_ratio,
'out_width': inp_width // self.opt.down_ratio}
return images, metactdet_detector中的process函数
def process(self, images, return_time=False):
with torch.no_grad():
#模型+图像向量--->结果
output = self.model(images)[-1]
hm = output['hm'].sigmoid_()
wh = output['wh']
reg = output['reg'] if self.opt.reg_offset else None
#False,跳过
if self.opt.flip_test:
hm = (hm[0:1] + flip_tensor(hm[1:2])) / 2
wh = (wh[0:1] + flip_tensor(wh[1:2])) / 2
reg = reg[0:1] if reg is not None else None
torch.cuda.synchronize()
forward_time = time.time()
#把这三部分变成(1*100*6)的值(x1,y1,x2,y2,score,classes)
dets = ctdet_decode(hm, wh, reg=reg, cat_spec_wh=self.opt.cat_spec_wh, K=self.opt.K)
if return_time:
return output, dets, forward_time
#执行这步
else:
return output, dets
#dets
#[ 95.8366, 61.3280, 99.6441, 64.2178, 0.3587, 2.0000]*100个类似ctdet_decode函数
def ctdet_decode(heat, wh, reg=None, cat_spec_wh=False, K=100):
batch, cat, height, width = heat.size()
#(1,80,128,128)
# heat = torch.sigmoid(heat)
# perform nms on heatmaps
heat = _nms(heat)
#
scores, inds, clses, ys, xs = _topk(heat, K=K)
if reg is not None:
reg = _tranpose_and_gather_feat(reg, inds)
reg = reg.view(batch, K, 2)
xs = xs.view(batch, K, 1) + reg[:, :, 0:1]
ys = ys.view(batch, K, 1) + reg[:, :, 1:2]
else:
xs = xs.view(batch, K, 1) + 0.5
ys = ys.view(batch, K, 1) + 0.5
wh = _tranpose_and_gather_feat(wh, inds)
#float型的(ys,xs,wh)都是(0~128)
if cat_spec_wh:
wh = wh.view(batch, K, cat, 2)
clses_ind = clses.view(batch, K, 1, 1).expand(batch, K, 1, 2).long()
wh = wh.gather(2, clses_ind).view(batch, K, 2)
else:
wh = wh.view(batch, K, 2)
clses = clses.view(batch, K, 1).float()
scores = scores.view(batch, K, 1)
bboxes = torch.cat([xs - wh[..., 0:1] / 2,
ys - wh[..., 1:2] / 2,
xs + wh[..., 0:1] / 2,
ys + wh[..., 1:2] / 2], dim=2)
detections = torch.cat([bboxes, scores, clses], dim=2)
#作用是把这些值变成(x1,y1,x2,y2,scores,clses)(1,100,6)
return detections
# [ 62.6475, 59.0259, 72.1761, 63.8676, 0.3664, 2.0000],
# [ 77.7357, 55.0493, 79.3302, 57.4312, 0.3656, 9.0000]
_topk
def _topk(scores, K=40):
batch, cat, height, width = scores.size()
#(1,80,128,128)
topk_scores, topk_inds = torch.topk(scores.view(batch, cat, -1), K)
#(heatmap值) (0~128*128)
#shape:(1,80,128*128)
# topk函数的作用是取最大值的前K个,这里就是100
topk_inds = topk_inds % (height * width)
#好像也就是跟前面的topk_inds一样啊
topk_ys = (topk_inds / width).int().float()
topk_xs = (topk_inds % width).int().float()
#(0~128)
topk_score, topk_ind = torch.topk(topk_scores.view(batch, -1), K)
#取80个类中的前100个中//的前100个。 shape:(1,100)
topk_clses = (topk_ind / K).int()
topk_inds = _gather_feat(
topk_inds.view(batch, -1, 1), topk_ind).view(batch, K)
topk_ys = _gather_feat(topk_ys.view(batch, -1, 1), topk_ind).view(batch, K)
topk_xs = _gather_feat(topk_xs.view(batch, -1, 1), topk_ind).view(batch, K)
#topk_inds(0~128*128),topk_ys,topk_xs ,是(0~128) shape都是(1,100)
return topk_score, topk_inds, topk_clses, topk_ys, topk_xs
#这个函数的作用就是先分别找每个类别heatmap值的前100,然后在这些前100中,找所有类的前100heatmap值。overctdet_detector中的post_process
def post_process(self, dets, meta, scale=1):
dets = dets.detach().cpu().numpy()
dets = dets.reshape(1, -1, dets.shape[2])
dets = ctdet_post_process(
dets.copy(), [meta['c']], [meta['s']],
meta['out_height'], meta['out_width'], self.opt.num_classes)
#[{1: [[858.762939453125, 296.41485595703125, 873.2911987304688, 338.3920593261719, 0.550717830657959]...],2:...}]
for j in range(1, self.num_classes + 1):
dets[0][j] = np.array(dets[0][j], dtype=np.float32).reshape(-1, 5)
dets[0][j][:, :4] /= scale
return dets[0]
'''
dets[0]
{1: array([[8.5876294e+02, 2.9641486e+02, 8.7329120e+02, 3.3839206e+02,
5.5071783e-01],[7.3865240e+02, 2.7424252e+02, 7.4700641e+02, 2.8662579e+02,
1.3952680e-01]], dtype=float32)
2: array...}
'''ctdet_post_process
def ctdet_post_process(dets, c, s, h, w, num_classes):
# dets: batch x max_dets x dim
# return 1-based class det dict
ret = []
for i in range(dets.shape[0]):
top_preds = {}
dets[i, :, :2] = transform_preds(
dets[i, :, 0:2], c[i], s[i], (w, h))
dets[i, :, 2:4] = transform_preds(
dets[i, :, 2:4], c[i], s[i], (w, h))
#从上面这里开始,尺寸变为了原尺寸。
#下面的函数作用是把100个框分散到80个类中
classes = dets[i, :, -1]
for j in range(num_classes):
inds = (classes == j)
top_preds[j + 1] = np.concatenate([
dets[i, inds, :4].astype(np.float32),
dets[i, inds, 4:5].astype(np.float32)], axis=1).tolist()
ret.append(top_preds)
return retmerge_outputs
def merge_outputs( detections):
results = {}
max_per_image = 100
for j in range(1, opt.num_classes + 1):
results[j] = np.concatenate(
[detection[j] for detection in detections], axis=0).astype(np.float32)
if opt.nms:
soft_nms(results[j], Nt=0.5, method=2)
scores = np.hstack(
[results[j][:, 4] for j in range(1, opt.num_classes + 1)])
if len(scores) > max_per_image:
kth = len(scores) - max_per_image
thresh = np.partition(scores, kth)[kth]
for j in range(1, opt.num_classes + 1):
keep_inds = (results[j][:, 4] >= thresh)
results[j] = results[j][keep_inds]
sum=0
for i in range (1,81):
m=results[i].shape
#print(results[i].shape)
sum=sum+m[0]
print(sum)
#print(results)
return resultsdebug
#该函数的作用是给框加上id、score和给框上色
def debug(debugger, images, dets, output, scale=1):
mean = np.array(opt.mean, dtype=np.float32).reshape(1, 1, 3)
std = np.array(opt.std, dtype=np.float32).reshape(1, 1, 3)
detection = dets.detach().cpu().numpy().copy()
detection[:, :, :4] *= opt.down_ratio
for i in range(1):
img = images[i].detach().cpu().numpy().transpose(1, 2, 0)
img = ((img * std + mean) * 255).astype(np.uint8)
pred = debugger.gen_colormap(output['hm'][i].detach().cpu().numpy())
debugger.add_blend_img(img, pred, 'pred_hm_{:.1f}'.format(scale))
debugger.add_img(img, img_id='out_pred_{:.1f}'.format(scale))
for k in range(len(dets[i])):
if detection[i, k, 4] > opt.center_thresh:
debugger.add_coco_bbox(detection[i, k, :4], detection[i, k, -1],
detection[i, k, 4],
img_id='out_pred_{:.1f}'.format(scale))show_results
def show_results( debugger, image, results):
pause = True
debugger.add_img(image, img_id='ctdet')
num = 0
for j in range(1, opt.num_classes + 1):
for bbox in results[j]:
#这里值得一提,过滤掉score<0.3的值
if bbox[4] > opt.vis_thresh:
num += 1
debugger.add_coco_bbox(bbox[:4], j - 1, bbox[4], img_id='ctdet')
print(num)
#debugger.show_all_imgs(pause=pause)ps:
参考自:https://blog.csdn.net/qq_41084756/article/details/101711202
下载models中的ctdet_coco_dla_2x.pth并放入CenterNet下的models下即可。
由于这里没有运用姿态检测,因此需要修改几个参数(参考自此处):
vim CenterNet/src/lib/models/networks/pose_dla_dcn.py
注释掉第313和第314行:在这里插入图片描述
vim CenterNet/src/lib/opts.py
将第323行改成
opt.flip_idx = False
不这样做的话,在训练时会去Google Drive上下载姿态检测相关的预训练模型,导致网络超时。