SSD目标检测算法详解(附tensorflow简洁版代码及解析)(二)代码详解
SSD目标检测算法详解 (二)代码详解
这一篇讲一下一个简洁版SSD的代码,源码传送门:
https://github.com/Sharpiless/SSD-tensorflow(欢迎关注我的Github账号呀)
(PS:ckpt文件超过100M传不上了,,,需要的话可以自己训练或者私戳我)
主要分几个程序:
1、config.py : 保存了整个项目的大部分参数;
2、calculate_IOU.py : 计算预选框和真值框的IOU值,用于筛选正负样本;以及定义了对坐标进行encode和decode的函数;
3、nms.py : 定义了非极大值抑制函数;
4、random_crop.py : 定义了一个Cropper类,通过随机裁剪和随机翻转进行数据增强;
5、read_data.py : 定义了一个Reader类,用于读取VOC2012数据集;
6、anchors.py : 对不同特征层生成相应大小和数目的default box;
7、label_anchors.py : 将不同的default box与真值框(true boxes)进行匹配;
8、network.py : 定义了一个Net类,并定义了SSD网络结构,用于训练并保存模型;
9、loss_function.py : 定义了损失函数,其中包含对正样本和负样本1:3比例的取样;
10、SSD_API.py : 定义了SSD_detector类,用于加载模型并输入图片进行目标检测;
———————分割线————————
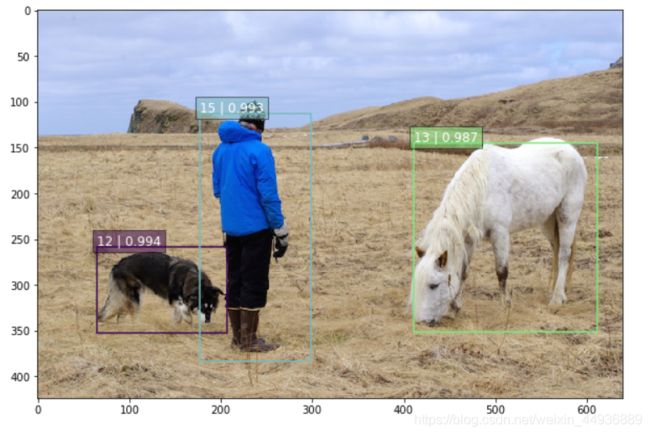
正文开始前,按照惯例闲扯一会……emmm吐槽一下markdown吧,,,复制上本地代码的时候还要每行重新多打一个回车心好累呀,,,再就没什么要说的了,,,那就下期预告吧:下一系列讲一下FCN语义分割吧,先放图——
———————分割线————————
1、config.py
保存了这个项目的参数,先上代码:
# config.py
import numpy as np
import os
NMS_THRESHOLD = 0.3 # nms(非极大值抑制)的阙值
DATA_PATH = '../VOC2012' # 数据集路径
ImageSets_PATH = os.path.join(DATA_PATH, 'ImageSets') # 保存图片坐标和类别信息的路径
BLOCKS = ['block4', 'block7', 'block8',
'block9', 'block10', 'block11', 'block12'] # 需要抽出的特征层名称
MAX_SIZE = 1000 # 图片最大边长
MIN_SIZE = 600 # 图片最小边长
EPOCHES = 2000 # 迭代次数
BATCHES = 64 # 一个epoch迭代多少个batch
THRESHOLD = 0.5 # 区分正负样本匹配的阙值
SCORE_THRESHOLD = 0.997 # 测试时正样本得分阙值
MIN_CROP_RATIO = 0.6 # 随机裁剪的最小比率
MAX_CROP_RATIO = 1.0 # 随机裁剪的最大比率
MODEL_PATH = './model/' # 模型保存路径
LEARNING_RATE = 2e-4 # 学习率
CLASSES = ['', 'aeroplane', 'bicycle', 'bird', 'boat', 'bottle', 'bus',
'car', 'cat', 'chair', 'cow', 'diningtable', 'dog', 'horse',
'motorbike', 'person', 'pottedplant', 'sheep', 'sofa',
'train', 'tvmonitor'] # 物体类别,第一个是背景类别
# 图片三像素均值
PIXEL_MEANS = np.array([[[122.7717, 115.9465, 102.9801]]])
# 不同层预选框的长宽比
RATIOS = [[2, .5],
[2, .5, 3, 1./3],
[2, .5, 3, 1./3],
[2, .5, 3, 1./3],
[2, .5, 3, 1./3],
[2, .5], [2, .5]]
# 每层的步长
STRIDES = [8, 16, 32, 64, 128, 256, 512]
# 论文中的s,认为是每层预选框的边长大小(比率大小)
S = [0.04, 0.1, 0.26, 0.42, 0.58, 0.74, 0.9, 1.06]
# 每层default box的边长,第二个元素是下一层default box的边长
Sk = [(20.48, 51.2),
(51.2, 133.12),
(133.12, 215.04),
(215.04, 296.96),
(296.96, 378.88),
(378.88, 460.8),
(460.8, 542.72)]
# 用于调整边框回归值在loss中的比率
PRIOT_SCALING = (0.1, 0.1, 0.2, 0.2)
参数都有备注,就不多说啦,挑几个比较重要的吧:
1、BLOCKS: BLOCKS保存了我们需要提取的特征层的名称(共七个),其中第一个特征层’block4’是VGG的一个中间层,其余六个特征层是SSD在VGG之层后额外添加的几个,每层的步长见‘STRIDES’参数;
2、RATIOS: RATIOS保存了七个层default box的几个长宽比,比如第一层有[2, 0.5]两个长宽比,代表第一个特征层每个特征点有长宽比分别为2, 0.5的额外两个default box;
3、Sk: Sk保存了每个特征层的default box的边长,注意这里的边长大小跟原论文不太一样;
然后config.py中的参数通过 import config as cfg 引用,参量用cfg.参数名即可。
———————分割线————————
2、calculate_IOU.py
这里定义了计算预选框和真值框的IOU值的函数,用于筛选正负样本;以及定义了对坐标进行encode和decode的函数;
先上代码:
# calculate_IOU.py
import numpy as np
import config as cfg
def encode_targets(true_box, anchors, prior_scaling=cfg.PRIOT_SCALING):
anchor_y_min = anchors[:, 0]
anchor_x_min = anchors[:, 1]
anchor_y_max = anchors[:, 2]
anchor_x_max = anchors[:, 3]
anchor_ctr_y = (anchor_y_max + anchor_y_min) / 2
anchor_ctr_x = (anchor_x_max + anchor_x_min) / 2
anchor_h = anchor_y_max - anchor_y_min
anchor_w = anchor_x_max - anchor_x_min
true_box_y_min = true_box[:, 0]
true_box_x_min = true_box[:, 1]
true_box_y_max = true_box[:, 2]
true_box_x_max = true_box[:, 3]
true_box_ctr_y = (true_box_y_max + true_box_y_min) / 2
true_box_ctr_x = (true_box_x_max + true_box_x_min) / 2
true_box_h = true_box_y_max - true_box_y_min
true_box_w = true_box_x_max - true_box_x_min
target_dy = (true_box_ctr_y-anchor_ctr_y)/anchor_h
target_dx = (true_box_ctr_x-anchor_ctr_x)/anchor_w
target_dh = np.log(true_box_h/anchor_h)
target_dw = np.log(true_box_w/anchor_w)
targets = np.stack([target_dy, target_dx, target_dh, target_dw], axis=1)
return np.reshape(targets, (-1, 4)) / prior_scaling
def decode_targets(anchors, targets, image_shape, prior_scaling=cfg.PRIOT_SCALING):
y_min = anchors[:, 0]
x_min = anchors[:, 1]
y_max = anchors[:, 2]
x_max = anchors[:, 3]
height, width = image_shape[:2]
ctr_y = (y_max + y_min) / 2
ctr_x = (x_max + x_min) / 2
h = y_max - y_min
w = x_max - x_min
targets = targets * prior_scaling
dy = targets[:, 0]
dx = targets[:, 1]
dh = targets[:, 2]
dw = targets[:, 3]
pred_ctr_y = dy*h + ctr_y
pred_ctr_x = dx*w + ctr_x
pred_h = h*np.exp(dh)
pred_w = w*np.exp(dw)
y_min = pred_ctr_y - pred_h/2
x_min = pred_ctr_x - pred_w/2
y_max = pred_ctr_y + pred_h/2
x_max = pred_ctr_x + pred_w/2
y_min = np.clip(y_min, 0, height)
y_max = np.clip(y_max, 0, height)
x_min = np.clip(x_min, 0, width)
x_max = np.clip(x_max, 0, width)
boxes = np.stack([y_min, x_min, y_max, x_max], axis=1)
return boxes
def fast_bbox_overlaps(holdon_anchor, true_boxes):
num_true = true_boxes.shape[0] # 真值框的个数 m
num_holdon = holdon_anchor.shape[0] # 候选框的个数(已删去越界的样本)n
true_y_max = true_boxes[:, 2]
true_y_min = true_boxes[:, 0]
true_x_max = true_boxes[:, 3]
true_x_min = true_boxes[:, 1]
anchor_y_max = holdon_anchor[:, 2]
anchor_y_min = holdon_anchor[:, 0]
anchor_x_max = holdon_anchor[:, 3]
anchor_x_min = holdon_anchor[:, 1]
true_h = true_y_max - true_y_min
true_w = true_x_max - true_x_min
true_h = np.expand_dims(true_h, axis=1)
true_w = np.expand_dims(true_w, axis=1)
anchor_h = holdon_anchor[:, 2] - holdon_anchor[:, 0]
anchor_w = holdon_anchor[:, 3] - holdon_anchor[:, 1]
true_area = true_w * true_h
anchor_area = anchor_w * anchor_h
min_y_up = np.expand_dims(true_y_max, axis=1) < anchor_y_max
min_y_up = np.where(min_y_up, np.expand_dims(
true_y_max, axis=1), np.expand_dims(anchor_y_max, axis=0))
max_y_down = np.expand_dims(true_y_min, axis=1) > anchor_y_min
max_y_down = np.where(max_y_down, np.expand_dims(
true_y_min, axis=1), np.expand_dims(anchor_y_min, axis=0))
lh = min_y_up - max_y_down
min_x_up = np.expand_dims(true_x_max, axis=1) < anchor_x_max
min_x_up = np.where(min_x_up, np.expand_dims(
true_x_max, axis=1), np.expand_dims(anchor_x_max, axis=0))
max_x_down = np.expand_dims(true_x_min, axis=1) > anchor_x_min
max_x_down = np.where(max_x_down, np.expand_dims(
true_x_min, axis=1), np.expand_dims(anchor_x_min, axis=0))
lw = min_x_up - max_x_down
pos_index = np.where(
np.logical_and(
lh > 0, lw > 0
)
)
overlap_area = lh * lw # (n, m)
overlap_weight = np.zeros(shape=lh.shape, dtype=np.int)
overlap_weight[pos_index] = 1
all_area = true_area + anchor_area
dialta_S = all_area - overlap_area
dialta_S = np.where(dialta_S > 0, dialta_S, all_area)
IOU = np.divide(overlap_area, dialta_S)
IOU = np.where(overlap_weight, IOU, 0)
IOU_s = np.transpose(IOU)
return IOU_s.astype(np.float32) # (n, m) 转置矩阵
if __name__ == "__main__":
pass
(1)
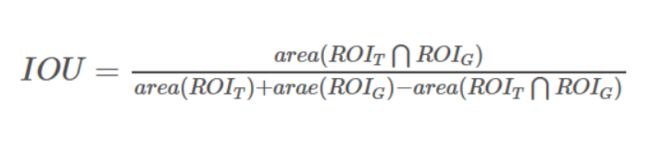
其中IOU用于描述两个线框的重叠程度,在SSD中,我们分别计算每个default box和每个true box的IOU值,其中最大IOU值大于0.5的标记为正样本,小于0.5的标记为负样本,再将与正样本IOU最大的true box的坐标框和类别作为该正样本的label。计算公式为:
这里利用numpy的广播机制,改进了计算IOU的传统方式(fast_bbox_overlaps函数)。
(2)
然后对坐标encode和decode指的是,VOC数据集的真值框坐标是[min_y, min_x, max_y, max_x],即真值框的四角坐标:
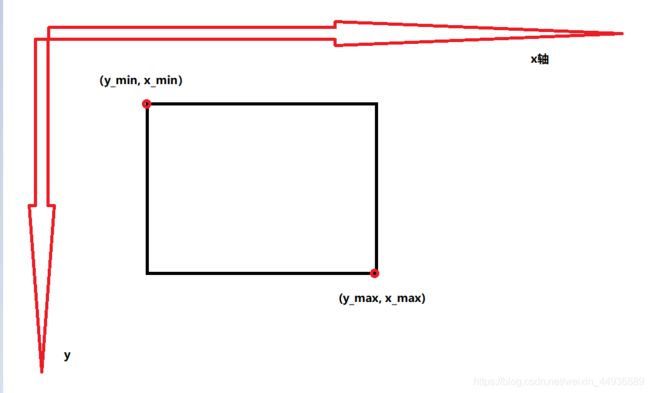
encode(encode_targets函数)指的是,先将default box(程序中用anchor表示)和true box的四角坐标[min_y, min_x, max_y, max_x],转换成[ctr_y, ctr_x, h, w]的形式,即中心点坐标和高度宽度,然后根据公式:
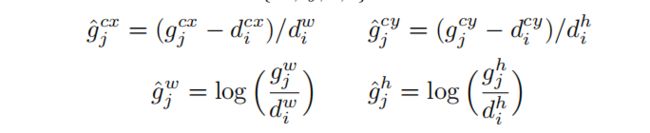
计算出 [dy, dx, dh, dw] 作为default box的坐标label。
(3)
decode(encode_targets函数)功能正好跟encode相反,这里就不多赘述了。
———————分割线————————
3、nms.py
非极大值抑制(Non-Maximum Suppression,NMS),功能是去除冗余的检测框,保留最好的一个。
如果不进行NMS,效果是这样的:
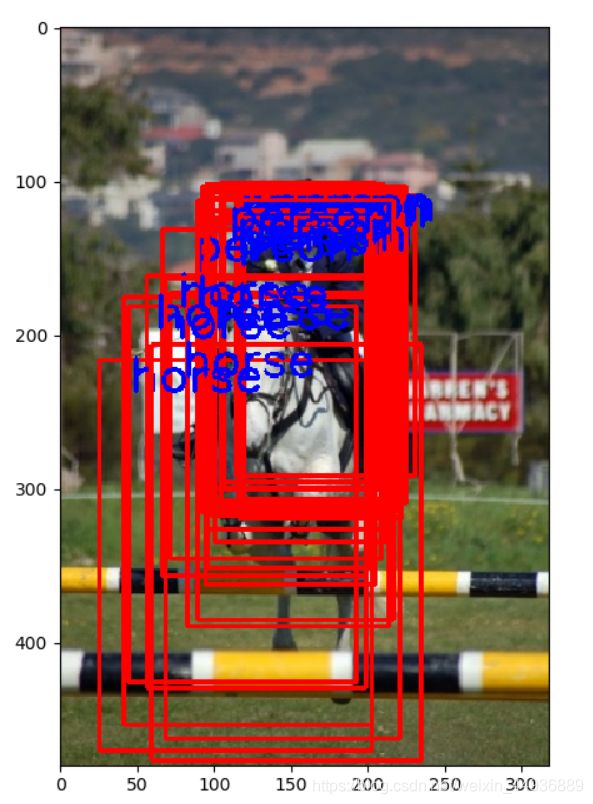

使用NMS之后,效果是这样的:

可以看到NMS除去了冗余的检测框,只保留了得分最大的那个。
上代码:
# nms.py
import numpy as np
import config as cfg
def py_cpu_nms(dets, thresh=cfg.NMS_THRESHOLD):
y1 = dets[:, 0]
x1 = dets[:, 1]
y2 = dets[:, 2]
x2 = dets[:, 3]
scores = dets[:, 4] # bbox打分
areas = (x2 - x1 + 1) * (y2 - y1 + 1)
# 打分从大到小排列,取index
order = scores.argsort()[::-1]
# keep为最后保留的边框
keep = []
while order.size > 0:
# order[0]是当前分数最大的窗口,肯定保留
i = order[0]
keep.append(i)
# 计算窗口i与其他所有窗口的交叠部分的面积
xx1 = np.maximum(x1[i], x1[order[1:]])
yy1 = np.maximum(y1[i], y1[order[1:]])
xx2 = np.minimum(x2[i], x2[order[1:]])
yy2 = np.minimum(y2[i], y2[order[1:]])
w = np.maximum(0.0, xx2 - xx1 + 1)
h = np.maximum(0.0, yy2 - yy1 + 1)
inter = w * h
# 交/并得到iou值
ovr = inter / (areas[i] + areas[order[1:]] - inter)
# inds为所有与窗口i的iou值小于threshold值的窗口的index,其他窗口此次都被窗口i吸收
inds = np.where(ovr <= thresh)[0]
# order里面只保留与窗口i交叠面积小于threshold的那些窗口,由于ovr长度比order长度少1(不包含i),所以inds+1对应到保留的窗口
order = order[inds + 1]
return keep
更详细的原理可以看一下这篇博客:https://www.cnblogs.com/makefile/p/nms.html
———————分割线————————
4、random_crop.py
这里定义了一个Cropper类,用于对图片和true box进行随即裁剪和随机翻转,进行数据增强。
先上代码:
# random_crop.py
import numpy as np
import config as cfg
import random
class Cropper(object):
def __init__(self):
self.min_ratio = cfg.MIN_CROP_RATIO
self.max_ratio = cfg.MAX_CROP_RATIO
def random_flip(self, image, boxes):
flag = random.randint(0, 1)
if flag:
image = np.flip(image, axis=1)
h, w = image.shape[:2]
y_min = boxes[:, 0]
x_min = boxes[:, 1]
y_max = boxes[:, 2]
x_max = boxes[:, 3]
new_y_min = y_max
new_y_max = y_min
new_x_min = w - x_max
new_x_max = w - x_min
# print('flip')
boxes = np.stack(
[new_y_min, new_x_min, new_y_max, new_x_max], axis=-1)
return image, boxes
else:
return image, boxes
def random_crop(self, image, boxes, labels):
h, w = image.shape[:2]
ratio = random.random()
scale = self.min_ratio + ratio * (self.max_ratio - self.min_ratio)
new_h = int(h*scale)
new_w = int(w*scale)
y = np.random.randint(0, h - new_h)
x = np.random.randint(0, w - new_w)
image = image[y:y+new_h, x:x+new_w, :]
y_min = boxes[:, 0]
x_min = boxes[:, 1]
y_max = boxes[:, 2]
x_max = boxes[:, 3]
raw_areas = (y_max - y_min) * (x_max - x_min)
y_min = y_min - y
y_max = y_max - y
x_min = x_min - x
x_max = x_max - x
y_min = np.clip(y_min, 0, new_h)
y_max = np.clip(y_max, 0, new_h)
x_min = np.clip(x_min, 0, new_w)
x_max = np.clip(x_max, 0, new_w)
new_areas = (y_max - y_min) * (x_max - x_min)
# keep_index = np.where(new_areas > raw_areas*0.7)[0]
boxes = np.stack([y_min, x_min, y_max, x_max], axis=-1)
# boxes = boxes[keep_index]
# labels = labels[keep_index]
return image, boxes, labels
(1)random_flip方法:
0.5的概率对图片进行水平翻转;
(2)random_crop方法:
对图片进行随机裁剪,裁剪区域为0.6~1.0随机大小;这里把选择保留裁剪后真值框大小大于原大小0.7倍的功能去掉了,如果想用的话把keep_index那部分的注释去掉就ok;
效果如图:
———————分割线————————
5、read_data.py
这里定义了一个Reader类,主要功能是读取VOC2012数据集的数据,并通过generate方法生成用于训练的图片和标签;
由于VOC2012格式的数据集,使用.xml文件保存用于检测的图片的标签:

我们使用 xml.etree.ElementTree 来解析.xml文件并获取数据。
先上代码:
# read_data.py
import config as cfg
import cv2
import xml.etree.ElementTree as ET
import numpy as np
import os
import pickle
import random
from random_crop import Cropper
class Reader(object):
def __init__(self, is_training):
self.data_path = cfg.DATA_PATH
self.cropper = Cropper()
self.is_training = is_training
self.max_size = cfg.MAX_SIZE
self.min_size = cfg.MIN_SIZE
self.CLASSES = cfg.CLASSES
self.pixel_means = cfg.PIXEL_MEANS
self.class_to_ind = dict(
zip(self.CLASSES, range(len(self.CLASSES)))
)
self.cursor = 0 # 游标,用于检测是否历遍完一遍图片
self.epoch = 1
self.true_labels = None
self.pre_process()
def read_image(self, path):
image = cv2.imread(path)
return image.astype(np.float)
def load_one_info(self, name):
filename = os.path.join(self.data_path, 'Annotations', name+'.xml')
tree = ET.parse(filename)
Objects = tree.findall('object')
objs_num = len(Objects)
Boxes = np.zeros((objs_num, 4), dtype=np.float32)
True_classes = np.zeros((objs_num), dtype=np.float32)
for i, obj in enumerate(Objects):
bbox = obj.find('bndbox')
x_min = float(bbox.find('xmin').text) - 1 # 注意VOC格式的坐标是以1为起始点
y_min = float(bbox.find('ymin').text) - 1
x_max = float(bbox.find('xmax').text) - 1
y_max = float(bbox.find('ymax').text) - 1
obj_cls = obj.find('name').text.lower().strip()
obj_cls = self.class_to_ind[obj_cls]
Boxes[i, :] = [y_min, x_min, y_max, x_max]
True_classes[i] = obj_cls
image_path = os.path.join(
self.data_path, 'JPEGImages', name + '.jpg')
return {'boxes': Boxes, 'classes': True_classes, 'image_path': image_path}
def load_labels(self):
is_training = 'train' if self.is_training else 'test'
if not os.path.exists('./dataset'):
os.makedirs('./dataset')
pkl_file = os.path.join('./dataset', is_training+'_labels.pkl')
if os.path.isfile(pkl_file):
print('Load Label From '+str(pkl_file))
with open(pkl_file, 'rb') as f:
labels = pickle.load(f)
return labels
# else
print('Load labels from: '+str(cfg.ImageSets_PATH))
if self.is_training:
txt_path = os.path.join(cfg.ImageSets_PATH, 'Main', 'trainval.txt')
# 这是用来存放训练集和测试集的列表的txt文件
else:
txt_path = os.path.join(cfg.ImageSets_PATH, 'Main', 'val.txt')
with open(txt_path, 'r') as f:
self.image_name = [x.strip() for x in f.readlines()]
labels = []
for name in self.image_name:
# 包括objet box坐标信息 以及类别信息(转换成dict后的)
true_label = self.load_one_info(name)
labels.append(true_label)
with open(pkl_file, 'wb') as f:
pickle.dump(labels, f)
print('Successfully saving '+is_training+'data to '+pkl_file)
return labels
def resize_image(self, image):
image_shape = image.shape
size_min = np.min(image_shape[:2])
size_max = np.max(image_shape[:2])
min_size = self.min_size
scale = float(min_size) / float(size_min)
image = cv2.resize(image, dsize=(0, 0), fx=scale, fy=scale)
return image, scale
def pre_process(self):
true_labels = self.load_labels()
if self.is_training:
np.random.shuffle(true_labels)
self.true_labels = true_labels
def generate(self):
image_path = self.true_labels[self.cursor]['image_path']
image = self.read_image(image_path)
true_boxes = self.true_labels[self.cursor]['boxes']
true_labels = self.true_labels[self.cursor]['classes']
image, true_boxes = self.cropper.random_flip(image, true_boxes)
image, true_boxes, true_labels = self.cropper.random_crop(
image, true_boxes, true_labels)
image, scale = self.resize_image(image)
true_boxes = true_boxes * scale
self.cursor += 1
if self.cursor >= len(self.true_labels):
np.random.shuffle(self.true_labels)
self.cursor = 0
self.epoch += 1
value = {'image': image, 'classes': true_labels,
'boxes': true_boxes, 'image_path': image_path, 'scale': scale}
if true_boxes.shape[0] == 0:
value = self.generate()
return value
(1)read_image方法:
读取图片;
(2)load_one_info方法:
从Annotation文件夹中解析图片的.xml文件,并获取其true box的坐标和类别;
(3)load_labels方法:
加载所有图片,并对每张分别使用load_one_info加载标签,然后将图片路径(注意不要直接保存图片,不然加载时会占用太多内存)和标签等信息保存在一个pkl文件中;如果已经保存过pkl文件则跳过这步,直接从pkl文件加载数据;
(4)resize_image方法:
改变图片大小,即按图片最小边调整为600的比率放缩图片,防止图片过小导致最后无法继续池化;
(5)pre_process方法:
在创建reader类时调用load_labels方法,加载数据;
(6)generate方法:
每次调用生成用于训练的图片和标签,格式是一个字典;
(7)注意:这里使用了递归,防止裁剪出没有true box的图片
———————分割线————————
6、anchors.py
这里用于生成default box(有的地方也叫Prior Box,先验框),由于输入的图片大小不一样,得到的特征层大小也会不同,这里就根据每层大小而定,生成相应数目的default box;(至于为什么叫anchor呢,,,因为anchor比default box短好写呀)
(如果还是不明白default box的话,可以先看我的上一篇博客)
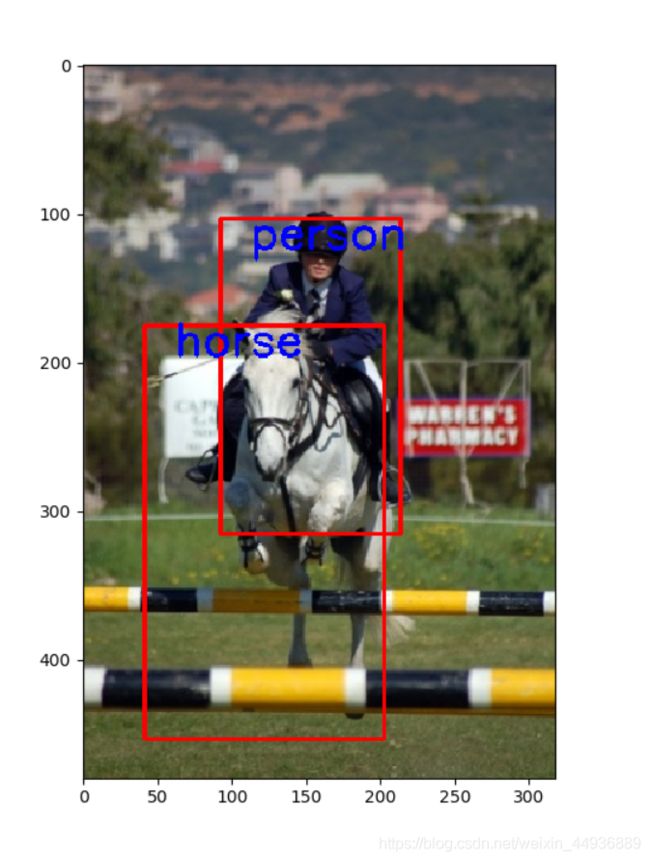
先用一张空图,看一下‘block9’特征层对应的default box生成效果:
再上代码:
# anchors.py
import numpy as np
import config as cfg
import math
import tensorflow as tf
def ssd_anchor_all_layers(image):
image_shape = image.shape
layers_shape, anchor_shapes = get_layers_shape(image_shape)
layers_anchors = []
for i, layer_size in enumerate(layers_shape):
anchor_size = anchor_shapes[i]
anchors = ssd_anchor_one_layer(
image_shape, layer_size, anchor_size, ratio=cfg.RATIOS[i], stride=cfg.STRIDES[i]
)
layers_anchors.append(anchors)
return layers_anchors
def ssd_anchor_one_layer(image_shape, layer_size, anchor_size, ratio, stride):
y, x = np.mgrid[0:layer_size[0], 0:layer_size[1]]
y = (y.astype(np.float)+0.5) * stride # 原图上的锚定点
x = (x.astype(np.float)+0.5) * stride # 原图上的锚定点
y = np.expand_dims(y, axis=-1)
x = np.expand_dims(x, axis=-1)
anchor_num = len(ratio) + len(anchor_size)
h = np.zeros((anchor_num, ), dtype=np.float)
w = np.zeros((anchor_num, ), dtype=np.float)
di = 1
h[0] = anchor_size[0]
w[0] = anchor_size[0]
if len(anchor_size) > 1:
h[1] = math.sqrt(anchor_size[0]*anchor_size[1])
w[1] = math.sqrt(anchor_size[0]*anchor_size[1])
di += 1
for i, r in enumerate(ratio):
h[i+di] = anchor_size[0] / math.sqrt(r)
w[i+di] = anchor_size[0] * math.sqrt(r)
anchors = convert_format(y, x, w, h)
return anchors.astype(np.float32)
def convert_format(y, x, w, h):
bias = get_conners_coord(w, h)
center_point = np.stack((y, x, y, x), axis=-1)
anchors = center_point + bias
anchors = np.reshape(
anchors, [y.shape[0], y.shape[1], bias.shape[0], 4])
return anchors
def get_conners_coord(w, h):
width = w
height = h
# 分别计算四点坐标
x_min = np.round(0 - 0.5 * width)
y_min = np.round(0 - 0.5 * height)
x_max = np.round(0 + 0.5 * width)
y_max = np.round(0 + 0.5 * height)
bias = np.stack((y_min, x_min, y_max, x_max), axis=-1)
return bias
def get_layers_shape(image_shape, Sk=cfg.Sk):
height, width = image_shape[:2]
H, W = height, width
layers_shape = []
for _ in range(3):
height = math.ceil(height/2)
width = math.ceil(width/2)
for i in range(7):
layers_shape.append((height, width))
height = math.ceil(height/2)
width = math.ceil(width/2)
anchor_shapes = np.array(Sk)
return layers_shape, anchor_shapes
(1)ssd_anchor_all_layers:
输入图片,输出相应图片对应的7个特征层的default box,保存在列表里;
(2)ssd_anchor_one_layer:
输入特征层的大小、相应特征层的default box的边长及长宽比,生成相应不同长宽比的default box;
(3)convert_format:
把坐标的(y, x, w, h)格式转换成(min_y, min_x, max_y, max_x)格式;
(4)get_conners_coord:
把(w, h)转换成(-0.5×h, 0.5×h, -0.5×w, 0.5×w );
(5)get_layers_shape:
传入图片大小,由于每次经过步长为2的池化层(或者个别步长为2的卷积层)时,特征图的大小就变为原来的1/2,故可以由此计算出每一个特征层的大小;
函数返回7个特征层的大小;
———————分割线————————
7、label_anchors.py
这里主要是给default box匹配true box,区分正样本和负样本,并给default box标注标签;
效果如图,其中绿色框和蓝色框是true box,红色框是正样本:

再上代码:
# label_anchors.py
import numpy as np
import config as cfg
from calculate_IOU import encode_targets, decode_targets, fast_bbox_overlaps
def ssd_bboxes_encode(anchors, true_boxes, true_labels, num_classes=len(cfg.CLASSES), threshold=cfg.THRESHOLD):
labels, scores, loc = ssd_bboxes_encode_layer(
anchors, true_boxes, true_labels, threshold=threshold
)
return labels.astype(np.float32), scores.astype(np.float32), loc.astype(np.float32)
def ssd_bboxes_encode_layer(anchors, true_boxes, true_labels, threshold=0.5):
anchors = np.reshape(anchors, (-1, 4))
true_boxes = np.reshape(true_boxes, (-1, 4))
IOUs = fast_bbox_overlaps(anchors, true_boxes)
max_arg = np.argmax(IOUs, axis=-1)
index = np.arange(0, max_arg.shape[0])
target_labels = true_labels[max_arg]
target_scores = IOUs[index, max_arg]
pos_index = np.where(target_scores > threshold)[0]
pos_anchors = anchors[pos_index]
pos_boxes = true_boxes[max_arg[pos_index]]
target_loc = np.zeros(shape=anchors.shape)
if pos_index.shape[0]:
pos_targets = encode_targets(pos_boxes, pos_anchors)
target_loc[pos_index, :] = pos_targets
return target_labels, target_scores, target_loc
(1)ssd_bboxes_encode:
对七个特征层的default box(源码记为anchor)分别跟true box进行匹配;
(2)ssd_bboxes_encode_layer:
对某一特整层的default box,选出正样本和负样本,并给default box匹配true box的类别和坐标label;
输出:
1.target_labels:每个default box与之最大IOU对应的true box的类别,;2.target_scores:每个default box的最大IOU值;
3.target_loc:正样本的回归坐标(负样本标注为零,不参与Loss的计算);
———————分割线————————
8、network.py
这里定义了一个Net类,主要搭建了SSD的网络结构(如图),并进行神经网络的训练和模型的保存,ckpt文件保存在./model文件夹下;
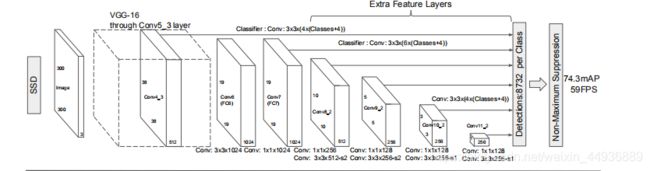
我们跟论文略有不同的是,论文中采取的是将图片裁剪成固定大小输入(300×300或512×512),我们输入的是按最短边调整为600的比率缩放的图片,这样训练的模型对小目标的检测效果会更好;
然后我们使用动量梯度下降法(gradient descent with momentum)进行训练,由于我们使用SGD(Stochastic gradientdescent)随机梯度下降法,即每次只迭代一张图片,会产生下降过程中Loss左右振荡的现象。而动量梯度下降法通过减小振荡对算法进行优化。
先上代码:
import config as cfg
import tensorflow as tf
from read_data import Reader
from anchors import ssd_anchor_all_layers
from label_anchors import ssd_bboxes_encode
from loss_function import loss_layer
import numpy as np
import os
slim = tf.contrib.slim
class Net(object):
def __init__(self, is_training):
self.reader = Reader(is_training)
self.is_training = is_training
self.learning_rate = cfg.LEARNING_RATE
self.class_num = len(cfg.CLASSES)
self.blocks = cfg.BLOCKS
self.ratios = cfg.RATIOS
self.Sk = cfg.Sk
self.x = tf.placeholder(tf.float32, [None, None, 3])
self.true_labels = tf.placeholder(tf.float32, [None])
self.true_boxes = tf.placeholder(tf.float32, [None, 4])
self.output = self.ssd_net(
tf.expand_dims(self.x, axis=0)
)
self.anchors = tf.numpy_function(
ssd_anchor_all_layers, [self.x],
[tf.float32]*7
)
self.saver = tf.train.Saver()
def ssd_net(self, inputs, scope='ssd_512_vgg'):
layers = {}
with tf.variable_scope(scope, 'ssd_512_vgg', [inputs], reuse=None):
# Block 1
net = slim.repeat(inputs, 2, slim.conv2d,
64, [3, 3], scope='conv1')
net = slim.max_pool2d(net, [2, 2], scope='pool1', padding='SAME')
# Block 2
net = slim.repeat(net, 2, slim.conv2d,
128, [3, 3], scope='conv2')
net = slim.max_pool2d(net, [2, 2], scope='pool2', padding='SAME')
# Block 3
net = slim.repeat(net, 3, slim.conv2d,
256, [3, 3], scope='conv3')
net = slim.max_pool2d(net, [2, 2], scope='pool3', padding='SAME')
# net = tf.layers.batch_normalization(net, training=self.is_training)
# Block 4
net = slim.repeat(net, 3, slim.conv2d,
512, [3, 3], scope='conv4')
layers['block4'] = net
net = slim.max_pool2d(net, [2, 2], scope='pool4', padding='SAME')
# Block 5
net = slim.repeat(net, 3, slim.conv2d,
512, [3, 3], scope='conv5')
# Block 6
net = slim.conv2d(net, 1024, [3, 3], rate=6, scope='conv6')
# Block 7
net = slim.conv2d(net, 1024, [1, 1], scope='conv7')
layers['block7'] = net
# Block 8
with tf.variable_scope('block8'):
net = slim.conv2d(net, 256, [1, 1], scope='conv1x1')
net = slim.conv2d(net, 512, [3, 3], 2,
scope='conv3x3', padding='SAME')
layers['block8'] = net
# Block 9
with tf.variable_scope('block9'):
net = slim.conv2d(net, 128, [1, 1], scope='conv1x1')
net = slim.conv2d(net, 256, [3, 3], 2,
scope='conv3x3', padding='SAME')
layers['block9'] = net
# Block 10
with tf.variable_scope('block10'):
net = slim.conv2d(net, 128, [1, 1], scope='conv1x1')
net = slim.conv2d(net, 256, [3, 3], 2,
scope='conv3x3', padding='SAME')
layers['block10'] = net
# Block 11
with tf.variable_scope('block11'):
net = slim.conv2d(net, 128, [1, 1], scope='conv1x1')
net = slim.conv2d(net, 256, [3, 3], 2,
scope='conv3x3', padding='SAME')
layers['block11'] = net
# Block 12
with tf.variable_scope('block12'):
net = slim.conv2d(net, 128, [1, 1], scope='conv1x1')
net = slim.conv2d(net, 256, [4, 4], 2,
scope='conv4x4', padding='SAME')
layers['block12'] = net
self.layers = layers
pred_loc = []
pred_score = []
for i, block in enumerate(self.blocks):
with tf.variable_scope(block+'_box'):
loc, score = self.ssd_multibox_layer(
layers[block], self.class_num, self.ratios[i], self.Sk[i]
)
pred_loc.append(loc)
pred_score.append(score)
return pred_loc, pred_score
def ssd_multibox_layer(self, inputs, class_num, ratio, size):
num_anchors = len(size) + len(ratio)
num_loc = num_anchors * 4
num_cls = num_anchors * class_num
# loc
loc_pred = slim.conv2d(
inputs, num_loc, [3, 3], activation_fn=None, scope='conv_loc')
# cls
cls_pred = slim.conv2d(
inputs, num_cls, [3, 3], activation_fn=None, scope='conv_cls')
loc_pred = tf.reshape(loc_pred, (-1, 4))
cls_pred = tf.reshape(cls_pred, (-1, class_num))
# softmax
cls_pred = slim.softmax(cls_pred, scope='softmax')
return loc_pred, cls_pred
def train_net(self):
self.target_labels = []
self.target_scores = []
self.target_loc = []
for i in range(7):
target_labels, target_scores, target_loc = tf.numpy_function(
ssd_bboxes_encode, [self.anchors[i], self.true_boxes,
self.true_labels, self.class_num],
[tf.float32, tf.float32, tf.float32]
)
self.target_labels.append(target_labels)
self.target_scores.append(target_scores)
self.target_loc.append(target_loc)
self.total_cross_pos, self.total_cross_neg, self.total_loc = loss_layer(
self.output, self.target_labels, self.target_scores, self.target_loc
)
self.loss = tf.add(
tf.add(self.total_cross_pos, self.total_cross_neg), self.total_loc
)
# gradients = self.optimizer.compute_gradients(self.loss)
self.optimizer = tf.compat.v1.train.MomentumOptimizer(
learning_rate=self.learning_rate, momentum=0.9)
# self.optimizer = tf.compat.v1.train.AdamOptimizer(self.learning_rate)
self.train_step = self.optimizer.minimize(self.loss)
with tf.Session() as sess:
sess.run(tf.compat.v1.global_variables_initializer())
ckpt = tf.train.get_checkpoint_state(cfg.MODEL_PATH)
if ckpt and ckpt.model_checkpoint_path:
# 如果保存过模型,则在保存的模型的基础上继续训练
self.saver.restore(sess, ckpt.model_checkpoint_path)
print('Model Reload Successfully!')
for i in range(cfg.EPOCHES):
loss_list = []
for batch in range(cfg.BATCHES):
value = self.reader.generate()
image = value['image'] - cfg.PIXEL_MEANS
true_labels = value['classes']
true_boxes = value['boxes']
feed_dict = {self.x: image,
self.true_labels: true_labels,
self.true_boxes: true_boxes}
test = sess.run(self.target_scores, feed_dict)
total_pos = 0
for v in test:
if np.max(v) > cfg.THRESHOLD:
total_pos += 1
if total_pos==0:
with open('NumError.txt', 'a') as f:
f.write(value['image_path']+'\n')
continue
try:
sess.run(self.train_step, feed_dict)
loss_0, loss_1, loss_2 = sess.run(
[self.total_cross_pos, self.total_cross_neg, self.total_loc], feed_dict)
except EOFError:
pass
loss_list.append(
np.array([loss_0, loss_1, loss_2])
)
print('batch:{},pos_loss:{},neg_loss:{},loc_loss:{}'.format(
batch, loss_0, loss_1, loss_2
), end='\r')
loss_values = np.array(loss_list) # (64, 3)
loss_values = np.mean(loss_values, axis=0)
with open('./result.txt', 'a') as f:
f.write(str(loss_values)+'\n')
self.saver.save(sess, os.path.join(
cfg.MODEL_PATH, 'model.ckpt'))
print('epoch:{},pos_loss:{},neg_loss:{},loc_loss:{}'.format(
self.reader.epoch, loss_values[0], loss_values[1], loss_values[2]
))
if __name__ == '__main__':
if not os.path.exists(cfg.MODEL_PATH):
os.makedirs(cfg.MODEL_PATH)
net = Net(is_training=True)
net.train_net()
注意:
由于我们使用了numpy进行图片default box的生成和匹配标签,这里需要再使用tf.numpy_function函数进行array和tensor的转换;tensorflow中的numpy_function近似于py_function,可以直接将一个python函数(主要指numpy函数)转换成tensorflow的张量输出;但是numpy_function应该是最近版本才更新的,实测tensorflow-gpu==1.14才出现,之前的版本可能会报错;
(1)ssd_net方法:
定义了SSD的网络结构,接受图片为输入,输出每个特征点的预测值(原论文中网络结构图输出有所省略,应该7个特征层都有输出):
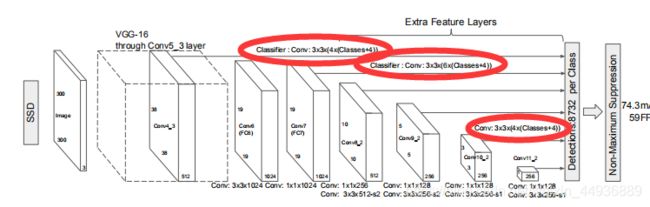
(2)ssd_multibox_layer方法:
ssd_multibox_layer方法在ssd_net方法中被调用,作用是对每个特征层计算该特征层每个特征点的default box数,并用卷积输出预测值;
(3)train_net方法:
这里主要是训练并保存模型,每迭代一次(64个batch)会在终端打印Loss值:
1.pos_loss:指的是正样本的分类Loss;
2.neg_loss:指的是负样本的分类Loss(物体和非物体二分类);
3.loc_loss:指的是正样本坐标回归Loss;
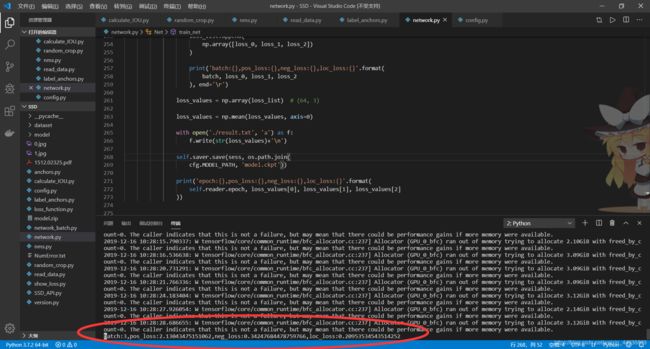
然后把Loss保存在工作区result.txt文件中,没有匹配到正样本的图片保存在NumError.txt文件中;
每次迭代也会保存一次模型,保存在工作区model文件夹下:

然后调用这个方法就可以开始训练啦~
———————分割线————————
9、loss_function.py
对正负样本1:3的取样,以及进行Loss的计算;
上代码:
import tensorflow as tf
def loss_layer(output, target_labels, target_scores, target_loc, threshold=0.5):
predictions_loc, predictions_score = output
dtype = predictions_loc[0].dtype
l_cross_pos = []
l_cross_neg = []
l_loc = []
for i in range(len(predictions_score)):
pred_loc = predictions_loc[i]
pred_score = predictions_score[i]
true_label = tf.cast(target_labels[i], tf.int32)
pos_mask = target_scores[i] > threshold
no_classes = tf.cast(pos_mask, tf.int32)
fpos_mask = tf.cast(pos_mask, dtype)
pos_num = tf.reduce_sum(fpos_mask)
neg_mask = tf.logical_not(pos_mask)
fneg_mask = tf.cast(neg_mask, dtype)
neg_values = tf.where(
neg_mask, pred_score[:, 0], 1.-fneg_mask)
neg_values_flat = tf.reshape(neg_values, [-1])
n_neg = tf.cast(3 * pos_num, tf.int32)
n_neg = tf.maximum(n_neg, tf.size(neg_values_flat) // 8)
n_neg = tf.maximum(n_neg, tf.shape(neg_values)[0] * 4)
max_neg_entries = tf.cast(tf.reduce_sum(fneg_mask), tf.int32)
n_neg = tf.minimum(n_neg, max_neg_entries)
val, idxes = tf.nn.top_k(-neg_values_flat, k=n_neg)
minval = val[-1]
neg_mask = tf.logical_and(neg_mask, -neg_values > minval)
fneg_mask = tf.cast(neg_mask, dtype)
with tf.name_scope('cross_entropy_pos'):
loss = tf.nn.sparse_softmax_cross_entropy_with_logits(
logits=pred_score, labels=true_label
)
loss = tf.losses.compute_weighted_loss(loss, fpos_mask)
l_cross_pos.append(loss)
with tf.name_scope('cross_entropy_neg'):
loss = tf.nn.sparse_softmax_cross_entropy_with_logits(
logits=pred_score[:, :2], labels=no_classes
)
loss = tf.losses.compute_weighted_loss(loss, fneg_mask)
l_cross_neg.append(loss)
with tf.name_scope('localization'):
weights = tf.expand_dims(fpos_mask, axis=-1)
loss = abs_smooth(
pred_loc - target_loc[i])
loss = tf.losses.compute_weighted_loss(loss, weights)
l_loc.append(loss)
with tf.name_scope('total'):
l_cross_pos = tf.gather(
l_cross_pos, tf.where(tf.not_equal(l_cross_pos, 0))
)
l_cross_neg = tf.gather(
l_cross_neg, tf.where(tf.not_equal(l_cross_neg, 0))
)
l_loc = tf.gather(
l_loc, tf.where(tf.not_equal(l_loc, 0))
)
total_cross_pos = tf.reduce_mean(l_cross_pos)
total_cross_neg = tf.reduce_mean(l_cross_neg)
total_loc = tf.reduce_mean(l_loc)
return total_cross_pos, total_cross_neg, total_loc
def abs_smooth(x):
absx = tf.abs(x)
minx = tf.minimum(absx, 1)
r = 0.5 * ((absx - 1) * minx + absx)
return r
注意:
1、这里是对每一层分别计算Loss,如果某一层正样本数>负样本数的1/3,需要对负样本数做出修正;
2、使用tf.losses.compute_weighted_loss()函数,通过设置weight矩阵某处值为1或0来决定某个default box是否参与Loss的计算;
10、SSD_API.py
这里定义了一个SSD_detector类,即定义了SSD算法的API接口,通过test_ssd方法传入单张图片路径或者保存了多张图片路径的列表,对图片上的物体的分类和位置进行预测,再通过decode方式转换坐标,最后通过matplotlib进行展示;
代码:
import tensorflow as tf
from network import Net
import config as cfg
import cv2
import numpy as np
from label_anchors import decode_targets
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
from nms import py_cpu_nms
class SSD_detector(object):
def __init__(self):
self.net = Net(is_training=False)
self.model_path = cfg.MODEL_PATH
self.pixel_means = cfg.PIXEL_MEANS
self.min_size = cfg.MIN_SIZE
self.pred_loc, self.pred_cls = self.net.output
self.score_threshold = cfg.SCORE_THRESHOLD
def pre_process(self, image_path):
image = cv2.imread(image_path)
image = image.astype(np.float)
image, scale = self.resize_image(image)
value = {'image': image, 'scale': scale, 'image_path': image_path}
return value
def resize_image(self, image):
image_shape = image.shape
size_min = np.min(image_shape[:2])
size_max = np.max(image_shape[:2])
scale = float(self.min_size) / float(size_min)
image = cv2.resize(image, dsize=(0, 0), fx=scale, fy=scale)
return image, scale
def test_ssd(self, image_paths):
if isinstance(image_paths, str):
image_paths = [image_paths]
with tf.Session() as sess:
sess.run(tf.compat.v1.global_variables_initializer())
ckpt = tf.train.get_checkpoint_state(cfg.MODEL_PATH)
if ckpt and ckpt.model_checkpoint_path:
# 如果保存过模型,则在保存的模型的基础上继续训练
self.net.saver.restore(sess, ckpt.model_checkpoint_path)
print('Model Reload Successfully!')
for path in image_paths:
value = self.pre_process(path)
image = value['image'] - self.pixel_means
feed_dict = {self.net.x: image}
pred_loc, pred_cls, layer_anchors = sess.run(
[self.pred_loc, self.pred_cls, self.net.anchors], feed_dict
)
pos_loc, pos_cls, pos_anchors, pos_scores = self.decode_output(
pred_loc, pred_cls, layer_anchors)
pos_boxes = decode_targets(pos_anchors, pos_loc, image.shape)
pos_scores = np.expand_dims(pos_scores, axis=-1)
self.draw_result(
value['image'], pos_boxes, pos_cls, value['scale']
)
keep_index = py_cpu_nms(np.hstack([pos_boxes, pos_scores]))
self.draw_result(
value['image'], pos_boxes[keep_index], pos_cls[keep_index], value['scale']
)
def draw_result(self, image, pos_boxes, pos_cls, scale, font=cv2.FONT_HERSHEY_SIMPLEX):
image = cv2.resize(image, dsize=(0, 0), fx=1/scale, fy=1/scale)
image = image.astype(np.int)
pos_boxes = pos_boxes * (1/scale)
for i in range(pos_boxes.shape[0]):
bbox = pos_boxes[i]
label = cfg.CLASSES[pos_cls[i]]
y_min, x_min, y_max, x_max = bbox.astype(np.int)
cv2.rectangle(image, (x_min, y_min),
(x_max, y_max), (0, 0, 255), thickness=2)
cv2.putText(image, label, (x_min+20, y_min+20),
font, 1, (255, 0, 0), thickness=2)
plt.imshow(image[:, :, [2, 1, 0]])
plt.show()
def decode_output(self, pred_loc, pred_cls, layer_anchors):
pos_loc, pos_cls, pos_anchors, pos_scores = [], [], [], []
for i in range(len(pred_cls)):
loc_ = pred_loc[i]
cls_ = pred_cls[i] # cls_是每个分类的得分
anchors = layer_anchors[i].reshape((-1, 4))
max_scores = np.max(cls_[:, 1:], axis=-1) # 非背景最大得分
cls_ = np.argmax(cls_, axis=-1) # 最大索引
pos_index = np.where(max_scores > self.score_threshold)[0] # 正样本
pos_loc.append(loc_[pos_index])
pos_cls.append(cls_[pos_index])
pos_anchors.append(anchors[pos_index])
pos_scores.append(max_scores[pos_index])
pos_loc = np.vstack(pos_loc)
pos_cls = np.hstack(pos_cls)
pos_anchors = np.vstack(pos_anchors)
pos_scores = np.hstack(pos_scores)
return pos_loc, pos_cls, pos_anchors, pos_scores
if __name__ == "__main__":
detector = SSD_detector()
detector.test_ssd('./1.jpg')
这里就大功告成啦~
———————分割线————————
11、训练时注意:
1、由于tf.numpy_function是最近版本才更新的,可能会报错 ‘tensorflow’ module has no attribute ‘numpy_function’,可能是tensorflow版本号过低导致;可以通过运行version.py查看版本;需要版本:python3.7 tensorflow1.14及以上;
2、可能报错AttributeError: ‘NoneType’ object has no attribute ‘astype’,应该是数据集路径问题,这是要修改config.py中的路径,并删除dataset文件夹(如果有的话)重新运行;
3、还有其他问题的话请留言哦,日常在线~
Ps:
博主码字不容易,随手点赞真情义;
万水千山总是情,给个关注行不行;
大佬们的支持就是我更新的最大动力(●’◡’●),下次写一下FCN语义分割;
我们下期再见~
联系我们:
权重文件或者有其他需要的请私戳作者~
(长期接私活~)
![]()
![]()
![]()
![]()
