从零使用强化学习训练AI玩儿游戏(6)——使用DQN(TensorFlow)
接上一篇,我们来继续讲讲神经网络DQN的搭建
下面是初始化神经网络的函数
def __init__(
self,
n_actions, # 需要输出多少个action的值,就是控制的动作 如左右
n_features,# 要接受多少个观测状态
learning_rate=0.01,# 学习率
reward_decay=0.9,# 奖励的衰减率 就是Sara里面的gamma
e_greedy=0.9,# 代表90%选择这个行为
replace_target_iter=300, # 隔多少步后 把估计神经网络的值全部复制给目标神经网络
memory_size=500, # 每个存储数据的大小
batch_size=32, # 随机梯度下降的值
e_greedy_increment=None,# 不断的缩小随机的范围
output_graph=False,# 是否输出图表
):
self.n_actions = n_actions
self.n_features = n_features
self.lr = learning_rate
self.gamma = reward_decay
self.epsilon_max = e_greedy
self.replace_target_iter = replace_target_iter
self.memory_size = memory_size
self.batch_size = batch_size
self.epsilon_increment = e_greedy_increment
self.epsilon = 0 if e_greedy_increment is not None else self.epsilon_max
# 一共学习了多少步
self.learn_step_counter = 0
# 初始化记忆库 RL.store_transition(observation, action, reward, observation_)
self.memory = np.zeros((self.memory_size, n_features * 2 + 2))
# 建立神经网络
self._build_net()
t_params = tf.get_collection('target_net_params')
e_params = tf.get_collection('eval_net_params')
self.replace_target_op = [tf.assign(t, e) for t, e in zip(t_params, e_params)]
self.sess = tf.Session()
if output_graph:
tf.summary.FileWriter("logs/", self.sess.graph)
self.sess.run(tf.global_variables_initializer())
self.cost_his = []下面是学习的函数。
def learn(self):
# 检查是否替换 target_net 参数
if self.learn_step_counter % self.replace_target_iter == 0:
self.sess.run(self.replace_target_op)
print('\ntarget_params_replaced\n')
# 从 memory 中随机抽取 batch_size 这么多记忆
# 它是一个batch一个batch的训练的 不是说每一步就训练哪一步
if self.memory_counter > self.memory_size:
sample_index = np.random.choice(self.memory_size, size=self.batch_size)
else:
sample_index = np.random.choice(self.memory_counter, size=self.batch_size)
batch_memory = self.memory[sample_index, :]
# 获取 q_next (target_net 产生了 q) 和 q_eval(eval_net 产生的 q)
q_next, q_eval = self.sess.run(
[self.q_next, self.q_eval],
feed_dict={
self.s_: batch_memory[:, -self.n_features:],
self.s: batch_memory[:, :self.n_features]
})
# 下面这几步十分重要. q_next, q_eval 包含所有 action 的值,
# 而我们需要的只是已经选择好的 action 的值, 其他的并不需要.
# 所以我们将其他的 action 值全变成 0, 将用到的 action 误差值 反向传递回去, 作为更新凭据.
# 这是我们最终要达到的样子, 比如 q_target - q_eval = [1, 0, 0] - [-1, 0, 0] = [2, 0, 0]
# q_eval = [-1, 0, 0] 表示这一个记忆中有我选用过 action 0, 而 action 0 带来的 Q(s, a0) = -1, 所以其他的 Q(s, a1) = Q(s, a2) = 0.
# q_target = [1, 0, 0] 表示这个记忆中的 r+gamma*maxQ(s_) = 1, 而且不管在 s_ 上我们取了哪个 action,
# 我们都需要对应上 q_eval 中的 action 位置, 所以就将 1 放在了 action 0 的位置.
# 下面也是为了达到上面说的目的, 不过为了更方面让程序运算, 达到目的的过程有点不同.
# 是将 q_eval 全部赋值给 q_target, 这时 q_target-q_eval 全为 0,
# 不过 我们再根据 batch_memory 当中的 action 这个 column 来给 q_target 中的对应的 memory-action 位置来修改赋值.
# 使新的赋值为 reward + gamma * maxQ(s_), 这样 q_target-q_eval 就可以变成我们所需的样子.
# 具体在下面还有一个举例说明.
q_target = q_eval.copy()
batch_index = np.arange(self.batch_size, dtype=np.int32)
eval_act_index = batch_memory[:, self.n_features].astype(int)# batch_memory就是之前储存下来的记忆,根据不同的需要有所改变
reward = batch_memory[:, self.n_features + 1]
q_target[batch_index, eval_act_index] = reward + self.gamma * np.max(q_next, axis=1)
"""
假如在这个 batch 中, 我们有2个提取的记忆, 根据每个记忆可以生产3个 action 的值:
q_eval =
[[1, 2, 3],
[4, 5, 6]]
q_target = q_eval =
[[1, 2, 3],
[4, 5, 6]]
然后根据 memory 当中的具体 action 位置来修改 q_target 对应 action 上的值:
比如在:
记忆 0 的 q_target 计算值是 -1, 而且我用了 action 0;
记忆 1 的 q_target 计算值是 -2, 而且我用了 action 2:
q_target =
[[-1, 2, 3],
[4, 5, -2]]
所以 (q_target - q_eval) 就变成了:
[[(-1)-(1), 0, 0],
[0, 0, (-2)-(6)]]
最后我们将这个 (q_target - q_eval) 当成误差, 反向传递会神经网络.
所有为 0 的 action 值是当时没有选择的 action, 之前有选择的 action 才有不为0的值.
我们只反向传递之前选择的 action 的值,
"""
# 训练 eval_net
_, self.cost = self.sess.run([self._train_op, self.loss],
feed_dict={self.s: batch_memory[:, :self.n_features],
self.q_target: q_target})
self.cost_his.append(self.cost) # 记录 cost 误差
# 逐渐增加 epsilon, 降低行为的随机性
self.epsilon = self.epsilon + self.epsilon_increment if self.epsilon < self.epsilon_max else self.epsilon_max
self.learn_step_counter += 1其他的函数都比较简单,所以这里直接po上全部源代码
# -*- coding: UTF-8 -*-
import numpy as np
import pandas as pd
import tensorflow as tf
np.random.seed(1)
tf.set_random_seed(1)
# Deep Q Network off-policy
class DeepQNetwork:
def __init__(
self,
n_actions, # 需要输出多少个action的值,就是控制的动作 如左右
n_features,# 要接受多少个观测状态
learning_rate=0.01,# 学习率
reward_decay=0.9,# 奖励的衰减率 就是Sara里面的gamma
e_greedy=0.9,# 代表90%选择这个行为
replace_target_iter=300, # 隔多少步后 把估计神经网络的值全部复制给目标神经网络
memory_size=500, # 每个存储数据的大小
batch_size=32, # 随机梯度下降的值
e_greedy_increment=None,# 不断的缩小随机的范围
output_graph=False,# 是否输出图表
):
self.n_actions = n_actions
self.n_features = n_features
self.lr = learning_rate
self.gamma = reward_decay
self.epsilon_max = e_greedy
self.replace_target_iter = replace_target_iter
self.memory_size = memory_size
self.batch_size = batch_size
self.epsilon_increment = e_greedy_increment
self.epsilon = 0 if e_greedy_increment is not None else self.epsilon_max
# 一共学习了多少步
self.learn_step_counter = 0
# 初始化记忆库 RL.store_transition(observation, action, reward, observation_)
self.memory = np.zeros((self.memory_size, n_features * 2 + 2))
# 建立神经网络
self._build_net()
t_params = tf.get_collection('target_net_params')
e_params = tf.get_collection('eval_net_params')
self.replace_target_op = [tf.assign(t, e) for t, e in zip(t_params, e_params)]
self.sess = tf.Session()
if output_graph:
tf.summary.FileWriter("logs/", self.sess.graph)
self.sess.run(tf.global_variables_initializer())
self.cost_his = []
def _build_net(self):
# ------------------ 建立评估神经网络 ------------------
self.s = tf.placeholder(tf.float32, [None, self.n_features], name='s') #输入状态值
self.q_target = tf.placeholder(tf.float32, [None, self.n_actions], name='Q_target') # 用来接收 q_target 的值, 这个之后会通过计算得到
with tf.variable_scope('eval_net'):
# c_names非常重要,是用来储存神经网络参数的,在后面的学习中会把整个参数全部复制给目标神经网络
c_names, n_l1, w_initializer, b_initializer = \
['eval_net_params', tf.GraphKeys.GLOBAL_VARIABLES], 10, \
tf.random_normal_initializer(0., 0.3), tf.constant_initializer(0.1) # 建立神经网络的参数
# 第一层,一个非常简单的神经元,y = relu(w1*x + b1) 输入进去的是状态值 输入给第二层神经网络的值
with tf.variable_scope('l1'):
w1 = tf.get_variable('w1', [self.n_features, n_l1], initializer=w_initializer, collections=c_names)
b1 = tf.get_variable('b1', [1, n_l1], initializer=b_initializer, collections=c_names)
l1 = tf.nn.relu(tf.matmul(self.s, w1) + b1)
# 第二层, 还是一个简单的神经元,y = w2*x + b2 输入是上一层的值,输出的是估计值,也就是Q估计
with tf.variable_scope('l2'):
w2 = tf.get_variable('w2', [n_l1, self.n_actions], initializer=w_initializer, collections=c_names)
b2 = tf.get_variable('b2', [1, self.n_actions], initializer=b_initializer, collections=c_names)
self.q_eval = tf.matmul(l1, w2) + b2
# 建立损失函数这里就是q_target - q_eval 来计算error q_target是目标神经网络的输出值,这里输入进来做期望
with tf.variable_scope('loss'):
self.loss = tf.reduce_mean(tf.squared_difference(self.q_target, self.q_eval))
# 训练优化器
with tf.variable_scope('train'):
self._train_op = tf.train.RMSPropOptimizer(self.lr).minimize(self.loss)
# 建立目标神经网络,目标神经网络的结构必须要跟估计神经网络一模一样,因为会做整个参数的赋值
self.s_ = tf.placeholder(tf.float32, [None, self.n_features], name='s_') # 输入 这里只有一个输入 因为他不需要做训练
with tf.variable_scope('target_net'):
c_names = ['target_net_params', tf.GraphKeys.GLOBAL_VARIABLES]
with tf.variable_scope('l1'):
w1 = tf.get_variable('w1', [self.n_features, n_l1], initializer=w_initializer, collections=c_names)
b1 = tf.get_variable('b1', [1, n_l1], initializer=b_initializer, collections=c_names)
l1 = tf.nn.relu(tf.matmul(self.s_, w1) + b1)
with tf.variable_scope('l2'):
w2 = tf.get_variable('w2', [n_l1, self.n_actions], initializer=w_initializer, collections=c_names)
b2 = tf.get_variable('b2', [1, self.n_actions], initializer=b_initializer, collections=c_names)
self.q_next = tf.matmul(l1, w2) + b2
# 储存记忆,从上往下储存,满了就循环
def store_transition(self, s, a, r, s_):
if not hasattr(self, 'memory_counter'):
self.memory_counter = 0
transition = np.hstack((s, [a, r], s_))
index = self.memory_counter % self.memory_size
self.memory[index, :] = transition
self.memory_counter += 1
# 选择动作,90%使用DQN选择,10%使用随机办法
def choose_action(self, observation):
observation = observation[np.newaxis, :]
if np.random.uniform() < self.epsilon:
# 向前输出 这里使用的是估计神经网络
actions_value = self.sess.run(self.q_eval, feed_dict={self.s: observation})
action = np.argmax(actions_value)
else:
action = np.random.randint(0, self.n_actions)
return action
def learn(self):
# 检查是否替换 target_net 参数
if self.learn_step_counter % self.replace_target_iter == 0:
self.sess.run(self.replace_target_op)
print('\ntarget_params_replaced\n')
# 从 memory 中随机抽取 batch_size 这么多记忆
# 它是一个batch一个batch的训练的 不是说每一步就训练哪一步
if self.memory_counter > self.memory_size:
sample_index = np.random.choice(self.memory_size, size=self.batch_size)
else:
sample_index = np.random.choice(self.memory_counter, size=self.batch_size)
batch_memory = self.memory[sample_index, :]
# 获取 q_next (target_net 产生了 q) 和 q_eval(eval_net 产生的 q)
q_next, q_eval = self.sess.run(
[self.q_next, self.q_eval],
feed_dict={
self.s_: batch_memory[:, -self.n_features:],
self.s: batch_memory[:, :self.n_features]
})
q_target = q_eval.copy()
batch_index = np.arange(self.batch_size, dtype=np.int32)
eval_act_index = batch_memory[:, self.n_features].astype(int)# batch_memory就是之前储存下来的记忆,根据不同的需要有所改变
reward = batch_memory[:, self.n_features + 1]
q_target[batch_index, eval_act_index] = reward + self.gamma * np.max(q_next, axis=1)
# 训练 eval_net
_, self.cost = self.sess.run([self._train_op, self.loss],
feed_dict={self.s: batch_memory[:, :self.n_features],
self.q_target: q_target})
self.cost_his.append(self.cost) # 记录 cost 误差
# 逐渐增加 epsilon, 降低行为的随机性
self.epsilon = self.epsilon + self.epsilon_increment if self.epsilon < self.epsilon_max else self.epsilon_max
self.learn_step_counter += 1
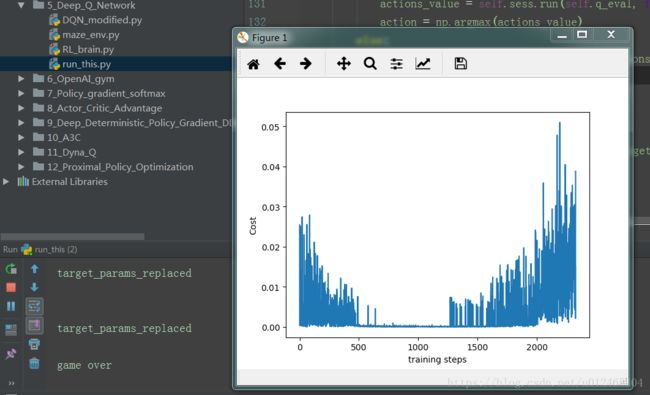
def plot_cost(self):
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
plt.plot(np.arange(len(self.cost_his)), self.cost_his)
plt.ylabel('Cost')
plt.xlabel('training steps')
plt.show()
输出的结果 如下:
图中走迷宫游戏并不能完美的体现DQN的实力,还有单细胞神经网络也过于简单了下一篇我们使用gym中的游戏再来测试一下DQN的实力。