Pointpillars代码阅读----predict函数篇
Brief
前面讲了大部分都是train方面的内容,但是在实际中还会在训练过程进行验证,而我目前自己的搭的网络是没有在训练时进行eval的过程。所以记录研究.
在经过了net的正向前馈后,每一个anchor会得到预测的cls分数和reg的box,这一部分就是后续的nms等后处理
这一部分仅仅是对eval而言的,对train没有这种问题
eval
之前拿之前训练过的一个kitti多分类的网络进行测试:
evaluate
--config_path=../configs/all.fhd.config
--model_dir=/home/sn/pointpillars/second/pre_train_model_dir/
--measure_time=True
--batch_size=1
主要pred函数在voxelnet.py的predict函数,注释如下:
this function don't contain any kitti-specific code.
Returns:
predict: list of pred_dict.
pred_dict: {
box3d_lidar: [N, 7] 3d box.
scores: [N]
label_preds: [N]
metadata: meta-data which contains dataset-specific information.
for kitti, it contains image idx (label idx),
for nuscenes, sample_token is saved in it.
}
需要对这个函数进行断点测试,因此我选择了kitti上的第79张图片,也就是bactch_szie=1时候的一个输入,如下,一会的检测框会以红色显示出来。

输入参数
example–集合了gt的target,anchor和voxel的dictpreds_dict–包含了box和cls的dict。
主要过程
- 得到主要函数变量
| 得到变量 | shape | 函数 |
|---|---|---|
batch_anchors |
[bs,168960,7] | batch_anchors = example["anchors"].view(batch_size, -1, example["anchors"].shape[-1]) |
batch_box_preds |
[bs,168960,7] | batch_box_preds = batch_box_preds.view(batch_size, -1,self._box_coder.code_size) |
batch_cls_preds |
[bs,168960,4] | batch_cls_preds = batch_cls_preds.view(batch_size, -1,num_class_with_bg) |
batch_dir_preds |
[bs,168960,2] | batch_dir_preds.view(batch_size, -1, self._num_direction_bins) |
post_center_range |
[bs,6] |
其具体含义看名称就知道了,就不细讲。
- 取一个bacth的数据
插入关于函数zip的使用方法:
zip(a,b)表示:zip()函数分别从a和b依次各取出一个元素组成元组,再将依次组成的元组组合成一个新的迭代器–新的zip类型数据。
作者如下:
for box_preds, cls_preds, dir_preds, a_mask, meta in zip(
batch_box_preds, batch_cls_preds, batch_dir_preds,
batch_anchors_mask, meta_list):
也就是说,这里的
batch_box_preds, batch_cls_preds, batch_dir_preds, batch_anchors_mask, meta_lis大小都是[bs,168960,* ]的,然后每一次都各自从这里面取出一个batch。也就是每一个都是[168960,* ](这里的a_mask=None,不用考虑)
插入结束
对每一个batch 以下的操作都是一样的,这里以一个batch为例.
- 找到方向最大索引和对
cls_pred进行sigmod函数处理
(1)找到dir方向得分最大值得索引。该过程如下图表示的那样.
实际上在预测的方向上,几乎都是两个相反方向
dir_labels = torch.max(dir_preds, dim=-1)[1]
(2)对
cls_preds进行sigmod。
在对cls_preds进行sigmod函数处理之前,其内容在我训练的模型上来看是,如果该类别是car,则该anchor的预测值大致是[10,-10,-10,-10];同理如果是van则大致是[-10,-10,-10,10]。处理后,就很在[-1,1]之间了。得到total_scores[ 168960 , 4 ] [168960,4] [168960,4]
total_scores = F.softmax(cls_preds, dim=-1)[..., 1:]
- 在BEV视角下使用计算nms需要的参数
(1)使用
rotat_nms
if self._use_rotate_nms:
nms_func = box_torch_ops.rotate_nms
(2)计算每一个的feature_map_size(不含有numclss)(168960/8=21120)
feature_map_size_prod = batch_box_preds.shape[
1] // self.target_assigner.num_anchors_per_location
(3)找到
total_scores中得分最高的分数和对应的索引(top_scores [ 168960 , 1 ] [168960,1] [168960,1]对应着[0],top_labels对应着[1] [ 168960 , 1 ] [168960,1] [168960,1])。也就是找到每一个anchor对应的label和其对应的得分.
top_scores, top_labels = torch.max(total_scores, dim=-1)
(4)根据预先设定的阈值晒选最小的nms(0.3),这里作者虽然用的是一个数组(len=4),但实际上只用了第一个元素,对所有的最高得分,需要超过0.3才能算作是前景预测。最后得到的
top_scores[num_more_than_0.3]都是大于0.3的得分,而top_scores_keep是一个 [ 168960 , 1 ] [168960,1] [168960,1]的bool量,其中为true的就是得分大于 0.3的那些类别.
if self._nms_score_thresholds[0] > 0.0:
top_scores_keep = top_scores >= self._nms_score_thresholds[0]
top_scores = top_scores.masked_select(top_scores_keep)
(5)根据得到的
top_scores得到对应候选proposals.(上面的步骤吧得分低于0.3的排除了,接下来就是对高的分的nms)。1’ 找到得分大于0.3的anchor预测的bbox;box_preds[num_more_than_0.3,7]
box_preds = box_preds[top_scores_keep]
2’ 找到得分大于0.3的anchor预测的dir;dir_labels[num_more_than_0.3,1]
dir_labels = dir_labels[top_scores_keep]
3’ 找到得分大于0.3的anchor预测的cls所对应的labels;top_labels[num_more_than_0.3,1]
top_labels = top_labels[top_scores_keep]
4’ 取出这些得分高的的bev视角下的参数( [ x , y , w , l , y a w ] [x,y,w,l,yaw] [x,y,w,l,yaw],可以根据xy坐标和对应的长宽计算二维参数,最后还需要旋转角yaw),
boxes_for_nms[70,5]
boxes_for_nms = box_preds[:, [0, 1, 3, 4, 6]]
- 使用nms_fun函数排除overlap的box
使用如下:
selected = nms_func(
boxes_for_nms,
top_scores,
pre_max_size=self._nms_pre_max_sizes[0],
post_max_size=self._nms_post_max_sizes[0],
iou_threshold=self._nms_iou_thresholds[0],
)
该函数在 box_torch_ops.py中,函数定义如下:
def rotate_nms(rbboxes,
scores,
pre_max_size=1000,
post_max_size=100,
iou_threshold=0.1):
| 输入参数 | shape | 含义 |
|---|---|---|
| rbboxes | [num_more_than_0.3,5] | 得分大于0.3的备选proposals的bev视角和yaw轴参数 |
| scores | [num_more_than_0.3,1] | 得分大于0.3的备选anchor的对应的labels的得分 |
| pre_max_size | [1] | 最多个备选proposals个数,和num_more_than_0.3谁小取谁的值 |
| post_max_size | [1] | 经过nms最后最多剩下的propospals的个数,和最后的个数谁小取谁 |
| iou_threshold | [1] | IOU重合度大于这个值得anchor剔除,保留得分最高的anchor |
主要函数过程:
(1)设置预先处理的最大proposals个数–min(num_more_than_0.3,pre_max_size),后面的维度就使用
pre_max_size代表需要处理的最小值。
num_keeped_scores = scores.shape[0]
pre_max_size = min(num_keeped_scores, pre_max_size)
(2)按照得分从大到小,取出这需要处理的
pre_max_size参数的scores[pre_max_size,1], indices[pre_max_size,1]。
scores, indices = torch.topk(scores, k=pre_max_size)
(3)把Box和得分concat在一起得到dets[pre_max_size,5+1]表示一个anchor完成的预测(回归+分类),并得到转换到numpy的表示
dets_np[pre_max_size,5+1]
dets = torch.cat([rbboxes, scores.unsqueeze(-1)], dim=1)
dets_np = dets.data.cpu().numpy()
(4)
rotate_nms_cc函数在cpu上对dets_np,iou_threshold进行计算
1’ 得到按照得分高低排列备选proposals。
order = scores.argsort()[::-1].astype(np.int32)
2’ 根据3D的proposals的中心和wl得到二维的corners[pre_max_size,4,2],这里用到的参数有(x,y,w,l,yaw),最后得到的是一个二维的带朝向的proposals.其size是[4,2],而不是[4]是因为加入了旋转变换矩阵,具体怎么操作的就没有细看了。应该是表示的是4个角点的坐标.
dets_corners = box_np_ops.center_to_corner_box2d(dets[:, :2], dets[:, 2:4],
dets[:, 4])
3’ 转化为标准的2维anchor的形式 [ x 1 , y 1 , x 2 , y 2 ] [x_1,y_1,x_2,y_2] [x1,y1,x2,y2],表示为
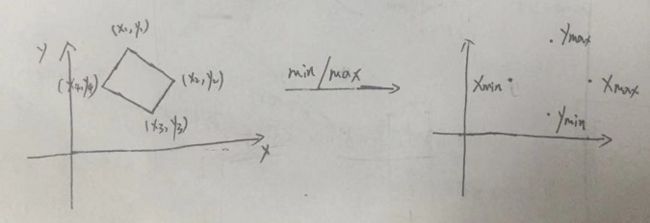
dets_standup[pre_max_size,4] (怎么表示旋转???),大致看了一下,如下图所示,取两坐标轴上分别的最大、最小值就好。
dets_standup = box_np_ops.corner_to_standup_nd(dets_corners)
4’ 计算在该模式下的IOU,输出的两个参数是同一个
dets_standup[pre_max_size,4],他们分别对该组其他的proposals计算IOU。standup_iou[pre_max_size,pre_max_size](对角上都是1–完全重合)
standup_iou = box_np_ops.iou_jit(dets_standup, dets_standup, eps=0.0)
5’ 对IOU重合度大于
iou_threshold都剔除而选择保留其中得分最高的。ret [min{post_max_size,final_post_num,1}]
ret =rotate_non_max_suppression_cpu(dets_corners, order, standup_iou,
thresh)
(5)上一步计算了最后剩下的proposals—
ret[final_post_num,1],这一步则是根据ret取出对应在num_more_than_0.3中的编号。并返回其对应的索引号.
keep = ret[:post_max_size]
- 根据最后IOU,nms得到的结果得到最中的bbox,labels,dir_labels,cls_scores
selected_boxes = box_preds[selected]
selected_dir_labels = dir_labels[selected]
selected_labels = top_labels[selected]
selected_scores = top_scores[selected]
- 后续整合,再发送。代码省略
预测效果
能看出来还是有很一些错检。