利用对极约束求基础矩阵与本质矩阵(OpenCV C++实现)
一、对极约束原理
参考链接:https://www.cnblogs.com/wangguchangqing/p/8151128.html
该链接讲述的比较清楚,源自于SLAM14讲
二、代码实现
void pose_estimation_2d2d (std::vector keypoints_1,
std::vector keypoints_2,
std::vector< DMatch > matches,
Mat& R, Mat& t )
{
// 相机内参, TUM Freiburg2
Mat K = ( Mat_ ( 3,3 ) << 520.9, 0, 325.1, 0, 521.0, 249.7, 0, 0, 1 );
//-- 把匹配点转换为 vector 的形式
vector points1;
vector points2;
for ( int i = 0; i < ( int ) matches.size(); i++ )
{
points1.push_back( keypoints_1[matches[i].queryIdx].pt );
points2.push_back( keypoints_2[matches[i].trainIdx].pt );
}
//-- 计算基础矩阵
Mat fundamental_matrix;
fundamental_matrix = findFundamentalMat ( points1, points2, CV_FM_8POINT );
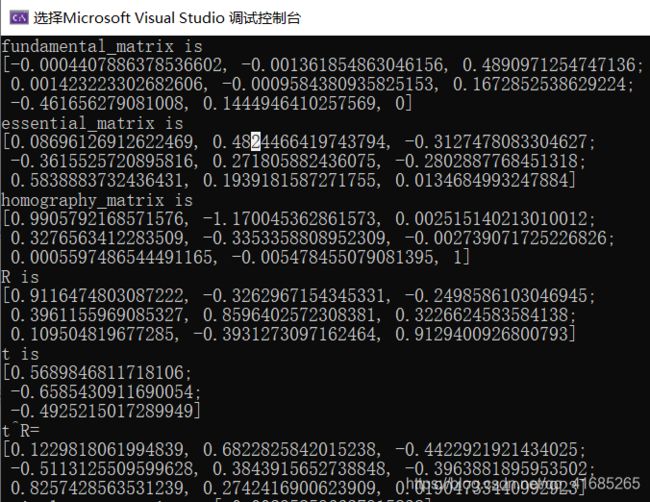
cout<<"fundamental_matrix is "< 代码不难,主要是几个函数的运用,求本质矩阵、基础矩阵和单应性矩阵等等的函数可以查看官方文档或者直接百度相关参数
三、求解
int main( int argc, char** argv )
{
if ( argc != 3 )
{
cout<<"usage: feature_extraction img1 img2"< keypoints_1, keypoints_2;
vector matches;
find_feature_matches( img_1, img_2, keypoints_1, keypoints_2, matches );
cout<<"一共找到了"<(3,3) <<0, -t.at(2,0), t.at(1,0),
t.at(2,0), 0, -t.at(0,0),
-t.at(1.0), t.at(0,0), 0);
cout<<"t^R="< ( 3,3 ) << 520.9, 0, 325.1, 0, 521.0, 249.7, 0, 0, 1 );
for ( DMatch m: matches )
{
Point2d pt1 = pixel2cam( keypoints_1[ m.queryIdx ].pt, K );
Mat y1 = (Mat_(3,1) << pt1.x, pt1.y, 1);
Point2d pt2 = pixel2cam( keypoints_2[ m.trainIdx ].pt, K );
Mat y2 = (Mat_(3,1) << pt2.x, pt2.y, 1);
Mat d = y2.t() * t_x * R * y1;
cout << "epipolar constraint = " << d << endl;
}
return 0;
} 求解结果为: