利用Tensorflow里的LSTM对北京PM2.5数据集Beijing PM2.5 Data Data Set进行预测
课程作业。
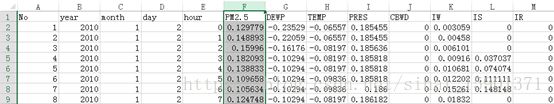
数据集:Beijing PM2.5 Data Data Set
这个数据集里有北京2010-2014的天气数据。每小时一条,适合用于回归模型。
这里我对数据进行了标准化处理
在学习LSTM的时候这两篇文章给了我很大帮助:
http://karpathy.github.io/2015/05/21/rnn-effectiveness/
https://www.zybuluo.com/hanbingtao/note/581764
直接上代码,代码很大程度上参考了某篇博文,在这里暂时找不到原代码链接了,以后有机会再补上。
# -*- coding: utf-8 -*-
"""
Created on Wed Jun 6 10:56:52 2018
@author: Administrator
"""
import tensorflow as tf
import pandas as pd
import numpy as np
import csv
tf.reset_default_graph()
rnn_unit = 50 #the amount of hidden lstm units
batch_size = 72 #the amount of data trained every time
input_size = 8 #size of input
output_size = 1 #size of output
lr = 0.006 #learn rate
train_x, train_y = [], [] #
f = open('C:\\Users\\Administrator\\Desktop\\BJair\\BjAirDat4.csv',encoding='UTF-8')
df = pd.read_csv(f) #read the csv file
#get data, use the data between 2010 ans 1013 for train,the data of 2014 as exam
weatherdata = df.iloc[0:39312 ,5:13] #weather with 7 items, not including PM2.5, for train
pm25data = df.iloc[0+batch_size:39312+batch_size ,5:6] #pm2.5 data, for train
weathertest = df.iloc[39312:, 5:13] #weatherdata with 7 items, not including PM2.5, for exam
pm25test = df.iloc[39312:, 5:6] #pm2.5 data, for exam
#train_x is a tensor which [?,batch_size,input_size]
#train_y is a tensor which [?,batch_size,output_size]
i = 0
while i < len(weatherdata):
x = weatherdata[i:i+batch_size].values #conver weatherdata to a tensor
y = pm25data[i:i+batch_size].values #the same with the pm25data
train_x.append(x.tolist()) #push them into train_x ans train_y
train_y.append(y.tolist())
i += batch_size
#placeholder
X = tf.placeholder(tf.float32, [None, batch_size, input_size]) #a placeholder as the input tensor
Y = tf.placeholder(tf.float32, [None, batch_size, output_size]) #the lable
#initialize the weights and biases [7,50] [50,1]
weights = {
'in':tf.Variable(tf.random_normal([input_size, rnn_unit])),
'out':tf.Variable(tf.random_normal([rnn_unit, output_size]))
}
biases = {
'in':tf.Variable(tf.random_normal([batch_size, rnn_unit])),
'out':tf.Variable(tf.random_normal([batch_size, output_size]))
}
def lstm(batch):
w_in = weights['in']
b_in = biases['in']
w_out = weights['out']
b_out = biases['out']
#convert the tensor(X Accepts value from outside function) to a 2-dimensional tensor, [?*7]
input_ = tf.reshape(X, [-1, input_size])
#make matrix multiplication between input_ and w_in, then add b_in
input_rnn = tf.matmul(input_, w_in) + b_in
#convert input_rnn to a 3-dimensional tensor as the input of BaicSTMCell
input_rnn = tf.reshape(input_rnn, [-1, batch, rnn_unit])
#BasicLSTMCell cell,the amount of rnn_unit
cell = tf.nn.rnn_cell.BasicLSTMCell(rnn_unit)
#initial cell,batch_size is equal with the input parameter BATCH
init_state = cell.zero_state(batch, dtype = tf.float32)
#outputs is a tensor of shape [batch_size, max_time, cell_state_size]
#final_state is a tensor of shape [batch_size, cell_state_size]
#Create a Cell
#time_major = True ==> Tensorshape [max_time, batch_size, ...] something goes wrong when FALSE
output_rnn, final_state = tf.nn.dynamic_rnn(cell, input_rnn, initial_state = init_state, dtype = tf.float32, time_major = True)
#convert the output tensor to a 2-dimensional tensor, then calculate the output
output = tf.reshape(output_rnn, [-1, rnn_unit])
#make matrix multiplication between output and w_out, then add b_out
pred = tf.matmul(output, w_out) + b_out
return pred,final_state
def train_lstm():
print('start train lstm')
print(len(train_x))
global batch_size
pred,_ = lstm(batch_size)
#calculate the loss, use the sum of variance between PRED and Y
##
##loss need to be improved
##
loss = tf.reduce_sum(tf.square(tf.reshape(pred, [-1]) - tf.reshape(Y, [-1])))
#use lr as the learn rate, to make the loss minimize
train_op = tf.train.AdamOptimizer(lr).minimize(loss)
#save the model
saver = tf.train.Saver(tf.global_variables())
with tf.Session() as sess:
sess.run(tf.global_variables_initializer())
for i in range(1000):
step = 0
start = 0
end = start + 1
while(end < len(train_x)-1):
loss_ = sess.run([train_op, loss], feed_dict = {X:train_x[start:end], Y:train_y[start+1:end+1]})
start += 1
end += 1
if step%100 == 0:
print('round: ' , i , ' step: ' , step, ' loss : ' , loss_)
if step % 1000 == 0:
saver.save(sess, "C:\\Users\\Administrator\\Desktop\\moxing\\model.ckpt")
print('save model')
step += 1
train_lstm()
def predection():
prev_seq = weathertest.values
predict = []
accurate = []
pred, _ = lstm(72)
saver = tf.train.Saver(tf.global_variables())
with tf.Session() as sess:
saver.restore(sess, "C:\\Users\\Administrator\\Desktop\\moxing\\model.ckpt")
start = 0
end = start+72
while(end < len(prev_seq)-100):
next_seq = sess.run(pred, feed_dict = {X:[prev_seq[start:end]]})
predict.append(next_seq[0:24].tolist())
accurate.append(pm25test[end:end+24].values.tolist())
start = start + 96
end = end +96
s = np.subtract(predict, accurate)
MSE = np.mean(np.multiply(s, s))
print(MSE)
#predection()
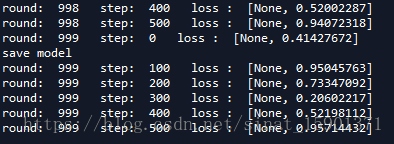
训练时候效果并不咋样
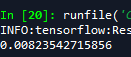
测试集的均方误差:
其实我也不知道怎么判断效果好不好